Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bleeder Resistance
Bleeder Resistance
Uploaded by
goputs6386Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sri Vishnu Sahasranamam Word-To-word TranslationDocument30 pagesSri Vishnu Sahasranamam Word-To-word Translationkaustavchakravarthy100% (7)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- An Industrial Training PPT On 50mva, 132/33 KV Grid Sub StationDocument35 pagesAn Industrial Training PPT On 50mva, 132/33 KV Grid Sub Stationishfaq222100% (3)
- Switch Yard and Its EquipmentsDocument48 pagesSwitch Yard and Its Equipmentsamit joshi86% (14)
- 436 Power CapacitorsDocument6 pages436 Power Capacitorselectrical civilNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation EquipmentDocument4 pagesElectrical Substation EquipmentPurbita ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- CSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumDocument14 pagesCSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumAshish MauryaNo ratings yet
- Oscillator: How To Build An InverterDocument7 pagesOscillator: How To Build An InverterGopal Prasad BansalNo ratings yet
- Deutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Document15 pagesDeutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Modesto Marcos Calderon CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Electrical Substation Components and Their WorkingsDocument22 pagesAssignment 1 Electrical Substation Components and Their WorkingsAP13 AP13No ratings yet
- Dc-Ac Inverters: Owner's ManualDocument32 pagesDc-Ac Inverters: Owner's Manualalex castroNo ratings yet
- (Ebook) Inverter ManualDocument40 pages(Ebook) Inverter Manualelavefenix741116No ratings yet
- Diode SDocument45 pagesDiode SGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Uday Edition 03Document12 pagesUday Edition 03Gulani Sai TejANo ratings yet
- A Power Supply UnitDocument11 pagesA Power Supply UnitShin Jae JiNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- RX TX and Power SupplyDocument10 pagesRX TX and Power SupplyPrashant LochamNo ratings yet
- Power Supply FunctionDocument4 pagesPower Supply FunctiondunkinkunatNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalDocument21 pagesSupplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalHassan Bin QasimNo ratings yet
- Main ProjectDocument15 pagesMain ProjectChandana K R 4UB20EE010No ratings yet
- Switchyard FinalDocument6 pagesSwitchyard FinalPritam SamantaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Code Lock Using One TransistorDocument18 pagesElectronics Code Lock Using One TransistorAnonymous TvXDUWDaol50% (2)
- 229 PE Innovative Practice 1Document2 pages229 PE Innovative Practice 1Sakshi BarapatreNo ratings yet
- The DC Power Supply Converts The Standard 120 VDocument6 pagesThe DC Power Supply Converts The Standard 120 VEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Hardware Implementation: 3.1 Block Diagram & Components DescriptionDocument10 pagesHardware Implementation: 3.1 Block Diagram & Components DescriptionRajaiah JagariNo ratings yet
- A Report On Summer Training AT 400 KV Substation Panki: SYAD SAMEER AHMAD (1804528209)Document18 pagesA Report On Summer Training AT 400 KV Substation Panki: SYAD SAMEER AHMAD (1804528209)Nitin SinghNo ratings yet
- Inverters General InformationDocument8 pagesInverters General InformationThành Nhân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Self Switching Power SupplyDocument20 pagesSelf Switching Power SupplyPutra Purechk TokyoNo ratings yet
- Filtered Power SupplyDocument39 pagesFiltered Power SupplyAngelo Mark Ordoña Porgatorio0% (1)
- Converter Vs InverterDocument8 pagesConverter Vs InverterPrasad ChandramohananNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument9 pagesPower SupplyMuhammed HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- HVDC PDFDocument52 pagesHVDC PDFmeraatNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Block Diagram & Components Description:: Fig: 3.1 Block Diagram of Cyclo-Converter Using MicrocontrollerDocument10 pages3.1 Block Diagram & Components Description:: Fig: 3.1 Block Diagram of Cyclo-Converter Using MicrocontrollerSwamyNo ratings yet
- Coupling & DecouplingDocument12 pagesCoupling & DecouplingCezanne Cruz100% (1)
- A Power Supply Is A Device That Supplies Electric Power To An Electrical LoadDocument14 pagesA Power Supply Is A Device That Supplies Electric Power To An Electrical LoadElizabeth HarrisNo ratings yet
- Power Supply - WikipediaDocument14 pagesPower Supply - WikipediaaronsanjayNo ratings yet
- Thy 2Document6 pagesThy 2rgr4321No ratings yet
- Distribution SubstationDocument8 pagesDistribution SubstationAmit Debnath100% (2)
- 2 NDDocument4 pages2 NDSyed Hassan Abbas RizviNo ratings yet
- Submitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Document15 pagesSubmitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Himanshu Soni100% (1)
- ApplicationsDocument3 pagesApplicationsPratik SutarNo ratings yet
- Cheap 12V To 220V InverterDocument3 pagesCheap 12V To 220V InverterAnaar KaliNo ratings yet
- Inversor 12V To 220V InverterDocument3 pagesInversor 12V To 220V InverterWILLIAM MONTOYA VILLANo ratings yet
- Substation AssignmentDocument17 pagesSubstation AssignmentBabar Ali100% (1)
- Term Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyDocument15 pagesTerm Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- Power Supply - WikipediaDocument4 pagesPower Supply - Wikipediaaravind balaNo ratings yet
- Noor Al-Salehi - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument22 pagesNoor Al-Salehi - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525647046No ratings yet
- SPVLineDiagram Mod5 Part1Document18 pagesSPVLineDiagram Mod5 Part1Anju JamesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview Questions With AnsDocument16 pagesElectrical Interview Questions With Ansvinoddeswal057100% (1)
- Electric Power Distribution-1Document61 pagesElectric Power Distribution-1ABRAR AHMADNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Power SuppliesDocument33 pagesAmplifier Power Suppliessarantapodarusa4009No ratings yet
- RCI QuestionDocument4 pagesRCI QuestionEngr. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: and His Team of Power Grid Agra Substation For Their Active Support andDocument22 pagesAcknowledgement: and His Team of Power Grid Agra Substation For Their Active Support andMitranshu RajNo ratings yet
- Applications Capacitores EpcosDocument3 pagesApplications Capacitores EpcosWaldir GavelaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Thiruvilwamala MahatmyamDocument4 pagesThiruvilwamala Mahatmyamgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Insurance TerminologiesDocument25 pagesInsurance Terminologiesgoputs6386100% (1)
- Epson EB 1930 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpson EB 1930 Datasheetgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Union BudgetDocument3 pagesBeginners Guide To Union Budgetgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Glossary: (In Order of Importance) Css Encryption: This Is The Encryption Method Used in Dvds. ThisDocument18 pagesGlossary: (In Order of Importance) Css Encryption: This Is The Encryption Method Used in Dvds. Thisgoputs6386No ratings yet
- 10 Windows 7 Commands Every Administrator Should KnowDocument3 pages10 Windows 7 Commands Every Administrator Should Knowgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Aapad Udharana Hanumath StotramDocument2 pagesAapad Udharana Hanumath Stotramgoputs6386No ratings yet
- VishnusathanamamDocument3 pagesVishnusathanamamgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Chemical Arithmetic and Reactions: ObjectivesDocument24 pagesChemical Arithmetic and Reactions: Objectivesgoputs6386No ratings yet
Bleeder Resistance
Bleeder Resistance
Uploaded by
goputs6386Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bleeder Resistance
Bleeder Resistance
Uploaded by
goputs6386Copyright:
Available Formats
A bleeder resistor is a resistor placed in parallel with a high-voltage supply for the purposes of discharging the energy stored
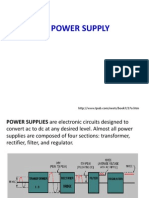
in the power source's filter capacitors or other components that store electrical energy when the equipment is turned off. Power supply circuits used to supply DC power needed by electronic devices, particularly switching mode power supplies, use a bridge rectifier to convert mains AC power into DC at 320 V (for 220 V mains) or 160 V (for 115 V. mains), before the voltage is reduced by thechopper. These incorporate a filter capacitor to smooth the pulsing output voltage from the rectifier. These must typically store enough energy at this high voltage to power the load during the zero crossings of the AC input. In fact, the capacitors in many supplies are large enough to support the load during AC outages lasting for a significant fraction of a second. This stored energy can remain in the capacitors for a long time after the unit has been turned off. It can be a potentially lethal shock hazard for the user, who may believe that because the device is turned off or unplugged it is safe. Therefore, to discharge the capacitor after the supply has been turned off, a large-value resistor is connected across its terminals. By choosing the proper size for this "bleeder resistor", the voltage will quickly decay to safe levels when the supply is switched off, yet the resistor will not consume too much power while the supply is on.
