Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quantum Physics Loop Cards
Quantum Physics Loop Cards
Uploaded by
derekboyle1973Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quantum Physics Loop Cards
Quantum Physics Loop Cards
Uploaded by
derekboyle1973Copyright:
Available Formats
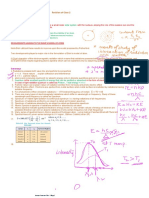
Frequency A band of colors, produced by separation of the components of light by their different degrees of refraction according to wavelength Planck
Constant Voltage required to stop the outward movement of electrons emitted by photoelectric or thermionic action. Electronvolt The theory that states that all objects can exhibit both wave and particle properties
Stopping potential The number of oscillations per unit time
Wave particle duality Constant used in quantum physics; 6.63 x 10-34 J s
Quantum The energy change of an electron when it moves through a potential difference of one volt. De Broglie wavelength The electrical energy transferred per unit charge when electrical energy is converted into some other form of energy Energy levels The emission of electrons from the surface of material when electromagnetic radiation is incident on the surface Spectra The work an object can do by virtue of its speed, measured in Joules(J); A scalar quantity
Potential difference A discrete, indivisible quantity
Photoelectric effect The quantum mechanical "wavelength" associated with a particle.
Kinetic energy One of the specific energies an electron can have in an atom
You might also like
- GCSC Physics GlossaryDocument8 pagesGCSC Physics GlossarysmeenaNo ratings yet
- Physics Key WordsDocument1 pagePhysics Key WordsKab MacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - WavesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - WavesQiun LeeNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics-104 Photoelectric EffectDocument11 pagesNuclear Physics-104 Photoelectric EffectshathaNo ratings yet
- Glossary A Level PhysicsDocument10 pagesGlossary A Level Physicsdanishali1090No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - WAVESDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - WAVESSiraf IldaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum PhysicsDocument72 pagesIntroduction To Quantum PhysicsarunsumbriaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Physical Chemistry Atkins & DepaulaDocument29 pagesElements of Physical Chemistry Atkins & DepaulaSub mNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum PhysicsDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Quantum PhysicsEr Ishan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Particle Properties of WavesDocument9 pagesChapter Two Particle Properties of WavesAmanuel BazeNo ratings yet
- QuantisationDocument3 pagesQuantisationNarjis FatimaNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electricity and Magnetism MidDocument3 pagesGlossary of Electricity and Magnetism MidPadmi RianiNo ratings yet
- XII Phy Ch11 DualNatureofRadiation&Matter TopconceptsDocument4 pagesXII Phy Ch11 DualNatureofRadiation&Matter TopconceptsBhagyashree IkNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument11 pagesDefinition of TermsTeresa PulgaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter - 231211 - 171724Document10 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter - 231211 - 171724kingbro298176No ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric EffectGlay Cabañero TacanayNo ratings yet
- All Definitions For Physics 0625 &0972Document8 pagesAll Definitions For Physics 0625 &0972Ahmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Blue Professional Background Paper Border A4 - 20231101 - 192456 - 0000Document11 pagesBlue Professional Background Paper Border A4 - 20231101 - 192456 - 0000bhabak0024No ratings yet
- Physics Definition List Form 5Document6 pagesPhysics Definition List Form 5Yinxin OngNo ratings yet
- Determination of Planck'S ConstantDocument4 pagesDetermination of Planck'S Constanthoangnghia_hcmupNo ratings yet
- Dual NatureDocument7 pagesDual Naturethinkiit100% (1)
- CH 12 NotesDocument2 pagesCH 12 NotesAila Kublai-sikNo ratings yet
- 12 UvDocument24 pages12 UvMohit KambojNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearDocument52 pagesPresented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearSandeep VermaNo ratings yet
- Lct-1 General Introduction - 2019Document38 pagesLct-1 General Introduction - 2019Abdelfattah Mohamed OufNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Wave FunctionDocument32 pagesLecture 2 - Wave FunctionTYSON PETRO JONATHANNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric Effecteducationalert42No ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum PhysicsDocument74 pagesIntroduction To Quantum PhysicsultimuNo ratings yet
- Bus BarDocument11 pagesBus BarDawit Adane KebedeNo ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document3 pagesNotebook 3api-335583967No ratings yet
- CH 16 - Quantam PhysicsDocument45 pagesCH 16 - Quantam PhysicsOKAY JAROD PUGNo ratings yet
- Science VocabularyDocument10 pagesScience VocabularyCandice LuNo ratings yet
- Physics A Level DefinitionsDocument12 pagesPhysics A Level DefinitionsNaillah Saba100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument14 pagesPhotoelectric EffectTamilselvan BaskaranNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Fluorescence: Energy-Dispersive Technique (EDXRF) : Advanced Physics Laboratory XRFDocument16 pagesX-Ray Fluorescence: Energy-Dispersive Technique (EDXRF) : Advanced Physics Laboratory XRFmantaptoNo ratings yet
- 4.5. Quantum PhysicsDocument4 pages4.5. Quantum PhysicsjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Phys StudyDocument4 pagesPhys StudyKatya AubryNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Techniques and Applications: Dr. Abhilasha MishraDocument7 pagesSpectroscopic Techniques and Applications: Dr. Abhilasha MishraABHILASHA MISHRANo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect PresentationDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric Effect PresentationXofoNo ratings yet
- Quantum PhysicsDocument67 pagesQuantum PhysicsxiaokiaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect - WikipediaDocument17 pagesPhotoelectric Effect - WikipediaPriyal SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFDocument16 pages7 - Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFthinkiit88% (8)
- Atomic Structure Live Class-3 Teacher NotesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure Live Class-3 Teacher Notestarun singhNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation: in 1 ShotDocument64 pagesDual Nature of Radiation: in 1 ShotDisney DoreamonNo ratings yet
- Dual NatureDocument19 pagesDual NaturebenitxmxnuNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect 3Document28 pagesPhotoelectric Effect 3adekogbeadedamolaNo ratings yet
- The Development of A New Atomic ModelDocument40 pagesThe Development of A New Atomic Modelahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Advanced Physics Laboratory XRF X-Ray Fluorescence: Energy-Dispersive Analysis (EDXRF)Document14 pagesAdvanced Physics Laboratory XRF X-Ray Fluorescence: Energy-Dispersive Analysis (EDXRF)Gandis YulianaNo ratings yet
- Fotoelectric EffectDocument12 pagesFotoelectric EffectDavid IssaNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 ADocument13 pagesPhysics 12 ALight yagami is KIRANo ratings yet
- CHEM 101 - L4 - Atomic Structure and Periodicity of Elements - Part BDocument41 pagesCHEM 101 - L4 - Atomic Structure and Periodicity of Elements - Part BlentlebuisanyangNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument11 pagesPhotoelectric EffectRivu BasuNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4 To Study The Variation of Photoelectric Effect With Intensity of LightDocument8 pagesExperiment No.4 To Study The Variation of Photoelectric Effect With Intensity of LightMuhammad Zubair SharifNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 HandoutDocument12 pagesTopic 6 HandoutnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared SpectrosDocument52 pagesFourier Transform Infrared SpectroschmsarfrazNo ratings yet
- Elementary Quantum Physics 20160926Document81 pagesElementary Quantum Physics 20160926Aruna KumarasiriNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics (A2 - Cambridge)Document23 pagesQuantum Physics (A2 - Cambridge)LoL TrendsNo ratings yet
- Phy Jan's ProjectDocument34 pagesPhy Jan's ProjectSakthiiNo ratings yet