Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - Hypovolemia
(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - Hypovolemia
Uploaded by
MacaRonie PepeRownie del RioCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanArisa Vijungco100% (4)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis82% (34)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue Perfusionderic83% (29)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageFluid Volume Deficitrozj0789% (28)
- Community Health Nursing Examination Part IDocument17 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Examination Part Iɹǝʍdןnos97% (64)
- Upper Face BotoxDocument32 pagesUpper Face Botoxyaseer arafat67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesEclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- NCP - Hypovolemic ShockDocument7 pagesNCP - Hypovolemic ShockDominique Excelsis J. Degamo71% (7)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion NCPDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion NCPJasmin Calata50% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionEuanne Orellano85% (13)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodYllejann Manez60% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionReginald Julia100% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDocument6 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaNursesLabs.com100% (7)
- NCP DysuriaDocument1 pageNCP DysuriaJerico Geronimo DacutNo ratings yet
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- NCP On Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesNCP On Electrolyte Imbalancefreyah_bc67% (3)
- Cast and TractionsDocument3 pagesCast and TractionsMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- Piezosurgery in Periodontics and Oral ImplantologyDocument31 pagesPiezosurgery in Periodontics and Oral Implantologysevattapillai100% (1)
- BIBC102 Dr. Gen-Sheng FengDocument10 pagesBIBC102 Dr. Gen-Sheng FengpuuuuyaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP - Fluid Volume DeficitPatrice LimNo ratings yet
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhageDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhagePatricia Franco100% (1)
- NCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNDocument2 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNMa. Elaine Carla Tating38% (8)
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPAyla Mar100% (1)
- Risk For BleedingDocument4 pagesRisk For Bleedinglouie roderos100% (1)
- NCP For DehydrationDocument1 pageNCP For Dehydrationjxhel63% (8)
- Pre EclampsiaDocument3 pagesPre EclampsiaJon Sayson100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPReina Samson100% (1)
- NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeRedwing_Dc_854758% (12)
- Hemorrhage NCPDocument4 pagesHemorrhage NCPElishaNo ratings yet
- NCP BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP Bleedingapi-316491996No ratings yet
- NCP Impaired SkinDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP - Acute PainDocument5 pagesNCP - Acute Painryan50% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogNo ratings yet
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- NCP FearDocument3 pagesNCP Fearエド パジャロン100% (1)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Document6 pagesPlacenta Previa NCP 1Faye Nervanna Alecha Alferez83% (18)
- NCP - Anxiety Hypertension)Document3 pagesNCP - Anxiety Hypertension)Jaja Jaime100% (2)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk For InfectionFielMendozaNo ratings yet
- Module 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Document4 pagesModule 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Raymond Edge100% (2)
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Document1 pageNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument7 pagesNCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaLilian Linogao100% (10)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionAngel Hernandez100% (1)
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocument4 pagesNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNo ratings yet
- NCP-risk For BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP-risk For BleedingAce Dioso Tubasco100% (2)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Syphilis Nursing ManagementDocument2 pagesSyphilis Nursing ManagementLizaEllaga67% (3)
- Anemia NCPDocument6 pagesAnemia NCPApril Jumawan ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- Burns - Fluid Volume, Risk For DeficientDocument3 pagesBurns - Fluid Volume, Risk For Deficientmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- NCP GrievingDocument5 pagesNCP GrievingEllenare Racion33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Datapia lestrangeNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument3 pagesNursing AssessmentJanine PelayoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsDocument17 pagesFluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsA.No ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageDengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume Deficitemman_abz100% (5)
- Sample Only USE The Other One BelowDocument3 pagesSample Only USE The Other One BelowMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- Student Head Nurse To Student Nurse: Rating SheetDocument3 pagesStudent Head Nurse To Student Nurse: Rating SheetMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- 09 Phases of CoparDocument17 pages09 Phases of CoparbeverlytuscanoNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis: Synonym: Amoebic Dysentery HistoryDocument152 pagesAmoebiasis: Synonym: Amoebic Dysentery HistoryMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- (NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaDocument3 pages(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaMacaRonie PepeRownie del Rio100% (4)
- The Hospital Operations and Management Information System Is A ComputerDocument29 pagesThe Hospital Operations and Management Information System Is A ComputerMacaRonie PepeRownie del Rio86% (7)
- HardwareDocument10 pagesHardwareMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument32 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisWoro Nugroho100% (4)
- White Blood Count (WBC) - MedlinePlus Medical TestDocument6 pagesWhite Blood Count (WBC) - MedlinePlus Medical TestMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- HRQo LDocument24 pagesHRQo LAdam QawasmiNo ratings yet
- Ra 11642Document43 pagesRa 11642pureroseroNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Anh Văn Chuyên Ngành Quản TrịDocument86 pagesĐề Thi Anh Văn Chuyên Ngành Quản TrịHiếu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering Instrument For Trainee'S Characteristics Name: Midel P. Mirasol Qualification: Events ManagementDocument2 pagesData Gathering Instrument For Trainee'S Characteristics Name: Midel P. Mirasol Qualification: Events ManagementLyka ollerasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemChe-Che BagasolNo ratings yet
- Social Issues Research Project HandoutDocument2 pagesSocial Issues Research Project HandoutPradhyumNo ratings yet
- A Study To Determine The Effectiveness of Aromatherapy On Back Pain Among The Staff Nurses in A Selected Hospital at BangaloreDocument5 pagesA Study To Determine The Effectiveness of Aromatherapy On Back Pain Among The Staff Nurses in A Selected Hospital at BangaloreAchmad RyandaNo ratings yet
- Fluoxetine in The Management of Pornography Addiction: Case ReportDocument3 pagesFluoxetine in The Management of Pornography Addiction: Case ReportRajat ChandelNo ratings yet
- The Spine Intervention MCQSDocument7 pagesThe Spine Intervention MCQSZunairaNo ratings yet
- SD Foam Ban 3529b enDocument8 pagesSD Foam Ban 3529b enMauricio Cesar DalzochioNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Flo - Rok Fr5-Max Part A (Resin)Document12 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Flo - Rok Fr5-Max Part A (Resin)rmsa17No ratings yet
- Safety in GSKDocument12 pagesSafety in GSKbaluchakpNo ratings yet
- CEP Compro Juni 2023Document67 pagesCEP Compro Juni 2023didi sudiNo ratings yet
- 1st Page REC Form 02E Study Protocol Assessment FormDocument5 pages1st Page REC Form 02E Study Protocol Assessment FormCARLOS JOSETON PAOLO SANTIAGO TORRENo ratings yet
- SCCL RecruitmentDocument6 pagesSCCL RecruitmentPreeti lambaNo ratings yet
- Dentascan Imaging of The Mandible and MaxillaDocument7 pagesDentascan Imaging of The Mandible and Maxillasonia sahliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Word Search - WordMintDocument1 pageRespiratory System Word Search - WordMintJulio Cesar Pineda BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Ingles Compresion LectoraDocument6 pagesIngles Compresion LectoraAlvaro Josue HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Stent PricingDocument1 pageCardiac Stent PricingNaz NassNo ratings yet
- Naval ForcesDocument11 pagesNaval ForcesSuperFLYNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 1Document21 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 1Jasmine A. Afinidad100% (1)
- Woodruff - Complaint (WCCC) - Submitted 5-12-23Document22 pagesWoodruff - Complaint (WCCC) - Submitted 5-12-23WDIV/ClickOnDetroitNo ratings yet
- Drug Calc Sample QuestionsDocument12 pagesDrug Calc Sample QuestionsRastie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Q4 HE Nail Care 9 Week 2Document3 pagesQ4 HE Nail Care 9 Week 2krinessa erika m. de chavezNo ratings yet
- College of Criminal Justice Education Professor: Subject Code & Descriptive Title: Section: ScheduleDocument24 pagesCollege of Criminal Justice Education Professor: Subject Code & Descriptive Title: Section: ScheduleFranco Angelo ReyesNo ratings yet
(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - Hypovolemia
(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - Hypovolemia
Uploaded by
MacaRonie PepeRownie del RioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - Hypovolemia
(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - Hypovolemia
Uploaded by
MacaRonie PepeRownie del RioCopyright:
Available Formats
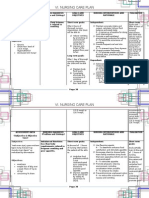
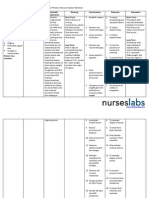
NURSING CARE PLAN (PRIORITY NUMBER 1) Assessment Subjective data: Nagdurugo ang aking sinapupunan as verbalized by the patient.
Objective data: With vaginal bleeding With blood loss of 220ml With decreased RBC (3.18x1012/L) (Feb. 14,2012) Weak in appearance With body malaise Nursing Diagnosis Deficient fluid volume: Hypovolemia related to increased vascularity of the chorionic villi as evidenced by vaginal bleeding, blood loss of 220 ml and decreased RBC count. Planning At the end of the shift, the patient will be able to: Verbalize understanding of causative factors and purpose of individual therapeutic interventions and medication. Demonstrat e behaviors to monitor and correct deficit, as indicated. Intervention Independent: Assess vital signs, noting the blood pressure and pulse rate. Rationale These changes in vital signs are associated with fluid volume loss and/ or hypovolemia. To reduce pressure on fragile skin and tissues. Evaluation Goals met: The patient verbalized understanding of causative factors and purpose of individual therapeutic interventions and medication. The patient also demonstrated behaviors to monitor and correct deficit indicated.
Change the position frequently, turn side to side every 2 hours if necessary. Discuss factors related to occurrence of deficit as individually appropriate.
Early identification of risk factors can decrease occurrence and severity of complications associated with hypovolemia.
Measure the amount of blood loss.
To note how blood loss affects the patients fluid volume status. To informed the patient for the possible therapeutic effects of the drug. To prevent the recurrence of vaginal bleeding associated with frequent motion/ movements.
To replace
Explain the drug which is ordered to the patient and how it takes its function. Instruct the patient to maintain at bed rest.
Provide Intravenous (IV) fluids as ordered by the physician.
and conserve blood volume contrary to the blood loss caused by vaginal bleeding.
You might also like
- Sickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanArisa Vijungco100% (4)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis82% (34)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue Perfusionderic83% (29)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageFluid Volume Deficitrozj0789% (28)
- Community Health Nursing Examination Part IDocument17 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Examination Part Iɹǝʍdןnos97% (64)
- Upper Face BotoxDocument32 pagesUpper Face Botoxyaseer arafat67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesEclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- NCP - Hypovolemic ShockDocument7 pagesNCP - Hypovolemic ShockDominique Excelsis J. Degamo71% (7)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion NCPDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion NCPJasmin Calata50% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionEuanne Orellano85% (13)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodYllejann Manez60% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionReginald Julia100% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDocument6 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaNursesLabs.com100% (7)
- NCP DysuriaDocument1 pageNCP DysuriaJerico Geronimo DacutNo ratings yet
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- NCP On Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesNCP On Electrolyte Imbalancefreyah_bc67% (3)
- Cast and TractionsDocument3 pagesCast and TractionsMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- Piezosurgery in Periodontics and Oral ImplantologyDocument31 pagesPiezosurgery in Periodontics and Oral Implantologysevattapillai100% (1)
- BIBC102 Dr. Gen-Sheng FengDocument10 pagesBIBC102 Dr. Gen-Sheng FengpuuuuyaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP - Fluid Volume DeficitPatrice LimNo ratings yet
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhageDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhagePatricia Franco100% (1)
- NCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNDocument2 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNMa. Elaine Carla Tating38% (8)
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume - NCPAyla Mar100% (1)
- Risk For BleedingDocument4 pagesRisk For Bleedinglouie roderos100% (1)
- NCP For DehydrationDocument1 pageNCP For Dehydrationjxhel63% (8)
- Pre EclampsiaDocument3 pagesPre EclampsiaJon Sayson100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit (GI Bleeding) NCPReina Samson100% (1)
- NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeRedwing_Dc_854758% (12)
- Hemorrhage NCPDocument4 pagesHemorrhage NCPElishaNo ratings yet
- NCP BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP Bleedingapi-316491996No ratings yet
- NCP Impaired SkinDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP - Acute PainDocument5 pagesNCP - Acute Painryan50% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogNo ratings yet
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- NCP FearDocument3 pagesNCP Fearエド パジャロン100% (1)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Document6 pagesPlacenta Previa NCP 1Faye Nervanna Alecha Alferez83% (18)
- NCP - Anxiety Hypertension)Document3 pagesNCP - Anxiety Hypertension)Jaja Jaime100% (2)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk For InfectionFielMendozaNo ratings yet
- Module 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Document4 pagesModule 13 - Cystoclysis (Student)Raymond Edge100% (2)
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Document1 pageNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument7 pagesNCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaLilian Linogao100% (10)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionAngel Hernandez100% (1)
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocument4 pagesNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNo ratings yet
- NCP-risk For BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP-risk For BleedingAce Dioso Tubasco100% (2)
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Syphilis Nursing ManagementDocument2 pagesSyphilis Nursing ManagementLizaEllaga67% (3)
- Anemia NCPDocument6 pagesAnemia NCPApril Jumawan ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- Burns - Fluid Volume, Risk For DeficientDocument3 pagesBurns - Fluid Volume, Risk For Deficientmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- NCP GrievingDocument5 pagesNCP GrievingEllenare Racion33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Datapia lestrangeNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument3 pagesNursing AssessmentJanine PelayoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsDocument17 pagesFluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsA.No ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageDengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume Deficitemman_abz100% (5)
- Sample Only USE The Other One BelowDocument3 pagesSample Only USE The Other One BelowMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- Student Head Nurse To Student Nurse: Rating SheetDocument3 pagesStudent Head Nurse To Student Nurse: Rating SheetMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- 09 Phases of CoparDocument17 pages09 Phases of CoparbeverlytuscanoNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis: Synonym: Amoebic Dysentery HistoryDocument152 pagesAmoebiasis: Synonym: Amoebic Dysentery HistoryMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- (NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaDocument3 pages(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaMacaRonie PepeRownie del Rio100% (4)
- The Hospital Operations and Management Information System Is A ComputerDocument29 pagesThe Hospital Operations and Management Information System Is A ComputerMacaRonie PepeRownie del Rio86% (7)
- HardwareDocument10 pagesHardwareMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument32 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisWoro Nugroho100% (4)
- White Blood Count (WBC) - MedlinePlus Medical TestDocument6 pagesWhite Blood Count (WBC) - MedlinePlus Medical TestMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- HRQo LDocument24 pagesHRQo LAdam QawasmiNo ratings yet
- Ra 11642Document43 pagesRa 11642pureroseroNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Anh Văn Chuyên Ngành Quản TrịDocument86 pagesĐề Thi Anh Văn Chuyên Ngành Quản TrịHiếu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering Instrument For Trainee'S Characteristics Name: Midel P. Mirasol Qualification: Events ManagementDocument2 pagesData Gathering Instrument For Trainee'S Characteristics Name: Midel P. Mirasol Qualification: Events ManagementLyka ollerasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemChe-Che BagasolNo ratings yet
- Social Issues Research Project HandoutDocument2 pagesSocial Issues Research Project HandoutPradhyumNo ratings yet
- A Study To Determine The Effectiveness of Aromatherapy On Back Pain Among The Staff Nurses in A Selected Hospital at BangaloreDocument5 pagesA Study To Determine The Effectiveness of Aromatherapy On Back Pain Among The Staff Nurses in A Selected Hospital at BangaloreAchmad RyandaNo ratings yet
- Fluoxetine in The Management of Pornography Addiction: Case ReportDocument3 pagesFluoxetine in The Management of Pornography Addiction: Case ReportRajat ChandelNo ratings yet
- The Spine Intervention MCQSDocument7 pagesThe Spine Intervention MCQSZunairaNo ratings yet
- SD Foam Ban 3529b enDocument8 pagesSD Foam Ban 3529b enMauricio Cesar DalzochioNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Flo - Rok Fr5-Max Part A (Resin)Document12 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Flo - Rok Fr5-Max Part A (Resin)rmsa17No ratings yet
- Safety in GSKDocument12 pagesSafety in GSKbaluchakpNo ratings yet
- CEP Compro Juni 2023Document67 pagesCEP Compro Juni 2023didi sudiNo ratings yet
- 1st Page REC Form 02E Study Protocol Assessment FormDocument5 pages1st Page REC Form 02E Study Protocol Assessment FormCARLOS JOSETON PAOLO SANTIAGO TORRENo ratings yet
- SCCL RecruitmentDocument6 pagesSCCL RecruitmentPreeti lambaNo ratings yet
- Dentascan Imaging of The Mandible and MaxillaDocument7 pagesDentascan Imaging of The Mandible and Maxillasonia sahliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Word Search - WordMintDocument1 pageRespiratory System Word Search - WordMintJulio Cesar Pineda BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Ingles Compresion LectoraDocument6 pagesIngles Compresion LectoraAlvaro Josue HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Stent PricingDocument1 pageCardiac Stent PricingNaz NassNo ratings yet
- Naval ForcesDocument11 pagesNaval ForcesSuperFLYNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 1Document21 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 1Jasmine A. Afinidad100% (1)
- Woodruff - Complaint (WCCC) - Submitted 5-12-23Document22 pagesWoodruff - Complaint (WCCC) - Submitted 5-12-23WDIV/ClickOnDetroitNo ratings yet
- Drug Calc Sample QuestionsDocument12 pagesDrug Calc Sample QuestionsRastie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Q4 HE Nail Care 9 Week 2Document3 pagesQ4 HE Nail Care 9 Week 2krinessa erika m. de chavezNo ratings yet
- College of Criminal Justice Education Professor: Subject Code & Descriptive Title: Section: ScheduleDocument24 pagesCollege of Criminal Justice Education Professor: Subject Code & Descriptive Title: Section: ScheduleFranco Angelo ReyesNo ratings yet