Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Area of A Surface Is The Size of The Surface. 2. (A) The Following Diagrams Show Two Different Shapes, I.E. A Square and A Rectangle
The Area of A Surface Is The Size of The Surface. 2. (A) The Following Diagrams Show Two Different Shapes, I.E. A Square and A Rectangle
Uploaded by
fakhrulfathiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grade 8 Area, Perimeter and Metric System TestDocument6 pagesGrade 8 Area, Perimeter and Metric System TestSheila Putri Syarah100% (1)
- Area of Shaded RegionDocument8 pagesArea of Shaded Regionwakarnasirkhan100% (1)
- Surface Area and Volume FormulasDocument7 pagesSurface Area and Volume FormulasshruthimNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark Type (Surface Area & Volumes)Document19 pages1 Mark Type (Surface Area & Volumes)radhavenkateshwaranNo ratings yet
- Gmail - INTERNAL ASSESSMENT)Document12 pagesGmail - INTERNAL ASSESSMENT)SengutuvanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Surface Areas and VolumesDocument4 pagesAssignment - Surface Areas and VolumeslwhmrvavrodrljeuwoNo ratings yet
- Maths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringDocument3 pagesMaths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringCape Town After-School TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - WS-11 - Ch. 9 Perimeter and AreaDocument3 pagesClass 7 - WS-11 - Ch. 9 Perimeter and Areajanvi mehtaNo ratings yet
- FilesDocument16 pagesFilespuramganeshNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Practice Paper 11Document4 pagesMaths Class X Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Practice Paper 11hxizisoz6No ratings yet
- Olympiad Questions Apr 2ndd WeekDocument2 pagesOlympiad Questions Apr 2ndd Weekphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument2 pagesMensurationAnkit RajaniNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - Perimeter and AreaDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - Perimeter and AreaNeel BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Sa SB SC S Abc S S S Ssasbsc: Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ)Document3 pagesSa SB SC S Abc S S S Ssasbsc: Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ)Ranjit KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetDocument3 pagesCH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetRuzal AnandNo ratings yet
- STD 8 Chap9 WsDocument3 pagesSTD 8 Chap9 Wsheersurti312No ratings yet
- Surface Area of SolidsDocument10 pagesSurface Area of SolidsomarNo ratings yet
- MENSURATIONDocument17 pagesMENSURATIONJayasuryaNo ratings yet
- Ows SSC MensurationDocument49 pagesOws SSC Mensurationlaw conquerorNo ratings yet
- Area, Perimeter 2Document6 pagesArea, Perimeter 2Zonish BakshNo ratings yet
- How Many Squares Grade 5Document4 pagesHow Many Squares Grade 5Greeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mensuration BasicsDocument9 pagesMensuration BasicsKimberly ArnoldNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document44 pagesCH 08Vincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument28 pagesMensurationrushabhNo ratings yet
- 11 AreaDocument4 pages11 AreaMohanlal PereraNo ratings yet
- 20TDY-661 - Mensuration - 2DDocument32 pages20TDY-661 - Mensuration - 2DAbhipriya MishraNo ratings yet
- CGVBHJNKDocument3 pagesCGVBHJNKAGNo ratings yet
- Similar Solids WorksheetDocument2 pagesSimilar Solids WorksheetEamon BarkhordarianNo ratings yet
- VolumesDocument7 pagesVolumesSushobhan SanyalNo ratings yet
- 09 Mensuration of Solid FiguresDocument14 pages09 Mensuration of Solid FiguresSalman ShakilNo ratings yet
- Class 9 (Heron's Formulae)Document2 pagesClass 9 (Heron's Formulae)alvina dhalaitNo ratings yet
- Quant Mock Test - 09 (Mensuration)Document4 pagesQuant Mock Test - 09 (Mensuration)rxsgrdpNo ratings yet
- AL Brothers Prakashan: 13. Surface Areas and Volumes Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term 2)Document16 pagesAL Brothers Prakashan: 13. Surface Areas and Volumes Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term 2)sshoeburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Mensuration: (Aptitude & Reasoning)Document23 pagesMensuration: (Aptitude & Reasoning)roshan rajNo ratings yet
- Gr9 Revision Worksheet Heron's FormulaDocument1 pageGr9 Revision Worksheet Heron's FormulaManiBal EducationNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Practice Test 11 Chapter 10 MensurationDocument2 pagesMaths Class VIII Practice Test 11 Chapter 10 MensurationRahul PawarNo ratings yet
- Measuration Part IIDocument22 pagesMeasuration Part IIChris GanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Class 6Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Class 6AnimeshNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Classwork - Student-1Document4 pagesMensuration Classwork - Student-1Priyanka KengarNo ratings yet
- New QuestionsDocument5 pagesNew QuestionsRajneesh SinghNo ratings yet
- MENSURATIONDocument30 pagesMENSURATIONManas YeldhurthiNo ratings yet
- P. The Radius of The Smaller Circle Is 2 M, The Radius of The Larger Circle Is 6 M and QPRDocument3 pagesP. The Radius of The Smaller Circle Is 2 M, The Radius of The Larger Circle Is 6 M and QPRTahmid RaihanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-5 Perimeter Class 4Document2 pagesWorksheet-5 Perimeter Class 4Prabhu VelNo ratings yet
- SA and Volume - MCQDocument3 pagesSA and Volume - MCQpmagrawal100% (1)
- Geometry F Area Perimeter v3Document19 pagesGeometry F Area Perimeter v3coffee080403No ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Chapter 12 and 13 Mensuration Unit Practice Paper 18Document3 pagesMaths Class Ix Chapter 12 and 13 Mensuration Unit Practice Paper 18devildudeishereNo ratings yet
- Foster&TomlinsonBK1CH16 PlaneShapes2Document10 pagesFoster&TomlinsonBK1CH16 PlaneShapes2shiva ramlalNo ratings yet
- (Jan01/Q8/M3) : DC 15 CM and BC 10 Cm. Given ThatDocument5 pages(Jan01/Q8/M3) : DC 15 CM and BC 10 Cm. Given ThatTahmid Raihan100% (1)
- Revision SheetDocument10 pagesRevision Sheethudaalhabibi786No ratings yet
- Mensuration 8th CorrectionsDocument30 pagesMensuration 8th CorrectionsnittypiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & AreaDocument124 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & Areaat2lk22No ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume WorksheetDocument3 pagesSurface Area and Volume WorksheetLavan Nims100% (1)
- IGCSE Class 10 Test - MensurationDocument2 pagesIGCSE Class 10 Test - Mensurationpapia.bera1994No ratings yet
- Quadrilateral Worksheet 1Document7 pagesQuadrilateral Worksheet 1Tisa Aini AbasNo ratings yet
- AreaDocument9 pagesAreaSushobhan SanyalNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Mensuration 1.: ABCDE Is A PyramidDocument4 pagesAssignment - Mensuration 1.: ABCDE Is A Pyramid567gjNo ratings yet
- Cube & Rectangular Solid ProblemsDocument6 pagesCube & Rectangular Solid ProblemsSatPrepVungTauNo ratings yet
- 10 M Surf Ar N VolumesDocument3 pages10 M Surf Ar N VolumesJaison D'CostaNo ratings yet
- Doc-20231204-Wa0006 231206 001654Document6 pagesDoc-20231204-Wa0006 231206 001654schoolclass677No ratings yet
- Mindful Maths 2: Use Your Geometry to Solve These Puzzling PicturesFrom EverandMindful Maths 2: Use Your Geometry to Solve These Puzzling PicturesNo ratings yet
- Skema Permarkahan ScienceDocument7 pagesSkema Permarkahan SciencefakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- JohorDocument14 pagesJohorfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
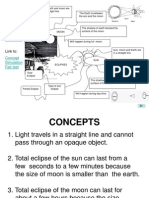
- Phases of The MoonDocument1 pagePhases of The MoonfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Animal WeatherDocument18 pagesAnimal WeatherfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- SpeedDocument4 pagesSpeedfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: . SCHOOLDocument3 pagesName: Class: . SCHOOLfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Friction: Effect Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument7 pagesFriction: Effect Advantages and DisadvantagesfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Link To:: Concept Simulation Fair TestDocument3 pagesLink To:: Concept Simulation Fair TestfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Life ProcosesDocument1 pageLife ProcosesfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Life CycleDocument3 pagesLife CyclefakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- All Objects That Humans Use Are Made of Either Natural or Man-Made MaterialsDocument7 pagesAll Objects That Humans Use Are Made of Either Natural or Man-Made MaterialsfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Animal EcreteDocument4 pagesAnimal EcretefakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
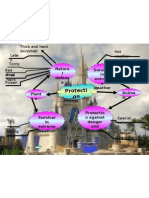
- Life ProtectionDocument1 pageLife ProtectionfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- LenghtDocument16 pagesLenghtfakhrulfathi100% (1)
- TknologiDocument32 pagesTknologifakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Start Sy4Document1 pageStart Sy4fakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Basic NeedsDocument1 pageBasic NeedsfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
The Area of A Surface Is The Size of The Surface. 2. (A) The Following Diagrams Show Two Different Shapes, I.E. A Square and A Rectangle
The Area of A Surface Is The Size of The Surface. 2. (A) The Following Diagrams Show Two Different Shapes, I.E. A Square and A Rectangle
Uploaded by
fakhrulfathiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Area of A Surface Is The Size of The Surface. 2. (A) The Following Diagrams Show Two Different Shapes, I.E. A Square and A Rectangle
The Area of A Surface Is The Size of The Surface. 2. (A) The Following Diagrams Show Two Different Shapes, I.E. A Square and A Rectangle
Uploaded by
fakhrulfathiCopyright:
Available Formats
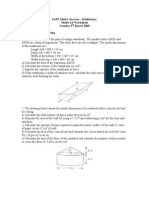
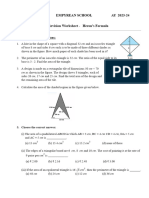
1. The area of a surface is the size of the surface. 2.
(a) The following diagrams show two different shapes, i.e. a square and a rectangle.
(b) Based on the diagrams, the rectangle has a 2 bigger area than the square. (c) This can be proved by using cards which measure 1 cm x 1 cm (1 cm) each. (d) Fill the square and the rectangle with these 1 cm cards and count the numbers of cards used.
(e) The square will use four pieces of these 1 cm cards while the rectangle will use six pieces. (f) Note that the number of these cards used for filling a shape is the same as the product of the length and the width of the shape. (g) Therefore, to measure the area of a regular shape, the following formula can be used:
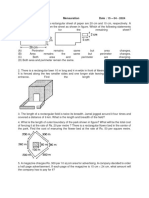
3. The standard units of area are: (a) square millimetres (mm) (b) square centimetres (cm) (c) square metres (m) (d) square kilometres (km)
4. The area of a small surface is measured in mm or cm. 5.The area of a large surface is measured in m or km.
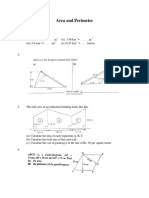
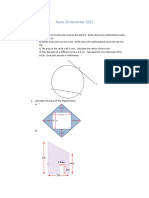
The following diagram shows a rectangle that has a length of 5 cm and a width of 4 cm. Calculate the area of the rectangle.
Solution Area = length x width = 5 cm x 4 cm = 20 cm
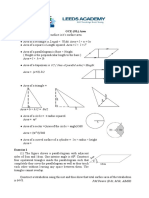
1.Basically, to measure the size of any square or rectangle, use the following formula:
You might also like
- Grade 8 Area, Perimeter and Metric System TestDocument6 pagesGrade 8 Area, Perimeter and Metric System TestSheila Putri Syarah100% (1)
- Area of Shaded RegionDocument8 pagesArea of Shaded Regionwakarnasirkhan100% (1)
- Surface Area and Volume FormulasDocument7 pagesSurface Area and Volume FormulasshruthimNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark Type (Surface Area & Volumes)Document19 pages1 Mark Type (Surface Area & Volumes)radhavenkateshwaranNo ratings yet
- Gmail - INTERNAL ASSESSMENT)Document12 pagesGmail - INTERNAL ASSESSMENT)SengutuvanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Surface Areas and VolumesDocument4 pagesAssignment - Surface Areas and VolumeslwhmrvavrodrljeuwoNo ratings yet
- Maths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringDocument3 pagesMaths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringCape Town After-School TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - WS-11 - Ch. 9 Perimeter and AreaDocument3 pagesClass 7 - WS-11 - Ch. 9 Perimeter and Areajanvi mehtaNo ratings yet
- FilesDocument16 pagesFilespuramganeshNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Practice Paper 11Document4 pagesMaths Class X Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Practice Paper 11hxizisoz6No ratings yet
- Olympiad Questions Apr 2ndd WeekDocument2 pagesOlympiad Questions Apr 2ndd Weekphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument2 pagesMensurationAnkit RajaniNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - Perimeter and AreaDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 7 Maths Worksheet - Perimeter and AreaNeel BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Sa SB SC S Abc S S S Ssasbsc: Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ)Document3 pagesSa SB SC S Abc S S S Ssasbsc: Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ)Ranjit KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetDocument3 pagesCH 12 Areas Related To Circles WorksheetRuzal AnandNo ratings yet
- STD 8 Chap9 WsDocument3 pagesSTD 8 Chap9 Wsheersurti312No ratings yet
- Surface Area of SolidsDocument10 pagesSurface Area of SolidsomarNo ratings yet
- MENSURATIONDocument17 pagesMENSURATIONJayasuryaNo ratings yet
- Ows SSC MensurationDocument49 pagesOws SSC Mensurationlaw conquerorNo ratings yet
- Area, Perimeter 2Document6 pagesArea, Perimeter 2Zonish BakshNo ratings yet
- How Many Squares Grade 5Document4 pagesHow Many Squares Grade 5Greeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mensuration BasicsDocument9 pagesMensuration BasicsKimberly ArnoldNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document44 pagesCH 08Vincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument28 pagesMensurationrushabhNo ratings yet
- 11 AreaDocument4 pages11 AreaMohanlal PereraNo ratings yet
- 20TDY-661 - Mensuration - 2DDocument32 pages20TDY-661 - Mensuration - 2DAbhipriya MishraNo ratings yet
- CGVBHJNKDocument3 pagesCGVBHJNKAGNo ratings yet
- Similar Solids WorksheetDocument2 pagesSimilar Solids WorksheetEamon BarkhordarianNo ratings yet
- VolumesDocument7 pagesVolumesSushobhan SanyalNo ratings yet
- 09 Mensuration of Solid FiguresDocument14 pages09 Mensuration of Solid FiguresSalman ShakilNo ratings yet
- Class 9 (Heron's Formulae)Document2 pagesClass 9 (Heron's Formulae)alvina dhalaitNo ratings yet
- Quant Mock Test - 09 (Mensuration)Document4 pagesQuant Mock Test - 09 (Mensuration)rxsgrdpNo ratings yet
- AL Brothers Prakashan: 13. Surface Areas and Volumes Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term 2)Document16 pagesAL Brothers Prakashan: 13. Surface Areas and Volumes Assignments in Mathematics Class IX (Term 2)sshoeburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Mensuration: (Aptitude & Reasoning)Document23 pagesMensuration: (Aptitude & Reasoning)roshan rajNo ratings yet
- Gr9 Revision Worksheet Heron's FormulaDocument1 pageGr9 Revision Worksheet Heron's FormulaManiBal EducationNo ratings yet
- Maths Class VIII Practice Test 11 Chapter 10 MensurationDocument2 pagesMaths Class VIII Practice Test 11 Chapter 10 MensurationRahul PawarNo ratings yet
- Measuration Part IIDocument22 pagesMeasuration Part IIChris GanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Class 6Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Class 6AnimeshNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Classwork - Student-1Document4 pagesMensuration Classwork - Student-1Priyanka KengarNo ratings yet
- New QuestionsDocument5 pagesNew QuestionsRajneesh SinghNo ratings yet
- MENSURATIONDocument30 pagesMENSURATIONManas YeldhurthiNo ratings yet
- P. The Radius of The Smaller Circle Is 2 M, The Radius of The Larger Circle Is 6 M and QPRDocument3 pagesP. The Radius of The Smaller Circle Is 2 M, The Radius of The Larger Circle Is 6 M and QPRTahmid RaihanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-5 Perimeter Class 4Document2 pagesWorksheet-5 Perimeter Class 4Prabhu VelNo ratings yet
- SA and Volume - MCQDocument3 pagesSA and Volume - MCQpmagrawal100% (1)
- Geometry F Area Perimeter v3Document19 pagesGeometry F Area Perimeter v3coffee080403No ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Chapter 12 and 13 Mensuration Unit Practice Paper 18Document3 pagesMaths Class Ix Chapter 12 and 13 Mensuration Unit Practice Paper 18devildudeishereNo ratings yet
- Foster&TomlinsonBK1CH16 PlaneShapes2Document10 pagesFoster&TomlinsonBK1CH16 PlaneShapes2shiva ramlalNo ratings yet
- (Jan01/Q8/M3) : DC 15 CM and BC 10 Cm. Given ThatDocument5 pages(Jan01/Q8/M3) : DC 15 CM and BC 10 Cm. Given ThatTahmid Raihan100% (1)
- Revision SheetDocument10 pagesRevision Sheethudaalhabibi786No ratings yet
- Mensuration 8th CorrectionsDocument30 pagesMensuration 8th CorrectionsnittypiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & AreaDocument124 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & Areaat2lk22No ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume WorksheetDocument3 pagesSurface Area and Volume WorksheetLavan Nims100% (1)
- IGCSE Class 10 Test - MensurationDocument2 pagesIGCSE Class 10 Test - Mensurationpapia.bera1994No ratings yet
- Quadrilateral Worksheet 1Document7 pagesQuadrilateral Worksheet 1Tisa Aini AbasNo ratings yet
- AreaDocument9 pagesAreaSushobhan SanyalNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Mensuration 1.: ABCDE Is A PyramidDocument4 pagesAssignment - Mensuration 1.: ABCDE Is A Pyramid567gjNo ratings yet
- Cube & Rectangular Solid ProblemsDocument6 pagesCube & Rectangular Solid ProblemsSatPrepVungTauNo ratings yet
- 10 M Surf Ar N VolumesDocument3 pages10 M Surf Ar N VolumesJaison D'CostaNo ratings yet
- Doc-20231204-Wa0006 231206 001654Document6 pagesDoc-20231204-Wa0006 231206 001654schoolclass677No ratings yet
- Mindful Maths 2: Use Your Geometry to Solve These Puzzling PicturesFrom EverandMindful Maths 2: Use Your Geometry to Solve These Puzzling PicturesNo ratings yet
- Skema Permarkahan ScienceDocument7 pagesSkema Permarkahan SciencefakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- JohorDocument14 pagesJohorfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Phases of The MoonDocument1 pagePhases of The MoonfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Animal WeatherDocument18 pagesAnimal WeatherfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- SpeedDocument4 pagesSpeedfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: . SCHOOLDocument3 pagesName: Class: . SCHOOLfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Friction: Effect Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument7 pagesFriction: Effect Advantages and DisadvantagesfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Link To:: Concept Simulation Fair TestDocument3 pagesLink To:: Concept Simulation Fair TestfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Life ProcosesDocument1 pageLife ProcosesfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Life CycleDocument3 pagesLife CyclefakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- All Objects That Humans Use Are Made of Either Natural or Man-Made MaterialsDocument7 pagesAll Objects That Humans Use Are Made of Either Natural or Man-Made MaterialsfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Animal EcreteDocument4 pagesAnimal EcretefakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Life ProtectionDocument1 pageLife ProtectionfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- LenghtDocument16 pagesLenghtfakhrulfathi100% (1)
- TknologiDocument32 pagesTknologifakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Start Sy4Document1 pageStart Sy4fakhrulfathiNo ratings yet
- Basic NeedsDocument1 pageBasic NeedsfakhrulfathiNo ratings yet