Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ms. Divyakrit Arora
Ms. Divyakrit Arora
Uploaded by
rkdivyaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ms. Divyakrit Arora
Ms. Divyakrit Arora
Uploaded by
rkdivyaCopyright:
Available Formats
By Divyakrit Arora
The small intestine is divided into three parts Duodenum- first part, about 25cm long Jejunum- middle segment, about 2.5m long Ileum- final segment, 3.5m long
In the small intestine are present various folds and projections to increase SA for absorptionPlica circularis circular folds Villi finger like projections Microvilli apical hair like projections Core of villus contains arteriole, capillary, venule, lacteal.
Small intestine is one of the major sites for absorption of :
Electrolytes such as Na+ , K+ ,Cl- and HCO3. Water from the mucosa of small intestine. Carbohydrates, lipids, dipeptides and tripeptides, iron and Ca2+.
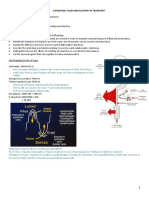
The absorption of sodium in the intestine can be either by Passive Transport or by Active Transport. Passive transport : Some of the sodium diffuses in or out of the small intestine depending on the concentration gradient. In addition, sodium is actively transported out of the lumen in small intestine by sodium-potassium pumps.
Sodium transport from ileum and jejunum to blood is facilitated by aldosterone. Active transport in small intestine : sodium helps in absorption of glucose, amino acids and some other substances. Its is referred to as Sodium Dependent Glucose Transporter (SDGT).
Movement of potassium across the mucosa takes place down its electrochemical
gradient.
There is also some secretion of potassium into the intestinal lumen, specially
as a component of mucus.
Net movement of potassium is directly proportional to the potential difference between blood and intestinal lumen.
Chloride is normally secreted into the lumen of small intestine by chloride channels, that are activated by cAMP. Intestinal absorption of chloride also occurs by its cotransport along with sodium and
potassium.
In ileum and large intestine, chloride is absorbed across brush border epithelium by chloride-bicarbonate exchanger.
There must be reabsorption of bicarbonate ions in small intestine because it is extensively secreted in duodenum. Bicarbonate is absorbed in an indirect manner asWhen sodium is absorbed, hydrogen ions are secreted into lumen in exchange for sodium. Hydrogen ions combine with bicarbonate ions to form carbonic acid which dissociates to water and carbon dioxide.
You might also like
- Chapter 27 GuytonDocument6 pagesChapter 27 GuytonGabriella ChafrinaNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Ionic Movements Across Renal and Digestive Tract EpitheliaDocument2 pagesCompare and Contrast Ionic Movements Across Renal and Digestive Tract EpitheliaDhruvalNo ratings yet
- Physiological Ion ChlorideDocument15 pagesPhysiological Ion ChlorideMohammad Arafat Siddiqui100% (2)
- Reabsorption of SodiumDocument19 pagesReabsorption of Sodiumpriya shettyNo ratings yet
- Lec 14 - Kidney PDFDocument16 pagesLec 14 - Kidney PDFrajeshNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology BY Dr. Olasupo. S. AdeniyiDocument6 pagesRenal Physiology BY Dr. Olasupo. S. AdeniyiUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Digestion Absorption2022Document32 pagesDigestion Absorption2022Baap ko Mat sikhaNo ratings yet
- Physio 2Document6 pagesPhysio 2Mohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Biokimia UrinDocument2 pagesBiokimia UrinAswin AgusNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation and Its CompositionDocument22 pagesUrine Formation and Its CompositionZahidKhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ExcretionDocument5 pagesChapter 13 ExcretionWezu heavenNo ratings yet
- Transport Mech 09192011Document38 pagesTransport Mech 09192011Wesley SeeNo ratings yet
- Inulin Clearance Is Indeed The Hallmark Method For Measuring GFRDocument12 pagesInulin Clearance Is Indeed The Hallmark Method For Measuring GFRVanathy KarunamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Distal Tubule Balance and Tubuloglomerular Feedback-Group 2Document42 pagesDistal Tubule Balance and Tubuloglomerular Feedback-Group 2Chuleha SethNo ratings yet
- Physiology Renal SystemDocument36 pagesPhysiology Renal SystemMohammad Jamal OwesatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document18 pagesLecture 9asakingofhNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Normal PencernaanDocument20 pagesFisiologi Normal PencernaanVaniaOlgaNo ratings yet
- Absorption of A Substance by The Intestine Signifies Its Passage Through The Intestinal Epithelium andDocument3 pagesAbsorption of A Substance by The Intestine Signifies Its Passage Through The Intestinal Epithelium andDella FerginaNo ratings yet
- 6-Drugs Acting On The Renal System - 2Document65 pages6-Drugs Acting On The Renal System - 2Hamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Reabsorption (Excretion Physiology)Document28 pagesReabsorption (Excretion Physiology)Ayesha IqbalNo ratings yet
- Tubular ReabsorptionDocument42 pagesTubular Reabsorptionmina mounirNo ratings yet
- Secretion of Ions in SalivaDocument5 pagesSecretion of Ions in SalivabhumiparikhNo ratings yet
- 24 Absorption in Gastrointestinal Tract and Motility of Gastrointestinal TractDocument34 pages24 Absorption in Gastrointestinal Tract and Motility of Gastrointestinal TractMi PatelNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarDocument49 pagesTubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarZia PhotostateNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) I. Brief DescriptionDocument3 pagesMetabolic Alkalosis (Base Bicarbonate Excess) I. Brief DescriptionAllyssa MackinnonNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year BiologyDocument3 pages2nd Year BiologyHina AliNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Chemical DigestionDocument4 pagesMechanical and Chemical Digestionsnehashreemohanty39No ratings yet
- POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS كيمياء سريريةDocument4 pagesPOTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS كيمياء سريريةMustafa Salah MahdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24. The Kidney.: 1. The Structure and Function of The NephronDocument8 pagesChapter 24. The Kidney.: 1. The Structure and Function of The NephronjeskevandiemenNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document11 pagesPresentation 3Najma xaaji caliNo ratings yet
- LOOP OF HENLE (Modified)Document25 pagesLOOP OF HENLE (Modified)Chuleha SethNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - US-Grade 4-BiochemistryDocument34 pagesPart 1 - US-Grade 4-BiochemistryFarah Bashar Al-RawachyNo ratings yet
- Renal Tubular TransportDocument38 pagesRenal Tubular TransportAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 14th EdDocument90 pagesChapter 28 14th EdchayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Pecularities of Renal Circulation and Acid-Base BalanceDocument17 pagesPecularities of Renal Circulation and Acid-Base Balancekazim786ahmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Urine FormationsDocument20 pagesMechanism of Urine FormationsGAURAVNo ratings yet
- The Collecting TubulesDocument1 pageThe Collecting TubulesMuhammad Naufal FadhillahNo ratings yet
- Nephron PhysiologyDocument8 pagesNephron PhysiologyHadeel A. AlkayedNo ratings yet
- Diuretics and Dialysis: DR Arpana HazarikaDocument104 pagesDiuretics and Dialysis: DR Arpana HazarikaArpana HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Renalphysiology3 150323053336 Conversion Gate01Document33 pagesRenalphysiology3 150323053336 Conversion Gate01Hema KamatNo ratings yet
- PHS RenalDocument44 pagesPHS Renaltewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Renal NoteDocument20 pagesRenal Noteiroreredavid8No ratings yet
- Digestive System - 2: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesDigestive System - 2: Learning ObjectivesMaggieLockeNo ratings yet
- L3 +L4 Renal System 2023Document31 pagesL3 +L4 Renal System 2023mizare29gNo ratings yet
- Role of The KIDNEYS in Homeostasis by D SiwaleDocument84 pagesRole of The KIDNEYS in Homeostasis by D Siwalenoahngoma41No ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument87 pagesUrinaryJohn Paolo Dalida SalazarNo ratings yet
- 5 Intestinal Fluid and Electrolyte Transport-1Document9 pages5 Intestinal Fluid and Electrolyte Transport-1Linh PhanNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Rhythms Tachycardia: Potassium Electrolyte HypokalemiaDocument7 pagesDangerous Rhythms Tachycardia: Potassium Electrolyte HypokalemiagorodoeNo ratings yet
- GUS1-K6-Reabsorpsi & Sekresi TubulusDocument33 pagesGUS1-K6-Reabsorpsi & Sekresi TubulusMarieta RitongaNo ratings yet
- Tubular Function (Distal Tubule)Document26 pagesTubular Function (Distal Tubule)Hakimah K. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument91 pagesRenal SystemKetheesaran LingamNo ratings yet
- Distal Convoluted Tubules, Counter Current Mechanism, MicturitionDocument94 pagesDistal Convoluted Tubules, Counter Current Mechanism, MicturitionSarah BirechNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and SecretionDocument21 pagesTubular Reabsorption and SecretionAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract PhysiologykulDocument72 pagesUrinary Tract PhysiologykulAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Ion TransportersDocument2 pagesIon TransportersfilipemedicinavrNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys and Formation of Urine 3 New 0Document22 pagesThe Kidneys and Formation of Urine 3 New 0Iph anyiNo ratings yet
- L5&6-Tubular Reabsorption& SecretionDocument38 pagesL5&6-Tubular Reabsorption& SecretionsairahhannahNo ratings yet
- Absorption Assimilation and EgestionDocument2 pagesAbsorption Assimilation and EgestionPrazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia: A Practical Approach To Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument17 pagesHypokalemia: A Practical Approach To Diagnosis and TreatmentIntan NoaNo ratings yet
- Enteral NutritionDocument62 pagesEnteral Nutritionrkdivya100% (2)
- Cancer For DummiesDocument26 pagesCancer For DummiesrkdivyaNo ratings yet
- Doppler Echocardiographic Indices of Diastolic Function Age 21-49 y Age 50 yDocument1 pageDoppler Echocardiographic Indices of Diastolic Function Age 21-49 y Age 50 yrkdivyaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy: Dr. Rajesh AroraDocument59 pagesOxygen Therapy: Dr. Rajesh ArorarkdivyaNo ratings yet