Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Remain in Its State of Rest or of Uniform Motion in A Straight Line
Remain in Its State of Rest or of Uniform Motion in A Straight Line
Uploaded by
Amalina SulaimanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyDocument13 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyMingNo ratings yet
- AADE 03 NTCE 35 PowerDocument9 pagesAADE 03 NTCE 35 PowerAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Borgnakke SonntagDocument215 pagesChapter 10 Borgnakke SonntagAmalina Sulaiman67% (3)
- Mass and InertiaDocument4 pagesMass and InertiaRishwin Singh SindaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)Document14 pagesLecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)verboseNo ratings yet
- Inertia and Mass: Newton's Laws NameDocument11 pagesInertia and Mass: Newton's Laws NameAlexander Van TilNo ratings yet
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDocument15 pagesNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityDocument26 pagesPhysics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityMiranda Febriani TanjungNo ratings yet
- Phy - NLM PDFDocument48 pagesPhy - NLM PDFKushagraNo ratings yet
- Mass and Inertia: Top - NextDocument4 pagesMass and Inertia: Top - NextPeter Lau NTNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics 1 - Newtons LawsDocument7 pagesAp Physics 1 - Newtons Lawsapi-293989776No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Aminudin Zakaria 20030184031Document2 pagesAssignment 1 Aminudin Zakaria 20030184031031Aminudin ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document74 pagesChapter 3Thalagawali RajagopalNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Newtl W AnswersDocument13 pagesCH 3 Newtl W AnswersKatlin CallahanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Document92 pagesTopic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Byron JimenezNo ratings yet
- Physics PathwaysDocument4 pagesPhysics PathwaysAdaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 A Newton's Laws of Motion: WS 5-U1-CH-1A7 Year 12 PhysicsDocument9 pagesChapter 1 A Newton's Laws of Motion: WS 5-U1-CH-1A7 Year 12 PhysicsSanjanaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument2 pagesNewton's Law of MotionKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Phys11 SM 03 2Document4 pagesPhys11 SM 03 2Elizabeth MeghaNo ratings yet
- Newtons First LawDocument1 pageNewtons First LawhlvijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Physics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawsDocument40 pagesPhysics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawssosatukiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- LM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1Document53 pagesLM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Primera Ley de Newton1Document9 pagesPrimera Ley de Newton1MelanieNo ratings yet
- N ' L M I: Ewton S Aws of OtionDocument8 pagesN ' L M I: Ewton S Aws of OtionSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- Physics_QADocument2 pagesPhysics_QAa.rohith1994No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument14 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionapi-325945020No ratings yet
- 3rd Week - Forces and Newton LawsDocument27 pages3rd Week - Forces and Newton LawsDoddy HardhienataNo ratings yet
- RH 7 LNG 5 eDocument47 pagesRH 7 LNG 5 euniathleisuresgNo ratings yet
- CLASS XI Laws of MotionDocument86 pagesCLASS XI Laws of MotionSanketNo ratings yet
- Physics Kinetics 3Document51 pagesPhysics Kinetics 3Hnz CodiNo ratings yet
- PHY01 - Course Outcome 2Document27 pagesPHY01 - Course Outcome 2April Anne LacroNo ratings yet
- The Centrifugal Force ParadoxDocument4 pagesThe Centrifugal Force ParadoxFrederick David TombeNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law in Motion1Document7 pagesNewton's Law in Motion1Chan LieslNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Forces-1Document46 pagesLesson 6 Forces-1bloomNo ratings yet
- Chap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceDocument32 pagesChap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceFranco FrecheroNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument11 pagesDynamicsBLESSIE ARCENIO0% (1)
- Phy 9th Unit 3Document4 pagesPhy 9th Unit 3Mohammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lec NewtonDocument40 pagesChapter 4 Lec Newtonsmcm11No ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument7 pagesLaws of MotionJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document104 pagesChapter 4William BoutrosNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument31 pagesNewton's Law of MotionIzzul SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Flip Chart-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageFlip Chart-WPS OfficeLinel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion: Law of Inertia and Law of AccelerationDocument4 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion: Law of Inertia and Law of AccelerationEileen NagaNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument8 pagesForce and MotionForsythe LearningNo ratings yet
- 17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionDocument18 pages17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionVicky Fortuna OliverosNo ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three Laws of MotionDocument28 pagesNewton's Three Laws of MotionDan Luigi TipactipacNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 pagesمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three (3) Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesNewton's Three (3) Laws of MotionCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- Ilm 1 ForceDocument3 pagesIlm 1 ForcehannaleigmactalNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q1-W2 - ForceDocument30 pagesScience 8 - Q1-W2 - Forcesteph ebonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Newton's Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesChapter 4. Newton's Laws of MotionBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- Inertia - Sci 8Document9 pagesInertia - Sci 8Ortigas Aileen Grace100% (1)
- 3 - DynamicsDocument2 pages3 - DynamicsStephen CamsolNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: 1 ForceDocument5 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: 1 ForceCharl CuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Newtons Law-FDocument67 pagesChapter Two - Newtons Law-Fnajjar119No ratings yet
- Week 6-8 Laws of MotionDocument56 pagesWeek 6-8 Laws of MotionangelicaelagunoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsDocument47 pagesLecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsThea MNo ratings yet
- Fisika Teknik Bab 4 PDFDocument31 pagesFisika Teknik Bab 4 PDFedo saputraNo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis in Commdity Markets Risk ReturnnnDocument21 pagesTechnical Analysis in Commdity Markets Risk ReturnnnAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Pin Diameter (MM) Pin Diameter (Pixel) FactorDocument2 pagesPin Diameter (MM) Pin Diameter (Pixel) FactorAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning NumpyDocument39 pagesMachine Learning NumpyAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Kus PreparationDocument3 pagesKus PreparationAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Geology 3153: Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Guide To Using Past ExamsDocument1 pageGeology 3153: Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Guide To Using Past ExamsAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Mind-5 Times Katam - Cara2 Solat - Mantapkan Aqidah - Like Facebook Agama - A - As - DD - FF - Ss - QQ - 33Document1 pageSpiritual Mind-5 Times Katam - Cara2 Solat - Mantapkan Aqidah - Like Facebook Agama - A - As - DD - FF - Ss - QQ - 33Amalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document9 pagesHW 1Amalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Math Lab: Mondays - Thursdays, 2:00-6:00 PM, KEP 379Document1 pageMath Lab: Mondays - Thursdays, 2:00-6:00 PM, KEP 379Amalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Effects of A Novel Compound On Fungal ContaminationDocument30 pagesEffects of A Novel Compound On Fungal ContaminationAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- HW#5-Solutions: Steven Tipton: The University of TulsaDocument10 pagesHW#5-Solutions: Steven Tipton: The University of TulsaAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Patrick Ahern-Informative Nature vs. NurtureDocument4 pagesPatrick Ahern-Informative Nature vs. NurtureAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
Remain in Its State of Rest or of Uniform Motion in A Straight Line
Remain in Its State of Rest or of Uniform Motion in A Straight Line
Uploaded by
Amalina SulaimanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Remain in Its State of Rest or of Uniform Motion in A Straight Line
Remain in Its State of Rest or of Uniform Motion in A Straight Line
Uploaded by
Amalina SulaimanCopyright:
Available Formats
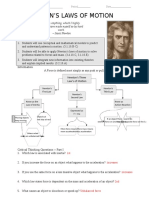
Physics Form 4: Chapter 2 - Newton First Law of Motion (Inertia)
Inertia is the tendency of an object to remain in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line. Law of inertia is also known as Newton's First Law of Motion Newton's First Law of Motion state that an object will in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless it is acted upon by a net external force.
Examples of effect of inertia:
When the cardboard is jerked quickly, the coin will fall into the glass. Explanation: The inertia of the coin resists the change of its initial state, which is stationary. As a result, the coin does not move with the cardboard and falls into the glass because of gravity.
Pull slowly - Thread A will snap.
Explanation:
Tension of thread A is higher than string B. Tension at A = Weight of the load + Pulling Force
Yank quickly - Thread B will snap.
Explanation: The inertia of the load prevents the force from being transmitted to thread A, hence causing thread B to snap.
You might also like
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyDocument13 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyMingNo ratings yet
- AADE 03 NTCE 35 PowerDocument9 pagesAADE 03 NTCE 35 PowerAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Borgnakke SonntagDocument215 pagesChapter 10 Borgnakke SonntagAmalina Sulaiman67% (3)
- Mass and InertiaDocument4 pagesMass and InertiaRishwin Singh SindaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)Document14 pagesLecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)verboseNo ratings yet
- Inertia and Mass: Newton's Laws NameDocument11 pagesInertia and Mass: Newton's Laws NameAlexander Van TilNo ratings yet
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDocument15 pagesNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityDocument26 pagesPhysics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityMiranda Febriani TanjungNo ratings yet
- Phy - NLM PDFDocument48 pagesPhy - NLM PDFKushagraNo ratings yet
- Mass and Inertia: Top - NextDocument4 pagesMass and Inertia: Top - NextPeter Lau NTNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics 1 - Newtons LawsDocument7 pagesAp Physics 1 - Newtons Lawsapi-293989776No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Aminudin Zakaria 20030184031Document2 pagesAssignment 1 Aminudin Zakaria 20030184031031Aminudin ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document74 pagesChapter 3Thalagawali RajagopalNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Newtl W AnswersDocument13 pagesCH 3 Newtl W AnswersKatlin CallahanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Document92 pagesTopic 2 Mechanics Part 2 2015-17Byron JimenezNo ratings yet
- Physics PathwaysDocument4 pagesPhysics PathwaysAdaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 A Newton's Laws of Motion: WS 5-U1-CH-1A7 Year 12 PhysicsDocument9 pagesChapter 1 A Newton's Laws of Motion: WS 5-U1-CH-1A7 Year 12 PhysicsSanjanaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument2 pagesNewton's Law of MotionKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Phys11 SM 03 2Document4 pagesPhys11 SM 03 2Elizabeth MeghaNo ratings yet
- Newtons First LawDocument1 pageNewtons First LawhlvijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Physics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawsDocument40 pagesPhysics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawssosatukiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- LM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1Document53 pagesLM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Primera Ley de Newton1Document9 pagesPrimera Ley de Newton1MelanieNo ratings yet
- N ' L M I: Ewton S Aws of OtionDocument8 pagesN ' L M I: Ewton S Aws of OtionSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- Physics_QADocument2 pagesPhysics_QAa.rohith1994No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument14 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionapi-325945020No ratings yet
- 3rd Week - Forces and Newton LawsDocument27 pages3rd Week - Forces and Newton LawsDoddy HardhienataNo ratings yet
- RH 7 LNG 5 eDocument47 pagesRH 7 LNG 5 euniathleisuresgNo ratings yet
- CLASS XI Laws of MotionDocument86 pagesCLASS XI Laws of MotionSanketNo ratings yet
- Physics Kinetics 3Document51 pagesPhysics Kinetics 3Hnz CodiNo ratings yet
- PHY01 - Course Outcome 2Document27 pagesPHY01 - Course Outcome 2April Anne LacroNo ratings yet
- The Centrifugal Force ParadoxDocument4 pagesThe Centrifugal Force ParadoxFrederick David TombeNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law in Motion1Document7 pagesNewton's Law in Motion1Chan LieslNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Forces-1Document46 pagesLesson 6 Forces-1bloomNo ratings yet
- Chap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceDocument32 pagesChap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceFranco FrecheroNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument11 pagesDynamicsBLESSIE ARCENIO0% (1)
- Phy 9th Unit 3Document4 pagesPhy 9th Unit 3Mohammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lec NewtonDocument40 pagesChapter 4 Lec Newtonsmcm11No ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument7 pagesLaws of MotionJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document104 pagesChapter 4William BoutrosNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument31 pagesNewton's Law of MotionIzzul SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Flip Chart-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageFlip Chart-WPS OfficeLinel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion: Law of Inertia and Law of AccelerationDocument4 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion: Law of Inertia and Law of AccelerationEileen NagaNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument8 pagesForce and MotionForsythe LearningNo ratings yet
- 17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionDocument18 pages17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionVicky Fortuna OliverosNo ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three Laws of MotionDocument28 pagesNewton's Three Laws of MotionDan Luigi TipactipacNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 pagesمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiNo ratings yet
- Newton's Three (3) Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesNewton's Three (3) Laws of MotionCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- Ilm 1 ForceDocument3 pagesIlm 1 ForcehannaleigmactalNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q1-W2 - ForceDocument30 pagesScience 8 - Q1-W2 - Forcesteph ebonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Newton's Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesChapter 4. Newton's Laws of MotionBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- Inertia - Sci 8Document9 pagesInertia - Sci 8Ortigas Aileen Grace100% (1)
- 3 - DynamicsDocument2 pages3 - DynamicsStephen CamsolNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: 1 ForceDocument5 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: 1 ForceCharl CuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Newtons Law-FDocument67 pagesChapter Two - Newtons Law-Fnajjar119No ratings yet
- Week 6-8 Laws of MotionDocument56 pagesWeek 6-8 Laws of MotionangelicaelagunoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsDocument47 pagesLecture 3 Forces and Newton - S LawsThea MNo ratings yet
- Fisika Teknik Bab 4 PDFDocument31 pagesFisika Teknik Bab 4 PDFedo saputraNo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis in Commdity Markets Risk ReturnnnDocument21 pagesTechnical Analysis in Commdity Markets Risk ReturnnnAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Pin Diameter (MM) Pin Diameter (Pixel) FactorDocument2 pagesPin Diameter (MM) Pin Diameter (Pixel) FactorAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning NumpyDocument39 pagesMachine Learning NumpyAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Kus PreparationDocument3 pagesKus PreparationAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Geology 3153: Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Guide To Using Past ExamsDocument1 pageGeology 3153: Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Guide To Using Past ExamsAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Mind-5 Times Katam - Cara2 Solat - Mantapkan Aqidah - Like Facebook Agama - A - As - DD - FF - Ss - QQ - 33Document1 pageSpiritual Mind-5 Times Katam - Cara2 Solat - Mantapkan Aqidah - Like Facebook Agama - A - As - DD - FF - Ss - QQ - 33Amalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document9 pagesHW 1Amalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Math Lab: Mondays - Thursdays, 2:00-6:00 PM, KEP 379Document1 pageMath Lab: Mondays - Thursdays, 2:00-6:00 PM, KEP 379Amalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Effects of A Novel Compound On Fungal ContaminationDocument30 pagesEffects of A Novel Compound On Fungal ContaminationAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- HW#5-Solutions: Steven Tipton: The University of TulsaDocument10 pagesHW#5-Solutions: Steven Tipton: The University of TulsaAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Patrick Ahern-Informative Nature vs. NurtureDocument4 pagesPatrick Ahern-Informative Nature vs. NurtureAmalina SulaimanNo ratings yet