Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Range
Range
Uploaded by
Denver GabitanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Practical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsFrom EverandPractical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument22 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyDenisho Dee88% (8)
- The PATHFINDER Training ProgramDocument5 pagesThe PATHFINDER Training ProgramLyell E. Petersen100% (1)
- Project 10 (StatisticsDocument14 pagesProject 10 (StatisticsArkin DuttaNo ratings yet
- BR Knauf Ceiling Solutions Mineral Solutions ND MEDocument94 pagesBR Knauf Ceiling Solutions Mineral Solutions ND MEsacdawoodNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy FormulaDocument8 pagesEngineering Economy FormulaDenver Gabitan50% (2)
- Architects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryDocument558 pagesArchitects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryFlavia ValNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 15Document7 pagesTutorial 15Yeong Zi YingNo ratings yet
- Financial Modelling: Statistical MeasuresDocument6 pagesFinancial Modelling: Statistical MeasuresManfredi SopraniNo ratings yet
- FXGFHGJHKJLKDocument19 pagesFXGFHGJHKJLKbethNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument1 pageDescriptive StatisticsMissMumtazNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and DispersionDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and DispersionArlan Joseph LopezNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument19 pagesDescriptive StatisticskailashNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument19 pagesDescriptive StatisticsAnnRubyAlcaideBlandoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion RangeDocument2 pagesMeasures of Dispersion RangeYeong Zi YingNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendancyDocument18 pagesMeasures of Central Tendancyolalekan.beckleyNo ratings yet
- Measures of Location - MIDocument12 pagesMeasures of Location - MISaudulla Jameel JameelNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument8 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyFariha AyazNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument35 pagesMeasure of Central TendencyPuttu Guru PrasadNo ratings yet
- Assim. 2 StatDocument5 pagesAssim. 2 StatMuhammad KhurramNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion 4th SEMDocument38 pagesMeasures of Dispersion 4th SEMAnika KumarNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersonDocument17 pagesMeasures of DispersonReshmaNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariationDocument20 pagesMeasures of VariationArman Benedict NuguidNo ratings yet
- Statistics Lecture 4 2k21Document17 pagesStatistics Lecture 4 2k21shaguftaNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariabilityDocument16 pagesMeasures of VariabilityCiashell LayeseNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument28 pagesWeek 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityMuhaimin Abdu AzizNo ratings yet
- Mean Median, ModeDocument15 pagesMean Median, Mode21010324029No ratings yet
- Mathematical AnalysisDocument46 pagesMathematical AnalysisGilbert Dwasi100% (1)
- Central TendencyDocument34 pagesCentral TendencyMd. Anhar Sharif MollahNo ratings yet
- Instructor'S Manual: Statistical Techniques in Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesInstructor'S Manual: Statistical Techniques in Financial Managementjoebloggs1888No ratings yet
- M-1 CH-3 Descriptive StatistcsDocument27 pagesM-1 CH-3 Descriptive StatistcsyoginibeautyparlourNo ratings yet
- Central TendencyDocument45 pagesCentral TendencyAggarwal YashvardhanNo ratings yet
- Part2 StatisticsDocument55 pagesPart2 StatisticsTechManager SaharaTvmNo ratings yet
- 3 Measures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median)Document32 pages3 Measures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median)Mohamed FathyNo ratings yet
- C4 Descriptive StatisticsDocument34 pagesC4 Descriptive StatisticsNAVANEETHNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument51 pagesMeasures of DispersionbapparoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Descriptive StatisticsDocument53 pagesIntroduction & Descriptive StatisticsArga pratamaaNo ratings yet
- Process Data AnalysisDocument24 pagesProcess Data AnalysisRidwan MahfuzNo ratings yet
- Measures Of: Central Tendency & DispersionDocument58 pagesMeasures Of: Central Tendency & DispersionAustine Ampofo TwumasiNo ratings yet
- Aathish PDFDocument9 pagesAathish PDFsaibhaskar9155No ratings yet
- Topic: Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of DispersionDocument45 pagesTopic: Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of DispersionHarshitha LokeshNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical Descriptions of Data: Dr. Amiya Ranjan PandaDocument35 pagesBasic Statistical Descriptions of Data: Dr. Amiya Ranjan PandaAnu agarwalNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument34 pagesMeasure of Central TendencyShailendra Kr YadavNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument15 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyAmit Gurav100% (15)
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocument30 pagesStatistics For Data ScienceArminSayadiNo ratings yet
- Bioe211 - Week 3 - MeasuresDocument4 pagesBioe211 - Week 3 - MeasuresFormosa G.No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document7 pagesUnit 2Peces Dorado MarinaNo ratings yet
- PR2 Lesson 6 Data Analysis UsingDocument30 pagesPR2 Lesson 6 Data Analysis UsingNiño RapfaeleNo ratings yet
- Merits and DemeritsDocument10 pagesMerits and DemeritsRamesh SafareNo ratings yet
- Standard DeviationDocument19 pagesStandard Deviationcoolaysuh9No ratings yet
- Basic Stats InformationDocument16 pagesBasic Stats InformationShankar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument33 pagesStatisticsAnonymous J5sNuoIy100% (2)
- Central Tendency + DispersionDocument28 pagesCentral Tendency + Dispersionneha.akshiNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency Mean, Mode, Median: DR. Hetal Koringa Assistant ProfessorDocument26 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency Mean, Mode, Median: DR. Hetal Koringa Assistant ProfessorHetal Koringa patelNo ratings yet
- Psychology 117 Study GuideDocument41 pagesPsychology 117 Study GuideVanessa100% (3)
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra RoyDocument34 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra Roybapparoy100% (1)
- Chapter Exercises:: Chapter 5:utilization of Assessment DataDocument6 pagesChapter Exercises:: Chapter 5:utilization of Assessment DataJessa Mae CantilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Evaluation of Experimental DataDocument55 pagesChapter 2 Evaluation of Experimental DataSyahshaiNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument33 pagesStatisticsRado Mayson SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument48 pagesMeasures of DispersionBiswajit RathNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument3 pagesMeasures of Central TendencystatiksNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3A-MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY Ungrouped DataDocument18 pagesLECTURE 3A-MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY Ungrouped DataHAFIZAH100% (1)
- f592b059 1643454320549Document39 pagesf592b059 1643454320549Zaubariya MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Elec 01Document15 pagesElec 01Denver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Assign 2Document1 pageAssign 2Denver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Project Toldo (Landscape)Document1 pageProject Toldo (Landscape)Denver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Vacuum TriodeDocument2 pagesVacuum TriodeDenver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDenver Gabitan0% (1)
- Theories in Environmental PsychologyDocument17 pagesTheories in Environmental PsychologyInshrah MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanism by Doughtie and James PDFDocument1 pageElements of Mechanism by Doughtie and James PDFChristian M. CalinayaNo ratings yet
- ARC VisionDocument2 pagesARC VisionmelvincabeNo ratings yet
- Either Silent or Switched OffDocument67 pagesEither Silent or Switched OffPankaj Kumar Singh100% (1)
- S475Document33 pagesS475Barjam KafexhiuNo ratings yet
- March 2015Document84 pagesMarch 2015Jn BmNo ratings yet
- Campion College Information Technology Assignment: Input and Output DevicesDocument2 pagesCampion College Information Technology Assignment: Input and Output DevicesAnthonya KnightNo ratings yet
- What Is Physics Through The Eyes of ScientistsDocument39 pagesWhat Is Physics Through The Eyes of ScientistsAHMET TOPRAKNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - Hypothesis, Theories, and Laws - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument3 pages1.3 - Hypothesis, Theories, and Laws - Chemistry LibreTextskulkarni.himani19940809No ratings yet
- 12 Lecture 4-Seismic Waves AFTER MidDocument80 pages12 Lecture 4-Seismic Waves AFTER MidusamaNo ratings yet
- Fracture CrurisDocument44 pagesFracture CrurisAnonymous turPUJtErNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 1 ProjectDocument2 pagesMEO Class 1 ProjectAshish Ranjan0% (1)
- NITIN Rdbms AssignmentDocument131 pagesNITIN Rdbms Assignmentnitinsingaur.bizNo ratings yet
- IFU 5902446 Port A-FrameDocument16 pagesIFU 5902446 Port A-FrameBeto AsaberNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document97 pagesCH 08albakili775514617No ratings yet
- Man of Sorrows PDFDocument4 pagesMan of Sorrows PDFjoao.beckNo ratings yet
- Royal Enfield Price ListDocument126 pagesRoyal Enfield Price Listmaniamson50% (20)
- "7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofDocument29 pages"7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofOliver Dennis100% (1)
- TPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3Document88 pagesTPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3DeniMestiWidiantoNo ratings yet
- Veeam Top 10 Reasons Choose Veeam 9 5Document2 pagesVeeam Top 10 Reasons Choose Veeam 9 5Anonymous xKgV3e6XLNo ratings yet
- Relative Range (RR) HandDocument13 pagesRelative Range (RR) HandSebastian Alejandro HerreraNo ratings yet
- 2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmDocument17 pages2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmForu MophiliaNo ratings yet
- IC Mask Design Essential Layout TechniquesDocument404 pagesIC Mask Design Essential Layout Techniquesramana459100% (2)
- AppendixDocument5 pagesAppendixAsim IqbalNo ratings yet
- S 125Document317 pagesS 125ronaldosilva2100% (1)
- 01-Basics of CorrosionDocument31 pages01-Basics of Corrosion이선엽No ratings yet
- 预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsDocument15 pages预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsSolo YehNo ratings yet
Range
Range
Uploaded by
Denver GabitanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Range
Range
Uploaded by
Denver GabitanCopyright:
Available Formats
RANGE
The range of a set of data is the difference between its largest (maximum) and smallest (minimum) values R = Xmax - Xmin Find the range of the following data: 29, 31, 24, 29, 30, 25 1- Arrange the data from smallest to largest: 24, 25, 29, 29, 30, 31 2- Identify the minimum and maximum values: Minimum = 24, Maximum = 31 3- Calculate the range: Range = 31-24 = 7 Advantages: -Easy to compute. -Easy to understand. - Scores exist in the data set Disadvantages: - Value depends only on two scores. - Influenced by sample size. - Very sensitive to outliers. - Insensitive to the distribution of scores within the two extremes. VARIANCE The average amount that a score deviates from the typical score. Score mean = difference score Average of difference scores = 0 In order to make this number not 0, square the
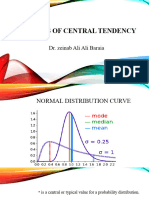
difference scores (no negatives to cancel out the positives). Advantages: - Takes all data into account. - Lends itself to computation of other stable measures (and is a prerequisite for many of them) Disadvantages: - Hard to interpret. -Unit is squared - Can be influenced by extreme scores. STANDARD DEVIATION It is a standardized score which is the average deviation about the mean. It is the square root of the variance. Advantages: - Lends itself to computation of other stable measures (and is a prerequisite for many of them). - Average of deviations around the mean - Majority of data within one standard deviation above or below the mean. - Not expressed in squared units, so makes more sense descriptively. Disadvantages: - Influenced by extreme scores.
You might also like
- Practical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsFrom EverandPractical Engineering, Process, and Reliability StatisticsNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument22 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyDenisho Dee88% (8)
- The PATHFINDER Training ProgramDocument5 pagesThe PATHFINDER Training ProgramLyell E. Petersen100% (1)
- Project 10 (StatisticsDocument14 pagesProject 10 (StatisticsArkin DuttaNo ratings yet
- BR Knauf Ceiling Solutions Mineral Solutions ND MEDocument94 pagesBR Knauf Ceiling Solutions Mineral Solutions ND MEsacdawoodNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy FormulaDocument8 pagesEngineering Economy FormulaDenver Gabitan50% (2)
- Architects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryDocument558 pagesArchitects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryFlavia ValNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 15Document7 pagesTutorial 15Yeong Zi YingNo ratings yet
- Financial Modelling: Statistical MeasuresDocument6 pagesFinancial Modelling: Statistical MeasuresManfredi SopraniNo ratings yet
- FXGFHGJHKJLKDocument19 pagesFXGFHGJHKJLKbethNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument1 pageDescriptive StatisticsMissMumtazNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and DispersionDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and DispersionArlan Joseph LopezNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument19 pagesDescriptive StatisticskailashNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument19 pagesDescriptive StatisticsAnnRubyAlcaideBlandoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion RangeDocument2 pagesMeasures of Dispersion RangeYeong Zi YingNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendancyDocument18 pagesMeasures of Central Tendancyolalekan.beckleyNo ratings yet
- Measures of Location - MIDocument12 pagesMeasures of Location - MISaudulla Jameel JameelNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument8 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyFariha AyazNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument35 pagesMeasure of Central TendencyPuttu Guru PrasadNo ratings yet
- Assim. 2 StatDocument5 pagesAssim. 2 StatMuhammad KhurramNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion 4th SEMDocument38 pagesMeasures of Dispersion 4th SEMAnika KumarNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersonDocument17 pagesMeasures of DispersonReshmaNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariationDocument20 pagesMeasures of VariationArman Benedict NuguidNo ratings yet
- Statistics Lecture 4 2k21Document17 pagesStatistics Lecture 4 2k21shaguftaNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariabilityDocument16 pagesMeasures of VariabilityCiashell LayeseNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument28 pagesWeek 2 Central Tendency and VariabilityMuhaimin Abdu AzizNo ratings yet
- Mean Median, ModeDocument15 pagesMean Median, Mode21010324029No ratings yet
- Mathematical AnalysisDocument46 pagesMathematical AnalysisGilbert Dwasi100% (1)
- Central TendencyDocument34 pagesCentral TendencyMd. Anhar Sharif MollahNo ratings yet
- Instructor'S Manual: Statistical Techniques in Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesInstructor'S Manual: Statistical Techniques in Financial Managementjoebloggs1888No ratings yet
- M-1 CH-3 Descriptive StatistcsDocument27 pagesM-1 CH-3 Descriptive StatistcsyoginibeautyparlourNo ratings yet
- Central TendencyDocument45 pagesCentral TendencyAggarwal YashvardhanNo ratings yet
- Part2 StatisticsDocument55 pagesPart2 StatisticsTechManager SaharaTvmNo ratings yet
- 3 Measures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median)Document32 pages3 Measures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median)Mohamed FathyNo ratings yet
- C4 Descriptive StatisticsDocument34 pagesC4 Descriptive StatisticsNAVANEETHNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument51 pagesMeasures of DispersionbapparoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Descriptive StatisticsDocument53 pagesIntroduction & Descriptive StatisticsArga pratamaaNo ratings yet
- Process Data AnalysisDocument24 pagesProcess Data AnalysisRidwan MahfuzNo ratings yet
- Measures Of: Central Tendency & DispersionDocument58 pagesMeasures Of: Central Tendency & DispersionAustine Ampofo TwumasiNo ratings yet
- Aathish PDFDocument9 pagesAathish PDFsaibhaskar9155No ratings yet
- Topic: Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of DispersionDocument45 pagesTopic: Measures of Central Tendency and Measures of DispersionHarshitha LokeshNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistical Descriptions of Data: Dr. Amiya Ranjan PandaDocument35 pagesBasic Statistical Descriptions of Data: Dr. Amiya Ranjan PandaAnu agarwalNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument34 pagesMeasure of Central TendencyShailendra Kr YadavNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument15 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyAmit Gurav100% (15)
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocument30 pagesStatistics For Data ScienceArminSayadiNo ratings yet
- Bioe211 - Week 3 - MeasuresDocument4 pagesBioe211 - Week 3 - MeasuresFormosa G.No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document7 pagesUnit 2Peces Dorado MarinaNo ratings yet
- PR2 Lesson 6 Data Analysis UsingDocument30 pagesPR2 Lesson 6 Data Analysis UsingNiño RapfaeleNo ratings yet
- Merits and DemeritsDocument10 pagesMerits and DemeritsRamesh SafareNo ratings yet
- Standard DeviationDocument19 pagesStandard Deviationcoolaysuh9No ratings yet
- Basic Stats InformationDocument16 pagesBasic Stats InformationShankar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument33 pagesStatisticsAnonymous J5sNuoIy100% (2)
- Central Tendency + DispersionDocument28 pagesCentral Tendency + Dispersionneha.akshiNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency Mean, Mode, Median: DR. Hetal Koringa Assistant ProfessorDocument26 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency Mean, Mode, Median: DR. Hetal Koringa Assistant ProfessorHetal Koringa patelNo ratings yet
- Psychology 117 Study GuideDocument41 pagesPsychology 117 Study GuideVanessa100% (3)
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra RoyDocument34 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra Roybapparoy100% (1)
- Chapter Exercises:: Chapter 5:utilization of Assessment DataDocument6 pagesChapter Exercises:: Chapter 5:utilization of Assessment DataJessa Mae CantilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Evaluation of Experimental DataDocument55 pagesChapter 2 Evaluation of Experimental DataSyahshaiNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument33 pagesStatisticsRado Mayson SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument48 pagesMeasures of DispersionBiswajit RathNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument3 pagesMeasures of Central TendencystatiksNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3A-MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY Ungrouped DataDocument18 pagesLECTURE 3A-MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY Ungrouped DataHAFIZAH100% (1)
- f592b059 1643454320549Document39 pagesf592b059 1643454320549Zaubariya MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Elec 01Document15 pagesElec 01Denver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Assign 2Document1 pageAssign 2Denver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Project Toldo (Landscape)Document1 pageProject Toldo (Landscape)Denver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Vacuum TriodeDocument2 pagesVacuum TriodeDenver GabitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Laws: Ohm'S LawDenver Gabitan0% (1)
- Theories in Environmental PsychologyDocument17 pagesTheories in Environmental PsychologyInshrah MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanism by Doughtie and James PDFDocument1 pageElements of Mechanism by Doughtie and James PDFChristian M. CalinayaNo ratings yet
- ARC VisionDocument2 pagesARC VisionmelvincabeNo ratings yet
- Either Silent or Switched OffDocument67 pagesEither Silent or Switched OffPankaj Kumar Singh100% (1)
- S475Document33 pagesS475Barjam KafexhiuNo ratings yet
- March 2015Document84 pagesMarch 2015Jn BmNo ratings yet
- Campion College Information Technology Assignment: Input and Output DevicesDocument2 pagesCampion College Information Technology Assignment: Input and Output DevicesAnthonya KnightNo ratings yet
- What Is Physics Through The Eyes of ScientistsDocument39 pagesWhat Is Physics Through The Eyes of ScientistsAHMET TOPRAKNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - Hypothesis, Theories, and Laws - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument3 pages1.3 - Hypothesis, Theories, and Laws - Chemistry LibreTextskulkarni.himani19940809No ratings yet
- 12 Lecture 4-Seismic Waves AFTER MidDocument80 pages12 Lecture 4-Seismic Waves AFTER MidusamaNo ratings yet
- Fracture CrurisDocument44 pagesFracture CrurisAnonymous turPUJtErNo ratings yet
- MEO Class 1 ProjectDocument2 pagesMEO Class 1 ProjectAshish Ranjan0% (1)
- NITIN Rdbms AssignmentDocument131 pagesNITIN Rdbms Assignmentnitinsingaur.bizNo ratings yet
- IFU 5902446 Port A-FrameDocument16 pagesIFU 5902446 Port A-FrameBeto AsaberNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document97 pagesCH 08albakili775514617No ratings yet
- Man of Sorrows PDFDocument4 pagesMan of Sorrows PDFjoao.beckNo ratings yet
- Royal Enfield Price ListDocument126 pagesRoyal Enfield Price Listmaniamson50% (20)
- "7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofDocument29 pages"7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofOliver Dennis100% (1)
- TPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3Document88 pagesTPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3DeniMestiWidiantoNo ratings yet
- Veeam Top 10 Reasons Choose Veeam 9 5Document2 pagesVeeam Top 10 Reasons Choose Veeam 9 5Anonymous xKgV3e6XLNo ratings yet
- Relative Range (RR) HandDocument13 pagesRelative Range (RR) HandSebastian Alejandro HerreraNo ratings yet
- 2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmDocument17 pages2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmForu MophiliaNo ratings yet
- IC Mask Design Essential Layout TechniquesDocument404 pagesIC Mask Design Essential Layout Techniquesramana459100% (2)
- AppendixDocument5 pagesAppendixAsim IqbalNo ratings yet
- S 125Document317 pagesS 125ronaldosilva2100% (1)
- 01-Basics of CorrosionDocument31 pages01-Basics of Corrosion이선엽No ratings yet
- 预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsDocument15 pages预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsSolo YehNo ratings yet