Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Full Time: Four Semester Course
Full Time: Four Semester Course
Uploaded by
Parag LambeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Power Line Communications: Theory and Applications for Narrowband and Broadband Communications over Power LinesFrom EverandPower Line Communications: Theory and Applications for Narrowband and Broadband Communications over Power LinesHendrik C. FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument33 pagesSyllabus PDFSourabh PatilNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ISUTDocument114 pagesSyllabus ISUTWaniBazillaNo ratings yet
- PrintingDocument130 pagesPrintingJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Btech s7 Electrical Electro Eng 20131466834599Document38 pagesBtech s7 Electrical Electro Eng 20131466834599Nikhil EdwardNo ratings yet
- BM Syllabus - 2009Document172 pagesBM Syllabus - 2009Rifas ZakirNo ratings yet
- ECDocument132 pagesECAkhil Paul VNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument186 pagesMechanicalश्रीराज् कथलियिल्No ratings yet
- Electronics & Communication 2006 Sem III NewDocument32 pagesElectronics & Communication 2006 Sem III NewJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- IC Syllabus For Calicut UniversityDocument135 pagesIC Syllabus For Calicut UniversityAnith MohanNo ratings yet
- University of Jammu: Course No. Course Name L T PDocument10 pagesUniversity of Jammu: Course No. Course Name L T PanmolankuNo ratings yet
- PT EeeDocument146 pagesPT Eeegovi007No ratings yet
- Scheme and Syl Applied Electronics and Instrumentation 2014Document123 pagesScheme and Syl Applied Electronics and Instrumentation 2014cijoNo ratings yet
- M Tech. SyllabusDocument73 pagesM Tech. Syllabusrakesh aseryNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology (Electronics & Communication, Electronics, Electronics & Instrumentation) Common For (ECE, EC, E&I) Scheme of Studies / Examination (Semester-3)Document67 pagesBachelor of Technology (Electronics & Communication, Electronics, Electronics & Instrumentation) Common For (ECE, EC, E&I) Scheme of Studies / Examination (Semester-3)Devesh Garg0% (1)
- Syl Btech EC 2014 PDFDocument122 pagesSyl Btech EC 2014 PDFnazlin sitharaNo ratings yet
- Communicationenggandsignalprocessingmtech SyllabusDocument70 pagesCommunicationenggandsignalprocessingmtech SyllabusRama SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- CS Syllabus 2012 Admissions OnwardsDocument78 pagesCS Syllabus 2012 Admissions OnwardsAnurag DeterminedNo ratings yet
- DR BAMU Me Etc Syllabus 18-June-13 FinalDocument39 pagesDR BAMU Me Etc Syllabus 18-June-13 FinalnitinsupekarNo ratings yet
- 20120711112402-BE IT Syllabus 2012-13Document57 pages20120711112402-BE IT Syllabus 2012-13Sambhav KapoorNo ratings yet
- Power SystemsDocument54 pagesPower SystemsBindu ChipiriNo ratings yet
- FT EieDocument83 pagesFT EieBalan PaulrajanNo ratings yet
- Computer SC PDFDocument155 pagesComputer SC PDFVipeesh ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Calicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusDocument150 pagesCalicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- S YBTechComputer Engg - SyllabusDocument31 pagesS YBTechComputer Engg - SyllabusRushabh Patel0% (1)
- SyllabusDocument131 pagesSyllabuspuneetpagalNo ratings yet
- Network Engineering PDFDocument44 pagesNetwork Engineering PDFAbin PaulNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanSheela RaviNo ratings yet
- CREDIT SYSTEM 3 Courses-3-Years23!04!2009Document10 pagesCREDIT SYSTEM 3 Courses-3-Years23!04!2009Kishore PotnuruNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing VTU Syllabus For Quick RevisionDocument44 pagesSignal Processing VTU Syllabus For Quick RevisionPavan KulkarniNo ratings yet
- ExtcDocument48 pagesExtcSagar KuchekarNo ratings yet
- Ec52 - Digital Signal ProcessingDocument17 pagesEc52 - Digital Signal ProcessingshankarNo ratings yet
- ECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 6 June, 2013Document58 pagesECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 6 June, 2013menilanjan89nLNo ratings yet
- EE407 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument2 pagesEE407 Digital Signal ProcessingbibuthomasNo ratings yet
- Mtech Electronics Syllabus VTUDocument48 pagesMtech Electronics Syllabus VTUmuqeetmmaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of TechnologyDocument65 pagesBachelor of TechnologyShivangi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ECE Andhra University SyllabusDocument91 pagesECE Andhra University Syllabush9emanth4No ratings yet
