Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acquired Hip Dislocation
Acquired Hip Dislocation
Uploaded by
Zul IsmailCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Femoral Neck FractureDocument21 pagesFemoral Neck FractureSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Hip DislocationDocument4 pagesHip DislocationcrunkestNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 - Internal Fixation - IIDocument21 pagesLect 8 - Internal Fixation - IIAnkit LakshyaNo ratings yet
- Pelvis and HipDocument90 pagesPelvis and Hipalsead798No ratings yet
- RevisedDocument71 pagesRevisedMayra FariasNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR JaneDocument73 pagesArthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR Janeumanantini06No ratings yet
- Spinal SurgeryDocument19 pagesSpinal SurgerySalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Definition: Is A Condition Resulting in Partial or Complete Separation of A Segment of Normal Hyaline Cartilage From It's Supporting BoneDocument8 pagesDefinition: Is A Condition Resulting in Partial or Complete Separation of A Segment of Normal Hyaline Cartilage From It's Supporting BoneKarla Chariz Fernandez BayagNo ratings yet
- Patient - Co.uk - Trusted Medical Information and Support: Knee Fractures and DislocationsDocument4 pagesPatient - Co.uk - Trusted Medical Information and Support: Knee Fractures and DislocationsHayelom MichaelNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis of HipDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritis of Hipjcachica21No ratings yet
- Dislocation of Hip-1Document44 pagesDislocation of Hip-1lionhearteagleNo ratings yet
- Knee Injuries: DR - Sindhu Meena MEM Resident MMHRCDocument30 pagesKnee Injuries: DR - Sindhu Meena MEM Resident MMHRCP Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Colles Fracture & Knee DislocationDocument38 pagesColles Fracture & Knee DislocationNap91No ratings yet
- Joint Instability: Hendradi Khumarga SPOT. FICSDocument48 pagesJoint Instability: Hendradi Khumarga SPOT. FICSJoshua ObrienNo ratings yet
- Hip Pain TreatmentDocument19 pagesHip Pain TreatmentLev KalikaNo ratings yet
- Ankle Instability: Dr. Syarif Hidayatullah, SP - OT, M.KesDocument75 pagesAnkle Instability: Dr. Syarif Hidayatullah, SP - OT, M.Kesahmad zakyNo ratings yet
- Pelvis: Stable Pelvic FracturesDocument4 pagesPelvis: Stable Pelvic FracturesEloise PateñoNo ratings yet
- Posterior Tibial Tendon DysfunctionDocument3 pagesPosterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunctionpioneers2011No ratings yet
- Presented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KDocument81 pagesPresented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Trochlear DysplasiaDocument23 pagesTrochlear DysplasiaSruthi SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Patella Injuries: Pain Associated With The KneecapDocument5 pagesPatella Injuries: Pain Associated With The KneecapmarkositozNo ratings yet
- Anterior Knee Pain Syndrome ReferatDocument28 pagesAnterior Knee Pain Syndrome ReferatnurulNo ratings yet
- Avascular NecrosisDocument49 pagesAvascular NecrosisvhugalabudeliNo ratings yet
- Andi Rahmat Hidayat C 111 07 104 Advisor: Dr. Andi Sirfa Dr. Helmiyadi Kuswardhana Supervisor: Dr. Henry Yurianto, M.Phill, PHD, SP - OtDocument30 pagesAndi Rahmat Hidayat C 111 07 104 Advisor: Dr. Andi Sirfa Dr. Helmiyadi Kuswardhana Supervisor: Dr. Henry Yurianto, M.Phill, PHD, SP - OtAndi Rahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Rehab - Week 7 - Group 1 1Document9 pagesRehab - Week 7 - Group 1 1api-468093714No ratings yet
- Ankel Heel PainDocument51 pagesAnkel Heel PainMeno Ali100% (1)
- Lower Extremity.Document80 pagesLower Extremity.singhsumit55650No ratings yet
- 36 Knee Conditions: EMQ Answers 87Document10 pages36 Knee Conditions: EMQ Answers 87Eunice LimNo ratings yet
- Fracture-Dislocation of The Hip-KaizarDocument69 pagesFracture-Dislocation of The Hip-KaizarKaizar Ennis100% (1)
- Gadline PrsentationDocument12 pagesGadline PrsentationsumardiNo ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff InjuriesDocument26 pagesRotator Cuff Injuriesanname_girlNo ratings yet
- Knee Injuries (My Notes)Document15 pagesKnee Injuries (My Notes)Palem meghana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sports Injuries in UE - Shoulder - Part 3.Document87 pagesSports Injuries in UE - Shoulder - Part 3.salmankhan09215No ratings yet
- Elbow Joint Injuries - Assessment & TreatmentDocument55 pagesElbow Joint Injuries - Assessment & TreatmentSushma ImmadiNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity ConditionsDocument39 pagesLower Extremity Conditions23120094No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis of Hip JointDocument25 pagesTuberculosis of Hip JointYousra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 pagesAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena Koushal100% (1)
- Lec3 DiscDocument50 pagesLec3 Discsana mumtazNo ratings yet
- FRAKTURE CasesDocument6 pagesFRAKTURE CasesJM MARQUEZNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Injuries of The AthleteDocument24 pagesFoot and Ankle Injuries of The AthleteSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- Hip Impingement FaiDocument8 pagesHip Impingement FaiLev KalikaNo ratings yet
- Postural DeformitiesDocument37 pagesPostural DeformitiesBalram Jha80% (5)
- Fractures: Mary Grace B. Gutierrez Resti Mariano Ma. Cindy O. BautistaDocument50 pagesFractures: Mary Grace B. Gutierrez Resti Mariano Ma. Cindy O. BautistaJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Hip DislocationDocument39 pagesHip DislocationSHAMENI VINODNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint DislocationDocument19 pagesHip Joint Dislocationshaoib.grandyNo ratings yet
- Patellar Tendon RuptureDocument13 pagesPatellar Tendon Rupturededyalkarni08No ratings yet
- Dislocation of Hip Joint: DR - PonnilavanDocument38 pagesDislocation of Hip Joint: DR - PonnilavanPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Chondro Malacia PatellaDocument16 pagesChondro Malacia Patellamedical- physio classesNo ratings yet
- S Pondy Lols Ys ThesisDocument35 pagesS Pondy Lols Ys ThesisSal LieNo ratings yet
- Hip Dislocation PresentationDocument24 pagesHip Dislocation PresentationHafizah Hoshni100% (1)
- Congenital Vertical Talus Relevant AnatomyDocument5 pagesCongenital Vertical Talus Relevant AnatomyJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Knee Osteoarthritis: DefinitionDocument19 pagesKnee Osteoarthritis: DefinitionShrouq BadrNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Disorders of Lumbar SpineDocument54 pagesDegenerative Disorders of Lumbar Spineapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Kneecap DislocationDocument2 pagesKneecap DislocationbiancaNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower LimbDocument7 pagesJoints of Lower LimbjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento No Convencional de ArtrosisDocument11 pagesTratamiento No Convencional de ArtrosisHenny CasanovaNo ratings yet
- 4 Perthes Ve SCFEDocument34 pages4 Perthes Ve SCFECharl UnalNo ratings yet
- Fracture Pelvis, Hip DislocationsDocument34 pagesFracture Pelvis, Hip DislocationsMisoNo ratings yet
- Arm:Leg Fracture PDFDocument11 pagesArm:Leg Fracture PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Distal Clavicle Osteolysis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDistal Clavicle Osteolysis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
Acquired Hip Dislocation
Acquired Hip Dislocation
Uploaded by
Zul IsmailOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acquired Hip Dislocation
Acquired Hip Dislocation
Uploaded by
Zul IsmailCopyright:
Available Formats
RISK FACTORS
Motor vehicle accidents (Wearing a seatbelt can greatly reduce your risk.) Falls from a height (such as a fall from a ladder) or industrial accidents can also generate enough force to dislocate a hip. Hip replacement surgery Rugby and American football
COMPLICATIONS
If there are associated fractures disrupt blood vessels and nerves blood supply to the bone is lost avascular necrosis or osteonecrosis increases the risk of developing arthritis in the joint. Complications include deep venous thrombosis (DVT), sciatic nerve injury, avascular necrosis (AVN), vascular injury, recurrent dislocation, arthritis, and chronic pain
TREATMENT and MANAGEMENT
Surgical realignment and traction Administer an anesthetic or a sedative and manipulate the bones back into their proper position / Reduction done in the operating room with anesthesia. X-rays and possibly a computed tomography (CT) scan to make sure that the bones are in the proper position Rehabilitation Controlled exercises using a continuous passive motion machine Patients can probably begin walking with crutches when free of pain. A walking aid, such as a cane, should be used until the limp disappears.
AETIOLOGY
Gradual: Progressive deformation of the hip joint. Common in children with neuromuscular condition; cerebral palsy, spina bifida) Acute: Trauma/ injury to the hip
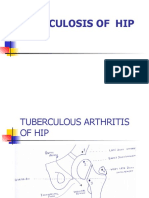
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
Acquired Hip Dislocation
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
X-rays will show whether there are any additional fractures in the hip.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint: the ball-shaped head of the femur fits inside a cup-shaped socket in the pelvis. The structure of a ball-and-socket joint gives it a great deal of stability and allows it to move freely. A great amount of force is required to pop the thighbone out of its socket.
PATHOGENESIS
Head of the femur slips out of its socket in the hip bone. 90% the femur is pushed out in a backwards direction. (posterior dislocation). Dislocate forward or anterior direction.
Pain Unable to move the leg Numb in the foot or ankle Posterior dislocations - affected limb will be shortened and internally rotated. Anterior dislocation - limb will not be lengthened and will be externally rotated. This dislocation is very painful and patients are unable to move when it occurs. Due to the dislocation, there could be some nerve damage resulting in loss of feeling in the foot or ankle.
You might also like
- Femoral Neck FractureDocument21 pagesFemoral Neck FractureSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Hip DislocationDocument4 pagesHip DislocationcrunkestNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 - Internal Fixation - IIDocument21 pagesLect 8 - Internal Fixation - IIAnkit LakshyaNo ratings yet
- Pelvis and HipDocument90 pagesPelvis and Hipalsead798No ratings yet
- RevisedDocument71 pagesRevisedMayra FariasNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR JaneDocument73 pagesArthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR Janeumanantini06No ratings yet
- Spinal SurgeryDocument19 pagesSpinal SurgerySalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Definition: Is A Condition Resulting in Partial or Complete Separation of A Segment of Normal Hyaline Cartilage From It's Supporting BoneDocument8 pagesDefinition: Is A Condition Resulting in Partial or Complete Separation of A Segment of Normal Hyaline Cartilage From It's Supporting BoneKarla Chariz Fernandez BayagNo ratings yet
- Patient - Co.uk - Trusted Medical Information and Support: Knee Fractures and DislocationsDocument4 pagesPatient - Co.uk - Trusted Medical Information and Support: Knee Fractures and DislocationsHayelom MichaelNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis of HipDocument3 pagesOsteoarthritis of Hipjcachica21No ratings yet
- Dislocation of Hip-1Document44 pagesDislocation of Hip-1lionhearteagleNo ratings yet
- Knee Injuries: DR - Sindhu Meena MEM Resident MMHRCDocument30 pagesKnee Injuries: DR - Sindhu Meena MEM Resident MMHRCP Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Colles Fracture & Knee DislocationDocument38 pagesColles Fracture & Knee DislocationNap91No ratings yet
- Joint Instability: Hendradi Khumarga SPOT. FICSDocument48 pagesJoint Instability: Hendradi Khumarga SPOT. FICSJoshua ObrienNo ratings yet
- Hip Pain TreatmentDocument19 pagesHip Pain TreatmentLev KalikaNo ratings yet
- Ankle Instability: Dr. Syarif Hidayatullah, SP - OT, M.KesDocument75 pagesAnkle Instability: Dr. Syarif Hidayatullah, SP - OT, M.Kesahmad zakyNo ratings yet
- Pelvis: Stable Pelvic FracturesDocument4 pagesPelvis: Stable Pelvic FracturesEloise PateñoNo ratings yet
- Posterior Tibial Tendon DysfunctionDocument3 pagesPosterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunctionpioneers2011No ratings yet
- Presented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KDocument81 pagesPresented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Trochlear DysplasiaDocument23 pagesTrochlear DysplasiaSruthi SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Patella Injuries: Pain Associated With The KneecapDocument5 pagesPatella Injuries: Pain Associated With The KneecapmarkositozNo ratings yet
- Anterior Knee Pain Syndrome ReferatDocument28 pagesAnterior Knee Pain Syndrome ReferatnurulNo ratings yet
- Avascular NecrosisDocument49 pagesAvascular NecrosisvhugalabudeliNo ratings yet
- Andi Rahmat Hidayat C 111 07 104 Advisor: Dr. Andi Sirfa Dr. Helmiyadi Kuswardhana Supervisor: Dr. Henry Yurianto, M.Phill, PHD, SP - OtDocument30 pagesAndi Rahmat Hidayat C 111 07 104 Advisor: Dr. Andi Sirfa Dr. Helmiyadi Kuswardhana Supervisor: Dr. Henry Yurianto, M.Phill, PHD, SP - OtAndi Rahmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Rehab - Week 7 - Group 1 1Document9 pagesRehab - Week 7 - Group 1 1api-468093714No ratings yet
- Ankel Heel PainDocument51 pagesAnkel Heel PainMeno Ali100% (1)
- Lower Extremity.Document80 pagesLower Extremity.singhsumit55650No ratings yet
- 36 Knee Conditions: EMQ Answers 87Document10 pages36 Knee Conditions: EMQ Answers 87Eunice LimNo ratings yet
- Fracture-Dislocation of The Hip-KaizarDocument69 pagesFracture-Dislocation of The Hip-KaizarKaizar Ennis100% (1)
- Gadline PrsentationDocument12 pagesGadline PrsentationsumardiNo ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff InjuriesDocument26 pagesRotator Cuff Injuriesanname_girlNo ratings yet
- Knee Injuries (My Notes)Document15 pagesKnee Injuries (My Notes)Palem meghana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sports Injuries in UE - Shoulder - Part 3.Document87 pagesSports Injuries in UE - Shoulder - Part 3.salmankhan09215No ratings yet
- Elbow Joint Injuries - Assessment & TreatmentDocument55 pagesElbow Joint Injuries - Assessment & TreatmentSushma ImmadiNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity ConditionsDocument39 pagesLower Extremity Conditions23120094No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis of Hip JointDocument25 pagesTuberculosis of Hip JointYousra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 pagesAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena Koushal100% (1)
- Lec3 DiscDocument50 pagesLec3 Discsana mumtazNo ratings yet
- FRAKTURE CasesDocument6 pagesFRAKTURE CasesJM MARQUEZNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Injuries of The AthleteDocument24 pagesFoot and Ankle Injuries of The AthleteSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- Hip Impingement FaiDocument8 pagesHip Impingement FaiLev KalikaNo ratings yet
- Postural DeformitiesDocument37 pagesPostural DeformitiesBalram Jha80% (5)
- Fractures: Mary Grace B. Gutierrez Resti Mariano Ma. Cindy O. BautistaDocument50 pagesFractures: Mary Grace B. Gutierrez Resti Mariano Ma. Cindy O. BautistaJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Hip DislocationDocument39 pagesHip DislocationSHAMENI VINODNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint DislocationDocument19 pagesHip Joint Dislocationshaoib.grandyNo ratings yet
- Patellar Tendon RuptureDocument13 pagesPatellar Tendon Rupturededyalkarni08No ratings yet
- Dislocation of Hip Joint: DR - PonnilavanDocument38 pagesDislocation of Hip Joint: DR - PonnilavanPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Chondro Malacia PatellaDocument16 pagesChondro Malacia Patellamedical- physio classesNo ratings yet
- S Pondy Lols Ys ThesisDocument35 pagesS Pondy Lols Ys ThesisSal LieNo ratings yet
- Hip Dislocation PresentationDocument24 pagesHip Dislocation PresentationHafizah Hoshni100% (1)
- Congenital Vertical Talus Relevant AnatomyDocument5 pagesCongenital Vertical Talus Relevant AnatomyJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Knee Osteoarthritis: DefinitionDocument19 pagesKnee Osteoarthritis: DefinitionShrouq BadrNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Disorders of Lumbar SpineDocument54 pagesDegenerative Disorders of Lumbar Spineapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Kneecap DislocationDocument2 pagesKneecap DislocationbiancaNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower LimbDocument7 pagesJoints of Lower LimbjsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento No Convencional de ArtrosisDocument11 pagesTratamiento No Convencional de ArtrosisHenny CasanovaNo ratings yet
- 4 Perthes Ve SCFEDocument34 pages4 Perthes Ve SCFECharl UnalNo ratings yet
- Fracture Pelvis, Hip DislocationsDocument34 pagesFracture Pelvis, Hip DislocationsMisoNo ratings yet
- Arm:Leg Fracture PDFDocument11 pagesArm:Leg Fracture PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Distal Clavicle Osteolysis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDistal Clavicle Osteolysis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet