Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Lab5 Thevenin
3 Lab5 Thevenin
Uploaded by
Brett HendricksCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab E1 RLC Circuit 1Document11 pagesLab E1 RLC Circuit 1Ching Wai Yong100% (1)
- Electrolux Washing Machine Wiring Diagram Service Manual Error Code Circuit Schematic Schema Repair Instruction Guide User Manual Free PDF Download PDFDocument8 pagesElectrolux Washing Machine Wiring Diagram Service Manual Error Code Circuit Schematic Schema Repair Instruction Guide User Manual Free PDF Download PDFBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab Report-1 PDFDocument27 pagesVirtual Lab Report-1 PDFCarlton Lobo0% (1)
- Experiment 7 - 0 and 8 - 0Document7 pagesExperiment 7 - 0 and 8 - 0efecakir03No ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis and Design Manual FinalDocument65 pagesCircuit Analysis and Design Manual Finalصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- Ee-316 - Circuit Theory LabDocument47 pagesEe-316 - Circuit Theory LabsureshhasiniNo ratings yet
- Exp3 Sem2 Edit 0506Document9 pagesExp3 Sem2 Edit 0506shavin699100% (1)
- Verification Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer Theorem: Experiment No.3 DateDocument16 pagesVerification Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer Theorem: Experiment No.3 DateSachin DevarakondaNo ratings yet
- LAB3Document11 pagesLAB3RajuKumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:: Basic Electrical Engineering (Lab Manual)Document6 pagesExperiment No:: Basic Electrical Engineering (Lab Manual)Nayana JangleNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurDocument36 pagesDC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurMuhammed UmarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualDocument30 pagesElectrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualJigar SoniNo ratings yet
- BE.01.08 Series Resistive Circuits SHDocument12 pagesBE.01.08 Series Resistive Circuits SHleslynjdNo ratings yet
- IEC - Lab Exp 3Document12 pagesIEC - Lab Exp 3sazidmohsin456No ratings yet
- 3 Phase Full Wave Bridge ConverterDocument4 pages3 Phase Full Wave Bridge Convertersubhasishpodder100% (1)
- Circuit LabDocument7 pagesCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- Circuits Exp3Document4 pagesCircuits Exp3ilker.ozcelikkanNo ratings yet
- Thevenin's Theorem Lab: Voltage, VDocument3 pagesThevenin's Theorem Lab: Voltage, VMd Johurul IslamNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Document6 pagesCapacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Mr_asad_20No ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Document6 pagesDC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Ratul kumarNo ratings yet
- Exp 6Document12 pagesExp 6Laura AcaciaNo ratings yet
- Ge320 Lab2Document7 pagesGe320 Lab2hbuddyNo ratings yet
- Lab E1 RLC CircuitDocument11 pagesLab E1 RLC CircuitChing Wai Yong100% (1)
- Iec Lab Report 3Document12 pagesIec Lab Report 3mahrabhasanchowdhury1No ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document5 pagesExperiment 4mohammad alaliNo ratings yet
- ELEC331 Lab Experiment#1Document16 pagesELEC331 Lab Experiment#1DavidNo ratings yet
- QXGQ7QX9 Lab3Document4 pagesQXGQ7QX9 Lab3Emre SelviliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDocument152 pagesElectrical Machines Lab ManualMazoon ButtNo ratings yet
- 5.2 SuperpositionDocument6 pages5.2 SuperpositionObed Kojo Kumi-LarbiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- DC Exp 6 Student ManualDocument6 pagesDC Exp 6 Student ManualAsifur R. HimelNo ratings yet
- 3 Lab 3: DC Motor Transfer Function Estimation by Explicit MeasurementDocument9 pages3 Lab 3: DC Motor Transfer Function Estimation by Explicit MeasurementRogger MezaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Thevenin TheoremDocument8 pagesLab 3 - Thevenin TheoremminhtridtaNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics LabDocument59 pagesApplied Physics LabEngr Waqas MalikNo ratings yet
- Circuits and NetworksDocument23 pagesCircuits and NetworksDei PehNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument9 pagesAC CircuitsAli AdnanNo ratings yet
- Circuits Lab Report Expt. 8Document8 pagesCircuits Lab Report Expt. 8Harold FilomenoNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Document5 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- Ee 303 3Document3 pagesEe 303 3api-288751705No ratings yet
- Lab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCDocument5 pagesLab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCAbdul QudoosNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Thevenin's & Norton's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferDocument5 pagesExperiment: Thevenin's & Norton's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferMunir Izkandaryan ZX'zNo ratings yet
- Kirchof'sDocument6 pagesKirchof'sMohamed EslamNo ratings yet
- Unti 4Document29 pagesUnti 4dhruvkareliya1004No ratings yet
- 9 Thevenin & Norton CircuitsDocument11 pages9 Thevenin & Norton CircuitsKhalidSa23No ratings yet
- Lab 6Document4 pagesLab 6yasir aliNo ratings yet
- Eee ManualDocument53 pagesEee ManualplsmcokNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument7 pagesDC CircuitsAmeer Bakry ZulkiffliNo ratings yet
- ENA Lab 9 Balanced Three-Phase Circuit (Software)Document12 pagesENA Lab 9 Balanced Three-Phase Circuit (Software)Mohammed Ahmad OsamaNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument9 pagesAC CircuitsAli AdnanNo ratings yet
- VOLTAGE & CURRENT DIVIDER and DELTA-WYE TRANSFORMATIONDocument10 pagesVOLTAGE & CURRENT DIVIDER and DELTA-WYE TRANSFORMATIONJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- American International University-Bangladesh: Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument4 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringRuham RofiqueNo ratings yet
- Exp11.Three Phase Full Wave Controlled ConvertersDocument4 pagesExp11.Three Phase Full Wave Controlled ConvertersJawad Rasheed SheikhNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2Document6 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2THE LEARNER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document6 pagesExp 3moha amroNo ratings yet
- 409064607103/virtualeducation/27597/contenidos/45970/LAB THEVENIN THEOREMDocument4 pages409064607103/virtualeducation/27597/contenidos/45970/LAB THEVENIN THEOREMJonathan David Campos JimenezNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Review of Norton'S Theorem and Jfet Biasing Pre-Lab InstructionsDocument8 pagesExperiment: Review of Norton'S Theorem and Jfet Biasing Pre-Lab InstructionsHamid AssadullahNo ratings yet
- Thevenins Theorem (Laboratory 7)Document5 pagesThevenins Theorem (Laboratory 7)Chooster TheScrosNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- RZ 05 - EE394J - 2 - Spring11 - Phasor - Time - Domain - PlotsDocument1 pageRZ 05 - EE394J - 2 - Spring11 - Phasor - Time - Domain - PlotsBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Z-Base Case. One Circuit Per Corridor. Y Matrix Analysis.: What Planning Can You Do With Y Matrix?Document2 pagesZ-Base Case. One Circuit Per Corridor. Y Matrix Analysis.: What Planning Can You Do With Y Matrix?Brett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Voltage Source Battery ResistanceDocument1 pageVoltage Source Battery ResistanceBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Z-Voltage Stability AnalysisDocument1 pageZ-Voltage Stability AnalysisBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Yt-Calculation and Experimental Checking of Fault Currents in The Medium-Voltage Distribution Network of Omiš As The Basis For Tuning of Numerical ProtectionDocument1 pageYt-Calculation and Experimental Checking of Fault Currents in The Medium-Voltage Distribution Network of Omiš As The Basis For Tuning of Numerical ProtectionBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- R.Z.-400kV 400kV Rishikesh Line Protection: D) RXEG - 27P - Under Voltage Protection RelayDocument1 pageR.Z.-400kV 400kV Rishikesh Line Protection: D) RXEG - 27P - Under Voltage Protection RelayBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Power To The DeltaDocument1 pagePower To The DeltaBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Zhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoDocument4 pagesZhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Proj. E. I 17 Selecting The Right RCDDocument1 pageProj. E. I 17 Selecting The Right RCDBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Negative Sequence Currents For Generators Connected To 345-kV Asymmetrical Transmission Lines From Measurement DataDocument10 pagesAssessment of Negative Sequence Currents For Generators Connected To 345-kV Asymmetrical Transmission Lines From Measurement DataBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Meeting CMTDocument1 pageMeeting CMTBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Powercad UputeDocument74 pagesPowercad UputeElmir Huseinbasic100% (1)
- PSDC Ex1 HydroTurbine PDFDocument8 pagesPSDC Ex1 HydroTurbine PDFBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Akademija Za Menadžment: Nastava Po Britanskim Standardima. Upišite Se Odmah. Promotivna Cena!Document8 pagesAkademija Za Menadžment: Nastava Po Britanskim Standardima. Upišite Se Odmah. Promotivna Cena!Brett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Hire Fleet CableDocument2 pagesHire Fleet CableBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Settings Overviewtext Title: ! (CdataDocument3 pagesSettings Overviewtext Title: ! (CdataBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Xenon Ps PDFDocument5 pagesXenon Ps PDFBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Zhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoDocument4 pagesZhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
3 Lab5 Thevenin
3 Lab5 Thevenin
Uploaded by
Brett HendricksCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Lab5 Thevenin
3 Lab5 Thevenin
Uploaded by
Brett HendricksCopyright:
Available Formats
EENG 2111 Circuit Analysis Lab Spring 2012 Lab 5.
Thevenin Equivalent and Maximum Power Transfer
NAME:____________________________ Date:______________________________ PRE-LABORATORY CALCULATIONS
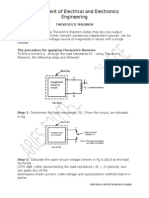
I.- Thevenins Theorem Thvenins Theorem is a process by which a complex circuit is reduced to an equivalent series circuit consisting of a single voltage source (VTH), a series resistance (RTH), and a load resistance (RL). After creating the Thvenin Equivalent Circuit, the load voltage VL or the load current IL may be easily determined. One of the main uses of Thvenins theorem is the replacement of a large part of a circuit, often a complicated and uninteresting part, by a very simple equivalent. The new simpler circuit enables us to make rapid calculations of the voltage, current, and power which the original circuit is able to deliver to a load. It also helps us to choose the best value of this load resistance for maximum power transfer. Thevenins Theorem states that a two terminal circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a voltage source, VTH, in series with a resistor, RTH, where VTH is the open-circuit voltage, VOC, at the terminals and RTH is equivalent to the resistance at the terminals when all independent sources are turned off.
Figure 1a) Simple circuit to be analyzed
Figure 1b) Thevenins equivalent of Fig. 1a)
1.- A simple Circuit. Determine the Thevenins equivalent of the circuit given in fig. 1a). Show all your calculations. VTH = __________ RTH = __________ a) For the simplified circuit in figure 1b), calculate the voltage, current, and power that will be supplied to the load resistor for a resistor value of RL = 100. b) Repeat a) for load values of: RL = 51 , 250 , 500 , and 1.5 k . Show below all your calculations.
EENG 2111 Circuit Analysis Lab Spring 2012 Lab 5. Thevenin Equivalent and Maximum Power Transfer
c) Using Matlab or Excel, plot VRL (vertical axis) vs RL (horizontal axis). d) Using Matlab or Excel, plot IRL (vertical axis) vs RL (horizontal axis). e) Using Matlab or Excel, plot PRL (vertical axis) vs RL (horizontal axis). f) Observe the three plots and write your observations. _______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 1A).- Repeat 1 using MultiSim to verify your results. Note: There is a measurement device in MultiSim to measure power. II.- Maximum Power Transfer Theorem states that an independent voltage source in series with a resistance RS delivers a maximum power to a load resistance RL for which RL = RS. In terms of a Thvenin Equivalent Circuit, maximum power is delivered to the load resistance RL when RL is equal to the Thvenin equivalent resistance RTH of the circuit. 2.- A More Complex Circuit Calculate the Thevenins equivalent for the circuit in fig. 2a). Consider the following values:
R1 = 270 , R2 = 560 , R3 = 560 , R4 = 300 , R5 = 820 , and VS = 15 V. For what value for RL the circuit will deliver maximum power ?. What will be this maximum power ? Show all your calculations in the space provided below.
Figure 2a) A more complex circuit to be analyzed
Fig. 2b) Thevenins equivalent of Fig. 2a)
VTH = _________ RTH = _________
RL (for max power transfer) = _______________ Maximum power delivered by the circuit = ____________________
EENG 2111 Circuit Analysis Lab Spring 2012 Lab 5. Thevenin Equivalent and Maximum Power Transfer
a) For the simplified circuit in figure 2b), calculate the voltage, current, and power that will be supplied to the load resistor for a load resistor value of RL = 100 . b) Repeat a) for load values of: RL = 51 , 250 , 500 , and 1.5 k. Show below all your calculations.
c) Using Matlab or Excel, plot VRL (vertical axis) vs RL (horizontal axis). d) Using Matlab or Excel, plot IRL (vertical axis) vs RL (horizontal axis). e) Using Matlab or Excel, plot PRL (vertical axis) vs RL (horizontal axis). f) Observe the three plots and write your observations. _______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 2A).- Repeat 2 using MultiSim to verify your results.
PreLab Verification: _________
EENG 2111 Circuit Analysis Lab Spring 2012 Lab 5. Thevenin Equivalent and Maximum Power Transfer
Experimental Verification of Thevenins Equivalent 1) Circuits in figures 1a) and 1b)
Determine by experimental procedure the Thevenin equivalent of the circuits in figure 1a) and 2a) . a) Build on the breadboard the original circuit [ fig. 1a)] b) Measure Voc, the open circuit voltage across terminals A-B (fig. 3a). Record this value in Table 1. c) Measure RTH by disconnecting the power supply Vs from the circuit and replacing it with a short circuit (a piece of wire). With the circuit in this configuration, measure the resistance across terminals A-B. Record this value in Table 1. d) Reconnect the power supply Vs and use the ammeter of your DMM to measure the short circuit current Isc for terminals A-B. To measure the short circuit current between two points use the ammeter (negligible resistance) to connect the two nodes being shorted (see Fig. 3b). Record this value in Table 1.
NOTE: BE SURE TO REMOVE ALL SHORTING WIRES MAKE SURE THAT THE POWER SUPPLY IS NOT DIRECTLY CONNECTED TO GROUND.
Figure 3a). Measuring the open circuit voltage, VOC
Figure 3b). Measuring the short circuit current, ISC
Measurement VTH = VA-B (open circuit) RTH = RA-B (power supply disconnected and shorted) Isc= IA-B (short circuit)
Measured Value
Calculated Value
% Difference
[(measure-calc) / calc]
Table 1. Experimental Results for fig 1a) e) Using results in Table 1, verify that RTH = VOC/ISC RTH = ________________
f)
For each circuit 1a) and 1b), measure the voltage, current, and calculate the power that is supplied to the load resistor for a load resistor value of RL = 51 , 100, 250 , 500 , and 1.5 k. Record your results in Table 2.
EENG 2111 Circuit Analysis Lab Spring 2012 Lab 5. Thevenin Equivalent and Maximum Power Transfer g) Using Matlab or Excel, plot PRL (vertical axis) vs RL (horizontal axis) using the PL values recorder in Table 2 (for both circuits 1a and 1b).
RL 51 100 250 500 1.5k
Circuit in Fig 1a) VL IL PL Measured Measured Calculated
Circuit in Fig 1b) VL PL IL Measured Calculated Measured
Table 2. Voltage and currents for different loads
2) Circuits in figures 2a) and 2b)
Repeat steps a) to g) for the circuits in figures 2a and 2b. Create similar Tables (Table 1 and 2) to report your results for the circuits in figure 2a and 2b.
Instructors Initials: _________
You might also like
- Lab E1 RLC Circuit 1Document11 pagesLab E1 RLC Circuit 1Ching Wai Yong100% (1)
- Electrolux Washing Machine Wiring Diagram Service Manual Error Code Circuit Schematic Schema Repair Instruction Guide User Manual Free PDF Download PDFDocument8 pagesElectrolux Washing Machine Wiring Diagram Service Manual Error Code Circuit Schematic Schema Repair Instruction Guide User Manual Free PDF Download PDFBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab Report-1 PDFDocument27 pagesVirtual Lab Report-1 PDFCarlton Lobo0% (1)
- Experiment 7 - 0 and 8 - 0Document7 pagesExperiment 7 - 0 and 8 - 0efecakir03No ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis and Design Manual FinalDocument65 pagesCircuit Analysis and Design Manual Finalصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- Ee-316 - Circuit Theory LabDocument47 pagesEe-316 - Circuit Theory LabsureshhasiniNo ratings yet
- Exp3 Sem2 Edit 0506Document9 pagesExp3 Sem2 Edit 0506shavin699100% (1)
- Verification Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer Theorem: Experiment No.3 DateDocument16 pagesVerification Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer Theorem: Experiment No.3 DateSachin DevarakondaNo ratings yet
- LAB3Document11 pagesLAB3RajuKumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:: Basic Electrical Engineering (Lab Manual)Document6 pagesExperiment No:: Basic Electrical Engineering (Lab Manual)Nayana JangleNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurDocument36 pagesDC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurMuhammed UmarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualDocument30 pagesElectrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualJigar SoniNo ratings yet
- BE.01.08 Series Resistive Circuits SHDocument12 pagesBE.01.08 Series Resistive Circuits SHleslynjdNo ratings yet
- IEC - Lab Exp 3Document12 pagesIEC - Lab Exp 3sazidmohsin456No ratings yet
- 3 Phase Full Wave Bridge ConverterDocument4 pages3 Phase Full Wave Bridge Convertersubhasishpodder100% (1)
- Circuit LabDocument7 pagesCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- Circuits Exp3Document4 pagesCircuits Exp3ilker.ozcelikkanNo ratings yet
- Thevenin's Theorem Lab: Voltage, VDocument3 pagesThevenin's Theorem Lab: Voltage, VMd Johurul IslamNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Document6 pagesCapacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Mr_asad_20No ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Document6 pagesDC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Ratul kumarNo ratings yet
- Exp 6Document12 pagesExp 6Laura AcaciaNo ratings yet
- Ge320 Lab2Document7 pagesGe320 Lab2hbuddyNo ratings yet
- Lab E1 RLC CircuitDocument11 pagesLab E1 RLC CircuitChing Wai Yong100% (1)
- Iec Lab Report 3Document12 pagesIec Lab Report 3mahrabhasanchowdhury1No ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document5 pagesExperiment 4mohammad alaliNo ratings yet
- ELEC331 Lab Experiment#1Document16 pagesELEC331 Lab Experiment#1DavidNo ratings yet
- QXGQ7QX9 Lab3Document4 pagesQXGQ7QX9 Lab3Emre SelviliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDocument152 pagesElectrical Machines Lab ManualMazoon ButtNo ratings yet
- 5.2 SuperpositionDocument6 pages5.2 SuperpositionObed Kojo Kumi-LarbiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- DC Exp 6 Student ManualDocument6 pagesDC Exp 6 Student ManualAsifur R. HimelNo ratings yet
- 3 Lab 3: DC Motor Transfer Function Estimation by Explicit MeasurementDocument9 pages3 Lab 3: DC Motor Transfer Function Estimation by Explicit MeasurementRogger MezaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Thevenin TheoremDocument8 pagesLab 3 - Thevenin TheoremminhtridtaNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics LabDocument59 pagesApplied Physics LabEngr Waqas MalikNo ratings yet
- Circuits and NetworksDocument23 pagesCircuits and NetworksDei PehNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument9 pagesAC CircuitsAli AdnanNo ratings yet
- Circuits Lab Report Expt. 8Document8 pagesCircuits Lab Report Expt. 8Harold FilomenoNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Document5 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- Ee 303 3Document3 pagesEe 303 3api-288751705No ratings yet
- Lab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCDocument5 pagesLab Handout - 10 Phase Shift Measurement Iof Series RLCAbdul QudoosNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Thevenin's & Norton's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferDocument5 pagesExperiment: Thevenin's & Norton's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferMunir Izkandaryan ZX'zNo ratings yet
- Kirchof'sDocument6 pagesKirchof'sMohamed EslamNo ratings yet
- Unti 4Document29 pagesUnti 4dhruvkareliya1004No ratings yet
- 9 Thevenin & Norton CircuitsDocument11 pages9 Thevenin & Norton CircuitsKhalidSa23No ratings yet
- Lab 6Document4 pagesLab 6yasir aliNo ratings yet
- Eee ManualDocument53 pagesEee ManualplsmcokNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument7 pagesDC CircuitsAmeer Bakry ZulkiffliNo ratings yet
- ENA Lab 9 Balanced Three-Phase Circuit (Software)Document12 pagesENA Lab 9 Balanced Three-Phase Circuit (Software)Mohammed Ahmad OsamaNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument9 pagesAC CircuitsAli AdnanNo ratings yet
- VOLTAGE & CURRENT DIVIDER and DELTA-WYE TRANSFORMATIONDocument10 pagesVOLTAGE & CURRENT DIVIDER and DELTA-WYE TRANSFORMATIONJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- American International University-Bangladesh: Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument4 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringRuham RofiqueNo ratings yet
- Exp11.Three Phase Full Wave Controlled ConvertersDocument4 pagesExp11.Three Phase Full Wave Controlled ConvertersJawad Rasheed SheikhNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2Document6 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2THE LEARNER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document6 pagesExp 3moha amroNo ratings yet
- 409064607103/virtualeducation/27597/contenidos/45970/LAB THEVENIN THEOREMDocument4 pages409064607103/virtualeducation/27597/contenidos/45970/LAB THEVENIN THEOREMJonathan David Campos JimenezNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Review of Norton'S Theorem and Jfet Biasing Pre-Lab InstructionsDocument8 pagesExperiment: Review of Norton'S Theorem and Jfet Biasing Pre-Lab InstructionsHamid AssadullahNo ratings yet
- Thevenins Theorem (Laboratory 7)Document5 pagesThevenins Theorem (Laboratory 7)Chooster TheScrosNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- RZ 05 - EE394J - 2 - Spring11 - Phasor - Time - Domain - PlotsDocument1 pageRZ 05 - EE394J - 2 - Spring11 - Phasor - Time - Domain - PlotsBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Z-Base Case. One Circuit Per Corridor. Y Matrix Analysis.: What Planning Can You Do With Y Matrix?Document2 pagesZ-Base Case. One Circuit Per Corridor. Y Matrix Analysis.: What Planning Can You Do With Y Matrix?Brett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Voltage Source Battery ResistanceDocument1 pageVoltage Source Battery ResistanceBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Z-Voltage Stability AnalysisDocument1 pageZ-Voltage Stability AnalysisBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Yt-Calculation and Experimental Checking of Fault Currents in The Medium-Voltage Distribution Network of Omiš As The Basis For Tuning of Numerical ProtectionDocument1 pageYt-Calculation and Experimental Checking of Fault Currents in The Medium-Voltage Distribution Network of Omiš As The Basis For Tuning of Numerical ProtectionBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- R.Z.-400kV 400kV Rishikesh Line Protection: D) RXEG - 27P - Under Voltage Protection RelayDocument1 pageR.Z.-400kV 400kV Rishikesh Line Protection: D) RXEG - 27P - Under Voltage Protection RelayBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Power To The DeltaDocument1 pagePower To The DeltaBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Zhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoDocument4 pagesZhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Proj. E. I 17 Selecting The Right RCDDocument1 pageProj. E. I 17 Selecting The Right RCDBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Negative Sequence Currents For Generators Connected To 345-kV Asymmetrical Transmission Lines From Measurement DataDocument10 pagesAssessment of Negative Sequence Currents For Generators Connected To 345-kV Asymmetrical Transmission Lines From Measurement DataBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Meeting CMTDocument1 pageMeeting CMTBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Powercad UputeDocument74 pagesPowercad UputeElmir Huseinbasic100% (1)
- PSDC Ex1 HydroTurbine PDFDocument8 pagesPSDC Ex1 HydroTurbine PDFBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Akademija Za Menadžment: Nastava Po Britanskim Standardima. Upišite Se Odmah. Promotivna Cena!Document8 pagesAkademija Za Menadžment: Nastava Po Britanskim Standardima. Upišite Se Odmah. Promotivna Cena!Brett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Hire Fleet CableDocument2 pagesHire Fleet CableBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Settings Overviewtext Title: ! (CdataDocument3 pagesSettings Overviewtext Title: ! (CdataBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Xenon Ps PDFDocument5 pagesXenon Ps PDFBrett HendricksNo ratings yet
- Zhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoDocument4 pagesZhejiang Ghorit Electrial Equipment CoBrett HendricksNo ratings yet