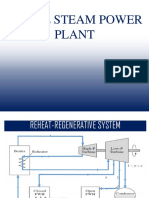
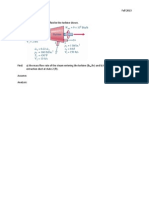
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement: Indian Standard
Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement: Indian Standard
Uploaded by
nagaraju3135Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement: Indian Standard
Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement: Indian Standard
Uploaded by
nagaraju3135Copyright:
Available Formats
IS : 4031 (Part 3) - 1988
(Reaffirmed 2000) Edition 2.1 (1993-03)
Indian Standard
METHODS OF PHYSICAL TESTS FOR HYDRAULIC CEMENT
PART 3 DETERMINATION OF SOUNDNESS
( First Revision )
(Incorporating Amendment No. 1)
UDC 666.94 : 620.17
BIS 2002
BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS
MANAK BHAVAN , 9 BAHADUR SHAH ZAFAR MARG NEW DELHI 110002
Price Group 2
IS : 4031 (Part 3) - 1988
Indian Standard
METHODS OF PHYSICAL TESTS FOR HYDRAULIC CEMENT
PART 3 DETERMINATION OF SOUNDNESS
( First Revision )
0. FOREWORD different equipment used for testing of cement, a brief description of which was also covered in the standard, had been published. In this revision, therefore, reference is given to different instrument specifications deleting the description of the instruments, as it has been recognized that reproducible and repeatable test results can be obtained only with standard testing equipment capable of giving desired level of accuracy. This part covers determination of soundness by Le-Chatelier method and autoclave test. 0.4 This edition 2.1 incorporates Amendment No. 1 (March 1993). Side bar indicates modification of the text as the result of incorporation of the amendment. 0.5 For the purpose of deciding whether a particular requirement of this standard is complied with, the final value, observed or calculated, expressing the result of a test or analysis, shall be rounded off in accordance with IS : 2-1960*. The number of significant places retained in the rounded off value should be the same as that of the specified value in this standard.
*Rules for rounding off numerical values ( revised ).
0.1 This Indian Standard (Part 3) (First Revision) was adopted by the Bureau of Indian Standards on 24 February 1988, after the draft finalized by the Cement and Concrete Sectional Committee had been approved by the Civil Engineering Division Council. 0.2 Standard methods of testing cement are essential adjunct to the cement specifications. This standard in different parts lays down the procedure for the tests to evaluate physical properties of different types of hydraulic cements. The procedure for conducting chemical tests of hydraulic cement is covered in IS : 4032-1985*. 0.3 Originally all the tests to evaluate the physical properties of hydraulic cements were covered in one standard but for facilitating the use of this standard and future revisions it has been decided to print the different tests as different parts of the standard and, accordingly this revised standard has been brought out in thirteen parts. This will also facilitate updating of individual tests. Further, since publication of the original standard in 1968, a number of standards covering the requirements of
*Method of chemical analysis of hydraulic cement ( first revision ).
1. SCOPE 1.1 This standard (Part 3) covers the procedures for determining the soundness of cement. 2. SAMPLING AND SELECTION OF TEST SPECIMEN 2.1 The samples of the cement shall be taken in accordance with the requirements of IS : 3535-1986* and the relevant standard specification for the type of cement being tested. The representative sample of the cement selected as above shall be thoroughly mixed before testing. 3. TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY 3.1 The temperature of the moulding room, dry materials and water shall be maintained at 27
*Methods revision ). of sampling hydraulic cements ( first
2C. The relative humidity of the laboratory shall be 65 5 percent. 3.2 The moist closet or moist room shall be maintained at 27 2C and at a relative humidity of not less than 90 percent. 4. GENERAL 4.1 Soundness of cement may be determined by two methods, namely Le-Chatelier method and autoclave method as described in 5 and 6. 5. LE-CHATELIER METHOD 5.1 Apparatus 5.1.1 The apparatus for conducting the LeChatelier test shall conform to IS : 5514-1969*.
*Specification for apparatus used in Le-Chatelier test.
IS : 4031 (Part 3) - 1988
5.1.2 Balance The balance shall conform to the following requirements: On balance in use, the permissible variation at a load of 1 000 g shall be plus or minus 1.0 g. The permissible variation on new balance shall be one-half of this value. The sensibility reciprocal shall be not greater than twice the permissible variation.
NOTE 1 The sensibility reciprocal is generally defined as the change in load required to change the position of rest of the indicating element or elements of a non-automatic indicating scale a definite amount at any load. NOTE 2 Self-indicating balance accuracy may also be used. with equivalent
mould gently together while this operation is being performed. Cover the mould with another piece of lightly oiled glass sheet, place a small weight on this covering glass sheet and immediately submerge the whole assembly in water at a temperature of 27 2C and keep there for 24 hours. 5.2.2 Measure the distance separating the indicator points to the nearest 0.5 mm. Submerge the mould again in water at the temperature prescribed above. Bring the water to boiling, with the mould kept submerged, in 25 to 30 minutes, and keep it boiling for three hours. Remove the mould from the water, allow it to cool and measure the distance between the indicator points. The difference between these two measurements indicates the expansion of the cement. 5.3 Calculation Calculate the mean of two values to the nearest 0.5 mm to represent the expansion of cement. 5.4 Retest In the event of cement failing to meet the test for soundness, a retest may be made after aeration. For this purpose, spread out the cement in a layer of 75 mm thickness and store it for 7 days in an atmosphere maintained at 27 2C and relative humidity of 50 to 80 percent. Retest this cement as described in 5.2. 6. AUTOCLAVE METHOD 6.1 Apparatus 6.1.1 Balance Same as 5.1.2. 6.1.2 Weights Same as 5.1.3. 6.1.3 Graduated Glass Cylinders Graduated glass cylinders of 150 ml capacity shall be used. The permissible variation on these cylinders shall be plus or minus one millilitre. The main graduation lines of the cylinders shall be in circles and shall be numbered. The least graduations shall extend at least one-seventh of the way around, and intermediate graduations shall extend at least one-fifth of the way around the cylinder. The graduation lines may be omitted for the lowest 5 ml. 6.1.4 Moulds Moulds of 25 25 mm size and 282 mm internal length and other accessories conforming to IS : 10086-1982*. 6.1.5 Autoclave The autoclave shall consist of a high pressure steam boiler equipped with suitable safety device. The capacity of heating unit shall be such that with maximum load (water plus specimens) the pressure of the saturated steam in the autoclave may be raised
*Specification for moulds for use in tests of cement and concrete.
5.1.3 Weights The permissible variations on weights in use in weighing the cement shall be as prescribed in Table 1.
TABLE 1 PERMISSIBLE VARIATIONS ON WEIGHTS PERMISSIBLE VARIATION ON WEIGHTS IN USE, P LUS OR MINUS g (2) 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01
WEIGHT
g (1) 500 300 250 200 100 50 20 10 5 2 1
5.1.4 Water Bath Water bath with means of heating, capable of containing immersed Le-Chatelier moulds with specimens and of raising their temperature from 27 2C to boiling in 27 3 minutes. 5.2 Procedure 5.2.1 Place the lightly oiled mould on a lightly oiled glass sheet and fill it with cement paste formed by gauging cement with 0.78 times the water required to give a paste of standard consistency [ see IS : 4031 (Part 4)-1988* ]. The paste shall be gauged in the manner and under the conditions prescribed in IS : 4031 (Part 4)1988*, taking care to keep the edges of the
*Methods of physical tests for hydrualic cement: Part 4 Determination of consistency of standard cement paste ( first revision ).
IS : 4031 (Part 3) - 1988
to a gauge pressure of 2.1 MPa or to an absolute pressure of about 2.2 MPa, in 1 to 1 hour from the time the heat is turned on. The automatic pressure control shall be capable of maintaining the pressure at 2.1 0.1 MPa corresponding to a temperature of 215.7 1.7C. The autoclave shall be designed to permit the pressure to drop from 2.1 MPa to less than 0.07 MPa in one hour after the heat supply has been shut off. It shall be equipped with a vent valve for allowing the escape of air during the early part of the heating period and for releasing any steam pressure remaining at the end of the one-hour cooling period. The pressure gauge shall have a nominal dial diameter of 115 mm and shall be graduated from 0 to 4.1 MPa with scale division of not more than 0.04 MPa. The error in the gauge shall not exceed plus or minus 0.02 MPa at the operating pressure of 2.1 MPa. 6.1.6 Length Comparator Changes in length of the test specimen shall be measured by an apparatus conforming to IS : 9459-1980*. 6.2 Preparation of Test Specimens 6.2.1 Preparation of Moulds The moulds shall be thinly covered with mineral oil. After this operation, the stainless steel or non-corroding metal reference inserts with knurl heads shall be set to obtain an effective gauge length of 250 mm, care being taken to keep them clean and free from oil. 6.2.2 Mixing Cement Paste The standard batch of cement paste shall consist of 500 g of cement, mixed with sufficient water to give a paste of standard consistency. Specimens Immediately 6.2.3 Moulding following the completion of mixing, the test specimens shall be moulded in one or two layers, each layer being compacted with the thumb or forefinger by pressing the paste into the corners, around the reference inserts, and along the surfaces of the moulds until a homogeneous specimen is obtained. After the top layer has been compacted, the paste shall be cut off flush with the top of the mould and the surface smoothed with a few strokes of the trowel. During the operations of mixing and moulding, the hand shall be protected by rubber gloves. 6.2.4 Storage of Test Specimen After the mould has been filled, it shall be immediately placed in a moist closet or a moist room. Specimens shall remain in the moulds in the moist room for at least 24 h. If removed from the moulds before 24 h, they shall be kept in the moist closet or moist room until tested.
*Specification for apparatus for use in measurement of length change of hardened cement paste, mortar and concrete.
6.3 Procedure 6.3.1 At 24 h after moulding, the specimens shall be removed from the moist atmosphere, measured for length, and placed in the autoclave at room temperature in a rack so that the four sides of each specimen shall be exposed to saturated steam. The autoclave shall contain enough water to maintain an atmosphere of saturated steam vapour during the entire period of test. Ordinarily, 7 to 10 percent of the volume of the autoclave shall be occupied by water. 6.3.2 To permit air to escape from the autoclave during the early portion of the heating period, the vent valve shall be left open until steam begins to escape ( see 6.4 ). The valve shall then be closed and the temperature of the autoclave shall be raised at such a rate as will bring the gauge pressure of the steam to 2.1 MPa in 1 to 1 h from the time the heat is turned on. The 2.1 0.1 MPa pressure shall be maintained for 3 h. At the end of 3 hours period, the heat supply shall be shut off and the autoclave cooled at a rate such that the pressure will be less than 0.1 MPa at the end of the hour, and any pressure remaining shall be slow released by partially opening the vent valve until atmospheric pressure is attained. The autoclave shall then be opened and the test specimens immediately placed in water, the temperature of which is above 90C. The water surrounding the bars shall then be cooled at a uniform rate by adding cold water so that the temperature of the water shall be lowered to 27 2C in 15 min. The water surrounding the specimens shall then be maintained at 27 2C in 15 min when the specimens shall be surface-dried and their lengths measured again. 6.4 Safety Precautions 6.4.1 The pressure gauge should have a maximum capacity of 4.2 MPa. This is important because with too small a capacity there is but a little length of arc in which the gauge hand may indicate pressure above the specified maximum working pressure. The operator must be sure that the gauge hand has not passed the maximum graduation on the scale. 6.4.2 It is well to leave the pressure gauge tested, but in any event thermometer shall always be used together with the pressure gauge, so as to provide a means of detecting any failure of the pressure gauge to operate properly and also to indicate any unusual conditions such as that resulting from loss of water from the autoclave during the test. 6.4.3 The automatic control shall be maintained in proper working order at all times. 3
IS : 4031 (Part 3) - 1988
6.4.4 The safety valve shall be set so as to relieve the pressure at about 6 to 10 percent above the maximum of 2.1 MPa specified, that is at about 2.3 MPa. The safety valve shall be tested at least twice a year, either with a gauge-testing device or by adjusting the automatic controls so as to allow the autoclave to reach a pressure of about 2.3 MPa at which pressure the safety valve shall either open or be adjusted to open. The safety valve discharge shall be directed away from the operator.
NOTE Unexpected combinations of conditions may really occur. For example, in one case the automatic control had failed, the safety valve had stuck, and the gauge hand, which at first glance appeared to be at about zero, had really passed the maximum graduation and had come to stop on the wrong side of the pin. This condition of the gauge was finally detected and the pressure, then of an unknown magnitude, was released before failure could occur in the apparatus.
6.4.6 It shall be remembered that for many of the autoclave pressure gauges now in use, the return of the gauge hand to the initial rest or starting point does not necessarily indicate zero pressure within the autoclave; there may then still remain an appreciable pressure. 6.4.7 A few drops of kerosene placed in the vent valve about once a week will aid in keeping the needle clean and in good-working condition. 6.5 Calculations The difference in lengths of the test specimen before and after autoclaving shall be calculated to the nearest 0.01 percent of the effective gauge length which is the length between the innermost points of the metal inserts used as reference points and shall be reported as the autoclave expansion of the cement. A contraction (negative expansion) shall be indicated by prefixing a minus sign to the percentage expansion reported. 6.6 Retests In the event of cement failing to meet the test for soundness, a retest may be made after aeration. For this purpose, spread out the sample in a layer of 75 mm thickness and store it for 7 days in an atmosphere maintained at 27 2C and relative humidity of 50 to 80 percent. Retest this cement as described in 6.2 and 6.3.
6.4.5 Heavy leather work gloves shall be worn to prevent burning of the hands when removing the top of the autoclave at the end of the test. The vent valve shall be directed away from the operator. When removing the autoclave lid, the lid shall be so tilted that any steam escaping from beneath the lid may be discharged away from the operator. Care shall be taken to avoid scalding by any liquid that may have been used in the autoclave well.
Bureau of Indian Standards BIS is a statutory institution established under the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986 to promote harmonious development of the activities of standardization, marking and quality certification of goods and attending to connected matters in the country. Copyright BIS has the copyright of all its publications. No part of these publications may be reproduced in any form without the prior permission in writing of BIS. This does not preclude the free use, in the course of implementing the standard, of necessary details, such as symbols and sizes, type or grade designations. Enquiries relating to copyright be addressed to the Director (Publications), BIS. Review of Indian Standards Amendments are issued to standards as the need arises on the basis of comments. Standards are also reviewed periodically; a standard along with amendments is reaffirmed when such review indicates that no changes are needed; if the review indicates that changes are needed, it is taken up for revision. Users of Indian Standards should ascertain that they are in possession of the latest amendments or edition by referring to the latest issue of BIS Catalogue and Standards : Monthly Additions. This Indian Standard has been developed by Technical Committee : CED 2 Amendments Issued Since Publication Amend No. Amd. No. 1 Date of Issue March 1993
BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS
Headquarters: Manak Bhavan, 9 Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg, New Delhi 110002. Telephones: 323 01 31, 323 33 75, 323 94 02 Regional Offices: Central Eastern : Manak Bhavan, 9 Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg NEW DELHI 110002 : 1/14 C. I. T. Scheme VII M, V. I. P. Road, Kankurgachi KOLKATA 700054
Telegrams: Manaksanstha (Common to all offices) Telephone
323 76 17 323 38 41
337 84 99, 337 85 61 337 86 26, 337 91 20
60 60
Northern : SCO 335-336, Sector 34-A, CHANDIGARH 160022 Southern : C. I. T. Campus, IV Cross Road, CHENNAI 600113 Western : Manakalaya, E9 MIDC, Marol, Andheri (East) MUMBAI 400093
38 43 20 25
235 02 16, 235 04 42 235 15 19, 235 23 15 832 92 95, 832 78 58 832 78 91, 832 78 92
Branches : A H M E D A B A D . B A N G A L O R E . B H O P A L . B H U B A N E S H W A R . C O I M B A T O R E . FARIDABAD. GHAZIABAD. GUWAHATI. HYDERABAD. JAIPUR. KANPUR. LUCKNOW. NAGPUR. NALAGARH. PATNA. PUNE. RAJKOT. THIRUVANANTHAPURAM. VISHAKHAPATNAM.
You might also like
- Solution Koretsky Completo PDFDocument738 pagesSolution Koretsky Completo PDFBruna P100% (3)
- ASTM D 2041-03a Standard Test Method For Theoretical Max Specific Gravity & Density of Bituminous Paving MixturesDocument4 pagesASTM D 2041-03a Standard Test Method For Theoretical Max Specific Gravity & Density of Bituminous Paving MixturesILSEN N. DAETNo ratings yet
- Solution Chapter 4 (Rayner Joel)Document22 pagesSolution Chapter 4 (Rayner Joel)Shenelle100% (2)
- IS 516 Part 2 Section 4Document12 pagesIS 516 Part 2 Section 4Maulik PanseriyaNo ratings yet
- Mix Design Using RAP 30Document4 pagesMix Design Using RAP 30Raghav100% (2)
- 4031 - 4 Part 4 Determination of Consistency of Standard Cement PasteDocument3 pages4031 - 4 Part 4 Determination of Consistency of Standard Cement Pastevelmurug_balaNo ratings yet
- Precast Concrete Kerbs, Channels, Edging, Quadrants and Other Associated Fittings - SpecificationDocument22 pagesPrecast Concrete Kerbs, Channels, Edging, Quadrants and Other Associated Fittings - SpecificationChandra Sekhar Babu GanjiNo ratings yet
- Is1205-2022-Softening Point BitumenDocument10 pagesIs1205-2022-Softening Point BitumenbaubleNo ratings yet
- Rap GSB and WMM PDFDocument4 pagesRap GSB and WMM PDFvenkateswara rao PothinaNo ratings yet
- 2386 (Part-II) - 1963 PDFDocument18 pages2386 (Part-II) - 1963 PDFSoundar Pachiappan100% (1)
- PW .KR B Èku JK (K&Lhesav B V Fof'Kf"V: HKKJRH EkudDocument11 pagesPW .KR B Èku JK (K&Lhesav B V Fof'Kf"V: HKKJRH EkudANMSNo ratings yet
- Is 14858 2000 Compression Testing Machine Used For Testing of Concrete and Mortar RequirementsDocument9 pagesIs 14858 2000 Compression Testing Machine Used For Testing of Concrete and Mortar RequirementsVanu VamalaiNo ratings yet
- Is 3117Document17 pagesIs 3117Amit Prasad100% (1)
- WMM Plant CalibrationDocument13 pagesWMM Plant CalibrationDeepakNo ratings yet
- 2021 Annex C &DDocument24 pages2021 Annex C &DSaurav Kumar100% (1)
- Is 15388 (2003) - Specification For Silica FumeDocument13 pagesIs 15388 (2003) - Specification For Silica FumeN GANESAMOORTHYNo ratings yet
- Rubber Content of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen: Soxhlet MethodDocument8 pagesRubber Content of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen: Soxhlet MethodLa FoliakNo ratings yet
- IS-1121 Part-1 Compressive StrengthDocument8 pagesIS-1121 Part-1 Compressive StrengthSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Vbe Calculation Washington State DOT SOP732Document18 pagesVbe Calculation Washington State DOT SOP732DigantNo ratings yet
- Methods For Testing Tar and Bituminous Materials - Determination of PenetrationDocument10 pagesMethods For Testing Tar and Bituminous Materials - Determination of PenetrationDevesh Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2017Document12 pages2017ਸੁਖਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਮਾਂਗਟNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 1 November 2012 TO Is 1786: 2008 High Strength Deformed Bars and Wires For Concrete Reinforcement - SpecificationDocument4 pagesAmendment No. 1 November 2012 TO Is 1786: 2008 High Strength Deformed Bars and Wires For Concrete Reinforcement - SpecificationThetarun100% (1)
- Is 1542 1992Document8 pagesIs 1542 1992kc_nk100% (1)
- Soil - Direct Shear Test (Is 2720 - P 13, 1986, Reaff.2011)Document10 pagesSoil - Direct Shear Test (Is 2720 - P 13, 1986, Reaff.2011)siddhi jadhav0% (1)
- Is: 383-2016Document21 pagesIs: 383-2016yurendraNo ratings yet
- As 2341.4-1994 Methods of Testing Bitumen and Related Roadmaking Products Determination of Dynamic ViscosityDocument2 pagesAs 2341.4-1994 Methods of Testing Bitumen and Related Roadmaking Products Determination of Dynamic ViscositySAI Global - APAC0% (1)
- Calibration of Rapid Moisture Meter (RMM)Document6 pagesCalibration of Rapid Moisture Meter (RMM)Kumar SachinNo ratings yet
- Designed Concrete MixDocument6 pagesDesigned Concrete MixniceseshaNo ratings yet
- MBIU Report Gorakhpur BypassDocument167 pagesMBIU Report Gorakhpur BypassRaghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Is:2386 1Document22 pagesIs:2386 1Ramesh0% (1)
- Paving Bitumen - Specification: Indian StandardDocument2 pagesPaving Bitumen - Specification: Indian StandardDevela Avinash100% (1)
- Is 1786 A2Document1 pageIs 1786 A2sivaramNo ratings yet
- (Kmatk Mkyus Osq Fy, Mkej Fof'Kf"V: HKKJRH EkudDocument6 pages(Kmatk Mkyus Osq Fy, Mkej Fof'Kf"V: HKKJRH Ekudvinayaka.vrNo ratings yet
- IS STD - IS 16714 - 2018 - GGBSDocument11 pagesIS STD - IS 16714 - 2018 - GGBSSoumyakanti S. Samanta (Pgdm 09-11, Batch II)50% (2)
- M20 Kerb - Mix Design Calculation: Volume of Cementicious Materials+Water+AdmixtureDocument1 pageM20 Kerb - Mix Design Calculation: Volume of Cementicious Materials+Water+Admixturevdbshamsabad labNo ratings yet
- IS 16014 - 2012 GabionDocument13 pagesIS 16014 - 2012 GabionOM BIHARI SINGHNo ratings yet
- IS 2185 (Part 1) 1979Document27 pagesIS 2185 (Part 1) 1979manishparetaNo ratings yet
- IS-2720 (Part 4) :1985 (Reaffirmed-May 2015) "Methods of Test For Soils: Grain Size Analysis". Grain Size Analysis by Wet and Dry Sieve AnalysisDocument1 pageIS-2720 (Part 4) :1985 (Reaffirmed-May 2015) "Methods of Test For Soils: Grain Size Analysis". Grain Size Analysis by Wet and Dry Sieve Analysisindrasab100% (1)
- Eiffic/Efuf (T:, RFRDT (FrrtfuDocument17 pagesEiffic/Efuf (T:, RFRDT (FrrtfuRamasubba RajuNo ratings yet
- Procedure of Redosing of Admixture at Site (IS:4926-2000)Document1 pageProcedure of Redosing of Admixture at Site (IS:4926-2000)Mahendra BabreNo ratings yet
- BS 1881-116-1983 - Testing Concrete Part 116 - Method For Determination of Compressive Strength of Concrete CubesDocument10 pagesBS 1881-116-1983 - Testing Concrete Part 116 - Method For Determination of Compressive Strength of Concrete CubesSarifNo ratings yet
- Appendix - 1800 - III (Sfgop-Tcipc)Document8 pagesAppendix - 1800 - III (Sfgop-Tcipc)kvijayasok100% (1)
- 3495 1Document8 pages3495 1Suraj Vishwakarma67% (3)
- BS 873-4 - 1987 Road Traffic Signs and Internally Illuminated Bollards Specification For Road StudsDocument18 pagesBS 873-4 - 1987 Road Traffic Signs and Internally Illuminated Bollards Specification For Road Studspaul reyesNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Impact Value (Is: 2386 (Part-Iv) )Document19 pagesAggregate Impact Value (Is: 2386 (Part-Iv) )ajit karandikarNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity of Filler: Determination Trial No AverageDocument1 pageSpecific Gravity of Filler: Determination Trial No AveragePrasanna S KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Job Mix Formula For Cement Treated Sub Base: (IRC SP 89-2010)Document1 pageJob Mix Formula For Cement Treated Sub Base: (IRC SP 89-2010)Dwijendra Chanumolu100% (2)
- ASTM D2940 Agregates For Base CourseDocument1 pageASTM D2940 Agregates For Base Courseتوفيق عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Soil FrecuncyDocument4 pagesSoil FrecuncyAnuj yadav100% (1)
- HKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH EkudDocument16 pagesHKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH Ekud HKKJRH EkudRajesh GangwalNo ratings yet
- N' +HÑR Oaqøhv Ijh (K.K I FR K¡: HKKJRH EkudDocument20 pagesN' +HÑR Oaqøhv Ijh (K.K I FR K¡: HKKJRH Ekudjitendra100% (2)
- Aashto T 283 - TSRDocument9 pagesAashto T 283 - TSRanant11235No ratings yet
- Is 383 2016Document22 pagesIs 383 2016Meena MurmuNo ratings yet
- Texture Depth Measurement: National Highways Authority of IndiaDocument1 pageTexture Depth Measurement: National Highways Authority of IndiaQuality JamNo ratings yet
- Is 4031-3 (1988) - Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement, Part 3 - Determination of SoundnessDocument4 pagesIs 4031-3 (1988) - Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement, Part 3 - Determination of SoundnessApurv PatelNo ratings yet
- IS 4031 - Part4Document3 pagesIS 4031 - Part4SohanNo ratings yet
- Methodsofphysicaltestsfor Hydrauliccement: Indian StandardDocument3 pagesMethodsofphysicaltestsfor Hydrauliccement: Indian StandardUppala Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement: Indian StandardDocument5 pagesMethods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement: Indian StandardIndira BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- IS 4031 - Part5Document4 pagesIS 4031 - Part5Sudhakaran PilicodeNo ratings yet
- Is 4031-4 (1988) - Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement, Part 4 - Determination of Consistency of Standard Cement PasteDocument2 pagesIs 4031-4 (1988) - Methods of Physical Tests For Hydraulic Cement, Part 4 - Determination of Consistency of Standard Cement PasteApurv PatelNo ratings yet
- Methodsofphysicaltestsfor Hydrauliccement: Indian StandardDocument3 pagesMethodsofphysicaltestsfor Hydrauliccement: Indian StandardUppala Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Methodsofphysicaltestsfor Hydrauliccement: Indian StandardDocument5 pagesMethodsofphysicaltestsfor Hydrauliccement: Indian StandardUppala Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Is 6452 High Alumina Cement For Structural Use-SpecificationDocument10 pagesIs 6452 High Alumina Cement For Structural Use-SpecificationRamarraju KalidindiNo ratings yet
- 8112Document17 pages8112rambinodNo ratings yet
- Is 4031 (Part-13) Method of Physical Tests For Hydraulic CemDocument3 pagesIs 4031 (Part-13) Method of Physical Tests For Hydraulic CemRamarraju KalidindiNo ratings yet
- IS 4031 - Part12Document3 pagesIS 4031 - Part12Nagaraju ChintaNo ratings yet
- Is 1489 (Part-2) Portland-Pozzolana Cement Specification (CADocument15 pagesIs 1489 (Part-2) Portland-Pozzolana Cement Specification (CARamarraju KalidindiNo ratings yet
- Is 4031 (Part-1) Method of Physical Tests For Hydraulic CemeDocument7 pagesIs 4031 (Part-1) Method of Physical Tests For Hydraulic CemeRamarraju KalidindiNo ratings yet
- Is 1727 Method of Test For Pozzolanic Material E21 R1.180180834Document51 pagesIs 1727 Method of Test For Pozzolanic Material E21 R1.180180834Hazem DiabNo ratings yet
- Is 1489 (Part-1) Portland-Pozzolana Cement Specification (FLDocument14 pagesIs 1489 (Part-1) Portland-Pozzolana Cement Specification (FLRamarraju Kalidindi80% (15)
- Is 12089 Specification For Granulated Slag For The ManufactuDocument11 pagesIs 12089 Specification For Granulated Slag For The ManufactuRamarraju Kalidindi100% (5)
- BIS 455 - Portland Slag Cement SpecificationDocument14 pagesBIS 455 - Portland Slag Cement Specificationvikramgoenka100% (1)
- Scada Systems For Industry 4.0 in RefrigerationDocument17 pagesScada Systems For Industry 4.0 in RefrigerationAnand PavithranNo ratings yet
- Safety Valves FK 46.72 (10) GB: Primary CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesSafety Valves FK 46.72 (10) GB: Primary CharacteristicsNguyen KhaNo ratings yet
- Vortex Flow Meters: Kaifeng AFT Instrument Co.,LtdDocument22 pagesVortex Flow Meters: Kaifeng AFT Instrument Co.,LtdgcortelliNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Properties of SteamDocument42 pagesUnit 8: Properties of Steamscha_shaaNo ratings yet
- Assignment L01 (Friday, 9.30) Marking SchemeDocument14 pagesAssignment L01 (Friday, 9.30) Marking SchemeMawareNo ratings yet
- PROJECT DushyanthDocument85 pagesPROJECT DushyanthHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Trampas de VaporDocument8 pagesTrampas de VaporAlberto HernandezNo ratings yet
- RefrigeratorDocument6 pagesRefrigeratorChooi San LaiNo ratings yet
- HW 7 SolutionsDocument9 pagesHW 7 SolutionsDamien SolerNo ratings yet
- Appendix (Steam Tabel,.Etc)Document43 pagesAppendix (Steam Tabel,.Etc)Akun RPNo ratings yet
- Endress-Hauser Proline Prowirl F 200 7F2CDocument13 pagesEndress-Hauser Proline Prowirl F 200 7F2CDorin SerbanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Notes 18ME81Document31 pagesModule 3 Notes 18ME81thrilok SuryaNo ratings yet
- 1-CHA 3-PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES LECTURE Revision PDFDocument33 pages1-CHA 3-PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES LECTURE Revision PDFWilliam SalazarNo ratings yet
- HTTP WWW - Spiraxsarco.com Resources Steam-Engineering-tutorials Control-Applications Pressure-Contr NewDocument15 pagesHTTP WWW - Spiraxsarco.com Resources Steam-Engineering-tutorials Control-Applications Pressure-Contr NewPalash KayathwalNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 - July 2022Document8 pagesPaper 2 - July 2022Ravi ShankarNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument8 pagesBoilersKarthiKeyanNo ratings yet
- 11 Mercury Steam Binary VCDocument3 pages11 Mercury Steam Binary VCSekhar Babu PendyalaNo ratings yet
- No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No YesDocument8 pagesNo Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No YesEkundayo JohnNo ratings yet
- Performance Testing Asme 4.1Document42 pagesPerformance Testing Asme 4.1EnzoNo ratings yet
- 17-Superheated Water ExtractionDocument43 pages17-Superheated Water ExtractionJayanath Nuwan SameeraNo ratings yet
- Ts-3 Effects of Drying Methods and Conditions On Drying Kinetics and Quality of Indian Gooseberry Flake - ThesisDocument96 pagesTs-3 Effects of Drying Methods and Conditions On Drying Kinetics and Quality of Indian Gooseberry Flake - ThesisHarpal SethiNo ratings yet
- Etd 2mark With AnswerDocument16 pagesEtd 2mark With AnswerERKATHIR100% (1)
- Steam Table ASMEDocument32 pagesSteam Table ASMEMeisy RadhistaNo ratings yet
- AAB2000C1Document11 pagesAAB2000C1marcos morillo0% (1)
- Homework BDocument28 pagesHomework BPravallika Kollipara0% (2)
- Evaporation CrystallizationDocument53 pagesEvaporation CrystallizationFren R.0% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Mcqs Part 2: Nts ResultsDocument20 pagesMechanical Engineering Mcqs Part 2: Nts Resultsfake7083No ratings yet
- Model Question Bank Energy Certification For Managers and AuditorsDocument312 pagesModel Question Bank Energy Certification For Managers and AuditorsVanyaChauhan100% (2)