Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE 434 Electromagnetic Waves, Spring 2010 Homework #11 Solution
EE 434 Electromagnetic Waves, Spring 2010 Homework #11 Solution
Uploaded by
punjabi_49Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE 434 Electromagnetic Waves, Spring 2010 Homework #11 Solution
EE 434 Electromagnetic Waves, Spring 2010 Homework #11 Solution
Uploaded by
punjabi_49Copyright:
Available Formats
EE 434 Electromagnetic Waves, Spring 2010 Homework #11 solution
9.3. The far eld power density radiated from an antenna is given by sin cos r W/m2 0 2 r where K is a constant. Determine the following P =K 2 2
(a) Azimuthal and elevation planes half-power beam widths. (b) Azimuthal and elevation planes rst null beam widths. (c) Directivity and directive gain. (a) In the azimuthal plane, the half-power beam width, 1 is dened as cos 2 is 1 = 120 .
2 2
1
2
1 = 2 . That
In the elevation plane, the half-power beam width, 1 is determined from sin 90
1
2
1 . 2
The solution is 1 = 120 .
(b) The azimuthal plane rst null beam width, 0 , is found from cos 20 = 0. The solution is 1 = 180 . The elevation plane rst null beam width is found from sin 90 20 = 0. 2 The solution is 0 = 180. (c) The directivity is D= The average power is found from
0
2
P Pavg
Pavg
1 = 2r 2
K
2
sin cos 2 r sin d d r2
2
K sin2 d = 2r 2 0 K 1 2 [ sin ] = 2 2r 2 2 K 2 = 2r 2 2 K = 2 2r
cos d
2
The directive gain is thus 1
D=K
sin cos 2r 2 = 2 sin cos r2 K
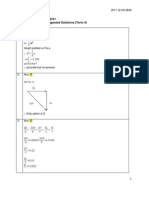
The directive gain is the maximum value of the directivity, which is at = 90 and = 0 . D0 = 2. 9.7. Consider an array of two isotropic sources. Obtain an expression for the AF and sketch the radiation pattern for the following conditions: (a) The separation distance is d = , and the two elements were fed equal 2 currents but of 180 phase dierence. (b) The separation distance is d = , and the two elements were fed equal 4 currents but of 90 phase dierence. (c) The separation distance is d = , and the two elements were fed equal currents but of 180 phase dierence. (a) We have = d cos . It is unclear whether the problem is referring to = 180 or = 180 . The expression is then AF = sin sin 2 = cos
The solid and dotted curves plot the two cases.
(b) Here we have AF = Here are the two cases sin sin 2 = cos 2 2
(c) Now we have AF = sin sin 2 = 2 cos
You might also like
- Assignment2 Antenna 2020 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAssignment2 Antenna 2020 SolutionsMalathi0% (1)
- Chapter04 Problems PDFDocument9 pagesChapter04 Problems PDFWaqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- H2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsDocument19 pagesH2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsonnoezNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsDocument14 pagesWBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Antenna MCQsDocument38 pagesAntenna MCQsAishwarya BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Solution 2 AntennaDocument7 pagesSolution 2 Antennaabdulwahab12100% (1)
- 1 BasicDocument39 pages1 BasicanililhanNo ratings yet
- Neet Question Paper 2021 Code O1Document71 pagesNeet Question Paper 2021 Code O1Deev SoniNo ratings yet
- AP SolnDocument4 pagesAP SolnSajad VmNo ratings yet
- Nsep Solution 2012Document14 pagesNsep Solution 2012Yatish GoyalNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2 PCM CombinedDocument25 pagesJEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2 PCM CombinedVeda Vikas DNo ratings yet
- Compile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviDocument10 pagesCompile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviSelma Regita MahardiniNo ratings yet
- Proiect AnteneDocument20 pagesProiect AnteneAndrei DuțanNo ratings yet
- HGDocument49 pagesHGZaheer Abbas QalooNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Parabolic Yagi-Uda Log-Periodic AntennaDocument92 pagesModule 6 Parabolic Yagi-Uda Log-Periodic AntennaAjit MeniyaNo ratings yet
- CH 1-Ch 7Document13 pagesCH 1-Ch 7Eligius MartinezNo ratings yet
- S. No Questions Solutions Sol:1 (D) : L L T S L LDocument8 pagesS. No Questions Solutions Sol:1 (D) : L L T S L LVaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main-17-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsDocument40 pagesJEE-Main-17-03-2021-Shift-1 (Memory Based) PhysicsSuvigya YadavNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Single Phase SystemDocument13 pagesAC Circuits Single Phase SystemClyde Ann CantagoNo ratings yet
- Rec3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesRec3 SolutionsOscar Martinez0% (1)
- ch32 PDFDocument14 pagesch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Antenna For All Application by John D. Kraus, 3rd Edt SolutionDocument40 pagesAntenna For All Application by John D. Kraus, 3rd Edt SolutionOmar Muñoz100% (2)
- Exam 2011 Questions and Answers Final RNDocument12 pagesExam 2011 Questions and Answers Final RNMYNAME100% (1)
- Questions On Electrostatic FieldsDocument31 pagesQuestions On Electrostatic Fieldskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media: Cristian VillegasDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Waves in Guided Media: Cristian VillegasCristian VillegasNo ratings yet
- New Power Transmission Assignment 2Document3 pagesNew Power Transmission Assignment 2ZabeehullahmiakhailNo ratings yet
- 3.electromagnetic Theory NET-JRF VKSDocument31 pages3.electromagnetic Theory NET-JRF VKSSijil SalimNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: PhysicsDocument74 pagesAnswers & Solutions: PhysicspiyushNo ratings yet
- GATE Problems in Antenna and Wave PropogationDocument6 pagesGATE Problems in Antenna and Wave PropogationShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution20for20Midterm 201420fallDocument5 pagesSolution20for20Midterm 201420fall3.14159265No ratings yet
- Ap2011 Solutions 06Document14 pagesAp2011 Solutions 06Sesario PratamaNo ratings yet
- Escuela Superior Politécnica De Chimborazo: D= P P U sin (θ) dθ d ∅ PDocument7 pagesEscuela Superior Politécnica De Chimborazo: D= P P U sin (θ) dθ d ∅ PJorge SaNo ratings yet
- Q1. Cellular Mobile Communication System: N I Ij+ JDocument13 pagesQ1. Cellular Mobile Communication System: N I Ij+ JSifun PadhiNo ratings yet
- H2 Physic 2010 A Level SolutionsDocument32 pagesH2 Physic 2010 A Level Solutionsonnoez50% (4)
- Cap. 32 PDFDocument75 pagesCap. 32 PDFwallaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension - PDF - Electronic Devices and Analog Circuits - Electronic Devices and Analog CircuitsDocument36 pagesComprehension - PDF - Electronic Devices and Analog Circuits - Electronic Devices and Analog Circuitssai JanhaviNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism II - Jackson Homework 8Document4 pagesElectricity and Magnetism II - Jackson Homework 8Ale GomezNo ratings yet
- Jest2022 QP and Revised AnswersDocument22 pagesJest2022 QP and Revised AnswersSkSNo ratings yet
- Conductors Conductor ConductorDocument5 pagesConductors Conductor Conductorjhon smithNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 Antenna 2020 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAssignment1 Antenna 2020 SolutionsMalathiNo ratings yet
- CUET Physics 2022 23rd Aug Slot 1Document71 pagesCUET Physics 2022 23rd Aug Slot 1NafeesNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper With Solutions (8th April - Morning)Document67 pagesJEE Main 2019 Question Paper With Solutions (8th April - Morning)Sionna KatiyarNo ratings yet
- 2021 20 JulyDocument37 pages2021 20 JulyDeeepakNo ratings yet
- Selfstudys Com FileDocument90 pagesSelfstudys Com Filepmanasi867No ratings yet
- 02 Experiment Manual 2 Determination of The Sound Wave Velocity With The Method of Lissajous Figures PDFDocument5 pages02 Experiment Manual 2 Determination of The Sound Wave Velocity With The Method of Lissajous Figures PDFNikko GalarosaNo ratings yet
- Homework 6Document5 pagesHomework 6Stephen RandallNo ratings yet
- Kcet 2018 Answer Keys by Expert Coaching Classes PDFDocument41 pagesKcet 2018 Answer Keys by Expert Coaching Classes PDFPrashanth GNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic1 PDFDocument43 pages1 Basic1 PDFameerNo ratings yet
- NEET UG 2024 Question Paper With Solutions - FREE PDF DownloadDocument81 pagesNEET UG 2024 Question Paper With Solutions - FREE PDF Downloadshivshankarinwate964No ratings yet
- Jest QuestionDocument16 pagesJest QuestionThirumugam SNo ratings yet
- Griffith AnswerDocument4 pagesGriffith AnswerDea Evan AyyatraNo ratings yet
- Em Waves JeeDocument14 pagesEm Waves JeeTobiramaNo ratings yet
- Antenna Parameters Are:: 1) What Is The Antenna? Write Short Notes About Its ParametersDocument7 pagesAntenna Parameters Are:: 1) What Is The Antenna? Write Short Notes About Its ParametersSujith ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Bnyy Byy Yyy Y Y Y Y Y BDocument5 pagesA Bnyy Byy Yyy Y Y Y Y Y BlawanNo ratings yet
- 2010 H2 Physics Paper 3 Soln - Updated For StudentsDocument8 pages2010 H2 Physics Paper 3 Soln - Updated For Studentslaslover100% (1)
- JEE Main 2022 (June 25 Morning Shift) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)Document24 pagesJEE Main 2022 (June 25 Morning Shift) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)avaneesh khadyeNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet