Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst
DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst
Uploaded by
Deba P SarmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Camel IntegumentDocument4 pagesCamel IntegumentDarkCupid Mynhero100% (1)
- The Integumentary SystemDocument33 pagesThe Integumentary SystemMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Dermal Cysts, Diagnostic FeaturesDocument11 pagesDermal Cysts, Diagnostic FeaturesDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst.Document11 pagesDR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst.Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Untitled1 PDFDocument10 pagesUntitled1 PDFMarzthNo ratings yet
- 09 - Skin and Its AppendagesDocument61 pages09 - Skin and Its AppendagesArjohn VegaNo ratings yet
- 1-Function Dermatology NotesDocument80 pages1-Function Dermatology Notesz9cz4zhv55No ratings yet
- Infundibular Cyst. M 64, Right Arm.Document6 pagesInfundibular Cyst. M 64, Right Arm.Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument36 pagesSkin and Its Appendagesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Integumentary Analab)Document2 pagesIntegumentary Analab)Kimberly Wyne SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- 6 Integumentary1Document66 pages6 Integumentary1api-159564163No ratings yet
- Infundibular Cyst. M 64, Right ArmDocument6 pagesInfundibular Cyst. M 64, Right ArmDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- And Its Appendages: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowDocument44 pagesAnd Its Appendages: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowCesar Ivan Ruiz DiazNo ratings yet
- Int - Sys ComDocument19 pagesInt - Sys ComBernard FernandezNo ratings yet
- Histology Skin & AppendagesDocument44 pagesHistology Skin & AppendagesMathew JosephNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 4 - IntegumentaryDocument45 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 4 - Integumentaryprincesinclair77No ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomy of The SkinDocument15 pages1 - Anatomy of The Skinumart4843No ratings yet
- Dermatology NotesDocument37 pagesDermatology NotesTamilmani n.mNo ratings yet
- Approach To Skin DiseasesDocument63 pagesApproach To Skin DiseasesPriya GK100% (1)
- Integument SystemDocument23 pagesIntegument SystemPRIYA DARSHINI GUNALANNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Integumentary System: References: Http://people - Upei.ca/hannaDocument22 pagesPathology of The Integumentary System: References: Http://people - Upei.ca/hannaLakshita Prajapati100% (1)
- Skin and Breast HistologyDocument8 pagesSkin and Breast HistologyPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Skin FunctionDocument50 pagesPhysiology of Skin FunctionPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- General DermatologyDocument31 pagesGeneral DermatologyMartaNo ratings yet
- The Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDocument72 pagesThe Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDeborahMcCloudNo ratings yet
- Hair Diseases: AnatomyDocument36 pagesHair Diseases: AnatomyMasithaNo ratings yet
- K1 Kulit Dan AdnexaDocument23 pagesK1 Kulit Dan AdnexaJimmy Fran IINo ratings yet
- Pablo Clark Integumentary PartsDocument5 pagesPablo Clark Integumentary PartsClark Vincent PabloNo ratings yet
- 4# Bisma Aslam (20-ARID-3222)Document8 pages4# Bisma Aslam (20-ARID-3222)TasbihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Notes - A&P 2022Document6 pagesChapter 5 Notes - A&P 2022Ashley MarieNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument49 pagesIntegumentary SystemCUEVA Cristine JaneNo ratings yet
- ColorimetricDocument6 pagesColorimetric4gen_5No ratings yet
- Pearls: 1889. Colour of Skin and Fitzpatrick Classification of Skin TypesDocument118 pagesPearls: 1889. Colour of Skin and Fitzpatrick Classification of Skin TypesswastikNo ratings yet
- Basic DermatologyDocument43 pagesBasic Dermatologyarslan63637363No ratings yet
- CylindromaDocument1 pageCylindromaDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument35 pagesThe Integumentary SystemVivek BhattNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument45 pagesIntegumentary SystemDASHNo ratings yet
- HIstology Experiment 12Document5 pagesHIstology Experiment 12Pearlregine Cianne MirandaNo ratings yet
- The Histology ofDocument15 pagesThe Histology ofEveryday FundayNo ratings yet
- SKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Document40 pagesSKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Sadia SohailNo ratings yet
- 1 LG) Histology of The SkinDocument25 pages1 LG) Histology of The SkinJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- Module 3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMDocument25 pagesModule 3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- III Components of The Integumentary System949Document4 pagesIII Components of The Integumentary System949Grimlock GrimmyNo ratings yet
- The Skin (Anaphy)Document2 pagesThe Skin (Anaphy)ALEXANDRA COLLEEN ALEGRENo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument52 pagesIntegumentary Systemyasin oumer0% (1)
- Dermatology FirecrackerDocument28 pagesDermatology FirecrackerKeham LeogNo ratings yet
- LG2 Histology of The SkinDocument26 pagesLG2 Histology of The SkinRawa AyubNo ratings yet
- Epidermis Dermis Hypodermis or Subcutaneous TissueDocument2 pagesEpidermis Dermis Hypodermis or Subcutaneous TissueCarmehlyn BalogbogNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument74 pagesIntegumentary SystemririyoruNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument10 pagesIntegumentary SystemharlynnsalmeoNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument40 pagesThe Integumentary SystemYuni AtiNo ratings yet
- 0401 Histo LectureDocument57 pages0401 Histo LectureJoe JNo ratings yet
- WorkbookModule14 Integumentary SystemDocument13 pagesWorkbookModule14 Integumentary Systemsarahfrancesca03No ratings yet
- 7 Integumentary SystemDocument38 pages7 Integumentary Systemvanderphys100% (1)
- Histology SkinDocument5 pagesHistology SkinFahd Abdullah Al-refaiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument38 pagesIntegumentary SystemTrista CincoNo ratings yet
- The Skin Structure: Presentation ofDocument35 pagesThe Skin Structure: Presentation ofdimple bachkaniwalaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIntegumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Skin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSkin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pilar Cyst With CrystalsDocument2 pagesPilar Cyst With CrystalsDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Solar Keratosis, M 67, Forehead PDFDocument6 pagesAcantholytic Solar Keratosis, M 67, Forehead PDFDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Accessory TragusDocument3 pagesAccessory TragusDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Actinic KeratosisDocument4 pagesAcantholytic Actinic KeratosisDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Dermatosis With DyskeratosisDocument11 pagesAcantholytic Dermatosis With DyskeratosisDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Bullous DiseaseDocument4 pagesAcantholytic Bullous DiseaseDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Results of Search in Google Scholar On 'Deba P Sarma'Document28 pagesResults of Search in Google Scholar On 'Deba P Sarma'Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDocument8 pagesAcantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis)Document3 pagesAcantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis)Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verrucous Carcinoma of The Foot, M 63, Left FootDocument8 pagesVerrucous Carcinoma of The Foot, M 63, Left FootDeba P Sarma100% (1)
- Xanthomatous Synovial Cyst (Xanthomatous Ganglion Cyst), M 74, Left PalmDocument7 pagesXanthomatous Synovial Cyst (Xanthomatous Ganglion Cyst), M 74, Left PalmDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Xanthogranuloma PPT DSDocument9 pagesXanthogranuloma PPT DSDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Balanitis Circumscripta Plasmacellularis (Zoon's Balanitis, Plasma Cell Balanitis)Document6 pagesBalanitis Circumscripta Plasmacellularis (Zoon's Balanitis, Plasma Cell Balanitis)Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Xanthogranuloma, M 30, Right ElbowDocument4 pagesXanthogranuloma, M 30, Right ElbowDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verrucous Carcinoma., M 58, Left Leg Amputation StumpDocument7 pagesVerrucous Carcinoma., M 58, Left Leg Amputation StumpDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verruca Vulgaris., M 22.,PPTDocument2 pagesVerruca Vulgaris., M 22.,PPTDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma In-Situ (VIN III), F 50, VulvaDocument6 pagesVulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma In-Situ (VIN III), F 50, VulvaDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verrucous Epidermal Nevus. F 43, ScalpDocument4 pagesVerrucous Epidermal Nevus. F 43, ScalpDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst
DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst
Uploaded by
Deba P SarmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst
DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst
Uploaded by
Deba P SarmaCopyright:
Available Formats
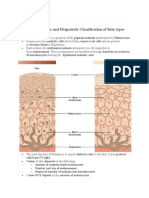
Dr Sarmas guide to mastering
Dermal cyst
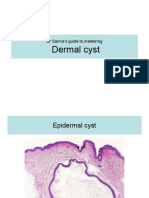
Epidermal cyst
Dermal cyst lined by epidermis with granular layer and containing flakey keratin.
Pilar cyst ( Trichilemmal cyst)
Dermal cyst lined by less basophilic trichilemmal epithelium containig compact pilar type keratin. Calcification is common.
Infundibular cyst (Pilar cyst, infundibular type)
Pilar cyst close to the epidermis arising from the infundibulum of the hair. Lined by trichilemmal (LT) as well as epidermal epithelium with granular layer (RT). Content of the cyst: Compact keratin.
Epidermal and pilar cyst
Compare the epidermal cyst with normal epidermis. Compare the pilar cyst with normal hair.
Dermoid cyst
Dermal cyst lined by epidermis with all normal adnexal structures. Lumen contains flakey keratin and hair.
Epidermal, pilar, dermoid cyst compared
Epidermal cyst: 1. Lining: Normal epidermis with granular layer. No adnexal structure. 2. Content: Flakey keratin.
Pilar cyst: 1.Lining: Pale trichilemmal epithelium, no granular layer. 2.Content: Compact keratin
Dermoid cyst: 1. Lining: Epidermis with adnexae. 2. Content: Flakey keratin, hair.
Ruptured epidermal cyst
Dermal cyst lined by giant cells, histiocytes,sometimes residual epidermis containing flakey keratin within the cyst cavity.
Hidrocystoma
Dermal cyst lined by small cuboidal cells of sweat duct. Cyst cavity contains fluid ( sweat ), but no keratin.
Steatocystoma
Multilocular dermal cyst lined by wavy squamous epithelium with sebaceous glands. Cyst cavity contains oily fluid, but no keratin. Origin of this cyst is the sebaceous gland duct.
Hidrocystoma and steatocystoma
Compare and contrast side by side.
You might also like
- Camel IntegumentDocument4 pagesCamel IntegumentDarkCupid Mynhero100% (1)
- The Integumentary SystemDocument33 pagesThe Integumentary SystemMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Dermal Cysts, Diagnostic FeaturesDocument11 pagesDermal Cysts, Diagnostic FeaturesDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- DR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst.Document11 pagesDR Sarma's Guide To Mastering Dermal Cyst.Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Untitled1 PDFDocument10 pagesUntitled1 PDFMarzthNo ratings yet
- 09 - Skin and Its AppendagesDocument61 pages09 - Skin and Its AppendagesArjohn VegaNo ratings yet
- 1-Function Dermatology NotesDocument80 pages1-Function Dermatology Notesz9cz4zhv55No ratings yet
- Infundibular Cyst. M 64, Right Arm.Document6 pagesInfundibular Cyst. M 64, Right Arm.Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument36 pagesSkin and Its Appendagesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Integumentary Analab)Document2 pagesIntegumentary Analab)Kimberly Wyne SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- 6 Integumentary1Document66 pages6 Integumentary1api-159564163No ratings yet
- Infundibular Cyst. M 64, Right ArmDocument6 pagesInfundibular Cyst. M 64, Right ArmDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- And Its Appendages: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowDocument44 pagesAnd Its Appendages: Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, LucknowCesar Ivan Ruiz DiazNo ratings yet
- Int - Sys ComDocument19 pagesInt - Sys ComBernard FernandezNo ratings yet
- Histology Skin & AppendagesDocument44 pagesHistology Skin & AppendagesMathew JosephNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 4 - IntegumentaryDocument45 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 4 - Integumentaryprincesinclair77No ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomy of The SkinDocument15 pages1 - Anatomy of The Skinumart4843No ratings yet
- Dermatology NotesDocument37 pagesDermatology NotesTamilmani n.mNo ratings yet
- Approach To Skin DiseasesDocument63 pagesApproach To Skin DiseasesPriya GK100% (1)
- Integument SystemDocument23 pagesIntegument SystemPRIYA DARSHINI GUNALANNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Integumentary System: References: Http://people - Upei.ca/hannaDocument22 pagesPathology of The Integumentary System: References: Http://people - Upei.ca/hannaLakshita Prajapati100% (1)
- Skin and Breast HistologyDocument8 pagesSkin and Breast HistologyPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Skin FunctionDocument50 pagesPhysiology of Skin FunctionPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- General DermatologyDocument31 pagesGeneral DermatologyMartaNo ratings yet
- The Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDocument72 pagesThe Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDeborahMcCloudNo ratings yet
- Hair Diseases: AnatomyDocument36 pagesHair Diseases: AnatomyMasithaNo ratings yet
- K1 Kulit Dan AdnexaDocument23 pagesK1 Kulit Dan AdnexaJimmy Fran IINo ratings yet
- Pablo Clark Integumentary PartsDocument5 pagesPablo Clark Integumentary PartsClark Vincent PabloNo ratings yet
- 4# Bisma Aslam (20-ARID-3222)Document8 pages4# Bisma Aslam (20-ARID-3222)TasbihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Notes - A&P 2022Document6 pagesChapter 5 Notes - A&P 2022Ashley MarieNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument49 pagesIntegumentary SystemCUEVA Cristine JaneNo ratings yet
- ColorimetricDocument6 pagesColorimetric4gen_5No ratings yet
- Pearls: 1889. Colour of Skin and Fitzpatrick Classification of Skin TypesDocument118 pagesPearls: 1889. Colour of Skin and Fitzpatrick Classification of Skin TypesswastikNo ratings yet
- Basic DermatologyDocument43 pagesBasic Dermatologyarslan63637363No ratings yet
- CylindromaDocument1 pageCylindromaDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument35 pagesThe Integumentary SystemVivek BhattNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument45 pagesIntegumentary SystemDASHNo ratings yet
- HIstology Experiment 12Document5 pagesHIstology Experiment 12Pearlregine Cianne MirandaNo ratings yet
- The Histology ofDocument15 pagesThe Histology ofEveryday FundayNo ratings yet
- SKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Document40 pagesSKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Sadia SohailNo ratings yet
- 1 LG) Histology of The SkinDocument25 pages1 LG) Histology of The SkinJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- Module 3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMDocument25 pagesModule 3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- III Components of The Integumentary System949Document4 pagesIII Components of The Integumentary System949Grimlock GrimmyNo ratings yet
- The Skin (Anaphy)Document2 pagesThe Skin (Anaphy)ALEXANDRA COLLEEN ALEGRENo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument52 pagesIntegumentary Systemyasin oumer0% (1)
- Dermatology FirecrackerDocument28 pagesDermatology FirecrackerKeham LeogNo ratings yet
- LG2 Histology of The SkinDocument26 pagesLG2 Histology of The SkinRawa AyubNo ratings yet
- Epidermis Dermis Hypodermis or Subcutaneous TissueDocument2 pagesEpidermis Dermis Hypodermis or Subcutaneous TissueCarmehlyn BalogbogNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument74 pagesIntegumentary SystemririyoruNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument10 pagesIntegumentary SystemharlynnsalmeoNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument40 pagesThe Integumentary SystemYuni AtiNo ratings yet
- 0401 Histo LectureDocument57 pages0401 Histo LectureJoe JNo ratings yet
- WorkbookModule14 Integumentary SystemDocument13 pagesWorkbookModule14 Integumentary Systemsarahfrancesca03No ratings yet
- 7 Integumentary SystemDocument38 pages7 Integumentary Systemvanderphys100% (1)
- Histology SkinDocument5 pagesHistology SkinFahd Abdullah Al-refaiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument38 pagesIntegumentary SystemTrista CincoNo ratings yet
- The Skin Structure: Presentation ofDocument35 pagesThe Skin Structure: Presentation ofdimple bachkaniwalaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIntegumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Skin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSkin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pilar Cyst With CrystalsDocument2 pagesPilar Cyst With CrystalsDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Solar Keratosis, M 67, Forehead PDFDocument6 pagesAcantholytic Solar Keratosis, M 67, Forehead PDFDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Accessory TragusDocument3 pagesAccessory TragusDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Actinic KeratosisDocument4 pagesAcantholytic Actinic KeratosisDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Dermatosis With DyskeratosisDocument11 pagesAcantholytic Dermatosis With DyskeratosisDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Bullous DiseaseDocument4 pagesAcantholytic Bullous DiseaseDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Results of Search in Google Scholar On 'Deba P Sarma'Document28 pagesResults of Search in Google Scholar On 'Deba P Sarma'Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDocument8 pagesAcantholytic Acanthoma. M 60, ScrotumDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Acantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis)Document3 pagesAcantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis)Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verrucous Carcinoma of The Foot, M 63, Left FootDocument8 pagesVerrucous Carcinoma of The Foot, M 63, Left FootDeba P Sarma100% (1)
- Xanthomatous Synovial Cyst (Xanthomatous Ganglion Cyst), M 74, Left PalmDocument7 pagesXanthomatous Synovial Cyst (Xanthomatous Ganglion Cyst), M 74, Left PalmDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Xanthogranuloma PPT DSDocument9 pagesXanthogranuloma PPT DSDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Balanitis Circumscripta Plasmacellularis (Zoon's Balanitis, Plasma Cell Balanitis)Document6 pagesBalanitis Circumscripta Plasmacellularis (Zoon's Balanitis, Plasma Cell Balanitis)Deba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Xanthogranuloma, M 30, Right ElbowDocument4 pagesXanthogranuloma, M 30, Right ElbowDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verrucous Carcinoma., M 58, Left Leg Amputation StumpDocument7 pagesVerrucous Carcinoma., M 58, Left Leg Amputation StumpDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verruca Vulgaris., M 22.,PPTDocument2 pagesVerruca Vulgaris., M 22.,PPTDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma In-Situ (VIN III), F 50, VulvaDocument6 pagesVulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma In-Situ (VIN III), F 50, VulvaDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Verrucous Epidermal Nevus. F 43, ScalpDocument4 pagesVerrucous Epidermal Nevus. F 43, ScalpDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet