Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1: Historical Overview: 1.1 Pile Foundation
Chapter 1: Historical Overview: 1.1 Pile Foundation
Uploaded by
Vikash PrasadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1: Historical Overview: 1.1 Pile Foundation
Chapter 1: Historical Overview: 1.1 Pile Foundation
Uploaded by
Vikash PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1: Historical Overview
1.1 Pile Foundation
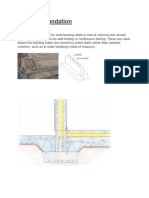
Piles are columnar elements in a foundation which have the function of transferring load from the superstructure through weak compressible strata or through water, onto stiffer or more compact and less
compressible soils or onto rock. They may be required to carry uplift loads when used to support tall structures subjected to overturning forces from winds or waves. Piles used in marine structures are subjected to lateral loads from the impact of berthing ships and from waves. Combinations of vertical and horizontal loads are carried where piles are used to support retaining walls, bridge piers and abutments, and machinery foundations.
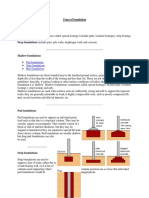
1.2 Types of pile foundation
Pile foundations can mainly be classified under following two
categories displacement and non-displacement piles. a. Displacement piles A large soil mass is displaced during the installation of the pile which significantly changes the soil characteristics around the pile. Driven piles fall under this category. b. Non displacement piles The soil surrounding the pile is undergoes small or insignificant change in its properties. Bored piles fall under this category. Piles can also be classified as cast in-situ or precast.
A useful classification for piles subjected to lateral loading is based on the relative stiffness of pile and soil. a. Short and rigid b. Long and flexible
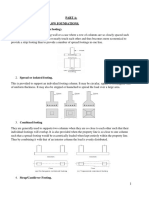
Chapter 2: Theoretical Background
2.1 Theory of subgrade reaction
You might also like
- Chapter 1-Pile Foundations-Lecture NoteDocument79 pagesChapter 1-Pile Foundations-Lecture NoteManal EsmaelNo ratings yet
- Foundation:: Different Types of FoundationDocument13 pagesFoundation:: Different Types of FoundationDwijendra ChanumoluNo ratings yet
- Module 18, FounDocument10 pagesModule 18, FounLeo DavifNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation: A Seminar Report ONDocument29 pagesPile Foundation: A Seminar Report ONSwap ImNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundation - Final Rev1Document75 pagesDeep Foundation - Final Rev1rossyNo ratings yet
- Anand Engineering College, Agra: Pile FoundationDocument30 pagesAnand Engineering College, Agra: Pile Foundationtoluca28No ratings yet
- Foundation and PilesDocument12 pagesFoundation and PilesTahir KhanNo ratings yet
- Types of FDN or PilesDocument15 pagesTypes of FDN or PilesSnaz_nedainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document57 pagesChapter 1Oromo Oromiya EtiophiaNo ratings yet
- Pile 1Document6 pagesPile 1Nisshant Singh SaudNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 PILE FoundationDocument57 pagesCHAPTER 1 PILE FoundationOromo Oromiya EtiophiaNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument27 pagesBuilding ConstructionMelaku DinkuNo ratings yet
- Centroid NotesDocument8 pagesCentroid NotesSupritha KNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument26 pagesIlovepdf Mergedsrishtisonkar15No ratings yet
- Pile Foundations NotesDocument11 pagesPile Foundations NotesPutinNo ratings yet
- Buildings-Types of FoundationsDocument5 pagesBuildings-Types of FoundationsRonit ChariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14-15 Pile Foundation and Bearing Capacity in Sand and ClayDocument14 pagesLecture 14-15 Pile Foundation and Bearing Capacity in Sand and ClayChauhdary Fazeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Types of FoundationDocument15 pagesTypes of FoundationMpumeleloNo ratings yet
- Jagannath University Faculty of Architecture and PlanningDocument14 pagesJagannath University Faculty of Architecture and PlanningSheetal BaidNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundations: Dr. Magdi ZumrawiDocument8 pagesDeep Foundations: Dr. Magdi Zumrawitemesgen yohannesNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Lecture NoteDocument15 pagesChapter-1 Lecture NoteWendimu TolessaNo ratings yet
- Vineet Shrivastava: Associate Professor Department of Planning & Architecture Mizoram UniversityDocument25 pagesVineet Shrivastava: Associate Professor Department of Planning & Architecture Mizoram UniversityMZU Barch 2020No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document14 pagesLecture 1Erica Jane TatelNo ratings yet
- Fe 2 PDFDocument11 pagesFe 2 PDFKiprono VincentNo ratings yet
- Types of Pile FoundationsDocument9 pagesTypes of Pile FoundationsAlex AnderNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhDocument13 pagesPile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhAmey Deshmukh100% (1)
- I. Deep Foundation: A. PileDocument7 pagesI. Deep Foundation: A. PileNikol CapulongNo ratings yet
- CEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringDocument36 pagesCEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringRamu KakaNo ratings yet
- Types of Building FoundationDocument4 pagesTypes of Building FoundationRajesh TandonNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering ShopworkDocument3 pagesCivil Engineering ShopworkJ O M A RNo ratings yet
- 4 LectureDocument37 pages4 LecturePranto KhanNo ratings yet
- Concrete PILINGDocument14 pagesConcrete PILINGDane Chybo TzNo ratings yet
- Case Study - FoundationDocument9 pagesCase Study - Foundationmunna rahmanNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Cast-In-situ Pile Foundation.Document5 pagesFactors Affecting Cast-In-situ Pile Foundation.Gaurav Dhang100% (1)
- 4.CEE 4101 3 MarchDocument44 pages4.CEE 4101 3 MarchPranto KhanNo ratings yet
- Cons Meth Group 2 Report CompilationDocument66 pagesCons Meth Group 2 Report CompilationBrian TanNo ratings yet
- Building FoundationDocument5 pagesBuilding FoundationvictorNo ratings yet
- Pad and Strip FoundationsDocument19 pagesPad and Strip FoundationsSyafiq_Richman_9904No ratings yet
- Program: B.E Subject Name: Geo Technical Engineering Subject Code: CE-8002 Semester: 8thDocument23 pagesProgram: B.E Subject Name: Geo Technical Engineering Subject Code: CE-8002 Semester: 8thFreak.h3No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Deep Foundation)Document57 pagesLecture 5 (Deep Foundation)Noor HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Assignment in FoundationDocument6 pagesAssignment in FoundationFrancis Prince ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Foundation: S.Manikandaprabhu at SaravananDocument65 pagesFoundation: S.Manikandaprabhu at SaravananpriyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Foundations.Document32 pagesPresentation On Foundations.shrikant100% (6)
- Foundation PilesDocument123 pagesFoundation PilesPravindNo ratings yet
- CH 4 FoundationDocument43 pagesCH 4 FoundationEyoatem Teferi100% (1)
- Building FoundationDocument5 pagesBuilding FoundationvictorNo ratings yet
- Design of Raft Foundation Based On Geotechnical Analysis PDFDocument114 pagesDesign of Raft Foundation Based On Geotechnical Analysis PDFNabanita Sharma100% (1)
- Foundation: Building Materials and ConstructionDocument59 pagesFoundation: Building Materials and Constructionbryan garciaNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Types of Shallow FoundationsDocument35 pagesCH-2 Types of Shallow Foundations19CE535 Mandar GawandeNo ratings yet
- Priya BeraDocument8 pagesPriya BeraPRIYA BERANo ratings yet
- Building Construction: Foundation SystemsDocument23 pagesBuilding Construction: Foundation SystemsAmmar MedeniNo ratings yet
- Chap1 IntroductionDocument24 pagesChap1 IntroductionMilki MesayNo ratings yet
- Shakib Sir URP - FoundationDocument48 pagesShakib Sir URP - FoundationHome Tutor Provider KhulnaNo ratings yet
- 13-Structural Foundation, Deep FoundationDocument37 pages13-Structural Foundation, Deep Foundationengsamim.walizadaNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundations: Kaidy DuarteDocument22 pagesDeep Foundations: Kaidy DuarteCynthia XiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesChapter-2 Literature ReviewKyaw Ye Htut HeinNo ratings yet
- Form Two Foundation NotesDocument6 pagesForm Two Foundation NotesTEMNo ratings yet
- Types of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Document14 pagesTypes of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Rahul Kumawat100% (1)
- Storage of Water Is Utilized For Following ObjectivesDocument11 pagesStorage of Water Is Utilized For Following Objectivesvineeth reddyNo ratings yet