Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiplication Algorithm Figure MTC
Multiplication Algorithm Figure MTC
Uploaded by
jhicks_mathCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Civil Service Examination - Math (Repaired)Document81 pagesCivil Service Examination - Math (Repaired)KIM RAGA100% (1)
- GAt Maths PDFDocument49 pagesGAt Maths PDFMushayyed Ali86% (21)
- Divisibility Rule: Divisibility Rules For Numbers 1-20Document16 pagesDivisibility Rule: Divisibility Rules For Numbers 1-20themathlover50% (2)
- GAt Maths PDFDocument49 pagesGAt Maths PDFAmmarahBatool95No ratings yet
- Square Root and Cube Root - 1st - ChapterDocument20 pagesSquare Root and Cube Root - 1st - ChapterWinston MosesNo ratings yet
- Multiplying Decimals ExampleDocument1 pageMultiplying Decimals Exampleapi-293308991No ratings yet
- Rational Numbers: Funda 1: De-ArrangementDocument8 pagesRational Numbers: Funda 1: De-Arrangementsinghalnitin1No ratings yet
- Vedic Maths: Multiply To Numbers Multiply 2 Numbers Close To 100,1000,10000, EtcDocument28 pagesVedic Maths: Multiply To Numbers Multiply 2 Numbers Close To 100,1000,10000, EtcGeorgettaPNo ratings yet
- Explanation in Some Items in Math.Document4 pagesExplanation in Some Items in Math.Garden Of PrayerNo ratings yet
- Grade 2: Parent Math Strategy GuideDocument2 pagesGrade 2: Parent Math Strategy Guideapi-300246618No ratings yet
- Number System 1 and 2 86Document23 pagesNumber System 1 and 2 86ParkingNo ratings yet
- Vedic Mathematics Worlds Fastest Mental Math SystemDocument31 pagesVedic Mathematics Worlds Fastest Mental Math SystemAbhishek Sharma100% (2)
- Impress Your Friends With Mental Math TricksDocument6 pagesImpress Your Friends With Mental Math Tricksray_xNo ratings yet
- HighSchool Math ProblemsDocument20 pagesHighSchool Math ProblemsEkaveera GouribhatlaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of EquationsDocument1 pageCompilation of EquationsChloe OberlinNo ratings yet
- 3 Grade Comprehensive CRCT Math Study Guide: Thousands OnesDocument31 pages3 Grade Comprehensive CRCT Math Study Guide: Thousands OnesTracy RemyNo ratings yet
- A Mother's Guide to Multiplication: For 7-11 Year OldsFrom EverandA Mother's Guide to Multiplication: For 7-11 Year OldsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vedic Mathematics and Calculation TechniquesDocument8 pagesVedic Mathematics and Calculation TechniquesGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Sharing: 16 Shared Equally Between 2 Gives You 8Document10 pagesSharing: 16 Shared Equally Between 2 Gives You 8ketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Magicsqaure 1Document5 pagesMagicsqaure 1api-360674086No ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument72 pagesPractice ProblemsGRE Dreamer KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsDocument89 pagesAnswer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsAnish Anand kumar100% (1)
- Math TricksDocument6 pagesMath TricksRoger nocomNo ratings yet
- Vedic Mathematics PresentationDocument31 pagesVedic Mathematics Presentationnd_lokesh100% (1)
- 2020 Chapter Competition SolutionsDocument11 pages2020 Chapter Competition SolutionsSup' Tan'No ratings yet
- Principles of Counting.: SolutionDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Counting.: SolutionERGUIZA, analizaNo ratings yet
- Calculation Year 5 3A 28 Calculation Year 5 PDFDocument6 pagesCalculation Year 5 3A 28 Calculation Year 5 PDFtizuliveNo ratings yet
- Level 4 Help PagesDocument14 pagesLevel 4 Help Pagesapi-235903058No ratings yet
- Vedic MathsDocument37 pagesVedic Mathsbarati_rao8747No ratings yet
- Problem Solving Strategies: STRATEGY #1: Use of PatternDocument13 pagesProblem Solving Strategies: STRATEGY #1: Use of PatternTherese Grace Postrero100% (1)
- X Which Gives A Remainder of 4 When Divided by 5, A Remainder of 7 WhenDocument5 pagesX Which Gives A Remainder of 4 When Divided by 5, A Remainder of 7 Whenmicro1234No ratings yet
- PEA 204 WorkbookDocument78 pagesPEA 204 WorkbookKhushi RanjanNo ratings yet
- WiproDocument20 pagesWiproMuthu ManiNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Parent BrochureDocument2 pagesGrade 3 Parent Brochureapi-305026398No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2BinomialTheoremiiDocument7 pagesWorksheet 2BinomialTheoremiitanmoy bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Kaplan 100math BasicsDocument4 pagesKaplan 100math Basicsapi-20011278No ratings yet
- Vedic Maths - TricksDocument41 pagesVedic Maths - Tricksvarun padhye100% (1)
- By Muralee.V. Whole NumbersDocument10 pagesBy Muralee.V. Whole NumbersMuralee VeeramalaiNo ratings yet
- Times TablesDocument29 pagesTimes Tableskamolpan@gmail.com67% (3)
- Math Solving LETDocument2 pagesMath Solving LETBRIANNo ratings yet
- Unit Study Guides - CRCT Study GuidesDocument4 pagesUnit Study Guides - CRCT Study Guidesapi-37741282No ratings yet
- CheckpointDocument8 pagesCheckpointp_kubebatu5565No ratings yet
- MATHINIKDocument6 pagesMATHINIKRTMunozNo ratings yet
- Class06 Math Grade10 Notes Oct 19-20Document11 pagesClass06 Math Grade10 Notes Oct 19-20mjysongNo ratings yet
- One Stop MBA - 2Document3 pagesOne Stop MBA - 2Quirking QuarkNo ratings yet
- The Number System and Mathematics LanguageDocument14 pagesThe Number System and Mathematics LanguagethabisoNo ratings yet
- Math Background: Concept Building ActivitiesDocument5 pagesMath Background: Concept Building Activitiesankita440No ratings yet
- Inclusion ExclusionDocument4 pagesInclusion ExclusionFantastiqueFessesNo ratings yet
- FALL WIN SEM (2023-24) STS1004 TH AP2023243000841 Reference Material II 07-Oct-2023 L12-Six Phrase-Squares and Square RootsDocument27 pagesFALL WIN SEM (2023-24) STS1004 TH AP2023243000841 Reference Material II 07-Oct-2023 L12-Six Phrase-Squares and Square RootsAkula MohansankerNo ratings yet
- Calcuation Policy 2013Document8 pagesCalcuation Policy 2013api-105903956No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Simple Equations NAME: - CLASS: VII SEC: - DATEDocument13 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Simple Equations NAME: - CLASS: VII SEC: - DATEHarishNo ratings yet
- Pry 6 Maths 3RD TermDocument41 pagesPry 6 Maths 3RD TermkuforijiifeoluwaNo ratings yet
- 1number SystemDocument24 pages1number SystemMamataMaharanaNo ratings yet
- Sonawane Academy: Jee-Main / AdvanceDocument5 pagesSonawane Academy: Jee-Main / AdvanceparamNo ratings yet
- Amigable (Math)Document4 pagesAmigable (Math)Alexren AmigableNo ratings yet
- Divisor 1 2: Divisibility Condition ExamplesDocument2 pagesDivisor 1 2: Divisibility Condition ExamplesAnkit ShettyNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation Word Problems2Document9 pagesLinear Equation Word Problems2sasyedaNo ratings yet
- Kindergarden Lesson StudyDocument20 pagesKindergarden Lesson Studyjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Mobius StripDocument1 pageMobius Stripjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Progressions in Area Models Would It Be Good To Connect:: CCSS - Math.Content.4.NBT.B.5Document1 pageProgressions in Area Models Would It Be Good To Connect:: CCSS - Math.Content.4.NBT.B.5jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Bundle and UnbundleDocument3 pagesBundle and Unbundlejhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document7 pagesDay 1jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Brownie Bits A3 Grade Lesson Study On The Distributive PropertyDocument10 pagesBrownie Bits A3 Grade Lesson Study On The Distributive Propertyjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Spirograph Activity PostDocument4 pagesSpirograph Activity Postjhicks_math100% (1)
- Lesson Study ProjectDocument13 pagesLesson Study Projectjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- FractionSlides Kansas 2012 09Document34 pagesFractionSlides Kansas 2012 09jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- TrickDocument3 pagesTrickjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Math Circle 1Document7 pagesMath Circle 1jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- RatioSlides Kansas 2012 09Document39 pagesRatioSlides Kansas 2012 09jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Kansas Teachers 2012 09Document100 pagesKansas Teachers 2012 09jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Sums of SquaresDocument3 pagesSums of Squaresjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Howe Place ValueDocument3 pagesHowe Place Valuejhicks_math100% (1)
- Learning Goal: Explore Strategies Teachers Can Use ToDocument10 pagesLearning Goal: Explore Strategies Teachers Can Use Tojhicks_mathNo ratings yet
Multiplication Algorithm Figure MTC
Multiplication Algorithm Figure MTC
Uploaded by
jhicks_mathOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multiplication Algorithm Figure MTC
Multiplication Algorithm Figure MTC
Uploaded by
jhicks_mathCopyright:
Available Formats
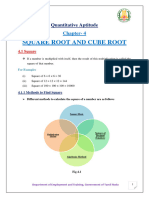
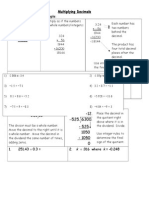
Written Methods for the Standard Multiplication Algorithm, 2-digit 2-digit Array/area drawing for 36 94 90 + 4 Area Method 1: 90 30 30 90 = 3 tens
ens 9 tens = 27 hundreds = 2700 6 90 = 6 9 tens 54 tens = 540 30 4 = 3 tens 4 = 12 tens = 120 30 + 6 2700 540 + 4 120 24 2700 540 120 24 1 3384
+ 6
Lattice Method 5: 6 4 = 24
tens
3 Th 1
ones
2 3 tens
36 94 = (30 + 6)(90 + 4) = 3090 + 304 + 690 + 64 Method 2: Showing the partial products Method 3: Recording the carries below for correct place value placement
3 H 5 4 2 4 6 ones
tens
ones
Method 4:
Traditional Method 6:
94 36 24 540 120 2700 1 3384
thinking: 64 6 9 tens 3 tens 4 3 tens 9 tens
94 36
52 2 1
1
94 36 564 3384
1 2 1
94 36 564 2820 3384
1
1 2
44
720
2820
3384
0 because we are multiplying by 3 tens in this row
Written Methods 2 and 3 are shown from right to left, but could go from left to right. In Methods 3 and 4, digits that represent newly composed tens and hundreds in the partial products are written below the line intead of above 94. This way, the 1 from 30 4 = 120 is placed correctly in the hundreds place, unlike in Traditional Method 6, where it is placed in the (incorrect) tens place. In Method 4, the 2 tens from 6 4 = 24 are added to the 4 tens from 6 90 = 540 and then crossed out so they will not be added again; the situation is similar for the 1 hundred from 30 4 = 120. In Method 3, all multiplying is done rst and then all adding. In Method 4 and Traditional Method 6, multiplying and adding alternate, which is more di cult for some students. Note that the 0 in the ones place of the second line of Methods 3, 4, and 6 is there because the whole line of digits is produced by multiplying by 30 (not 3).
You might also like
- Civil Service Examination - Math (Repaired)Document81 pagesCivil Service Examination - Math (Repaired)KIM RAGA100% (1)
- GAt Maths PDFDocument49 pagesGAt Maths PDFMushayyed Ali86% (21)
- Divisibility Rule: Divisibility Rules For Numbers 1-20Document16 pagesDivisibility Rule: Divisibility Rules For Numbers 1-20themathlover50% (2)
- GAt Maths PDFDocument49 pagesGAt Maths PDFAmmarahBatool95No ratings yet
- Square Root and Cube Root - 1st - ChapterDocument20 pagesSquare Root and Cube Root - 1st - ChapterWinston MosesNo ratings yet
- Multiplying Decimals ExampleDocument1 pageMultiplying Decimals Exampleapi-293308991No ratings yet
- Rational Numbers: Funda 1: De-ArrangementDocument8 pagesRational Numbers: Funda 1: De-Arrangementsinghalnitin1No ratings yet
- Vedic Maths: Multiply To Numbers Multiply 2 Numbers Close To 100,1000,10000, EtcDocument28 pagesVedic Maths: Multiply To Numbers Multiply 2 Numbers Close To 100,1000,10000, EtcGeorgettaPNo ratings yet
- Explanation in Some Items in Math.Document4 pagesExplanation in Some Items in Math.Garden Of PrayerNo ratings yet
- Grade 2: Parent Math Strategy GuideDocument2 pagesGrade 2: Parent Math Strategy Guideapi-300246618No ratings yet
- Number System 1 and 2 86Document23 pagesNumber System 1 and 2 86ParkingNo ratings yet
- Vedic Mathematics Worlds Fastest Mental Math SystemDocument31 pagesVedic Mathematics Worlds Fastest Mental Math SystemAbhishek Sharma100% (2)
- Impress Your Friends With Mental Math TricksDocument6 pagesImpress Your Friends With Mental Math Tricksray_xNo ratings yet
- HighSchool Math ProblemsDocument20 pagesHighSchool Math ProblemsEkaveera GouribhatlaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of EquationsDocument1 pageCompilation of EquationsChloe OberlinNo ratings yet
- 3 Grade Comprehensive CRCT Math Study Guide: Thousands OnesDocument31 pages3 Grade Comprehensive CRCT Math Study Guide: Thousands OnesTracy RemyNo ratings yet
- A Mother's Guide to Multiplication: For 7-11 Year OldsFrom EverandA Mother's Guide to Multiplication: For 7-11 Year OldsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vedic Mathematics and Calculation TechniquesDocument8 pagesVedic Mathematics and Calculation TechniquesGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Sharing: 16 Shared Equally Between 2 Gives You 8Document10 pagesSharing: 16 Shared Equally Between 2 Gives You 8ketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Magicsqaure 1Document5 pagesMagicsqaure 1api-360674086No ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument72 pagesPractice ProblemsGRE Dreamer KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsDocument89 pagesAnswer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsAnish Anand kumar100% (1)
- Math TricksDocument6 pagesMath TricksRoger nocomNo ratings yet
- Vedic Mathematics PresentationDocument31 pagesVedic Mathematics Presentationnd_lokesh100% (1)
- 2020 Chapter Competition SolutionsDocument11 pages2020 Chapter Competition SolutionsSup' Tan'No ratings yet
- Principles of Counting.: SolutionDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Counting.: SolutionERGUIZA, analizaNo ratings yet
- Calculation Year 5 3A 28 Calculation Year 5 PDFDocument6 pagesCalculation Year 5 3A 28 Calculation Year 5 PDFtizuliveNo ratings yet
- Level 4 Help PagesDocument14 pagesLevel 4 Help Pagesapi-235903058No ratings yet
- Vedic MathsDocument37 pagesVedic Mathsbarati_rao8747No ratings yet
- Problem Solving Strategies: STRATEGY #1: Use of PatternDocument13 pagesProblem Solving Strategies: STRATEGY #1: Use of PatternTherese Grace Postrero100% (1)
- X Which Gives A Remainder of 4 When Divided by 5, A Remainder of 7 WhenDocument5 pagesX Which Gives A Remainder of 4 When Divided by 5, A Remainder of 7 Whenmicro1234No ratings yet
- PEA 204 WorkbookDocument78 pagesPEA 204 WorkbookKhushi RanjanNo ratings yet
- WiproDocument20 pagesWiproMuthu ManiNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Parent BrochureDocument2 pagesGrade 3 Parent Brochureapi-305026398No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2BinomialTheoremiiDocument7 pagesWorksheet 2BinomialTheoremiitanmoy bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Kaplan 100math BasicsDocument4 pagesKaplan 100math Basicsapi-20011278No ratings yet
- Vedic Maths - TricksDocument41 pagesVedic Maths - Tricksvarun padhye100% (1)
- By Muralee.V. Whole NumbersDocument10 pagesBy Muralee.V. Whole NumbersMuralee VeeramalaiNo ratings yet
- Times TablesDocument29 pagesTimes Tableskamolpan@gmail.com67% (3)
- Math Solving LETDocument2 pagesMath Solving LETBRIANNo ratings yet
- Unit Study Guides - CRCT Study GuidesDocument4 pagesUnit Study Guides - CRCT Study Guidesapi-37741282No ratings yet
- CheckpointDocument8 pagesCheckpointp_kubebatu5565No ratings yet
- MATHINIKDocument6 pagesMATHINIKRTMunozNo ratings yet
- Class06 Math Grade10 Notes Oct 19-20Document11 pagesClass06 Math Grade10 Notes Oct 19-20mjysongNo ratings yet
- One Stop MBA - 2Document3 pagesOne Stop MBA - 2Quirking QuarkNo ratings yet
- The Number System and Mathematics LanguageDocument14 pagesThe Number System and Mathematics LanguagethabisoNo ratings yet
- Math Background: Concept Building ActivitiesDocument5 pagesMath Background: Concept Building Activitiesankita440No ratings yet
- Inclusion ExclusionDocument4 pagesInclusion ExclusionFantastiqueFessesNo ratings yet
- FALL WIN SEM (2023-24) STS1004 TH AP2023243000841 Reference Material II 07-Oct-2023 L12-Six Phrase-Squares and Square RootsDocument27 pagesFALL WIN SEM (2023-24) STS1004 TH AP2023243000841 Reference Material II 07-Oct-2023 L12-Six Phrase-Squares and Square RootsAkula MohansankerNo ratings yet
- Calcuation Policy 2013Document8 pagesCalcuation Policy 2013api-105903956No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Simple Equations NAME: - CLASS: VII SEC: - DATEDocument13 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore - East Mathematics Simple Equations NAME: - CLASS: VII SEC: - DATEHarishNo ratings yet
- Pry 6 Maths 3RD TermDocument41 pagesPry 6 Maths 3RD TermkuforijiifeoluwaNo ratings yet
- 1number SystemDocument24 pages1number SystemMamataMaharanaNo ratings yet
- Sonawane Academy: Jee-Main / AdvanceDocument5 pagesSonawane Academy: Jee-Main / AdvanceparamNo ratings yet
- Amigable (Math)Document4 pagesAmigable (Math)Alexren AmigableNo ratings yet
- Divisor 1 2: Divisibility Condition ExamplesDocument2 pagesDivisor 1 2: Divisibility Condition ExamplesAnkit ShettyNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation Word Problems2Document9 pagesLinear Equation Word Problems2sasyedaNo ratings yet
- Kindergarden Lesson StudyDocument20 pagesKindergarden Lesson Studyjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Mobius StripDocument1 pageMobius Stripjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Progressions in Area Models Would It Be Good To Connect:: CCSS - Math.Content.4.NBT.B.5Document1 pageProgressions in Area Models Would It Be Good To Connect:: CCSS - Math.Content.4.NBT.B.5jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Bundle and UnbundleDocument3 pagesBundle and Unbundlejhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document7 pagesDay 1jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Brownie Bits A3 Grade Lesson Study On The Distributive PropertyDocument10 pagesBrownie Bits A3 Grade Lesson Study On The Distributive Propertyjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Spirograph Activity PostDocument4 pagesSpirograph Activity Postjhicks_math100% (1)
- Lesson Study ProjectDocument13 pagesLesson Study Projectjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- FractionSlides Kansas 2012 09Document34 pagesFractionSlides Kansas 2012 09jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- TrickDocument3 pagesTrickjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Math Circle 1Document7 pagesMath Circle 1jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- RatioSlides Kansas 2012 09Document39 pagesRatioSlides Kansas 2012 09jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Kansas Teachers 2012 09Document100 pagesKansas Teachers 2012 09jhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Sums of SquaresDocument3 pagesSums of Squaresjhicks_mathNo ratings yet
- Howe Place ValueDocument3 pagesHowe Place Valuejhicks_math100% (1)
- Learning Goal: Explore Strategies Teachers Can Use ToDocument10 pagesLearning Goal: Explore Strategies Teachers Can Use Tojhicks_mathNo ratings yet