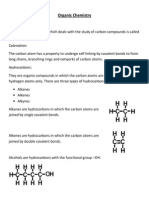
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid Hydrazides From Esters Methyl - 3nitrobenzoate-1
Acid Hydrazides From Esters Methyl - 3nitrobenzoate-1
Uploaded by
Chu Thi Hien ThuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Talk Time 1 PDFDocument98 pagesTalk Time 1 PDFSanae Ihsane100% (9)
- Production of AcetaldehydeDocument24 pagesProduction of AcetaldehydeAhmed Hassan RashedNo ratings yet
- Mono Methyl at IonDocument15 pagesMono Methyl at Ionlocolocolocoxoxo100% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- MicroGrid II User ManualDocument162 pagesMicroGrid II User ManualChu Thi Hien Thu100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Made SimpleDocument411 pagesOrganic Chemistry Made SimpleFarooq Muhammad88% (24)
- Production of HydrazineDocument5 pagesProduction of Hydrazineحيدر الجغمنيNo ratings yet
- 0304 S1 Abs PDFDocument7 pages0304 S1 Abs PDFFajar RumantoNo ratings yet
- Acetic AcidDocument4 pagesAcetic AcidMohit YaduwanshiNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsDocument55 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsMaria AGNo ratings yet
- Acetaldehyde Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument6 pagesAcetaldehyde Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811100% (3)
- Aldehydes and Ketones FinalDocument67 pagesAldehydes and Ketones FinalAnil Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Role of Acids in The Degradation of Alkanolamine During Co2Document7 pagesRole of Acids in The Degradation of Alkanolamine During Co2cargscribNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document52 pagesChapter 21Seung Eun KimNo ratings yet
- GO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesGO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidcikaifaNo ratings yet
- OXIDATIONDocument36 pagesOXIDATIONMansab AliNo ratings yet
- ALDEHYSES (Autosaved)Document46 pagesALDEHYSES (Autosaved)az713511No ratings yet
- Paten Basf Asam AsetatDocument2 pagesPaten Basf Asam Asetatwilliam fathNo ratings yet
- Surge Tank: Gas Sweetening ProcessesDocument5 pagesSurge Tank: Gas Sweetening ProcessesAjaykumarNo ratings yet
- AldolDocument7 pagesAldolGindo Baroes WanNo ratings yet
- Esters EtcDocument8 pagesEsters EtcBoobalan Maria SusaiNo ratings yet
- PPDDocument79 pagesPPDEddie ChangNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2 PDFDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 PDFEnica RichardNo ratings yet
- Industerial Chemistry Lecture 2Document37 pagesIndusterial Chemistry Lecture 2amirmisrNo ratings yet
- HCNDocument12 pagesHCNAsriNovitaSariJuremiNo ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument17 pagesAmmoniaMubarak Ahmad100% (1)
- Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones, To: (1) Clemmsens MethodDocument9 pagesReduction of Aldehydes, Ketones, To: (1) Clemmsens MethodHawra JawadNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ManufacturingDocument16 pagesAmmonia ManufacturingMuhammad Irfan MalikNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives NotesDocument45 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives NotesAtirahSakinahNo ratings yet
- Acrylic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument8 pagesAcrylic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Us2438259 PDFDocument3 pagesUs2438259 PDFDakota EllisonNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarDocument53 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarPaul Jhon EugenioNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia Via Steam Reforming of Natural GasDocument1 pageProduction of Ammonia Via Steam Reforming of Natural Gasvaratharajan g rNo ratings yet
- Receipe For MethylamineDocument3 pagesReceipe For MethylamineCharles Sullivan100% (1)
- UreaDocument19 pagesUreakrit138No ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisecse.220840131017No ratings yet
- Ether and AldehydeDocument112 pagesEther and Aldehydejhapindra adhikariNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesAldehydes and Ketonesnvmohankumar85No ratings yet
- US2542315Document6 pagesUS2542315Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Urea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceDocument18 pagesUrea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceAdam RizkyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Methods: 1. Methanol Carbonylation 2. Acetaldehyde Oxidation 3. Ethylene Oxidation 4. Anerobic FermentationDocument39 pagesManufacturing Methods: 1. Methanol Carbonylation 2. Acetaldehyde Oxidation 3. Ethylene Oxidation 4. Anerobic Fermentationkumari svgNo ratings yet