You might also like
- Sri Vishnu Sahasranamam Word-To-word TranslationDocument30 pagesSri Vishnu Sahasranamam Word-To-word Translationkaustavchakravarthy100% (7)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- An Industrial Training PPT On 50mva, 132/33 KV Grid Sub StationDocument35 pagesAn Industrial Training PPT On 50mva, 132/33 KV Grid Sub Stationishfaq222100% (3)
- Switch Yard and Its EquipmentsDocument48 pagesSwitch Yard and Its Equipmentsamit joshi86% (14)
- 436 Power CapacitorsDocument6 pages436 Power Capacitorselectrical civilNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation EquipmentDocument4 pagesElectrical Substation EquipmentPurbita ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- CSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumDocument14 pagesCSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumAshish MauryaNo ratings yet
- Oscillator: How To Build An InverterDocument7 pagesOscillator: How To Build An InverterGopal Prasad BansalNo ratings yet
- Deutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Document15 pagesDeutsch: Register To Download Premium Content!Modesto Marcos Calderon CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Electrical Substation Components and Their WorkingsDocument22 pagesAssignment 1 Electrical Substation Components and Their WorkingsAP13 AP13No ratings yet
- Dc-Ac Inverters: Owner's ManualDocument32 pagesDc-Ac Inverters: Owner's Manualalex castroNo ratings yet
- (Ebook) Inverter ManualDocument40 pages(Ebook) Inverter Manualelavefenix741116No ratings yet
- Diode SDocument45 pagesDiode SGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Uday Edition 03Document12 pagesUday Edition 03Gulani Sai TejANo ratings yet
- A Power Supply UnitDocument11 pagesA Power Supply UnitShin Jae JiNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- RX TX and Power SupplyDocument10 pagesRX TX and Power SupplyPrashant LochamNo ratings yet
- Power Supply FunctionDocument4 pagesPower Supply FunctiondunkinkunatNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalDocument21 pagesSupplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalHassan Bin QasimNo ratings yet
- Main ProjectDocument15 pagesMain ProjectChandana K R 4UB20EE010No ratings yet
- Switchyard FinalDocument6 pagesSwitchyard FinalPritam SamantaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Code Lock Using One TransistorDocument18 pagesElectronics Code Lock Using One TransistorAnonymous TvXDUWDaol50% (2)
- 229 PE Innovative Practice 1Document2 pages229 PE Innovative Practice 1Sakshi BarapatreNo ratings yet
- The DC Power Supply Converts The Standard 120 VDocument6 pagesThe DC Power Supply Converts The Standard 120 VEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Hardware Implementation: 3.1 Block Diagram & Components DescriptionDocument10 pagesHardware Implementation: 3.1 Block Diagram & Components DescriptionRajaiah JagariNo ratings yet
- A Report On Summer Training AT 400 KV Substation Panki: SYAD SAMEER AHMAD (1804528209)Document18 pagesA Report On Summer Training AT 400 KV Substation Panki: SYAD SAMEER AHMAD (1804528209)Nitin SinghNo ratings yet
- Inverters General InformationDocument8 pagesInverters General InformationThành Nhân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Self Switching Power SupplyDocument20 pagesSelf Switching Power SupplyPutra Purechk TokyoNo ratings yet
- Filtered Power SupplyDocument39 pagesFiltered Power SupplyAngelo Mark Ordoña Porgatorio0% (1)
- Converter Vs InverterDocument8 pagesConverter Vs InverterPrasad ChandramohananNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument9 pagesPower SupplyMuhammed HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- HVDC PDFDocument52 pagesHVDC PDFmeraatNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Block Diagram & Components Description:: Fig: 3.1 Block Diagram of Cyclo-Converter Using MicrocontrollerDocument10 pages3.1 Block Diagram & Components Description:: Fig: 3.1 Block Diagram of Cyclo-Converter Using MicrocontrollerSwamyNo ratings yet
- Coupling & DecouplingDocument12 pagesCoupling & DecouplingCezanne Cruz100% (1)
- A Power Supply Is A Device That Supplies Electric Power To An Electrical LoadDocument14 pagesA Power Supply Is A Device That Supplies Electric Power To An Electrical LoadElizabeth HarrisNo ratings yet
- Power Supply - WikipediaDocument14 pagesPower Supply - WikipediaaronsanjayNo ratings yet
- Thy 2Document6 pagesThy 2rgr4321No ratings yet
- Distribution SubstationDocument8 pagesDistribution SubstationAmit Debnath100% (2)
- 2 NDDocument4 pages2 NDSyed Hassan Abbas RizviNo ratings yet
- Submitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Document15 pagesSubmitted To, Name-Mr. Ankush Tandon Sir (Assistant Professor)Himanshu Soni100% (1)
- ApplicationsDocument3 pagesApplicationsPratik SutarNo ratings yet
- Cheap 12V To 220V InverterDocument3 pagesCheap 12V To 220V InverterAnaar KaliNo ratings yet
- Inversor 12V To 220V InverterDocument3 pagesInversor 12V To 220V InverterWILLIAM MONTOYA VILLANo ratings yet
- Substation AssignmentDocument17 pagesSubstation AssignmentBabar Ali100% (1)
- Term Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyDocument15 pagesTerm Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- Power Supply - WikipediaDocument4 pagesPower Supply - Wikipediaaravind balaNo ratings yet
- Noor Al-Salehi - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument22 pagesNoor Al-Salehi - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525647046No ratings yet
- SPVLineDiagram Mod5 Part1Document18 pagesSPVLineDiagram Mod5 Part1Anju JamesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview Questions With AnsDocument16 pagesElectrical Interview Questions With Ansvinoddeswal057100% (1)
- Electric Power Distribution-1Document61 pagesElectric Power Distribution-1ABRAR AHMADNo ratings yet
- Amplifier Power SuppliesDocument33 pagesAmplifier Power Suppliessarantapodarusa4009No ratings yet
- RCI QuestionDocument4 pagesRCI QuestionEngr. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: and His Team of Power Grid Agra Substation For Their Active Support andDocument22 pagesAcknowledgement: and His Team of Power Grid Agra Substation For Their Active Support andMitranshu RajNo ratings yet
- Applications Capacitores EpcosDocument3 pagesApplications Capacitores EpcosWaldir GavelaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Thiruvilwamala MahatmyamDocument4 pagesThiruvilwamala Mahatmyamgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Insurance TerminologiesDocument25 pagesInsurance Terminologiesgoputs6386100% (1)
- Epson EB 1930 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpson EB 1930 Datasheetgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Union BudgetDocument3 pagesBeginners Guide To Union Budgetgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Glossary: (In Order of Importance) Css Encryption: This Is The Encryption Method Used in Dvds. ThisDocument18 pagesGlossary: (In Order of Importance) Css Encryption: This Is The Encryption Method Used in Dvds. Thisgoputs6386No ratings yet
- 10 Windows 7 Commands Every Administrator Should KnowDocument3 pages10 Windows 7 Commands Every Administrator Should Knowgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Aapad Udharana Hanumath StotramDocument2 pagesAapad Udharana Hanumath Stotramgoputs6386No ratings yet
- VishnusathanamamDocument3 pagesVishnusathanamamgoputs6386No ratings yet
- Chemical Arithmetic and Reactions: ObjectivesDocument24 pagesChemical Arithmetic and Reactions: Objectivesgoputs6386No ratings yet