Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3-Phase Dual Converter Drives
3-Phase Dual Converter Drives
Uploaded by
Anb BajwaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3-Phase Dual Converter Drives
3-Phase Dual Converter Drives
Uploaded by
Anb BajwaCopyright:
Available Formats
4-8
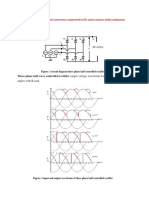
Three Phase Dual Converters (H.Rashid):
In many variable speed drives, the four quadrant operation is required and 3- dual converters are extensively used in applications up to the 2000 kw levels.
Fig (4-10 a) shows three phase dual converter, where two 3- converters are connected back to back. As due to the instantaneous voltage differences between the output voltages of converters, a circulating current flows through the converters (as already described in single phase dual converters).
The circulating current is normally limited by circulating reactor L r.
The two converters are controlled in such a way that if delay angle of converter 2 is
is the delay angle of converter 1, then the
Fig (4-10b) shows the waveforms for input voltage, output voltages and the voltage across inductor L r.
The operation of each converter is exactly similar to that of three phase full converter.
During the period (
) t(
) , the line to line voltage
appears across the
output of converter 1 and voltage
appears across the output of converter 2.
If the three line-neutral voltages are defined as; =V =V =V
m
sin t sin ( t ( sin ( t + ( )) ))
The corresponding line-to-line voltages are; = = = Where V
m
= = =
V V V
sin ( t + ( )) sin ( t ( )) sin ( t + ( ))
is the peak phase voltage of Wye-connected source.
If & are the output voltages of the converters 1 & converter 2 then; the instantaneous Voltage across the inductor during interval ( ) t( ) is obtained as; Vr= =>
=> =>
( (
( ) ( )
sin ( t ( )
Sin ( t ( )] - - - - - - - - - - - (4-63)
=>
( )]
The circulating current can be found from;
I r (t) = ( => (
) ( ) (
)
) ( ( )] ( )
=>
)[sin (
( )]
sin
- - - - - - - - - - - (4-64)
The circulating current depends on delay angle and on inductance L r. This current is maximum when t = ( ) and
= 0.
Such converters would be continuously running due the circulating current as a result of ripple voltage across the inductor (even without any external load). This allows smooth reversal of load current during the change over from one quadrant operation to another and provides fast dynamic responses, especially for electrical motor drives.
You might also like
- Line-Commutated and Active PWMDocument2 pagesLine-Commutated and Active PWMAnonymous HyOfbJ650% (2)
- Automotive Sensors & ActuatorsDocument108 pagesAutomotive Sensors & ActuatorsSatyaAditham90% (10)
- In Line Fuel InjectionDocument146 pagesIn Line Fuel InjectionRaphael Lomonaco97% (33)
- Erial Ine Plitter: Input: RS-232, RS-422, NMEA0183Document1 pageErial Ine Plitter: Input: RS-232, RS-422, NMEA0183Thang PhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter Thirteen: DC Drives Using Controlled RectifiersDocument38 pagesChapter Thirteen: DC Drives Using Controlled Rectifiersyemane gebremichal100% (2)
- 4.circle Diagram of Three Phase Induction Motor From No Load & Blocked Rotor TestsDocument4 pages4.circle Diagram of Three Phase Induction Motor From No Load & Blocked Rotor Testsmandadi_sailesh67% (3)
- Ee 1004 Power Quality Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesEe 1004 Power Quality Two Mark Questions and Answersscientistabbas100% (4)
- Sheet 5 AnswersDocument11 pagesSheet 5 AnswersCj Llemos100% (1)
- F 19 Stealth Fighter PDFDocument2 pagesF 19 Stealth Fighter PDFSabrinaNo ratings yet
- Accenture Smart Disaster Recovery With Amazon Web Services 092014Document16 pagesAccenture Smart Disaster Recovery With Amazon Web Services 092014Mangaras Yanu FlorestiyantoNo ratings yet
- The Design of Precast Concrete Segmental Bridge PiersDocument10 pagesThe Design of Precast Concrete Segmental Bridge PiersMrAgidasNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Full Wave Converter DrivesDocument5 pages3-Phase Full Wave Converter DrivesAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Three Phase Half & Full Controlled DrivesDocument5 pagesDC Motor Three Phase Half & Full Controlled DrivesUjjal Dey0% (1)
- Viva Questions On AlternatorsDocument6 pagesViva Questions On AlternatorsKashif Hussain RazwiNo ratings yet
- Trransistor Switching TimesDocument6 pagesTrransistor Switching TimesManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- IC 723 Voltage RegulatorsDocument16 pagesIC 723 Voltage RegulatorsAtheessh .B0% (1)
- Chapter - 4: Synchronous Motor DrivesDocument16 pagesChapter - 4: Synchronous Motor DrivesSuganthiVasan67% (3)
- 180 & 120 Degree Conduction Mode InverterDocument27 pages180 & 120 Degree Conduction Mode Invertersuriyamariappan80% (5)
- Single Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDocument10 pagesSingle Phase Fully Controlled ConverterDeepu Chinna75% (4)
- Double Revolving Field TheoryDocument2 pagesDouble Revolving Field TheoryNaresh Gollapalli100% (1)
- Power System Reactance Diagram Questions PDFDocument22 pagesPower System Reactance Diagram Questions PDFHota bNo ratings yet
- Construction of DC MachineDocument10 pagesConstruction of DC MachineMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Series InverterDocument9 pagesSingle Phase Series InverterDhivya NNo ratings yet
- Determine The Main Dimension of The CoreDocument2 pagesDetermine The Main Dimension of The CoreDipesh PatelNo ratings yet
- EE3411 EM-II Lab Manual FinalDocument71 pagesEE3411 EM-II Lab Manual FinalManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1-2 Three-Phase Half Controlled Converter PDFDocument2 pagesExperiment 1-2 Three-Phase Half Controlled Converter PDFRAJENDRA KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Tutsheet5 SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutsheet5 SolutionsDevendra Singhaniya90% (10)
- Network Analysis and Synthesis PDFDocument2 pagesNetwork Analysis and Synthesis PDFLakum Hitesh100% (3)
- 50 TOP FET Questions and Answers PDFDocument10 pages50 TOP FET Questions and Answers PDFAasheeshSingh100% (3)
- Experiment# 10: Measure The Power and Power Factor by Three Ammeter MethodDocument10 pagesExperiment# 10: Measure The Power and Power Factor by Three Ammeter MethodFarwa MunirNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using ChopperDocument16 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using Choppersunil kumarNo ratings yet
- EE2303 - TD - 2 Marks With Answers & 16 Marks Questions - SHADHIKDocument34 pagesEE2303 - TD - 2 Marks With Answers & 16 Marks Questions - SHADHIKSaran Arun100% (1)
- Switch Gear and Protection 1Document5 pagesSwitch Gear and Protection 1Irfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Major Faults in An Alternator and Their ProtectionDocument13 pagesMajor Faults in An Alternator and Their Protectiongreg100% (2)
- Experiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip TestDocument3 pagesExperiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip Test61EEPrabhat PalNo ratings yet
- Traction MathDocument21 pagesTraction MathSomenath DuttaNo ratings yet
- Sreekavithaengineerig College: Scott Connection of TransformersDocument4 pagesSreekavithaengineerig College: Scott Connection of Transformersmandadi_saileshNo ratings yet
- Fractional Kilowatt MotorsDocument37 pagesFractional Kilowatt MotorsPavan Kumar100% (1)
- Bee4113 Chapter 4Document31 pagesBee4113 Chapter 4Kung ChinHan100% (4)
- Voltage Control of InvertersDocument38 pagesVoltage Control of InvertersSindhujaSindhu100% (3)
- Wind and SolarDocument2 pagesWind and SolarAnonymous HyOfbJ6No ratings yet
- Graetz Bridge LCCDocument42 pagesGraetz Bridge LCCKaran Singhania100% (3)
- EM-I Lab Viva Questions Updated OnDocument6 pagesEM-I Lab Viva Questions Updated OnNagamohan BilluNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and Drives Year Question PaperDocument2 pagesElectrical Machines and Drives Year Question PapersivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- TSSC & TCSCDocument5 pagesTSSC & TCSCAbhinaw Rai0% (2)
- Essential Components of Indicating InstrumentsDocument6 pagesEssential Components of Indicating InstrumentsHina AsifNo ratings yet
- Satellite EclipseDocument22 pagesSatellite EclipseAma WeshNo ratings yet
- Merz Price Differential Protection For TransformerDocument2 pagesMerz Price Differential Protection For Transformerapjbalamurugan100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions With Answers On Power Electronics and DrivesDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions With Answers On Power Electronics and DrivesRaees AslamNo ratings yet
- Worked Examples For A Three - Phase Induction MachineDocument12 pagesWorked Examples For A Three - Phase Induction MachineAli AltahirNo ratings yet
- Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesGeneration of Rotating Magnetic FieldSUNIL MAURYA100% (1)
- Questions & Answers On Three Phase TransformersDocument26 pagesQuestions & Answers On Three Phase Transformerskibrom atsbha50% (2)
- DC Motor 2 Marks QuestionsDocument3 pagesDC Motor 2 Marks QuestionsAbhishek100% (1)
- Ece III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesDocument111 pagesEce III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesGautam Sharma80% (10)
- Ug Cables - Grading of CablesDocument22 pagesUg Cables - Grading of Cablessrinimeha@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Lab ManualDocument11 pagesInduction Motor Lab ManualRabah ZaimeddineNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Ac-Ac Conversion: Ac Voltage ControllerDocument56 pagesChapter Five: Ac-Ac Conversion: Ac Voltage Controllerfor lifeNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument15 pagesThree Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersAnonymous 78iAn6100% (1)
- Objective Question Protection and SwitchgearDocument20 pagesObjective Question Protection and SwitchgearRaja Desingu100% (1)
- Controlled RectifiersDocument16 pagesControlled RectifiersVishal Parekh100% (2)
- 3-Phase Half Wave ConverterDocument3 pages3-Phase Half Wave ConverterAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- L3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersDocument68 pagesL3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersSourabh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Single Phase Full Bridge Converter Using LTspiceDocument9 pagesSimulation of Single Phase Full Bridge Converter Using LTspicegoten10daNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineDocument25 pagesChapter 4 AC To AC Converters: Outlinet1m0thyNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controller (AC-AC Converter)Document9 pagesAC Voltage Controller (AC-AC Converter)Nurindah Atika100% (4)
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- D-49 Working of Contractors: S. N o Contract orDocument2 pagesD-49 Working of Contractors: S. N o Contract orAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Kinect Grid Mapping: by S. M. Bilal Ahmed Adeel Afzal Ammar NaveedDocument8 pagesKinect Grid Mapping: by S. M. Bilal Ahmed Adeel Afzal Ammar NaveedAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Class LibDocument119 pagesClass LibarunascarletNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument49 pagesComputer NotesAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Industrial Electronics EngineeringDocument1 pageInstitute of Industrial Electronics EngineeringAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Practical File: Submitted To: Sir Asif Memon Submitted By: Nasir Aziz (2030) Dated: 18-01-2010Document1 pageElectronics Practical File: Submitted To: Sir Asif Memon Submitted By: Nasir Aziz (2030) Dated: 18-01-2010Anb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Far NellDocument1 pageFar NellAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Privacy Information For Installation Features Windows 7 Privacy Statement For Installation FeaturesDocument13 pagesPrivacy Information For Installation Features Windows 7 Privacy Statement For Installation Featuresjoe littlefield jrNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument8 pagesProjectAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- The Socio-Moral Code of IslamDocument70 pagesThe Socio-Moral Code of IslamAnb Bajwa50% (2)
- Lab Assignment # 9 Objective: Feedback Control of Thermal System at The Mid of The Steady-State (Of Open Loop) Temperature RangeDocument1 pageLab Assignment # 9 Objective: Feedback Control of Thermal System at The Mid of The Steady-State (Of Open Loop) Temperature RangeAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Thermo Chap IIIDocument22 pagesThermo Chap IIIAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Thermo Chap - IVDocument12 pagesThermo Chap - IVAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Water Level MeasurementDocument2 pagesWater Level MeasurementAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Lab File: Signal and System (IE-302)Document1 pageLab File: Signal and System (IE-302)Anb BajwaNo ratings yet
- PCSIR - Institute of Industrial Electronics Engineering: Third YearDocument1 pagePCSIR - Institute of Industrial Electronics Engineering: Third YearAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Trans Curve TracerDocument8 pagesTrans Curve TracerAnb Bajwa100% (1)
- Vice President Technology in New York City Resume Brian SchaaffDocument2 pagesVice President Technology in New York City Resume Brian SchaaffBrianSchaaffNo ratings yet
- Dapped End Strengtheningof Precast Prestressed Concrete Double Tee Beamswith FRPCompositesDocument157 pagesDapped End Strengtheningof Precast Prestressed Concrete Double Tee Beamswith FRPCompositesMeganathan MegaNo ratings yet
- 21 Structural Conceptual Design ReportDocument12 pages21 Structural Conceptual Design Reportsofianina05No ratings yet
- солнечная батарея swissDocument2 pagesсолнечная батарея swissigor kNo ratings yet
- Q-Flex Data Sheet 210058 RevCDocument5 pagesQ-Flex Data Sheet 210058 RevCarzeszutNo ratings yet
- Rule: Spent Nuclear Fuel and High-Level Radioactive Waste Independent Storage Licensing Requirements: Approved Spent Fuel Storage Casks ListDocument2 pagesRule: Spent Nuclear Fuel and High-Level Radioactive Waste Independent Storage Licensing Requirements: Approved Spent Fuel Storage Casks ListJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Multicluster Aen112011wDocument20 pagesMulticluster Aen112011wVăn ST QuangNo ratings yet
- Group 9 Organizational MarketDocument2 pagesGroup 9 Organizational MarketSofia NadineNo ratings yet
- ARTCAM PRO9.0 InglésDocument466 pagesARTCAM PRO9.0 InglésYamen Issa100% (2)
- SIRIUS IC10 Complete English 2018 201712111415265308Document1,440 pagesSIRIUS IC10 Complete English 2018 201712111415265308Catarina ContenteNo ratings yet
- ST8A-EM 11.3 W/4000K 900 MM: Product DatasheetDocument4 pagesST8A-EM 11.3 W/4000K 900 MM: Product DatasheetАлина ВладиславовнаNo ratings yet
- LPS1181 Part One 1.1Document27 pagesLPS1181 Part One 1.1alex metalNo ratings yet
- Betriebsanleitung eDocument102 pagesBetriebsanleitung eRogerioNo ratings yet
- Sharp LC 50le458x TV Service ManualDocument41 pagesSharp LC 50le458x TV Service ManualNikhil Suresh100% (1)
- Sr. No. Activity Description Responsibility: 4.0 ActivitiesDocument1 pageSr. No. Activity Description Responsibility: 4.0 ActivitiesKamal SolankiNo ratings yet
- Define The Equation For Converting or Correcting The Specific Gravity of Oil at AnyDocument2 pagesDefine The Equation For Converting or Correcting The Specific Gravity of Oil at AnyTatsNo ratings yet
- Senior Economist Planner Environmental Manager in Seattle WA Resume David ClarkDocument3 pagesSenior Economist Planner Environmental Manager in Seattle WA Resume David ClarkDavidClark2No ratings yet
- Healthcare ModelDocument7 pagesHealthcare ModelStanley ANo ratings yet
- Service Manual Swift 2 PDFDocument115 pagesService Manual Swift 2 PDFEngSafwanQadousNo ratings yet
- PEST On ProtonDocument2 pagesPEST On ProtonStarvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- The Digital Radiography SystemDocument9 pagesThe Digital Radiography SystemReza Apa Ja'erNo ratings yet
- Leica M60 Brochure LS enDocument12 pagesLeica M60 Brochure LS enYanmedSumedangNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Management in Universities in Uganda A Social PerspectiveDocument6 pagesKnowledge Management in Universities in Uganda A Social PerspectiveAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- MDT218AJ10 Data Sheet ImperialDocument12 pagesMDT218AJ10 Data Sheet Imperialamsterdamer2003No ratings yet