- Acrylic Acid - MohitDocument42 pagesAcrylic Acid - MohitvickuNo ratings yet
- Environmental 52 Assignment 2Document10 pagesEnvironmental 52 Assignment 2Fiesta LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Chem - Expt 10Document4 pagesChem - Expt 10Mirzi TurbolenciaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones-1 PDF ChemicalDocument32 pagesAldehydes and Ketones-1 PDF ChemicalSaeed UrrehmanNo ratings yet
- Químicos Basados en El MetanoDocument22 pagesQuímicos Basados en El MetanoArianna PadillaNo ratings yet
- Acetaldehyde 16.05.2020Document3 pagesAcetaldehyde 16.05.2020sathiya sathiyaNo ratings yet
- Formulation of Ketones, Reaction With Organocopper Compounds. Discussed in Sec 18.6Document3 pagesFormulation of Ketones, Reaction With Organocopper Compounds. Discussed in Sec 18.6Rizka Hannum LubisNo ratings yet
- 2-Preparation of Aldehyde and KetonesDocument21 pages2-Preparation of Aldehyde and Ketonesapi-336924036No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsDocument39 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsashathtNo ratings yet
- AmidesDocument20 pagesAmidessafiabarkat5No ratings yet
- Notes PharmaDocument24 pagesNotes Pharmashubhyog PawarNo ratings yet
- Exp 18Document8 pagesExp 18nicolef_20No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Group: Shahzad KhanDocument45 pagesCarbonyl Group: Shahzad KhanShahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: Patented Feb. 6, 1951Document2 pagesUnited States Patent: Patented Feb. 6, 1951Rian Pratama AkbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document52 pagesChapter 21aggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- Acetaldehyde Report - Final PDFDocument20 pagesAcetaldehyde Report - Final PDFDinesh guhanNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 1Document63 pages06 Chapter 1Dintakurthi PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Amines Via Hofmann, Curtius, Schmidt, and Lossen - Comprehensive Organic Synthesis PDFDocument34 pagesAmines Via Hofmann, Curtius, Schmidt, and Lossen - Comprehensive Organic Synthesis PDFpcube100% (1)
- Preparation of Methylene Chloride (Greene 1879)Document2 pagesPreparation of Methylene Chloride (Greene 1879)j9cr4zrdxxNo ratings yet
- Hydroformylation: Fundamentals, Processes, and Applications in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandHydroformylation: Fundamentals, Processes, and Applications in Organic SynthesisNo ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- Bio-Based SolventsFrom EverandBio-Based SolventsFrançois JérômeNo ratings yet
- Chimie GB 2013 FinalDocument11 pagesChimie GB 2013 FinalChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- International Selection: Physics (Minors) : Exercise 1: Ideal GasDocument3 pagesInternational Selection: Physics (Minors) : Exercise 1: Ideal GasChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- ForensicSerology PDFDocument4 pagesForensicSerology PDFChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Genetics: Session 2013 Selection InternationaleDocument4 pagesCell Biology and Genetics: Session 2013 Selection InternationaleChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Crosslinking Reagents Handbook PDFDocument56 pagesCrosslinking Reagents Handbook PDFChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Physics: Semiconductors and Band TheoryDocument23 pagesPhysics: Semiconductors and Band TheoryChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Broad Specificity Profiling of Talens Results in Engineered Nucleases With Improved Dna-Cleavage SpecificityDocument9 pagesBroad Specificity Profiling of Talens Results in Engineered Nucleases With Improved Dna-Cleavage SpecificityChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
Acid Hydrazides From Esters Methyl - 3nitrobenzoate-1
Acid Hydrazides From Esters Methyl - 3nitrobenzoate-1
Uploaded by
Chu Thi Hien ThuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Hydrazides From Esters Methyl - 3nitrobenzoate-1
Acid Hydrazides From Esters Methyl - 3nitrobenzoate-1
Uploaded by
Chu Thi Hien ThuCopyright:
Available Formats
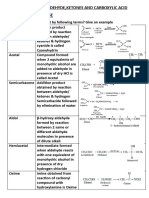
Amide and Acid hydrazides from Esters
Amides cannot be easily prepared by the direct reaction of ammonia or amines withcarboxylic acids because amines function as bases to convert carboxylic acids into their unreactive ammonium carboxylate salts. Although these salts may beconverted into amides by heating to high temperatures (200 C), the forcing natureof these conditions severely limits the applicability of this method.
