Professional Documents
Culture Documents
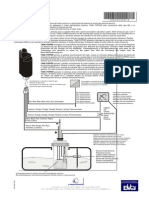
Engine Control System Diagram
Engine Control System Diagram
Uploaded by
Gowher QadriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engine Control System Diagram
Engine Control System Diagram
Uploaded by
Gowher QadriCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE
59
3. Engine Control System Diagram
Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Resister Vapor Pressure Sensor VSV (for EVAP)
VSV for Pressure Switch Valve
Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Filter Intake Temp. Sensor Fuel Pump
Throttle Position Sensor
Circuit Opening Relay
Mass Air Flow Meter
Charcoal Canister Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
VSV for Canister Closed Valve
Injector Injector Ignition Coil (with Igniter)
Camshaft Position Sensor
*1
Ignition Coil (with Igniter)
*2
*2
Knock Sensor *2 Knock Sensor Crankshaft Position Sensor *2
ECM Starter Air Conditioning MIL Battery DLC3 *1: Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor *2: Heated Oxygen Sensor Electronic Controlled Transmission Solenoid Valves
196EG09
Vehicle Speed Sensor (for Transmission)
Park / Neutral Position Switch
60
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE
4. Layout of Components
Park/Neutral Position Switch
Combination Meter Throttle Positoin Sensor Knock Sensor 2 Ignition Coil with Igniter Accelerator Pedal Injector Position Sensor VSV (for EVAP)
VSV (for Pressure Switching Valve)
Fuel Pump Relay ECM
Mass Air Flow Meter
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Charcoal Canister Vapor Pressure Sensor DLC3
Throttle Control Motor (with Magnetic Clutch)
Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 2) Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) Knock Sensor 1 VSV (for Canister Closed Valve)
Crankshaft Position Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor
Fuel Pump Resister
Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
196EG10
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE
61
5. Main Components of Engine Control System
General The main components of the 2UZ-FE engine control system are as follows: Component Mass Air Flow Meter Crankshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth) Camshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth) Throttle Position Sensor Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Knock Sensor Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) (Bank 1, Sensor 2) (Bank 2, Sensor 1) (Bank 2, Sensor 2) Injector Mass Air Flow Meter The 2UZ-FE engine adopts the hot-wire type mass air flow meter designed for direct electrical measurement of the intake air mass flow. This mass air flow meter offers superior measuring precision and its plastic housing is shaped for minimal flow resistance. It has the following features: D Compact and lightweight The pressure loss caused by this sensor is small and offers only slight intake air flow resistance. D Superior response and measuring accuracy. D Ability to measure a wide airflow range. D Having no mechanical functions, it offers a superior durability.
140EG45
Outline Hot-Wire Type Pick-Up Coil Type (36-2) Pick-Up Coil Type (1) Linear Type Linear Type Built-In Piezoelectric Type
Quantity 1 1 1 2 2 2
With Heater Type
4-Hole Type
Intake Air Temp. Sensor
Hot Wire
62 Crankshaft Position Sensor
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE
The crankshaft position sensor is mounted on the oil pump body as illustrated below. The rotors teeth are spaced 10_ apart, according to crankshaft angle, but since there are 2 teeth missing, as illustrated below, there is a total of 34 teeth. Accordingly, the ECM can detect the crankshaft angle in addition to the crankshaft speed.
Timing Rotor
Crankshaft Position Sensor
151EG18
Camshaft Position Sensor The camshaft position sensor is mounted on the left bank cylinder head. To detect the camshaft position, a protrusion that is provided on the timing pulley is used to generate 1 pulse for every 2 revolutions of the crankshaft. Timing Rotor
Camshaft Position Sensor
156EG26
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE
63
6. ETCS-i (Electronic Throttle Control System-intelligent)
General D The ETCS-i, which realizes excellent throttle control in all the operating ranges, has been adopted. D In the conventional throttle body, the throttle valve opening is determined invariably by the amount of the accelerator pedal effort. In contrast, the ETCS-i uses the ECM to calculate the optimal throttle valve opening that is appropriate for the respective driving condition and uses a throttle control motor to control the opening. D The ETCS-i controls the ISC (Idle Speed Control) system, the cruise control system, the TRAC (Traction Control), and the VSC (Vehicle Skid Control) system. D A duplicate system is provided to ensure a high level of reliability, and the system shuts off in case of an abnormal condition. Even when the system is shut off, the accelerator pedal can be used to operate the vehicle in the limp mode.
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
Throttle Valve Throttle Position Sensor Throttle Control Motor Magnetic Clutch
ECM
Skid Control ECU
150EG41
64 Construction
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE
Limp Mode Lever
Throttle Valve Throttle Position Sensor
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
Throttle Control Motor Magnetic Clutch 1) Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor The accelerator pedal position sensor, which is mounted on the throttle body, is integrated with the throttle lever, which is connected to the cable that extends from the accelerator pedal. The accelerator pedal position sensor converts the amount of accelerator pedal effort into two types of electrical signals with distinct output characteristics. The signals are then input into the ECM. V 5 Output Voltage VPA2 Open
156EG30
Close
VPA 0 Close Open Accelerator Pedal Depressed Angle
150EG39
E2
VPA2 VPA
VC
150EG40
2) Throttle Position Sensor The throttle position sensor converts the throttle valve opening into an electrical signal and inputs into the ECM. The output characteristics are the same as those of the accelerator positon pedal sensor. 3) Throttle Control Motor A DC motor with excellent response and minimal power consumption is used for the throttle control motor. The ECM performs the duty ratio control of the direction and the amperage of the current that flows to the throttle control motor in order to regulate the opening of the throttle valve.
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 4) Magnetic Crutch
65
Ordinarily, the magnetic clutch engages the clutch to enable the throttle control motor to open and close the throttle valve. In case that a malfunction occurs in the system, this clutch is disengaged to prevent the throttle control motor to open and close the throttle valve. Operation 1) General The ECM drives the throttle control motor by determining the target throttle valve opening in accordance with the respective operating condition. 1) Non-Linear Control 2) Idle Speed Control 3) TRAC Throttle Control 4) VSC Coordination Control 5) Cruise Control 2) Non-Linear Control Controls the throttle to an optimal throttle valve opening that is appropriate for the driving condition such as the amount of the accelerator pedal effort and the engine speed in order to realize excellent throttle control and comfort in all operating ranges.
"
Control Examples During Acceleration and Deceleration A : With Control : No Control "
Vehicles Longitudinal G 0 " Throttle Valve Opening Angle 0 " Ignition Timing 0 Time !
150EG37
3) Idle Speed Control Previously, a step motor type IAC valve was used to perform idle speed control such as fast idle during cold operating conditions and idle-up. In conjunction with the adoption of the ETCS-i, controls the ECM and the throttle valve in order to constantly effect ideal idle speed control.
66 4) TRAC Throttle Control
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE
As part of the TRAC system, the throttle valve is closed by a demand signal from the skid control ECU if an excessive amount of slippage is created at a driving wheel, thus facilitating the vehicle in ensuring stability and driving force. 5) VSC Coordination Control In order to bring the effectiveness of the VSC system control into full play, the throttle valve opening angle is controlled by effecting a coordination control with the skid control ECU. 6) Cruise Control Previously the vehicle speed was controlled by the cruise control ECU, which open and closed the throttle valve. In conjunction with the adoption of the ETCS-i, an ECM with an integrated cruise control ECU diretly actuates the throttle valve to effect the operation. Fail-Safe If an abnormal condition occurs with the ETCS-i, the MIL illuminates to alert the driver. At the same time, the current to the throttle control motor and magnetic clutch are cut off in order not to operate the ETCS-i. This enables the return spring to close the throttle valve. Even in this situation, the accelerator pedal can be used to operate the limp mode lever, which operates the throttle valve to enable the vehicle to be driven in the limp mode.
Open Limp Mode Lever
Throttle Position Sensor Throttle Control Motor
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
Throttle Valve
Magnetic Clutch
150EG42
Diagnosis The diagnostic trouble codes can be output via DLC3 to an OBD-II scan tool or a hand-held tester. For details, refer to the 2001 Sequoia Repair Manual (Pub. No. RM832U).
You might also like
- Gasoline Direct InjectionDocument21 pagesGasoline Direct InjectionhoangNo ratings yet
- Ais 137 (Part - 4) Bs ViDocument446 pagesAis 137 (Part - 4) Bs ViVenkatesh GirdharNo ratings yet
- 3grfse 1Document42 pages3grfse 1Zoli Borbely100% (3)
- 1MZ-FE Engine Control SystemRX300 99Document11 pages1MZ-FE Engine Control SystemRX300 99Jose Calle100% (1)
- Sfi SystemDocument96 pagesSfi SystemWawan SatiawanNo ratings yet
- GdiDocument22 pagesGdiAnonymous ysrxggk21c100% (1)
- Classification OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE PDFDocument65 pagesClassification OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE PDFProcy FerrerNo ratings yet
- BS IV To BS VI Tata Motors PDFDocument3 pagesBS IV To BS VI Tata Motors PDFKaranNo ratings yet
- Gasoline EngineDocument41 pagesGasoline EngineRalph JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Boost Pressure Sensor (BPS)Document50 pagesBoost Pressure Sensor (BPS)Gian Fran0% (1)
- L Jetronic BMWDocument38 pagesL Jetronic BMWcasecaseinter7No ratings yet
- Continuously Variable Valve TimingDocument12 pagesContinuously Variable Valve TiminggamerpipeNo ratings yet
- Engine Theory and CalculationsDocument11 pagesEngine Theory and Calculationsmuhammad husnainNo ratings yet
- Engine Performance Optimization - GT PowerDocument2 pagesEngine Performance Optimization - GT Powermanoj262400/2No ratings yet
- I VTECDocument20 pagesI VTECraju100% (2)
- 2008-09 ABR Crafter enDocument107 pages2008-09 ABR Crafter enErick DavidNo ratings yet
- Dual Clutch TransmissionDocument11 pagesDual Clutch TransmissionKunalLuthraNo ratings yet
- GDI OperationDocument9 pagesGDI OperationPablo VarelaNo ratings yet
- G50 and G55 Manual Transmissions: DescriptionDocument7 pagesG50 and G55 Manual Transmissions: DescriptionCarlos Machado100% (1)
- Sensores y Actuadores - SPDocument89 pagesSensores y Actuadores - SPGarcia Sanchez Teo100% (1)
- Development of CNG Injection EngineDocument8 pagesDevelopment of CNG Injection EngineShasahank JoshiNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual Octavia Automatic Gearbox Edition 0896 s0051165020Document208 pagesWorkshop Manual Octavia Automatic Gearbox Edition 0896 s0051165020Zafer IlhanNo ratings yet
- Halderman AutoTec ch29Document37 pagesHalderman AutoTec ch29Pardeep100% (2)
- Q7 2009 4.2L BarDocument294 pagesQ7 2009 4.2L BarPirulo ZatjaichukNo ratings yet
- Obdii Fuel TrimDocument4 pagesObdii Fuel TrimJulieta MastronardiNo ratings yet
- BOSCH - StartstoppDocument16 pagesBOSCH - StartstoppNuno PiresNo ratings yet
- ActuatorsDocument48 pagesActuatorsnahom100% (1)
- NEW COLT 13AMultipointFuelInjectionDocument51 pagesNEW COLT 13AMultipointFuelInjectionjcanadaNo ratings yet
- SSP - 358 - Hot-Film Air-Mass Meter HFM 6Document20 pagesSSP - 358 - Hot-Film Air-Mass Meter HFM 6dromakiNo ratings yet
- Mivec: MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic Control System)Document5 pagesMivec: MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic Control System)alibababujanglapokNo ratings yet
- Tank FopperDocument1 pageTank FoppersmomisNo ratings yet
- Halderman AutoTec ch09Document29 pagesHalderman AutoTec ch09tornomanNo ratings yet
- On Board Diagnosis For Three-Way Catalytic ConvertersDocument33 pagesOn Board Diagnosis For Three-Way Catalytic ConvertersMaher Al-busaidiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-AEEDocument92 pagesUnit 4-AEEMrs G Hemalatha PSG-PTCNo ratings yet
- KAYO EFI Instructions: 1 Operating PrincipleDocument16 pagesKAYO EFI Instructions: 1 Operating Principlekenny nieuwenwegNo ratings yet
- BT 3aDocument12 pagesBT 3aMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Tightening Torques Items N.M KGF.M LB-FT: 4 Wheel Drive (4WD) SystemDocument35 pagesTightening Torques Items N.M KGF.M LB-FT: 4 Wheel Drive (4WD) SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Twin Spark TechDocument23 pagesTwin Spark TechJainul PatelNo ratings yet
- PT Cruiser 2009 2.2LDocument275 pagesPT Cruiser 2009 2.2LPatrik MendozaNo ratings yet
- Distributor Less Ignition SystemsDocument4 pagesDistributor Less Ignition SystemsxLibelle100% (5)
- SolexDocument3 pagesSolexAnish Sukumar100% (1)
- Variable Valve TimingDocument3 pagesVariable Valve Timingsandesh ganigaNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual - 74714763 - Injection - Power - Stage - HPI - 5Document20 pagesOperation Manual - 74714763 - Injection - Power - Stage - HPI - 5Aussi SidNo ratings yet
- 2010 Ford Hybrid OBD IIDocument108 pages2010 Ford Hybrid OBD IIdavid_sierra_nNo ratings yet
- Multi AirsystemDocument13 pagesMulti AirsystemSivaji Liar100% (1)
- Delphi Heavy Duty Emissions Brochure 2011 2012Document100 pagesDelphi Heavy Duty Emissions Brochure 2011 2012Younwoo NamNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles: By: Davin Matsuda EE453 Electric Drives Winter 01Document31 pagesHybrid Electric Vehicles: By: Davin Matsuda EE453 Electric Drives Winter 01Denis GintingNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injectors ModifiedDocument10 pagesFuel Injectors ModifiedSarath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Fuel Injection SystemsDocument17 pagesPowerpoint Fuel Injection Systemsanitadas19No ratings yet
- Piston Engine ConstructionDocument150 pagesPiston Engine ConstructionHastian SuryaNo ratings yet
- Gasoline Engines: 2. 2. Automaker TrendsDocument8 pagesGasoline Engines: 2. 2. Automaker TrendsNguyen ThaiNo ratings yet
- EPS Toyota BackgroundDocument8 pagesEPS Toyota BackgroundDilan Senarathne100% (1)
- 3s FuelDocument310 pages3s FuelPrecisionetica100% (3)
- GDIDocument7 pagesGDIlinhda561No ratings yet
- Sistema de Control de EmisionesDocument45 pagesSistema de Control de EmisionesDavid ParariNo ratings yet
- 1zzVS2zz 6Document16 pages1zzVS2zz 6Ofi de Mo100% (1)
- 4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFADocument24 pages4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFARusonegroNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument4 pagesElectronicsMarcusNo ratings yet
- 2uz HistoryDocument130 pages2uz HistoryTaimoor Ahmed100% (2)
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet