Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part I: A Review of The Indian Constitution
Part I: A Review of The Indian Constitution
Uploaded by
Chitvan BansalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Part I: A Review of The Indian Constitution
Part I: A Review of The Indian Constitution
Uploaded by
Chitvan BansalCopyright:
Available Formats
hapter One: Historical Perspective Chapter Two: Policies And Plans After Independence Chapter Three: Infrastructure Chapter
Four: Environment Chapter Five: Health Chapter Six: Agriculture Chapter Seven: Rural Development Chapter Eight: Industry Chapter Nine: Energy Chapter Ten: Nuclear Scince Chapter Eleven: Electronics Chapter Twelve: Information Technology Chapter Thirteen: Defence Research Chapter Fourteen: Space Research Chapter Fifteen: Ocean Development Chapter Sixteen: Earth And Atmospheric Sciences Chapter Seventeen: Biotechnology Chapter Eighteen: Lasers Chapter Nineteen: Superconductivity Chapter Twenty: Indian Scientists Terminology: Gsm And Cdma Technologies Abbreviations At A Glance Appendix Developments Up To 2010 Table of Contents PART I : A REVIEW OF THE INDIAN CONSTITUTION The Constitution of India at a Glance 1. Historical Perspective 2. Framing the Constitution 3. Features and Philosophy of the Constitution 4. Territory of the Union and Reorganisation of the States 5. Citizenship 6. Fundamental Rights 7. Directive Principles of State Policy 8. Fundamental Duties 9. The Union Executive 10. The Union Legislature 11. Comptroller and Auditor-General 12. The State Executive 13. The State Legislature 14. The State of Jammu and Kashmir 15. Local Government 16. Union Territories and Special Areas 17. The Judiciary 18. Indian Federalism 19. Emergency Provisions 20. Civil Services and Public Service Commissions 21. Elections 22. Official Language 23. Provisions Relating to Special Classes
24. Amendment of the Constitution 25. Schedules of the Constitution PART II : INDIAN POLITY: TOPICAL ISSUES 1. Reviewing the Constitution 2. Does India Need to Switch Over to the Presidential System of Government? 3. Problems of Governability 4. Role of Neo-Governments in Governance 5. Problems of Nation-Building in India 6. Civil Society: Meaning and Nature 7. Article 356: Scope and Effect 8. Strong Union and Strong States 9. A New Look at the Centre-State Relations 10. Cooperative Trends in Indian Federalism 11. Role of Governors 12. Coalition Government 13. The President and Caretaker Governments 14. Electoral Systems 15. On Communal Electorates 16. Money Power and Elections 17. Indias Electoral System: Maladies and Remedies 18. Issue of Right to Recall Elected Representatives 19. Controversy Over Publication of the Results of Exit Polls 20. On Corruption in Public Life 21. Criminalisation of Politics 22. What Ails Bureaucracy in India? 23. Pressure Groups in India 24. Public Opinion 25. The Issue of Regionalism vis-a-vis Nationalism 26. Do Regional Groupings Threaten Stability? 27. Regional Chauvinism versus Democratic Space 28. Identity Politics in India 29. Changing Trends in Political Parties 30. Regional Parties in India 31. Dynastic Politics: How Democratic? 32. New and Smaller StatesHow Viable? 33. Expanding Scope of Legislative Power 34. Legislative Privileges and Press Freedom 35. The Status of the Indian Parliament 36. Relevance of The Rajya Sabha 37. Degeneration of Parliament and Need for Code of Conduct 38. Anti-Defection Law: A Remedy or A Malady? 39. The Judiciary: A Review 40. Judicial Activism 41. Judicial Reforms : An Urgent Need 42. The Issue of Delayed Justice 43. The Issue of Judicial Overreach 44. Issue of Judicial Accountability 45. Public Interest Litigation: How Useful 46. The Issue of Reservation 47. Uniform Civil Code 48. Caste and Politics in India 49. The Issue of Good Governance 50. e-Governance
51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64.
Panchayati Raj: A Mid-Term Review Office of Profit Issue Parliament and Judiciary: Issue of Jurisdiction Media and Democracy The Emergency: Test of Indian Democracy Democracy and Social Transformation in India Popular Movements: Emergence and Implications Mob Violence and the Rule of Law Terrorism and Insurgency: Threat to Democracy The Menace of Naxalism Police Reforms: Need of the Hour Prison System and Reforms Should Military Service be made Compulsory? Indias Foreign Policy
PART III : GENERAL INFORMATION 1. Jurisdiction and Seats of High Courts 2. Thirteen Lok Sabhas: Polls and Term 3. Officers of the Indian Government 4. Table of Precedence 5. National Insignia 6. Political Parties of India 7. Important Commissions 8. Recent Legislations of Importance 9. Some Important Supreme Court Judgements 10. Political Terminology in India and abroad. Cover Design : Bindia Thapar Table of Contents Preface 1. India AND THE WORLD : Europe; The Arab World; Africa 2. Northern INDIA : AGE OF THE THREE EMPIRES (800-1000) : The Struggle for Domination in North India : The Palas; The Pratiharas; The Rashtrakutas; Political Ideas and Organisation 3. South INDIA : THE CHOLA Empire (900-1200) : The Rise of the Chola Empire; Age of Rajaraja and Rajendra; Chola Government-Local Self Government; Cultural Life 4. ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL LIFE, Education AND Religious BELIEFS (800-1200) : Trade and Commerce; Nature of Society; the Caste System; Condition of Women; Dress, Food and Amusements; Education, Science and Religious Learning; Religious Movements and Beliefs 5. THE AGE OF CONFLICT (CIRCA 1000-1200) : The Ghaznavids; the Rajput States; the Turkish Conquest of North India; the Battle of Tarain; Turkish Conquest of the Ganga Valley; Causes of the Defeat of the Rajputs 6. THE Delhi SULTANAT-I (CIRCA 1200-1400) : The Mameluk Sultans (Thirteenth Century); Struggle for the Establishment of a Strong Monarch); Iltutmish (1210-36); Raziya; Era of Balban (1246-87); the Mongols and the Problem of the Northwest Frontier; Internal Rebellions and the Struggle for Territorial Consolidation of the Delhi Sultanat 7. THE DELHI SULTANAT-II (CIRCA 1200-1400) : The Khaljis and the Tughlaqs; the Khaljis (1290-1320); the Tughlaqs (1320-1412); Expansion of the Delhi Sultanat; Internal Reforms and Experiments Muhammad Tughlaq's Experiments; Decline and Disintergration of the Delhi Sultanat : Firuz and his Successors 8. GOVERNMENT, AND ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL LIFE UNDER THE DELHI SULTANAT :
o o o
The Sultan; Central Administration; Local Administration; Economic and Social Life; Peasants and Rural Gentry; Trade, Industry and the Merchants; the Sultan and the Nobles; Town Life : Slaves, Artisans and Others; Caste, Social Manners and Customs; Nature of the State; Religious Freedom under the Sultanat 9. THE AGE OF Vijayanagara AND THE BAHMANIDS, AND THE COMING OF THE Portuguese (CIRCA 1350-1565) : The Vijayanagara Empire-Its Foundation and Conflict with the Bahmani Kingdom; the Bahmani Kingdom-Its Expansion and Disintegration; Mahmud Gawan; Climax of the Vijayanagara Empire and its Disintegration; The Advent of the Portuguese 10. STRUGGLE FOR EMPIRE IN NORTH INDIA-I (CIRCA 1400-1525) : Eastern India-Bengal, Assam and Orissa; Western India-Gujarat, Malwa and Mewar; Mahmud Begarha; Malwa; Mewar; Northwest and North India-the Sharqis, the Lodi Sultans and Kashmir; Kashmir 11. CULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA (1300-1500) : Architecture; Religious Ideas and Beliefs; the Sufi Movement; the Chishti and Suharwardi Silsilahs; the Bhakti Movement; the Vaishnavite Movement; Literature and Fine Arts; Fine Arts 12. STRUGGLE FOR EMPIRE IN NORTH INDIA-II Mughals AND Afghans (1525-1555) : Central Asia and Babur; Conquest of India; the Battle of Panipat (20 April 1526); the Battle of Khanwa; the Afghans; Significance of Babur's Advent into India; Humayun's Conquest of Gujarat and his Tussle with Sher Shah; Sher Khan; Sher Shah and the Sur Empire (1540-55); Contribution of Sher Shah 13. CONSOLIDATION OF THE Mughal EMPIRE AGE OF Akbar : Early Phase-Contest with the Nobility (1556-67); Early Expansion of the Empire (1560-76); Administration; Mansabdari System and the Army; Organization of Government; Relations with the Rajputs; Rebellions and Further Expansion of the Mughal Empire; Towards Integration : State, Religion and Social Reforms 14. THE Deccan AND SOUTH INDIA (UP TO 1656) : Mughal Advance Towards the Deccan; Conquest of Berar, Ahmadnagar and Khandesh; Rise of Malik Ambar and Frustration of Mughal Attempt at Consolidation; Extinction of Ahmadnagar, and Acceptance of Mughal Suzerainty by Bijapur and Golconda; Cultural Contribution of the Deccan States 15. INDIA IN THE FIRST HALF OF THE SEVENTEENTH CENTURY : Political and Administrative Developments in India; Nur Jahan; Shah Jahan's Rebellion; Mahabat Khan; Foreign Policy of the Mughals; Shah Jahan's Balkh Campaign; Mughal-Persian Relations-the Last Phase; Growth of Administration : Mansabdari System and the Mughal Army; The Mughal Army 16. ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL LIFE UNDER THE MUGHALS : Economic and Social Conditions; Standard of Living : Pattern of Village Life and the Masses ; The Ruling Classes : The Nobles and Zamindars; Zamindars and the Rural Gentry; The Middle Strata; Organization of Trade and Commerce; Foreign Trade and the European Traders 17. CULTURAL AND RELIGIOUS DEVELOPMENTS : Architecture; Painting; Language, Literature and Music; Music; Religious Ideas and Beliefs, and Problems of Integration 18. CLIMAX AND DISINTEGRATION OF THE MUGHAL EMPIRE-I : Problems of Succession; Aurangzeb's Reign-His Religious Policy; Political Developments-North India; Northeast and East India; Popular Revolts and Movements for Regional Independence : Jats, Afghans and Sikhs; Relations with the Rajputs-Breach with Marwar and Mewar 19. CLIMAX AND DISINTEGRATION OF THE MUGHAL EMPIRE-N : The Rise of the Marathas; Early Career of Shivaji; Treaty of Purandar and Shivaji's Visit to Agra; Final Breach with Shivaji-Shivaji's Administration and Achievements; Aurangzeb and the Deccani States (1658-87); The First Phase (1658-68); The Second Phase (1668-84); The Third Phase (1684-87); Aurangzeb, the Marathas and the Deccan-the Last Phase (1687-1707); Decline of the Mughal EmpireResponsibility of Aurangzeb
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Customer Experience Book - How To Design, Measure and Improve Customer Experience in Your Business (PDFDrive)Document233 pagesThe Customer Experience Book - How To Design, Measure and Improve Customer Experience in Your Business (PDFDrive)Vera Pratiwi Goenfi100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Polyphonic HMI Case PresentationDocument48 pagesPolyphonic HMI Case PresentationUtpal Biyani100% (4)
- Creating Custom SU01 Transaction Code With Display and Password Reset Buttons PDFDocument7 pagesCreating Custom SU01 Transaction Code With Display and Password Reset Buttons PDFSanjay DesaiNo ratings yet
- Retail ProjectDocument114 pagesRetail ProjectSowjanya KunareddyNo ratings yet
- Designer MilkDocument30 pagesDesigner MilkParashuram Shanigaram67% (6)
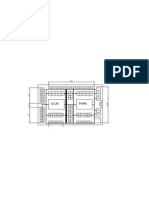
- Elitra Housing PlanDocument1 pageElitra Housing PlanChitvan BansalNo ratings yet
- Explain The Algorithm of The Hardy Cross Method For The Pipe Network AnalysisDocument2 pagesExplain The Algorithm of The Hardy Cross Method For The Pipe Network AnalysisChitvan BansalNo ratings yet
- Highway EngineeringDocument3 pagesHighway EngineeringChitvan Bansal100% (1)
- CV Practical TainingDocument1 pageCV Practical TainingChitvan BansalNo ratings yet
- 329672001-Jacobs Engineering Group IncDocument5 pages329672001-Jacobs Engineering Group IncJaram Johnson67% (3)
- The Alexander Technique and Flute PlayingDocument7 pagesThe Alexander Technique and Flute PlayingCarlos Andres CarpizoNo ratings yet
- Cse320 MCQDocument12 pagesCse320 MCQAnsh Gulati ji100% (1)
- Unit 1 Introduction To JainismDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To JainismVertika guptaNo ratings yet
- HPTM Machine DetailsDocument7 pagesHPTM Machine DetailsK Srinivasa Sagar100% (1)
- CDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideDocument18 pagesCDP Virtual Appliance Getting Started GuideJulio RodanesNo ratings yet
- Hair Stylist Cover LetterDocument7 pagesHair Stylist Cover Letterzys0vemap0m3100% (2)
- Polycab Solar PDFDocument6 pagesPolycab Solar PDFVivek RamachandranNo ratings yet
- DB en Macx MCR T Ui Up 104595 en 10Document49 pagesDB en Macx MCR T Ui Up 104595 en 10Dante LupuNo ratings yet
- Paper and PaperboardDocument62 pagesPaper and PaperboardKumkum CrNo ratings yet
- The Masterbuilder - February 2012 - Road Engineering SpecialDocument238 pagesThe Masterbuilder - February 2012 - Road Engineering SpecialChaitanya Raj GoyalNo ratings yet
- Online QDA - How and What To CodeDocument5 pagesOnline QDA - How and What To CodeRockyNo ratings yet
- Reduced Graphene Oxide Filled Cellulose Films For Flexible Temperature SensorDocument8 pagesReduced Graphene Oxide Filled Cellulose Films For Flexible Temperature SensorMicu CristiNo ratings yet
- Hank Kolb 3Document3 pagesHank Kolb 3gr8_amaraNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory of San Bernardino, IncDocument40 pagesClinical Laboratory of San Bernardino, Inckharberson1613No ratings yet
- FMEADocument5 pagesFMEAmz007No ratings yet
- Analog Communication Model ExamDocument20 pagesAnalog Communication Model ExamwalternampimadomNo ratings yet
- Wisconsin Public Library Standards 6th Edition 2018 FINALDocument49 pagesWisconsin Public Library Standards 6th Edition 2018 FINALemac1983No ratings yet
- United States Patent: Serban Et AlDocument9 pagesUnited States Patent: Serban Et AlMutia Herlisa14No ratings yet
- Report On VSATDocument19 pagesReport On VSATchinu meshramNo ratings yet
- Test Oil Compressor #4067 (06-12-22)Document1 pageTest Oil Compressor #4067 (06-12-22)albertoNo ratings yet
- FLOWERSDocument1 pageFLOWERSikkopal92No ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuit Design Fourth Edition Solutions To ExercisesDocument8 pagesMicroelectronic Circuit Design Fourth Edition Solutions To Exercisesreky_georgeNo ratings yet
- Pinelands National ReserveDocument2 pagesPinelands National ReservesallyNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan - PDF - Crane (Machine) - Mechanical EngineeringDocument25 pagesLifting Plan - PDF - Crane (Machine) - Mechanical EngineeringAdonis CaraanNo ratings yet