Amore general method for preparing amides involves a two-step procedure in which the carboxylic acid is first converted to an acid chloride that is then treated with an amine to give the desired amide according to following equation. Acid chlorides are among the most reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids and thus are often used to prepare other organic compounds having an acyl group, including esters and aryl alkyl ketones.
Methyl and ethyl esters react with hydrazine to giveacid hydrazides: RCO2Me + H2NNH2 RCONHNH2 + MeOH The hydrazides are often crystalline and then serve as useful derivatives. Estersof higher alcohols should be converted first to the methyl esters by boiling withsodium methoxide in methanol or ethanol.
Procedure for the preparation of 3-nitrobenzoic acid hydrazide
Methyl 3-nitrobenzoate ester (7 g, 0.041 mol) was dissolved in absolute ethanol (40 mL) and takenin a flask fitted with a reflux condenser. Hydrazine hydrate (80%,13 mL) was added, and then, the reaction mixture was refluxed for 4 hours. The reflux time could be monitored by TLC. After the completion of the reaction, the excess hydrazine and ethanol solvent were distilled off by simple distillation. The crude solid of acid hydrazide was collected, washed with water and recrystallized from 50% aqueous ethanol.Yield 90%, m.p. 152155C.
You might also like
- Talk Time 1 PDFDocument98 pagesTalk Time 1 PDFSanae Ihsane100% (9)
- Production of AcetaldehydeDocument24 pagesProduction of AcetaldehydeAhmed Hassan RashedNo ratings yet
- Mono Methyl at IonDocument15 pagesMono Methyl at Ionlocolocolocoxoxo100% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- MicroGrid II User ManualDocument162 pagesMicroGrid II User ManualChu Thi Hien Thu100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Made SimpleDocument411 pagesOrganic Chemistry Made SimpleFarooq Muhammad88% (24)
- Production of HydrazineDocument5 pagesProduction of Hydrazineحيدر الجغمنيNo ratings yet
- 0304 S1 Abs PDFDocument7 pages0304 S1 Abs PDFFajar RumantoNo ratings yet
- Acetic AcidDocument4 pagesAcetic AcidMohit YaduwanshiNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsDocument55 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ReactionsMaria AGNo ratings yet
- Acetaldehyde Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument6 pagesAcetaldehyde Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811100% (3)
- Aldehydes and Ketones FinalDocument67 pagesAldehydes and Ketones FinalAnil Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Role of Acids in The Degradation of Alkanolamine During Co2Document7 pagesRole of Acids in The Degradation of Alkanolamine During Co2cargscribNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document52 pagesChapter 21Seung Eun KimNo ratings yet
- GO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesGO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidcikaifaNo ratings yet
- OXIDATIONDocument36 pagesOXIDATIONMansab AliNo ratings yet
- ALDEHYSES (Autosaved)Document46 pagesALDEHYSES (Autosaved)az713511No ratings yet
- Paten Basf Asam AsetatDocument2 pagesPaten Basf Asam Asetatwilliam fathNo ratings yet
- Surge Tank: Gas Sweetening ProcessesDocument5 pagesSurge Tank: Gas Sweetening ProcessesAjaykumarNo ratings yet
- AldolDocument7 pagesAldolGindo Baroes WanNo ratings yet
- Esters EtcDocument8 pagesEsters EtcBoobalan Maria SusaiNo ratings yet
- PPDDocument79 pagesPPDEddie ChangNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2 PDFDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 PDFEnica RichardNo ratings yet
- Industerial Chemistry Lecture 2Document37 pagesIndusterial Chemistry Lecture 2amirmisrNo ratings yet
- HCNDocument12 pagesHCNAsriNovitaSariJuremiNo ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument17 pagesAmmoniaMubarak Ahmad100% (1)
- Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones, To: (1) Clemmsens MethodDocument9 pagesReduction of Aldehydes, Ketones, To: (1) Clemmsens MethodHawra JawadNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ManufacturingDocument16 pagesAmmonia ManufacturingMuhammad Irfan MalikNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives NotesDocument45 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives NotesAtirahSakinahNo ratings yet
- Acrylic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument8 pagesAcrylic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Us2438259 PDFDocument3 pagesUs2438259 PDFDakota EllisonNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarDocument53 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarPaul Jhon EugenioNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia Via Steam Reforming of Natural GasDocument1 pageProduction of Ammonia Via Steam Reforming of Natural Gasvaratharajan g rNo ratings yet
