Professional Documents
Culture Documents
References: K K K K
References: K K K K
Uploaded by
united1313Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 20160229Document8 pages20160229a_oucharNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesDocument92 pagesMechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesZain Ahmed85% (13)
- Mechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesDocument84 pagesMechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesKajal Khan100% (2)
- PC235W13 Assignment9 SolutionsDocument16 pagesPC235W13 Assignment9 Solutionskwok0% (1)
- ME4213 Tutorial 2aDocument4 pagesME4213 Tutorial 2aLinShaodun100% (1)
- Dispersion Relation Derivation PDFDocument12 pagesDispersion Relation Derivation PDFKartikay5No ratings yet
- Normal ModesDocument49 pagesNormal ModesEsteban RodríguezNo ratings yet
- References: 10m/s 60cm 60cmDocument9 pagesReferences: 10m/s 60cm 60cmAliOucharNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Two DOF Systems - Part 2Document12 pagesUnit 4 Two DOF Systems - Part 2efgh21177No ratings yet
- EE222 Nonlinear Systems: Analysis, Stability, and Control Problem Set 1Document3 pagesEE222 Nonlinear Systems: Analysis, Stability, and Control Problem Set 1wynnthomasNo ratings yet
- EED600 Assignment 1Document1 pageEED600 Assignment 1RETRO GAMERSNo ratings yet
- Spring 2011 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2 - 8 - 2 - 4 W - 3Document4 pagesSpring 2011 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2 - 8 - 2 - 4 W - 3rujintoNo ratings yet
- Clamped 1Document21 pagesClamped 1Rajeswari MachirajuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SET A - Model AnswerDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 SET A - Model Answershriramdhumal24744No ratings yet
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3sharadpjadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Ii Introduction To ModellingDocument50 pagesChapter-Ii Introduction To ModellingAHMEDNo ratings yet
- Coursework Sheet of Structural Dynamics: y M M U U K K K K K U U M MDocument1 pageCoursework Sheet of Structural Dynamics: y M M U U K K K K K U U M MnicholasomodingNo ratings yet
- Quantenoptik Vorlesung2 PDFDocument4 pagesQuantenoptik Vorlesung2 PDFErinSuttonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrix Methods For Structural Analysis: Definitions ElementsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Matrix Methods For Structural Analysis: Definitions ElementsprakharNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument7 pagesPDFAliOucharNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6: Energy Method (Lagrange's Method)Document35 pagesChapter-6: Energy Method (Lagrange's Method)ideepujNo ratings yet
- Limitation Imposed On Structural DesignerDocument2 pagesLimitation Imposed On Structural DesignerdvarsastryNo ratings yet
- Final Project PDFDocument2 pagesFinal Project PDFWillian MitziNo ratings yet
- Es386 2018Document6 pagesEs386 2018Luke HoganNo ratings yet
- 3 International Physics Olympiad 1969, Brno, Czechoslovakia: BandcofmassesmDocument9 pages3 International Physics Olympiad 1969, Brno, Czechoslovakia: BandcofmassesmJoseph TrujilloNo ratings yet
- 10 - SHM, Springs, DampingDocument4 pages10 - SHM, Springs, DampingBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Physics ExamDocument13 pagesSemiconductor Physics ExamSudhamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 - Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemDocument23 pagesChapter - 12 - Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemArsalan IdreesNo ratings yet
- This Exam Is Formed of Three Exercises in Four Pages. The Use of Non-Programmable Calculators Is RecommendedDocument6 pagesThis Exam Is Formed of Three Exercises in Four Pages. The Use of Non-Programmable Calculators Is Recommendedincandescentglow96No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - (12th & 13th) Paper 2Document5 pagesPHYSICS - (12th & 13th) Paper 2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 07 08 II ms1Document5 pages07 08 II ms1Mahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Spring 2007 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2Document5 pagesSpring 2007 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2paimoNo ratings yet
- Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemDocument23 pagesVibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemDewa Ayu Mery AgustinNo ratings yet
- ch36 PDFDocument11 pagesch36 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- HW4 Solutions ECE Mark Lundstrom Purdue UniversityDocument16 pagesHW4 Solutions ECE Mark Lundstrom Purdue University0307aliNo ratings yet
- MIT2 003SCF11 Pset9 SolDocument10 pagesMIT2 003SCF11 Pset9 SolDasaka BrahmendraNo ratings yet
- Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom Systems Solved ProblemsDocument17 pagesVibration of Two Degree of Freedom Systems Solved ProblemsDevananda R SNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Enter Your Examination Centre HereDocument4 pagesInstructions: Enter Your Examination Centre HereSarvesh R GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Vibration TheoryDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Vibration TheoryKavya M BhatNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Tutorial 5 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanical Vibrations Tutorial 5 PDFthelightrayNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Problem 2.1 (20 PTS)Document5 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Problem 2.1 (20 PTS)Mayank SinghNo ratings yet
- MME09MM 1101numerical Related To CrystallographyDocument53 pagesMME09MM 1101numerical Related To CrystallographyMaria PhiriNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Tapered Beam Piezoelectric Energy HarvestersDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Tapered Beam Piezoelectric Energy HarvestersshikhamaharanaNo ratings yet
- DMX5533 Tma01 2017 2018Document7 pagesDMX5533 Tma01 2017 2018Shenal FernandoNo ratings yet
- TYK 7 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTYK 7 QuestionsIsaac HanssenNo ratings yet
- Vibration & Fault DiagnosisDocument4 pagesVibration & Fault DiagnosisSheraNo ratings yet
- PHYS3001 - Quantum Mechanics and Its Applications: Test: 28 September 2013 Time: 50 Minutes Total: 20Document1 pagePHYS3001 - Quantum Mechanics and Its Applications: Test: 28 September 2013 Time: 50 Minutes Total: 20Lucas Mosimanegape GaileleNo ratings yet
- Dynamics and VibrationsDocument19 pagesDynamics and Vibrationsadhi2796No ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Module 2Document24 pagesElectromagnetics Module 2Mike Dexter PatacsilNo ratings yet
- Natural Freq and Modal ShapesDocument5 pagesNatural Freq and Modal ShapesHelen HerodicoNo ratings yet
- Me3360 HW1-SP2013Document3 pagesMe3360 HW1-SP2013elm391229No ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Mechanical Systems and Electrical SystemsDocument49 pagesMathematical Modeling of Mechanical Systems and Electrical SystemsMary DunhamNo ratings yet
- Sheet (4) SimulinkDocument3 pagesSheet (4) SimulinkSherif SaidNo ratings yet
- Multiple Degrees of FreedomDocument44 pagesMultiple Degrees of FreedomShafiq Ahmed Shahbaz100% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
References: K K K K
References: K K K K
Uploaded by
united1313Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
References: K K K K
References: K K K K
Uploaded by
united1313Copyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Mechanical Vibrations 4600:431 Name:
Homework 01 Due: 23 Jan 2013
Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., box in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work. . . please use lots of paper.
References
[1] Balachandran, B., and Magrab, E. B., 2004, Vibrations, Brooks/ColeThomson. [2] Kelly, S. G., 2000, Fundamentals of Mechanical Vibrations, McGraw-Hill, 2nd ed. Problem 1: [1, 0214] Determine the equivalent stiness for each of the systems shown in the gure. Each system consists of three linear springs with stiness k1 , k2 , and k3 .
k1 k3 k1 k3 k2 k2
Problem 2: [1, 0221] Determine the equivalent damping for the system shown in the gure.
x
c1
c2
c3
Problem 3: [1, 0226] Represent the vibratory system given in the gure as an equivalent stiness ke , and equivalent damping coecient ce .
k1
x k2 m c1 c2
Problem 4: [2, 0155] Determine the deection of each spring from its unstretched length when the system shown is in equilibrium. Assume that in the absence of gravity the springs are unstretched in the equilibrium position. You must draw a separate free-body diagram on both the disk and the block.
k2
r2
r1
k1
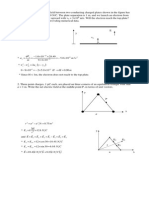
Problem 5: Consider the two harmonic signals x1 (t) = (70 cm) sin((6 rad/s) t), x2 (t) = (30 cm) cos((6 rad/s) t).
Find the amplitude and phase shift of the combination x(t) = x1 (t) + x2 (t), and plot the result in MATLAB for 0 s t 10 s. Problem 6: [1, 0228] For a vibratory system with a mass m = 10 kg, k = 1500 N/m, and c = 2500 N/(m/s), and given that the displacement response has the form x(t) = (0.2 m) sin((9 rad/s) t), plot the graphs of m x, the spring force k x, and the damper force c x versus time. Finally, combine these and plot the quantity m x + c x + k x. Use MATLAB.
You might also like
- 20160229Document8 pages20160229a_oucharNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesDocument92 pagesMechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesZain Ahmed85% (13)
- Mechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesDocument84 pagesMechanical Vibration Solved ExamplesKajal Khan100% (2)
- PC235W13 Assignment9 SolutionsDocument16 pagesPC235W13 Assignment9 Solutionskwok0% (1)
- ME4213 Tutorial 2aDocument4 pagesME4213 Tutorial 2aLinShaodun100% (1)
- Dispersion Relation Derivation PDFDocument12 pagesDispersion Relation Derivation PDFKartikay5No ratings yet
- Normal ModesDocument49 pagesNormal ModesEsteban RodríguezNo ratings yet
- References: 10m/s 60cm 60cmDocument9 pagesReferences: 10m/s 60cm 60cmAliOucharNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Two DOF Systems - Part 2Document12 pagesUnit 4 Two DOF Systems - Part 2efgh21177No ratings yet
- EE222 Nonlinear Systems: Analysis, Stability, and Control Problem Set 1Document3 pagesEE222 Nonlinear Systems: Analysis, Stability, and Control Problem Set 1wynnthomasNo ratings yet
- EED600 Assignment 1Document1 pageEED600 Assignment 1RETRO GAMERSNo ratings yet
- Spring 2011 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2 - 8 - 2 - 4 W - 3Document4 pagesSpring 2011 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2 - 8 - 2 - 4 W - 3rujintoNo ratings yet
- Clamped 1Document21 pagesClamped 1Rajeswari MachirajuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SET A - Model AnswerDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 SET A - Model Answershriramdhumal24744No ratings yet
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3sharadpjadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Ii Introduction To ModellingDocument50 pagesChapter-Ii Introduction To ModellingAHMEDNo ratings yet
- Coursework Sheet of Structural Dynamics: y M M U U K K K K K U U M MDocument1 pageCoursework Sheet of Structural Dynamics: y M M U U K K K K K U U M MnicholasomodingNo ratings yet
- Quantenoptik Vorlesung2 PDFDocument4 pagesQuantenoptik Vorlesung2 PDFErinSuttonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrix Methods For Structural Analysis: Definitions ElementsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Matrix Methods For Structural Analysis: Definitions ElementsprakharNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument7 pagesPDFAliOucharNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6: Energy Method (Lagrange's Method)Document35 pagesChapter-6: Energy Method (Lagrange's Method)ideepujNo ratings yet
- Limitation Imposed On Structural DesignerDocument2 pagesLimitation Imposed On Structural DesignerdvarsastryNo ratings yet
- Final Project PDFDocument2 pagesFinal Project PDFWillian MitziNo ratings yet
- Es386 2018Document6 pagesEs386 2018Luke HoganNo ratings yet
- 3 International Physics Olympiad 1969, Brno, Czechoslovakia: BandcofmassesmDocument9 pages3 International Physics Olympiad 1969, Brno, Czechoslovakia: BandcofmassesmJoseph TrujilloNo ratings yet
- 10 - SHM, Springs, DampingDocument4 pages10 - SHM, Springs, DampingBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Physics ExamDocument13 pagesSemiconductor Physics ExamSudhamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 - Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemDocument23 pagesChapter - 12 - Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemArsalan IdreesNo ratings yet
- This Exam Is Formed of Three Exercises in Four Pages. The Use of Non-Programmable Calculators Is RecommendedDocument6 pagesThis Exam Is Formed of Three Exercises in Four Pages. The Use of Non-Programmable Calculators Is Recommendedincandescentglow96No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - (12th & 13th) Paper 2Document5 pagesPHYSICS - (12th & 13th) Paper 2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 07 08 II ms1Document5 pages07 08 II ms1Mahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Spring 2007 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2Document5 pagesSpring 2007 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2paimoNo ratings yet
- Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemDocument23 pagesVibration of Two Degree of Freedom SystemDewa Ayu Mery AgustinNo ratings yet
- ch36 PDFDocument11 pagesch36 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- HW4 Solutions ECE Mark Lundstrom Purdue UniversityDocument16 pagesHW4 Solutions ECE Mark Lundstrom Purdue University0307aliNo ratings yet
- MIT2 003SCF11 Pset9 SolDocument10 pagesMIT2 003SCF11 Pset9 SolDasaka BrahmendraNo ratings yet
- Vibration of Two Degree of Freedom Systems Solved ProblemsDocument17 pagesVibration of Two Degree of Freedom Systems Solved ProblemsDevananda R SNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Enter Your Examination Centre HereDocument4 pagesInstructions: Enter Your Examination Centre HereSarvesh R GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Vibration TheoryDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Vibration TheoryKavya M BhatNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Tutorial 5 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanical Vibrations Tutorial 5 PDFthelightrayNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Problem 2.1 (20 PTS)Document5 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Problem 2.1 (20 PTS)Mayank SinghNo ratings yet
- MME09MM 1101numerical Related To CrystallographyDocument53 pagesMME09MM 1101numerical Related To CrystallographyMaria PhiriNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Tapered Beam Piezoelectric Energy HarvestersDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Tapered Beam Piezoelectric Energy HarvestersshikhamaharanaNo ratings yet
- DMX5533 Tma01 2017 2018Document7 pagesDMX5533 Tma01 2017 2018Shenal FernandoNo ratings yet
- TYK 7 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTYK 7 QuestionsIsaac HanssenNo ratings yet
- Vibration & Fault DiagnosisDocument4 pagesVibration & Fault DiagnosisSheraNo ratings yet
- PHYS3001 - Quantum Mechanics and Its Applications: Test: 28 September 2013 Time: 50 Minutes Total: 20Document1 pagePHYS3001 - Quantum Mechanics and Its Applications: Test: 28 September 2013 Time: 50 Minutes Total: 20Lucas Mosimanegape GaileleNo ratings yet
- Dynamics and VibrationsDocument19 pagesDynamics and Vibrationsadhi2796No ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Module 2Document24 pagesElectromagnetics Module 2Mike Dexter PatacsilNo ratings yet
- Natural Freq and Modal ShapesDocument5 pagesNatural Freq and Modal ShapesHelen HerodicoNo ratings yet
- Me3360 HW1-SP2013Document3 pagesMe3360 HW1-SP2013elm391229No ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Mechanical Systems and Electrical SystemsDocument49 pagesMathematical Modeling of Mechanical Systems and Electrical SystemsMary DunhamNo ratings yet
- Sheet (4) SimulinkDocument3 pagesSheet (4) SimulinkSherif SaidNo ratings yet
- Multiple Degrees of FreedomDocument44 pagesMultiple Degrees of FreedomShafiq Ahmed Shahbaz100% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet