Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Quarter Math Skills
2nd Quarter Math Skills
Uploaded by
api-93111231Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Quarter Math Skills
2nd Quarter Math Skills
Uploaded by
api-93111231Copyright:
Available Formats
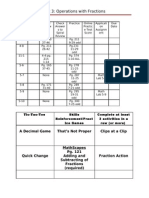
2nd Quarter Math Skills Learning Goals
Interim Progress
Assignment/Assessment & Date:
6.RP.1 Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. For example, The ratio of wings to beaks in the bird house at the zoo was 2:1, because for every 2 wings there was 1 beak. For every vote candidate A received, candidate C received nearly three votes. 6.RP.2 Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship.
For example, This recipe has a ratio of 3 cups of flour to 4 cups of sugar, so there is 3/4 cup of flour for each cup of sugar. We paid $75 for 15 hamburgers, which is a rate of $5 per hamburger. (Expectations for
unit rates in this grade are limited to non-complex fractions.)
6.RP.3 Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve realworld and mathematical problems, e.g., by
Quarter Final
reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. M06-S1C1-03 Demonstrate an understanding of fractions as rates, division of whole numbers, parts of a whole, parts of a set, and locations on a real number line. 6.RP.3 a. Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantities with whole-number measurements, find missing values in the tables, and plot the pairs of values on the coordinate plane. Use tables to compare ratios. M06-S1C1-03 Demonstrate an understanding of fractions as rates, division of whole numbers, parts of a whole, parts of a set, and locations on a real number line 6.RP.3 b. Solve unit rate problems including those involving unit pricing and constant speed. 6.RP.3 c. Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 times the quantity); solve problems involving finding the whole, given a part and the percent.
M06-S1C1-03 Demonstrate an understanding of fractions as rates, division of whole numbers, parts of a whole, parts of a set, and locations on a real number line. M06-S4C4-02 Solve problems involving conversion within the U.S. Customary and within the metric system. 6.RP.3 d. Use ratio reasoning to convert measurement units; manipulate and transform units appropriately when multiplying or dividing quantities. M06-S4C4-04 Solve problems involving the area of simple polygons using formulas for rectangles and triangles M06-S4C4-05 Solve problems involving area and perimeter of regular and irregular polygons. M06-S5C1-02 Create and justify an algorithm to determine the area of a given compound figure using parallelograms and triangles. 6.G.1 Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or
decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving realworld and mathematical problems. M06-S4C4-06 Describe the relationship between the volume of a figure and the area of its base. (filling to determine volume, no focus on fractional units or formal application of formula) 6.G.2 Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with fractional edge lengths by packing it with unit cubes of the appropriate unit fraction edge lengths, and show that the volume is the same as would be found by multiplying the edge lengths of the prism. Apply the formulas V = l w h and V = b h to find volumes of right rectangular prisms with fractional edge lengths in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. 6.G.4 Represent threedimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving realworld and mathematical problems.
M06-S4C1-01 Define(pi) as the ratio between the circumference and diameter of a circle and explain the relationship among the diameter, radius, and circumference. M06-S4C1-02 Solve problems using properties of supplementary, complementary, and vertical angles.
You might also like
- Math 10 Diagnostic Test 2018 2019Document4 pagesMath 10 Diagnostic Test 2018 2019Eric de Guzman80% (20)
- Standards-K-12 6th GradeDocument3 pagesStandards-K-12 6th Gradeapi-296039056No ratings yet
- Sixth Math StandardsDocument3 pagesSixth Math Standardsapi-233655908No ratings yet
- 7th Grade StandardsDocument8 pages7th Grade Standardsapi-251069371No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Math Curriculum MapDocument6 pages6th Grade Math Curriculum Mapapi-109360342No ratings yet
- Iskl Grade 7 MathsDocument5 pagesIskl Grade 7 MathsMathiarasu MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Tnready Blueprint g6 MathDocument9 pagesTnready Blueprint g6 Mathapi-282869532No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Curriculum MapDocument6 pagesGrade 6 Curriculum Mapapi-260971765No ratings yet
- Math 7 Syllabus 2014-2015Document5 pagesMath 7 Syllabus 2014-2015api-266524097No ratings yet
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5Document20 pagesAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5establoid1169No ratings yet
- 6thgrade Math I Can StatementsDocument155 pages6thgrade Math I Can StatementsRhonda GrossNo ratings yet
- Seventh Math StandardsDocument3 pagesSeventh Math Standardsapi-233655908No ratings yet
- Second Draft of 6-8 Benchmarks With Standards 8-28Document9 pagesSecond Draft of 6-8 Benchmarks With Standards 8-28justin fellerNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade 13-14 Math Common Core Standards by QuarterDocument3 pages5th Grade 13-14 Math Common Core Standards by QuartermrkballNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 5 08 11Document6 pagesMath Grade 5 08 11api-246939068No ratings yet
- CCSS Checklist For Math 3rdDocument9 pagesCCSS Checklist For Math 3rdodie01No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocument6 pages6th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardNo ratings yet
- 4th Nine WeeksDocument1 page4th Nine Weeksapi-233072472No ratings yet
- 8 ThgradecurriculumDocument5 pages8 Thgradecurriculumapi-254290621No ratings yet
- Ccss One Per PagDocument39 pagesCcss One Per PagjhooleyNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanDocument7 pages6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanBecky JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Common Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeDocument171 pagesCommon Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeJessicaNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade StandardDocument7 pages8th Grade Standardapi-251069371No ratings yet
- Tnready Blueprint g5 MathDocument9 pagesTnready Blueprint g5 Mathapi-282869532No ratings yet
- Unit 2 MapDocument1 pageUnit 2 Mapapi-256798980No ratings yet
- FREEMATHCommonCoreStateStandards68Checklist 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFREEMATHCommonCoreStateStandards68Checklist 1 PDFKatt DuangmalaiNo ratings yet
- Tnready Blueprint g3 MathDocument9 pagesTnready Blueprint g3 Mathapi-282869532No ratings yet
- Standards-K-12 8th GradeDocument3 pagesStandards-K-12 8th Gradeapi-296039056No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Math Common Core I Can StatementsDocument6 pages6th Grade Math Common Core I Can Statementsapi-233930784No ratings yet
- Fraction Vertical ProgressionDocument4 pagesFraction Vertical Progressionapi-709744639No ratings yet
- "I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade MathDocument6 pages"I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade Mathapi-303193556No ratings yet
- Oct 26-30Document3 pagesOct 26-30api-272841990No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksLindaNo ratings yet
- CCSS Unpacking Template ExampleDocument7 pagesCCSS Unpacking Template Examplechardz10No ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenDocument7 pagesMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenestabloid1169No ratings yet
- Math Grade 3 08 11Document6 pagesMath Grade 3 08 11api-246939068No ratings yet
- I Can Math 6Document6 pagesI Can Math 6api-365969613No ratings yet
- KS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapDocument20 pagesKS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapGrace TabfNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocument6 pages8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 OverviewDocument5 pagesGrade 3 Overviewapi-233351761No ratings yet
- School Ytd by Strand and SkillDocument70 pagesSchool Ytd by Strand and Skillapi-236897542No ratings yet
- Overland TrailDocument8 pagesOverland Trailapi-245623862No ratings yet
- 7 Grade Math Instructional GuideDocument7 pages7 Grade Math Instructional Guideapi-323730622No ratings yet
- 3 Grade Math Common Core Standards: At-A-Glance Operations & Algebraic ThinkingDocument4 pages3 Grade Math Common Core Standards: At-A-Glance Operations & Algebraic Thinkingapi-298986760No ratings yet
- Presents: The Common Core State Standards Checklist Grades 3-5Document19 pagesPresents: The Common Core State Standards Checklist Grades 3-5Katt DuangmalaiNo ratings yet
- cmp3 GlossaryDocument66 pagescmp3 Glossaryapi-299469383No ratings yet
- FKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch3 Student WorkbookDocument130 pagesFKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch3 Student WorkbookSelvi RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Es Table Grade 6 Pba Mya For Parcc FinalDocument8 pagesEs Table Grade 6 Pba Mya For Parcc Finalapi-115680157No ratings yet
- Grade5seqeunce Map Full StandardsDocument4 pagesGrade5seqeunce Map Full Standardsapi-297750365No ratings yet
- Geometry Crns 12-13 4th Nine WeeksDocument15 pagesGeometry Crns 12-13 4th Nine Weeksapi-201428071No ratings yet
- Fourth Math StandardsDocument3 pagesFourth Math Standardsapi-233655908No ratings yet
- Tennessee's State Mathematics Standards - Grade 8Document4 pagesTennessee's State Mathematics Standards - Grade 8api-333440532No ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenDocument7 pagesMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenapi-365969613No ratings yet
- Mathematics 8 2022 2023Document8 pagesMathematics 8 2022 2023Princess Mae LumawagNo ratings yet
- New Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Document18 pagesNew Jersey Student Learning Standards Mathematics - Grade 6Terrence AkinolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MathxDocument5 pagesGrade 8 Mathxapi-2542992270% (1)
- CCSSI Math Standards 7Document6 pagesCCSSI Math Standards 7establoid1169No ratings yet
- 7 Grade Math Ratios & Proportional Relationships CCSS "I Can" StatementsDocument71 pages7 Grade Math Ratios & Proportional Relationships CCSS "I Can" Statementsapi-271033247No ratings yet
- CCSSI Math Standards 5Document6 pagesCCSSI Math Standards 5establoid1169No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Timeline of The Cold WarDocument3 pagesTimeline of The Cold Warapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Geometry Map Project RubricDocument2 pagesGeometry Map Project Rubricapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Unit 4-Ratios Rates and ProportionsDocument1 pageUnit 4-Ratios Rates and Proportionsapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Unit 4 QuestionsDocument1 pageUnit 4 Questionsapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Math Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMath Cheat Sheetapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Geometry Map ProjectDocument1 pageGeometry Map Projectapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Unit 6 QuestionsDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Questionsapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Unit 5 QuestionsDocument1 pageUnit 5 Questionsapi-93111231No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Math ChecklistDocument3 pages1st Quarter Math Checklistapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Center DocumentDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Center Documentapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Ccss Math PracticesDocument1 pageCcss Math Practicesapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Toothpick Bridge RubricDocument1 pageToothpick Bridge Rubricapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Toothpick Bridge ProjectDocument3 pagesToothpick Bridge Projectapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Procedures Used in Summative AssessmentDocument2 pagesProcedures Used in Summative Assessmentapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Multiplying and Dividing Decimal NotesDocument4 pagesMultiplying and Dividing Decimal Notesapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Sts Session 1Document1 pageSts Session 1api-93111231No ratings yet
- Unpacking The Common Core MathDocument2 pagesUnpacking The Common Core Mathapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Science Level CardsDocument4 pagesScience Level Cardsapi-93111231No ratings yet
- Tooling Design For Tubing Medical Tubing ExtrusionDocument9 pagesTooling Design For Tubing Medical Tubing ExtrusionHamid Rnd100% (1)
- Schedule Lesson No.: 1-3: Represents of A Whole or A CollectionDocument19 pagesSchedule Lesson No.: 1-3: Represents of A Whole or A CollectionSofia ApuyanNo ratings yet
- Golden Ratio in Clothing DesignDocument3 pagesGolden Ratio in Clothing DesignKristen100% (1)
- DLP Day 1Document4 pagesDLP Day 1Aisley Mae EspinarNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m1 Copy Ready Materials PDFDocument37 pagesMath g7 m1 Copy Ready Materials PDFJeremias A BangiNo ratings yet
- Holt Algebra 1 - Chapter 03 - Quiz 2Document2 pagesHolt Algebra 1 - Chapter 03 - Quiz 2StanleyNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education - Grade 8: I. Introductory ConceptDocument13 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education - Grade 8: I. Introductory ConceptSharalyn SiaNo ratings yet
- A Concise Guide To Compositional Data AnalysisDocument134 pagesA Concise Guide To Compositional Data Analysismaynardjameskeenan100% (2)
- C12 Concrete Mix DesignDocument5 pagesC12 Concrete Mix DesignadelalwailyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mathematics Curriculum GuideDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Mathematics Curriculum GuideGlenn RosalesNo ratings yet
- BUSMATH SLM March 06-10, 2023Document6 pagesBUSMATH SLM March 06-10, 2023Jemar AlipioNo ratings yet
- Maths. Workbook. Age 11-14 - Rich, Gillian, Author - 2014 - London - Letts Educational - 9781844197569 - Anna's ArchiveDocument92 pagesMaths. Workbook. Age 11-14 - Rich, Gillian, Author - 2014 - London - Letts Educational - 9781844197569 - Anna's Archivecatherinejodi159No ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument43 pagesPrinciples of Designapi-231911898100% (1)
- Holt Algebra 1 - Chapter 03 - Quiz 3Document2 pagesHolt Algebra 1 - Chapter 03 - Quiz 3StanleyNo ratings yet
- 6 Standard MathDocument96 pages6 Standard Mathtaaniakhan11100% (1)
- Bannockburn 1314Document38 pagesBannockburn 1314Javier GonzalezNo ratings yet
- PercentDocument25 pagesPercentFrost DogNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical CalculationDocument49 pagesPharmaceutical CalculationDekaria AlamandaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of NAVIO Show Students The ReadingDocument14 pagesPresentation of NAVIO Show Students The ReadingEsteban Malaquias ChavezNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Ratio and Proportion 1st LevelDocument22 pagesUnit 8 Ratio and Proportion 1st LevelyonesNo ratings yet
- Aritmetic Booster WorkshopDocument6 pagesAritmetic Booster WorkshopRaghunath BeheraNo ratings yet
- Math - Ratio and ProportionDocument41 pagesMath - Ratio and ProportionninigraceNo ratings yet
- Wittkower The Changing Concept of ProportionDocument18 pagesWittkower The Changing Concept of Proportiondadaesttout100% (1)
- Average and Percentage: IBPS Clerk (PRE) Exam 2017Document6 pagesAverage and Percentage: IBPS Clerk (PRE) Exam 2017Himanshu GargNo ratings yet
- RecoDocument23 pagesRecoJoel MangallayNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4791 - 10 Flat and Elongated Particles in Coarse AggregateDocument6 pagesASTM D4791 - 10 Flat and Elongated Particles in Coarse AggregateParth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rate AnalysisDocument18 pagesRate Analysisanjali sajiNo ratings yet
- Frequency and Morbidity MeasuresDocument17 pagesFrequency and Morbidity MeasuresIvan Cryolle AbuyuanNo ratings yet
- QA & DI Test 9Document22 pagesQA & DI Test 9Sumeet GuptaNo ratings yet