- RF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversFrom EverandRF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Digital and Kalman Filtering: An Introduction to Discrete-Time Filtering and Optimum Linear Estimation, Second EditionFrom EverandDigital and Kalman Filtering: An Introduction to Discrete-Time Filtering and Optimum Linear Estimation, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Noise and Vibration Analysis: Signal Analysis and Experimental ProceduresFrom EverandNoise and Vibration Analysis: Signal Analysis and Experimental ProceduresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Spacecraft Systems EngineeringFrom EverandSpacecraft Systems EngineeringPeter FortescueRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Next Generation Wireless Communications Using Radio over FiberFrom EverandNext Generation Wireless Communications Using Radio over FiberNo ratings yet
- Microwave and Millimeter Wave Circuits and Systems: Emerging Design, Technologies and ApplicationsFrom EverandMicrowave and Millimeter Wave Circuits and Systems: Emerging Design, Technologies and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- LTE-Advanced and Next Generation Wireless Networks: Channel Modelling and PropagationFrom EverandLTE-Advanced and Next Generation Wireless Networks: Channel Modelling and PropagationNo ratings yet
- RF and Microwave Engineering: Fundamentals of Wireless CommunicationsFrom EverandRF and Microwave Engineering: Fundamentals of Wireless CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Computational Strategies for Spectroscopy: from Small Molecules to Nano SystemsFrom EverandComputational Strategies for Spectroscopy: from Small Molecules to Nano SystemsVincenzo BaroneNo ratings yet
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationFrom EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo ratings yet
- Vibration-based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive ApplicationsFrom EverandVibration-based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Computational Number Theory and Modern CryptographyFrom EverandComputational Number Theory and Modern CryptographyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Trilogy of Connectors: Basic Principles and Connector Design ExplanationsFrom EverandTrilogy of Connectors: Basic Principles and Connector Design ExplanationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Microwave Component Measurements: with Advanced VNA TechniquesFrom EverandHandbook of Microwave Component Measurements: with Advanced VNA TechniquesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
Full Time: Four Semester Course
Full Time: Four Semester Course
Uploaded by
Parag LambeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Full Time: Four Semester Course
Full Time: Four Semester Course
Uploaded by
Parag LambeCopyright:
Available Formats
ThefollowingshallbetheschemeofinstructionandexaminationforMasterofEngineering(Electronics) formJune2002. FullTime:FourSemesterCourse Part I(FirstTerm) Sub.SubjectTeachingSchemeExaminationScheme(Max.Marks) No.LPr./Tu.TotalPaperTw.Pr.
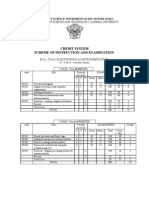
/OralTotal 123456789 01AdvancedDigital 42610025 125 SignalProcessing 02DigitalSystems42610025 125 Design 03AdvancedInstrumentation4 2610025 125 Systems 04DigitalComm.42610025 125 Systems 05Elective I426100 25 125 06SeminarI 0101 25 25 TotalofPart I201131500150 650
Part II(SecondTerm) Sub.SubjectTeachingSchemeExaminationScheme(Max.Marks) No.LPr./Tu.TotalPaperTw.Pr./OralTotal 12 3456789 07ComputerNetworks42610025 125 08Embeddedsystem42610025 125 Design 09AdvancedPower42610025 125 Electronics 10AdvancedComputer42610025 125 System 11ElectiveII42610025 125 12SeminarII 0101 25 25 TotalofPart II20 1131500150 650 PartIII Sub.SubjectTeachingSchemeExaminationScheme(Max.Marks) No.LPr./Tu.TotalPaperTw.Pr./OralTotal 1 23456789 13Dissertation(Part I) 66 50 50 TotalofPartIII 66 50 50 Part IV(FourthTerm) Sub.SubjectTeachingSchemeExaminationScheme(Max.Marks) No.LPr./Tu.Total PaperTw.Pr./OralTotal 123456789 14Dissertation(PartII) 66 50200250 TotalofPart I,II,III,&IV 10004002001600
Group IGroup IIGroup III Computer SignalCommunication ApplicationsProcessing Elective IComputerSystemDigitalImageWireless&Mobile Software ProcessingCommunication Elective IIArtificialNeuralPatternAdvanced NetworksRecognition Telematics ThestudenthavetochooseoneoftheGroupasElectiveI&IIfortheCourseforMaserofEngineering inElectronics.
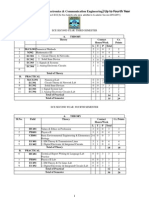
PartTime:SixSemesterCourse Part I(FirstTerm) Sub.SubjectTeachingSchemeExaminationScheme(Max.Marks) No.LPr./Tu.TotalPaperTw.Pr./OralTotal 123456789 01AdvancedDigital42610025 125 SignalProcessing 02AdvancedInstrumentation42610025 125 Systems 03DigitalComm. 42610025 125 Systems TotalOfPart I1261830075 375 Part II(SecondTerm) Sub.SubjectTeachingSchemeExaminationScheme(Max.Marks) No.LPr./Tu.TotalPaperTw.Pr./OralTotal 12345678 9 04DigitalSystem42610025 125 Design 05AdvancedComputer42610025 125 System 06Elective I42610025 125 TotalOfPart I1261830075 375
Part III (Third Term) Sub. No. 1 07 Subject Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme (Max. Marks) L Pr./Tu. Total Paper Tw. Pr./Oral Total 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 4 2 6 100 25 125 4 08 2 01 5 6 01 13 100 200 25 25 75 125 25 275
2 Advanced Power Electronics 08 Computer Networks 09 Seminar I Total Of Part III
Part IV (Fourth Term) Sub. No. 1 10 Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme (Max. Marks) L Pr./Tu. Total Paper Tw. Pr./Oral Total 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Embedded System 4 2 6 100 25 125 Design 11 Elective II 4 2 6 100 25 125 12 Seminar II 01 01 25 25 Total Of Part IV 08 5 13 200 75 275 Subject
Part V (Fifth Term) Sub. Subject Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme (Max. Marks) No. L Pr./Tu. Total Paper Tw. Pr./Oral Total 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 13 Dissertation (PartI) 6 6 50 50 Total Part V 6 6 50 50 Part VI (Sixth Term) Sub. Subject Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme (Max. Marks) No. L Pr./Tu. Total Paper Tw. Pr./Oral Total 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 14 Dissertation (Part II) 6 6 50 200 250 Total of Part I to Part VI 1000 400 200 1600
CLASS:ME(EC) Advanced DigitalSignalProcessing
(Onepaper:3hours,100marks,Termwork:25marks) Overview:Ztransforms,DiscreteFouriertransforms,FFT,radix2,radix4,SplitRadixFFTalgorithms, ImplementationofFFTalgorithms,FFTalgorithmsinLinearfiltering& correlation,Quantization ErrorinFFTalgorithms. Designof FIR Filters: Design of Linear phase FIR filters using windows, frequency sampling method, designofoptimumequiripplelinearphaseFIRFiltersdesignofFIRdifferentiators,Hilberttransformers comparisonofFIRfilterdesignmethods. Designof IIR filters: Design of IIR filters byapproximation of derivatives, Impulse invariance bilinear transformation,matchedZtransforms,DesignofIIRfiltersbyfrequencytransformationsinanalogand digitaldomain. DesignofDigitalfiltersbasedonleastsquaresmethodpadieapproximationmethodleastsquaredesign methodFIRleastsquareInverse(Wiener)filters.DesignofIIRinthefrequencydomain. Linear prediction: Innovations representation of a stationary Randomprocess, Relationship between the filterparametersandtheautocorrelationsequence,Autoregressive(AR)&movingaverage(MA)process, forward&backwardlinearreduction. Power Spectrum estimation: Estimation of spectra from finite duration observations of signals, energy density spectrum, estimation of autocorrelation and power spectrum use of DFT in power spectrum estimation, Adaptivefilters: Adaptive implementation of wiener filter, correlation canceller loop,Windrowhoff LMS adaptation algorithm,Adaptivelinearcombiner,FIRWienerfilters,Speedofconvergence,Adaptiveechocancellor, AdaptiveNoisecanceller(ANC)adaptivelinearenhancer(ALE)Adaptivelinearprediction.
DIGITALSYSTEMSDESIGN (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,Termwork:25marks) Design state machine More and mealy machine, state diagram, ASM techniques, Implementation of Combinational, synchronous sequential & Asynchronous sequential machine, Algorithmic synchronous machine Modelling:Functionalmodelingatthelogiclevel,functionalmodelingatregisterlevel,structuralmodels levelofmodeling. Logic simulation: Applications, problems in simulation based design verification, types of simulation, Unknown logic value compiled simulation event driven simulation, delay models, elements, evaluation,Hazarddetection,simulationengines. Faultmodeling:Generalfaultsimulationtechniques,statisticalfaultanalysis. Testingforsinglestuckfault:Basicissues,ATGforSSFincombinedckts.ATGforSSFsinsequential ckts.PLAtesting. Design for Testability: Classical testability scan design, compression tech. Built in self test logic level diagnosis,selfcheckingdesign. Specific digital system: Design such as digital IC tester Micricontrolleo cards PC add on cards design, PLAbasedproductdesign.
ADVANCEDINSTRUMENTATIONSYSTEM (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,Termwork:25marks) ReviewofControlsystemprinciples: Basic concept, variables & degrees of freedom, control modes and controllers on off, P,PI,PD,PID, controllers,feedback&feedforwordcontrol,ratio,cascade,selectiveAdaptiveOptimisingcontroltuning ofcontrollers. Computer controls: Advantages, Implementation problems sampling Quantization, Aspect of control theoryTransferfunctionapproach,statespaceapproachsystemDesignoptimalcontrol,selftuningand adaptivecontrol,Mathematicalmodeling,Designofdigitalcontroller generalsynthesismethods,Dahlin design,kalmandesign. Onlinecontrol, offlinecontrol,directdigitalcontrol SCADA,computerinterfacingtechniques,programmablelogiccontrollers Evaluation,specifications,applications,relayladders,eg.BoilercontrolandothersNC,CNC,andDNC. Simulationandprocesscontrol:Studyofplant,subplantandinstrumentationprocessusedthermalpower station,sugercementpaperandpharmaceuticalindustries. IntroductionofElectronicInstrumentation: Measurements on Transmitters and receivers: General performance characteristics, Basic and special measurements, measurement on transmitting Receiving systems, sensitivity, modulation, acceptance bandwidth,signaltonoiseratio,equipmentspecifications. Microwave signal Analysis Power measurement, spectrum analysis, wave analyzers, Electromagnetic interference measurements, Microwave Network analysis, Automatic analyzer systems and Automatic Testsystems.
DIGITALCOMMUNICATIONSYSTEMS (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,Termwork:25marks) 1) Review: PMA,PTM and PPM generation and reception, Digital PAM formats transmission, powerspectra,noiseanderrors.Regenerativerepeaters, BandlimitedPAMsystems,Synchronizationtechniques. 2) Digital modulation: OOK,FSK, PSK,BPSK,MSK,QAM,QOSK, their comparison Optimum detection. 3) PCMgenerationandreconstruction,linearandnonlinearquantisation,channels,bandwidth,noise inPCM,itscomparisonwithnoiseinAM,DPCM,DM,ADMtechniques,systemsandcomparison, therealldetailswithmodifications. 4) Error Detection and correction: Repetition and parity check codes, code vectors and hamming distance,FECandARQsystems,linearblockcodes,convolutioncodinganddecodingtechniques andsystem,Turbocodes,Dataencryption,distortionandreshapingofthewaveforms. 5) Information and detection theory: Probability stochastic Processes Information measure and source coding information transmission on discrete channels, continuous channels and system comparison,signalspace,Optimumdigitaldetection. 6) NarrowbandandBroadbandISDNoverviewandsomeapplication.NetworksprotocolHierachies. 7) Spread spectrum signal, Direct spread spectrum, frequency of spread spectrum, performance, CDMAsystembasedonFHSSsystem,synchronizationspreadspectrumsystem.
Group II DigitalImageProcessing(ElectiveI) (Onepaper3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) 1)Introduction : Digital Image Representation, Fundamental steps in image Processing, Elements of DigitalImageProcessingsystems,JPEGsJPG,Tifbmpimageformat. 2)Digital Image Fundamentals: Elements of Visual Perception, A simple Image Model, Sampling and Quantisation,SomebasicrelationshipbetweenPixels,ImageGeometry,PhotographicFilm. 3)Image Transforms: Introduction to the Fourier Transform, The Discrete Fourier Transform, Some propertiesoftheTwodimensionalFourierTransform,TheFastFourierTransform,HadamandHough Hotelling,wavelettransforms. 4)Image Enhancement: Background Enhancement by point processing, spatial filtering Enhancement in theFrequencyDomain,GenerationofSpatialMaskfromFrequencyDomainSpecification,ColorImage Processing. 5)Image Restoration: Degradation Model, Diagonalisation of Circulant and Block circulant Matrices, Algebraic approach to Restoration, Inverse Filtering, Least Mean Square(Wiener) Filter, Constrained Least Square Restoration, Interactive Restoration, Restoration I the Spatial Domain Geometric Transformation. 6)ImageCompression:FundamentalsImageCompressionModels,ElementsofInformationtheory,Error freeCompressionLossyCompression,ImageCompressionStandards. 7)ImageSegmentation:DetectionofDiscontinuous,EdgeLinkingandBoundaryDetection,Thresholding ,Region Segmentation,TheuseofMotioninSegmentation. 8)RepresentationAndDescription:RepresentationSchemesBoundaryDiscriptors,RegionalDescriptions Morphology,RelationalDescriptors. 9)Recognition and Interpretation: Elements of Image Analysis, Pattern and Pattern Classes, Decision ThereticMethods,StructuralMethods,Interpretation.
Group III WIRELESSANDMOBILECOMMUNICATION(ElectiveI) (Onepaper3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) Introductiontomobilecomm.,Cellularmobile,telephonearchitecture,IPtelephonyoverview. Cellular Radio System Design: Frequency assignments, Frequency reuse channels, concept of cell splitting,Handoverincellularsystem,Handoffalgorithms. Multipleaccessschemesinmobilecommunication:TDMA,FDMA,CDMA,Randommultipleaccessin, Performance analysis issue. MAC layer, scheduling & connection admission in mobile communications interferencesuppression&powercontrol. Teletrafficmodeling&Queueingtheroticanalysisofcellularmobilenetworks. Resourceallocation&mobilitymanagement. Practical Cellularmobile system:AMPSandGSMsystemarchitectureoverview.Callmanagement & systemoperation,CDMAbasedcellularsystemwirelessinlocalloopDECTandCDMAWLL.
Group I COMPUTERSYSTEMSOFTWARE(Elective I) (Onepaper3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) System Programming: Language processor data structures for language processing, Single / two pass assemblerdesign,Micros&Microprocessorsforprogramdevelopment. Operating system: Evaluation , Memory management processor management, Device management, Information(File)management,Security&protection. MultiprogrammingO.S.,DistributedO.S.,Multiprocessorsystem Implementation: Input / Output : Principle & Programming, Design & Implementation of Kernel of MultitaskingO.S.(KMOS)
EMBEDDEDSYSTEMDESIGN (Onepaper 3hours,100marks,termwork25marks) Introductionandscopeofembeddedsystem:OverviewofMCS89C51IC,Internalarchitectureand programmingofmicrochipPIC16F84Microcomputer. ApplicationusingMCS89C51 On chip timers, watch dog timers, on chip serial ports, inter facing ADC, DAC power devices EXT,RAM/ROM,DMprinters,LED/LCDdisplay,relayRS232. Useofdevelopmenttoolslikeassemblers,compilers,simulators,emulators,RTOS. PROMprogrammingflash,ROMprogramming. IntroductiontoMCS96family. MCS968096BHarchitecture,programmingandhardwaredesigning. Development support tools : 8096/196 software development packages, VLSI/ CE96 in circuit Emulators,Realtimetransparent80C196incircuitemulators. ProjectDesign:Conceptdesigning,Methodologyfortheflowingcasestudies i) Cellularphone(using8bitmicrocontroller) ii) Digitalcamera(using16bitmicrocontroller) Introductionto32bitmicrocontrollerpowerPC80960.
COMPUTERNETWORKS (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) 1) System Network Architecture : Path control, transmission control, data flow control, RS449 interface,X.25standardARPANET,TCP/INTERNET. 2) Protocoldesign:Designissues,basicflowcontrol,slidingwindowprotocol,protocolcorrectness, datalinkcontrolprotocol,Kermitprotocol,protocolhierarchies. 3) Wireless networks : Specifications for a wireless network, IEEE 802.11, mobile phone service fundamentals,cell,frequencyutilization,allocationchannelcenterfrequency,channelutilization, TDMA,TDMAframe,timeslotformat,subscribetobasestationslotformat.GSM,GSMmulti frame,multi frameformat. CDMA , CDMA downlink channel structure, CDMA channel parameters, CDMAair interface protocol stack Data compression, Huffman code rumlength encoding, relative encoding,LampelZivencoding,imagecompression,JPEG,MPEG. 4) Electronicsmail:X400&X500standards,NETWORKsecurity. 5) ISDN:ISDNArchitecture,physicalframeformat,ISDNOverview, ISDNInterfacesandFunctions:Transmissionandstructure,usernetworkinterfaceconfigurations, protocolarchitecture,ISDNconnectionsAddressing,Interworkingphysicalanddatalayers. 6) Global Mobile Satellite System : Iridium system, Globalstar system, ICO system, Teledesic system. 7) Network Management : Network management tools, network statistics measurement systems, NetworkManagementsystems. Applications for configuration management, fault management, performance management, securitymanagement,accruingmanagement,expertmanagement.
ADAVANCEDCOMPUTERSYSTEMS (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) 1) ArchitecturefeaturesofPentium,Registerstructure,Memorymanagement. 2) Advancedmicrocontrollers :8096,COP*ACC7,COP*SGX5,COP888EBanddesignofsystem forapplicationslike a) TemperatureController b) DataAcquisitionsystem c) Powermanagement. Withcomputerinterface. 3) Parallel Processing : Processor requirement for parallel processing, multi processor Operating system,Vectorprocessors,Pipelineprocessing,paralleldatabases,parallelsystemmemory. 4) Multimedia:MultimediaOperatingSystems,JPEG,MPEG,DVI,Datacompressiontechniques, multimediaresearchissues,multimediaapplications. 5) Vocoders, homomorphic, linear predictive, voice over IP networking, voice over IP gateways, voice over frame relay, voice over ATM., Speech coding techniques for audio and video like performancecomparisonPCM,ADM,Vocoders. CODECICslikeLM4540,LM4548applications. 6) Imperfectionsincommunicationcausesofnoise&distortion,delays&blocking,computerdialing connectionstimings.
ADVANCEDPOWERELECTRONICS (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) 1) Review of power electronic devices such as SCR, TRIAC, DIAC, UJT, SUS, SBS, MOSFET, IGBT,etc. Their ratings, characteristics, turn ONOFF mechanisms, triggering circuit design, protection, selectioncriteria. 2) StudyofdifferentcharacteristicsofvariousAC/DCdrives,Speedcontrol.Reviewofconventional speed control methods used for DC and AC induction motor design. Review of Thyristor converters and DC choppers, phase control inverter, regeneration by phase control inverters. Regeneration by phase control, chopper control microprocessors and microcontroller based systems. 3) Classificationofinverter,forcedcommunicationmethods,Inverters,frequencyandvoltagecontrol harmonic limitation, choice of SCR inverters, Inverter control circuit, phase control cyclo converters, speed control of Induction motorusing microprocessor and microcontroller system. Economicselectionofelectricdrives,recenttrendsindevelopmentsofvariablespeeddrives.
ARTIFICIALNEURALNETWORKS(ELETIVEII) (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) 1) Basics of ANN : Neural networks, Neuron topology, Activation dynamics models, synaptic dynamicsmodels,Stability&convergence. 2) Uncertainty, Shannon entropy, Boltzman entropy, measures of confusion, measures of non specificity. 3) Fuzzylogic:crispsets,fuzzysets,operationonfuzzysets,fuzzyrelations,ERIC(ExtendedRule Based System for Intelligent Control), FP3000 digital fuzzy processor, analog fuzzy processor, interfacechip,defussificationchip. 4) Neural networks : Analysis of feed forward, feedback neural networks, stability of neural networks,noisesuppression. 5) Application likepatternrecognition,Architectureforcomplexpatternrecognitiontasks,pattern mapping,stabilityplasticitydilemma,temporalpattern,patternvariability. 6) Neural Networks learning rules, Hebbian perception delta widrowHoff, correlation, winner take alloutstar. 7) ANN model, active building blocks for realizing the systems design of fuzzy controller, applications of ANN like auto vehicle navigation, speech recognition, hand written digit recognition, fuzzy based washing machine, vacuum cleaners, video equipment, automatic train operation.
SEMINARII (TermWork:25marks) Seminar attheendofsecondsemesteroffulltimecourseandfourthsemesterofpart timecourseinM.E.(Electronics)willbebaseduponthetechnicalessayorareportoranalysistopicof dissertationchosenbythecandidate.He/sheshallsubmitshortreportonthetopicandwilldelivera talkthereonwhichalongwiththereportwillbeassessedbytwointernalexaminers,oneofwhomwill betheguideandtheotherbeingappointedbyPrincipaloftheInstitution.
DISSERTATION(PARTI) (TermWork:25marks) Dissertation(part I) at the end of third semesterof full timecourseand fifth semester of parttimecourseinM.E.(Electronics)willbebaseduponthedissertationchosenbythecandidate.He /Shewilldeliveratalkthereon,whichwillbeassessedbytwointernalexaminers,oneofwhomwill betheguideandtheotherbeingappointedbyPrincipal.
DISSERTATION(PARTII) (TermWork:50marks,Practical:200marks) The dissertation shall consist of a report on any research work done by the candidate or Detailedreportoftheprojectworkconsistingofadesignanddevelopmentworkthatthecandidatehas done. ThecandidateshallsubmitthedissertationreportintriplicatetotheHeadoftheInstitution, dulycertifiedthattheworkhasbeensatisfactorilycompleted. TERM WORK : The dissertation will be assessed by two internal examiners, appointed by the PrincipaloftheInstitution,oneofwhomwillbetheguideandtheotheraSeniorstaffmemberofthe respectiveDepartment.
Practical Examination : It shall consists of a defence presented by the examinee on his work in the presence of examiners, appointed by the University, one of whom eill be the guide and other an externalexaminer.
PATTERNRECOGNITION(ELCETIVEII) (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks) 1) Introductiontopatternrecognition:MachinePerception,theclassificationmodel,theDescriptive Approach. 2) BayesDecisionTheory:BayesDecisionTheory,minimumerrorrate,classification,classifiers, Discriminate Functions and Decision surfaces, Error Probabilities and Integral, The Normal DensityDiscriminatefunctionfortheNormalDensityBayesianDecisionTheory. 3) Parameter Estimation and Supervised leasning the mean of a Normal Density, General Bayesian Learning,SufficientstaticsandExponentialfamily,ProblemsofDimensionality,Estimatingthe Errorrate. 4) NonparametricTechnique:DensityEstimationParzenwindows,KNearestneighborEstimation, Estimation of a Posteriori Probability, the nearest Neighbor Rule, Approximation by series Expansion,ApproximationfortheBinarycase,Fisherslineardiscriminate,Multiplediscriminate analysis. 5) LinearDiscriminantFunctions:LinearDiscriminantfunctionsanddecisionsurfaces,Generalised Linear Descriminant functions, the two category linearly separable case, Minimizing the perception Criterion function, Relaxation procedures, Nonseparable behavior, minimum squared errorprocedures,HoKashyapprocedures,linearprogrammingprocedures,themethodofpotential function,multicategorygenelalizations. 6) Unsupervisedlearningandclustering:mixturedensitiesandidentifiability,maximumlikelihood estimates,Applicationtonormalmixtures,UnsupervisedBayesian learning,datadescriptionand clustering, criterion functions for clustering, iterative optimization, hierarchical clustering, graph theoreticmethods,clusteringanddimensionalityreduction. 7) Introduction to seene analysis representation and initial simplifications, the spatial frequency domain, description of line and shape, perspective transformations, projective invariants, descriptivemethodsinsceneanalysis.
ADVANCEDTELEMATICS(ELECTIVEII) (Onepaper:3hours,100marks,TermWork:25marks)
1) Telephonenetworkoverviewcircuitswitchingandpacketswitching,Electronicexchange. 2) Line coding technique, interfacing, ADSL, Switching techniques & their comparison. ISDN overview,ITU Standardizationsector. 3) ISDN interfaces & functions: Transmission structures, user network interface configuration, Protocolarchitecture,ISDNconnectionaddressing,Interworkingphysical&datalayers. 4) Frame relay: Introduction, Protocol, Architecture frame mode call control LAPF core protocol, Framerelaycongestioncontrol. 5) BroadbandISDN:Architecture,standards,Servicesrequirementsprotocols. ATMprotocols:Overview,Hierarchy,ATMcells,theirdetailsandtransmissions, AAL,ATM,traffic&congestioncontrol. NetworksProtocolsHierarchies,Designissuesforthelayer,OSI&TCP/IP referencemodel,comparison,Novelnetwork,ARPANET,NSFNET,INTERNET, TCP/UDP,SMDS,X25Networks,Framerelay,BroadbandISDN&ATMNetwork standardization,Networksecurity,Highspeed&bridgedLAN,INTERNET working. 6) IPTelephony:H.323andageneralbackground,sessioninitiationprotocolmedia gatewaytomediacontrollerprotocol,Voicetechnologybackgroundnetworks.
SEMINARII (TermWork:25marks) Seminar attheendofsecondsemesteroffulltimecourseandfourthsemesterofpart timecourseinM.E.(Electronics)willbebaseduponthetechnicalessayorareportoranalysistopicof dissertationchosenbythecandidate.He/sheshallsubmitshortreportonthetopicandwilldelivera talkthereonwhichalongwiththereportwillbeassessedbytwointernalexaminers,oneof whomwill betheguideandtheotherbeingappointedbyPrincipaloftheInstitution.
DISSERTATION(PARTI) (TermWork:25marks) Dissertation(part I) at the end of third semesterof full timecourseand fifth semester of parttimecourseinM.E.(Electronics)willbebaseduponthedissertationchosenbythecandidate.He /Shewilldeliveratalkthereon,whichwillbeassessedbytwointernalexaminers,oneofwhomwill betheguideandtheotherbeingappointedbyPrincipal.
DISSERTATION(PARTII) (TermWork:50marks,Practical:200marks) The dissertation shall consist of a report on any research work done by the candidate or Detailedreportoftheprojectworkconsistingofadesignanddevelopmentworkthatthecandidatehas done. ThecandidateshallsubmitthedissertationreportintriplicatetotheHeadoftheInstitution, dulycertifiedthattheworkhasbeensatisfactorilycompleted. TERM WORK : The dissertation will be assessed by two internal examiners, appointed by the PrincipaloftheInstitution,oneofwhomwillbetheguideandtheotheraSeniorstaffmemberofthe respectiveDepartment.
Practical Examination : It shall consists of a defence presented by the examinee on his work in the presence of examiners, appointed by the University, one of whom eill be the guide and other an externalexaminer.
You might also like
- Power Line Communications: Theory and Applications for Narrowband and Broadband Communications over Power LinesFrom EverandPower Line Communications: Theory and Applications for Narrowband and Broadband Communications over Power LinesHendrik C. FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument33 pagesSyllabus PDFSourabh PatilNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ISUTDocument114 pagesSyllabus ISUTWaniBazillaNo ratings yet
- PrintingDocument130 pagesPrintingJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Btech s7 Electrical Electro Eng 20131466834599Document38 pagesBtech s7 Electrical Electro Eng 20131466834599Nikhil EdwardNo ratings yet
- BM Syllabus - 2009Document172 pagesBM Syllabus - 2009Rifas ZakirNo ratings yet
- ECDocument132 pagesECAkhil Paul VNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument186 pagesMechanicalश्रीराज् कथलियिल्No ratings yet
- Electronics & Communication 2006 Sem III NewDocument32 pagesElectronics & Communication 2006 Sem III NewJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- IC Syllabus For Calicut UniversityDocument135 pagesIC Syllabus For Calicut UniversityAnith MohanNo ratings yet
- University of Jammu: Course No. Course Name L T PDocument10 pagesUniversity of Jammu: Course No. Course Name L T PanmolankuNo ratings yet
- PT EeeDocument146 pagesPT Eeegovi007No ratings yet
- Scheme and Syl Applied Electronics and Instrumentation 2014Document123 pagesScheme and Syl Applied Electronics and Instrumentation 2014cijoNo ratings yet
- M Tech. SyllabusDocument73 pagesM Tech. Syllabusrakesh aseryNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology (Electronics & Communication, Electronics, Electronics & Instrumentation) Common For (ECE, EC, E&I) Scheme of Studies / Examination (Semester-3)Document67 pagesBachelor of Technology (Electronics & Communication, Electronics, Electronics & Instrumentation) Common For (ECE, EC, E&I) Scheme of Studies / Examination (Semester-3)Devesh Garg0% (1)
- Syl Btech EC 2014 PDFDocument122 pagesSyl Btech EC 2014 PDFnazlin sitharaNo ratings yet
- Communicationenggandsignalprocessingmtech SyllabusDocument70 pagesCommunicationenggandsignalprocessingmtech SyllabusRama SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- CS Syllabus 2012 Admissions OnwardsDocument78 pagesCS Syllabus 2012 Admissions OnwardsAnurag DeterminedNo ratings yet
- DR BAMU Me Etc Syllabus 18-June-13 FinalDocument39 pagesDR BAMU Me Etc Syllabus 18-June-13 FinalnitinsupekarNo ratings yet
- 20120711112402-BE IT Syllabus 2012-13Document57 pages20120711112402-BE IT Syllabus 2012-13Sambhav KapoorNo ratings yet
- Power SystemsDocument54 pagesPower SystemsBindu ChipiriNo ratings yet
- FT EieDocument83 pagesFT EieBalan PaulrajanNo ratings yet
- Computer SC PDFDocument155 pagesComputer SC PDFVipeesh ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Calicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusDocument150 pagesCalicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- S YBTechComputer Engg - SyllabusDocument31 pagesS YBTechComputer Engg - SyllabusRushabh Patel0% (1)
- SyllabusDocument131 pagesSyllabuspuneetpagalNo ratings yet
- Network Engineering PDFDocument44 pagesNetwork Engineering PDFAbin PaulNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanSheela RaviNo ratings yet
- CREDIT SYSTEM 3 Courses-3-Years23!04!2009Document10 pagesCREDIT SYSTEM 3 Courses-3-Years23!04!2009Kishore PotnuruNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing VTU Syllabus For Quick RevisionDocument44 pagesSignal Processing VTU Syllabus For Quick RevisionPavan KulkarniNo ratings yet
- ExtcDocument48 pagesExtcSagar KuchekarNo ratings yet
- Ec52 - Digital Signal ProcessingDocument17 pagesEc52 - Digital Signal ProcessingshankarNo ratings yet
- ECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 6 June, 2013Document58 pagesECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 6 June, 2013menilanjan89nLNo ratings yet
- EE407 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument2 pagesEE407 Digital Signal ProcessingbibuthomasNo ratings yet
- Mtech Electronics Syllabus VTUDocument48 pagesMtech Electronics Syllabus VTUmuqeetmmaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of TechnologyDocument65 pagesBachelor of TechnologyShivangi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ECE Andhra University SyllabusDocument91 pagesECE Andhra University Syllabush9emanth4No ratings yet
- RF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversFrom EverandRF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Digital and Kalman Filtering: An Introduction to Discrete-Time Filtering and Optimum Linear Estimation, Second EditionFrom EverandDigital and Kalman Filtering: An Introduction to Discrete-Time Filtering and Optimum Linear Estimation, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Noise and Vibration Analysis: Signal Analysis and Experimental ProceduresFrom EverandNoise and Vibration Analysis: Signal Analysis and Experimental ProceduresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Spacecraft Systems EngineeringFrom EverandSpacecraft Systems EngineeringPeter FortescueRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Next Generation Wireless Communications Using Radio over FiberFrom EverandNext Generation Wireless Communications Using Radio over FiberNo ratings yet
- Microwave and Millimeter Wave Circuits and Systems: Emerging Design, Technologies and ApplicationsFrom EverandMicrowave and Millimeter Wave Circuits and Systems: Emerging Design, Technologies and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- LTE-Advanced and Next Generation Wireless Networks: Channel Modelling and PropagationFrom EverandLTE-Advanced and Next Generation Wireless Networks: Channel Modelling and PropagationNo ratings yet
- RF and Microwave Engineering: Fundamentals of Wireless CommunicationsFrom EverandRF and Microwave Engineering: Fundamentals of Wireless CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Computational Strategies for Spectroscopy: from Small Molecules to Nano SystemsFrom EverandComputational Strategies for Spectroscopy: from Small Molecules to Nano SystemsVincenzo BaroneNo ratings yet
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationFrom EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo ratings yet
- Vibration-based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive ApplicationsFrom EverandVibration-based Condition Monitoring: Industrial, Aerospace and Automotive ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Computational Number Theory and Modern CryptographyFrom EverandComputational Number Theory and Modern CryptographyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Trilogy of Connectors: Basic Principles and Connector Design ExplanationsFrom EverandTrilogy of Connectors: Basic Principles and Connector Design ExplanationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Microwave Component Measurements: with Advanced VNA TechniquesFrom EverandHandbook of Microwave Component Measurements: with Advanced VNA TechniquesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)