- Receipe For MethylamineDocument3 pagesReceipe For MethylamineCharles Sullivan100% (1)
- UreaDocument19 pagesUreakrit138No ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisecse.220840131017No ratings yet
- Ether and AldehydeDocument112 pagesEther and Aldehydejhapindra adhikariNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument4 pagesAldehydes and Ketonesnvmohankumar85No ratings yet
- US2542315Document6 pagesUS2542315Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Urea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceDocument18 pagesUrea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceAdam RizkyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Methods: 1. Methanol Carbonylation 2. Acetaldehyde Oxidation 3. Ethylene Oxidation 4. Anerobic FermentationDocument39 pagesManufacturing Methods: 1. Methanol Carbonylation 2. Acetaldehyde Oxidation 3. Ethylene Oxidation 4. Anerobic Fermentationkumari svgNo ratings yet
- Acrylic Acid - MohitDocument42 pagesAcrylic Acid - MohitvickuNo ratings yet
- Environmental 52 Assignment 2Document10 pagesEnvironmental 52 Assignment 2Fiesta LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Chem - Expt 10Document4 pagesChem - Expt 10Mirzi TurbolenciaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones-1 PDF ChemicalDocument32 pagesAldehydes and Ketones-1 PDF ChemicalSaeed UrrehmanNo ratings yet
- Químicos Basados en El MetanoDocument22 pagesQuímicos Basados en El MetanoArianna PadillaNo ratings yet
- Acetaldehyde 16.05.2020Document3 pagesAcetaldehyde 16.05.2020sathiya sathiyaNo ratings yet
- Formulation of Ketones, Reaction With Organocopper Compounds. Discussed in Sec 18.6Document3 pagesFormulation of Ketones, Reaction With Organocopper Compounds. Discussed in Sec 18.6Rizka Hannum LubisNo ratings yet
- 2-Preparation of Aldehyde and KetonesDocument21 pages2-Preparation of Aldehyde and Ketonesapi-336924036No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsDocument39 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsashathtNo ratings yet
- AmidesDocument20 pagesAmidessafiabarkat5No ratings yet
- Notes PharmaDocument24 pagesNotes Pharmashubhyog PawarNo ratings yet
- Exp 18Document8 pagesExp 18nicolef_20No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Group: Shahzad KhanDocument45 pagesCarbonyl Group: Shahzad KhanShahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: Patented Feb. 6, 1951Document2 pagesUnited States Patent: Patented Feb. 6, 1951Rian Pratama AkbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document52 pagesChapter 21aggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- Acetaldehyde Report - Final PDFDocument20 pagesAcetaldehyde Report - Final PDFDinesh guhanNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 1Document63 pages06 Chapter 1Dintakurthi PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Amines Via Hofmann, Curtius, Schmidt, and Lossen - Comprehensive Organic Synthesis PDFDocument34 pagesAmines Via Hofmann, Curtius, Schmidt, and Lossen - Comprehensive Organic Synthesis PDFpcube100% (1)
- Preparation of Methylene Chloride (Greene 1879)Document2 pagesPreparation of Methylene Chloride (Greene 1879)j9cr4zrdxxNo ratings yet
- Hydroformylation: Fundamentals, Processes, and Applications in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandHydroformylation: Fundamentals, Processes, and Applications in Organic SynthesisNo ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- Bio-Based SolventsFrom EverandBio-Based SolventsFrançois JérômeNo ratings yet
- Chimie GB 2013 FinalDocument11 pagesChimie GB 2013 FinalChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- International Selection: Physics (Minors) : Exercise 1: Ideal GasDocument3 pagesInternational Selection: Physics (Minors) : Exercise 1: Ideal GasChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- ForensicSerology PDFDocument4 pagesForensicSerology PDFChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology and Genetics: Session 2013 Selection InternationaleDocument4 pagesCell Biology and Genetics: Session 2013 Selection InternationaleChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Crosslinking Reagents Handbook PDFDocument56 pagesCrosslinking Reagents Handbook PDFChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Physics: Semiconductors and Band TheoryDocument23 pagesPhysics: Semiconductors and Band TheoryChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet
- Broad Specificity Profiling of Talens Results in Engineered Nucleases With Improved Dna-Cleavage SpecificityDocument9 pagesBroad Specificity Profiling of Talens Results in Engineered Nucleases With Improved Dna-Cleavage SpecificityChu Thi Hien ThuNo ratings yet