Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsBasis & Vectors
Basis & Vectors
Uploaded by
Vel Murugan KTThis document discusses basics of signal and image processing including basis vectors, spans, normalization, orthogonality, orthonormality, and polyphase structures. It provides examples of representing a vector as a linear combination of basis vectors, normalizing a vector, checking orthogonality and orthonormality of vectors, and representing a signal using a polyphase structure.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Solved Problems GroupsDocument10 pagesSolved Problems GroupsmementoNo ratings yet
- q2 SolnDocument2 pagesq2 SolnMaloy GhoshNo ratings yet
- Examen Matrices Nombre: Perez Condori Helen Curso: 1° "A"Document3 pagesExamen Matrices Nombre: Perez Condori Helen Curso: 1° "A"Di MinyunNo ratings yet
- Probleme Rezolvate AlgadDocument3 pagesProbleme Rezolvate AlgadCristian Giorgian LovinNo ratings yet
- MTH 501-Assignment # 1 Spring 2022: Name: Ayesha Noor ID: BC210202124Document4 pagesMTH 501-Assignment # 1 Spring 2022: Name: Ayesha Noor ID: BC210202124Ayesha NoorNo ratings yet
- Capítulo Ii: Sección 2.1: El Espacio RDocument13 pagesCapítulo Ii: Sección 2.1: El Espacio RMarquitos BloeckNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pert - 12, JawabDocument5 pagesTugas Pert - 12, JawabMuhlasinNo ratings yet
- Assign2 Sol PDFDocument6 pagesAssign2 Sol PDFPrathiksha RavishankarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Fall 2022Document9 pagesFinal Exam Fall 2022Amna OmerNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document6 pagesHW 4awaisNo ratings yet
- Bagdasar2013 NEWDocument27 pagesBagdasar2013 NEWDennis YartelNo ratings yet
- Vectors Scalar ProductDocument3 pagesVectors Scalar ProductAli khan7No ratings yet
- Math 3171-Spring2016-Final-Exam-Make-Up-SolutionDocument5 pagesMath 3171-Spring2016-Final-Exam-Make-Up-Solutionbk4f7fn2tkNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument18 pagesUNIT II Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsRushi Jadhav100% (2)
- Exercise 2.1 (Advanced)Document2 pagesExercise 2.1 (Advanced)abhyudaipathwayNo ratings yet
- Arlyn Ragudos Bsa1 MathDocument3 pagesArlyn Ragudos Bsa1 MathArlyn Ragudos BSA1No ratings yet
- JEEMain Reliable Mathematics 26-02-2021 Shift2Document18 pagesJEEMain Reliable Mathematics 26-02-2021 Shift2Rupak DattaNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Document18 pagesJEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Dharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Document18 pagesJEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Kalyan MarutiNo ratings yet
- MathDocument18 pagesMathPrathmesh GuravNo ratings yet
- Home Work Week 3 Function 2 Applied Mathematics For Environmental Engineering by Rahman Fajar IrnawanDocument28 pagesHome Work Week 3 Function 2 Applied Mathematics For Environmental Engineering by Rahman Fajar IrnawanRahman Fajar IrnawanNo ratings yet
- Answers Paper AIEEEDocument17 pagesAnswers Paper AIEEESuyash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The Three-Dimensional Coordinate System PDFDocument16 pagesThe Three-Dimensional Coordinate System PDFResty BalinasNo ratings yet
- Relations, Functions - ITF SolutionsDocument76 pagesRelations, Functions - ITF SolutionsDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Test Zbi 2013Document144 pagesTest Zbi 2013lformula6429No ratings yet
- Mathematics FormulasDocument2 pagesMathematics FormulasgopalmyneniNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture: Tutorial 6Document22 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture: Tutorial 6John DoeNo ratings yet
- 2010 Revision Solution - StudentDocument12 pages2010 Revision Solution - StudentmosesNo ratings yet
- PT-2 QP 2021-22 Set-QDocument5 pagesPT-2 QP 2021-22 Set-QGunjan MeshramNo ratings yet
- Nishant Math AssingmentDocument15 pagesNishant Math AssingmentNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- QM Problem Set 1Document9 pagesQM Problem Set 1Aniruddha GhoshNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier-2 2010 Maths by CrackuDocument42 pagesSSC CGL Tier-2 2010 Maths by CrackuRohit BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 1: B1 + TB1 Statistics For Engineers (Mat-2001) Prof. Kalaivani KDocument9 pagesDigital Assignment 1: B1 + TB1 Statistics For Engineers (Mat-2001) Prof. Kalaivani KHappy AsiamNo ratings yet
- Resume Vector 3 Dimension Multiple Variable CalculusDocument9 pagesResume Vector 3 Dimension Multiple Variable CalculusRendy B. SuharsonoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Algebra Lineal 1Document52 pagesEjercicios de Algebra Lineal 1Ruben Dario RamirezNo ratings yet
- Periodic Solutions For Non-Linear Systems of Integral EquationsDocument16 pagesPeriodic Solutions For Non-Linear Systems of Integral EquationsInternational Journal of Engineering Inventions (IJEI)No ratings yet
- hw1 Math3410 S23solutionsDocument5 pageshw1 Math3410 S23solutionstaxin90604No ratings yet
- Ichiro 30 Nov 2023Document8 pagesIchiro 30 Nov 2023wisnuNo ratings yet
- DM E Class 1 Group E Assignment 1Document8 pagesDM E Class 1 Group E Assignment 1EkaNo ratings yet
- Shadow FunctionsDocument14 pagesShadow FunctionsAngus 鄧雋杰 TangNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 March 18 Question Paper With Solutions by R - dxUKhGJDocument69 pagesJEE Main 2021 March 18 Question Paper With Solutions by R - dxUKhGJhari kishoreNo ratings yet
- Mat1503 A04Document20 pagesMat1503 A04Duncan Jäger DMninetynineNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Answer & SolutionDocument5 pagesMathematics: Answer & SolutionBhupatrai FalduNo ratings yet
- Ipvive ChallengeDocument8 pagesIpvive ChallengeTrung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Math Sample Paper-1 (With Solutions)Document21 pagesMath Sample Paper-1 (With Solutions)Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2011: Mathematics Paper IIDocument9 pagesIIT JEE 2011: Mathematics Paper IIkapilNo ratings yet
- Eko Budi Hartanto 41121110087 (Analisa Struktur 3)Document4 pagesEko Budi Hartanto 41121110087 (Analisa Struktur 3)Eko Budi HartantoNo ratings yet
- STA 421 LNoteDocument20 pagesSTA 421 LNotesanusi bello bakuraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document76 pagesLecture 2mjiabir12007No ratings yet
- Example 1:: 3.examples of SVMDocument4 pagesExample 1:: 3.examples of SVMDeadNo ratings yet
- Matemáticas II: Tarea Semanal # 1 Unidad # 1Document7 pagesMatemáticas II: Tarea Semanal # 1 Unidad # 1Nani brockNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument36 pagesVectorstizzy768020No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MDocument18 pagesAssignment 2 MabadittadesseNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Video y ForoDocument2 pagesEjercicios Video y ForoJackeline posada barreraNo ratings yet
- 18th March Shift-1 Mathematics (Crackjee - Xyz)Document12 pages18th March Shift-1 Mathematics (Crackjee - Xyz)StockPlusIndiaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design: Circuits & LayoutDocument48 pagesVLSI Design: Circuits & LayoutVel Murugan KTNo ratings yet
- LICDocument89 pagesLICBala913No ratings yet
- DSP Lab Sample Viva QuestionsDocument5 pagesDSP Lab Sample Viva QuestionsVel Murugan KTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Write VHDL Code For Realize All Logic Gates.Document65 pagesExperiment 1: Write VHDL Code For Realize All Logic Gates.sudharsan79% (43)
Basis & Vectors
Basis & Vectors
Uploaded by
Vel Murugan KT0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views9 pagesThis document discusses basics of signal and image processing including basis vectors, spans, normalization, orthogonality, orthonormality, and polyphase structures. It provides examples of representing a vector as a linear combination of basis vectors, normalizing a vector, checking orthogonality and orthonormality of vectors, and representing a signal using a polyphase structure.
Original Description:
vector decrption...
Original Title
Copy of Basis & Vectors
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses basics of signal and image processing including basis vectors, spans, normalization, orthogonality, orthonormality, and polyphase structures. It provides examples of representing a vector as a linear combination of basis vectors, normalizing a vector, checking orthogonality and orthonormality of vectors, and representing a signal using a polyphase structure.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views9 pagesBasis & Vectors
Basis & Vectors
Uploaded by
Vel Murugan KTThis document discusses basics of signal and image processing including basis vectors, spans, normalization, orthogonality, orthonormality, and polyphase structures. It provides examples of representing a vector as a linear combination of basis vectors, normalizing a vector, checking orthogonality and orthonormality of vectors, and representing a signal using a polyphase structure.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
BASICS & TRANSFORMS IN
SIGNAL & IMAGE PROCESSING
Dr. ILA.VENNILA
Associate Professor,
EEE Dept.,
PSG College of Technology,
Coimbatore.
Date:15-12-2011
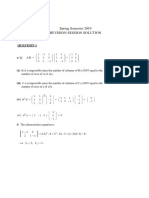
Basis vectors
x = [ 1 0 0], y = [ 0 1 0] , z = [ 0 0 1]
Let Vector A = [3 1 2]
A = 3x+1y+2z
Any vector can be expressed as linear
combination of basis vectors
Basic Vector
x1 = [ 1 0 0], y1 = [ 0 1 0] , z1 = [ 0 0 1] - Basis vectors
A = [3 2 5]
A = 3x+2y+5z
So x1,y1,z1 is span of R
3
x2 = [ 1 0 0], y2 = [ 1 1 0] , z2 = [ 0 0 1]
A= we cant form vector using x2,y2,z2
So x2,y2,z2 is not span of R
3
Span R
3
A = [3 1 2]
Magnitude =
= 3.742
Normalized A = [3 1 2] / 3.742
= [0.8017 0.2672 0.5345 ]
2 2 2
2 1 3 + +
Normalization
Orthogonal
Two Vectors a and b are said to be orthogonal if
their dot product is zero
a=[ 2 2 -1] , b = [ -1 2 2]
a.*b = [ 2 2 -1]
Every vector is perpendicular to every other vector
0
2
2
1
=
(
(
(
+
+
Orthonormal
Two Vectors a1 and a2 are said to be orthonormal
a1=[ 1 0 1] , a2 = [ 1 1 -1], b1 = [ 0 1 1], b2 = [ 0 1 0]
a1.*b1 = [ 1 0 1]
a2.*b1 = [ 1 1 -1]
1
1
1
0
=
(
(
(
0
1
1
0
=
(
(
(
a1=[ 1 0 1] , a2 = [ 1 1 -1], b1 = [ 0 1 1], b2 = [ 0 1 0]
a1.*b2 = [ 1 0 1]
a2.*b2 = [ 1 1 -1]
Now a1 and a2 are orthonormal
a
i
.b
j
= 0
= 1
0
0
1
0
=
(
(
(
1
0
1
0
=
(
(
(
j i =
j i =
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Polyphase structure
X
x
0
x
1
x
2
X = x
0
+x
1
+x
2
You might also like
- Solved Problems GroupsDocument10 pagesSolved Problems GroupsmementoNo ratings yet
- q2 SolnDocument2 pagesq2 SolnMaloy GhoshNo ratings yet
- Examen Matrices Nombre: Perez Condori Helen Curso: 1° "A"Document3 pagesExamen Matrices Nombre: Perez Condori Helen Curso: 1° "A"Di MinyunNo ratings yet
- Probleme Rezolvate AlgadDocument3 pagesProbleme Rezolvate AlgadCristian Giorgian LovinNo ratings yet
- MTH 501-Assignment # 1 Spring 2022: Name: Ayesha Noor ID: BC210202124Document4 pagesMTH 501-Assignment # 1 Spring 2022: Name: Ayesha Noor ID: BC210202124Ayesha NoorNo ratings yet
- Capítulo Ii: Sección 2.1: El Espacio RDocument13 pagesCapítulo Ii: Sección 2.1: El Espacio RMarquitos BloeckNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pert - 12, JawabDocument5 pagesTugas Pert - 12, JawabMuhlasinNo ratings yet
- Assign2 Sol PDFDocument6 pagesAssign2 Sol PDFPrathiksha RavishankarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Fall 2022Document9 pagesFinal Exam Fall 2022Amna OmerNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document6 pagesHW 4awaisNo ratings yet
- Bagdasar2013 NEWDocument27 pagesBagdasar2013 NEWDennis YartelNo ratings yet
- Vectors Scalar ProductDocument3 pagesVectors Scalar ProductAli khan7No ratings yet
- Math 3171-Spring2016-Final-Exam-Make-Up-SolutionDocument5 pagesMath 3171-Spring2016-Final-Exam-Make-Up-Solutionbk4f7fn2tkNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument18 pagesUNIT II Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsRushi Jadhav100% (2)
- Exercise 2.1 (Advanced)Document2 pagesExercise 2.1 (Advanced)abhyudaipathwayNo ratings yet
- Arlyn Ragudos Bsa1 MathDocument3 pagesArlyn Ragudos Bsa1 MathArlyn Ragudos BSA1No ratings yet
- JEEMain Reliable Mathematics 26-02-2021 Shift2Document18 pagesJEEMain Reliable Mathematics 26-02-2021 Shift2Rupak DattaNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Document18 pagesJEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Dharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Document18 pagesJEE (Main) 2021: PAPER-1 (B.E./B. TECH.)Kalyan MarutiNo ratings yet
- MathDocument18 pagesMathPrathmesh GuravNo ratings yet
- Home Work Week 3 Function 2 Applied Mathematics For Environmental Engineering by Rahman Fajar IrnawanDocument28 pagesHome Work Week 3 Function 2 Applied Mathematics For Environmental Engineering by Rahman Fajar IrnawanRahman Fajar IrnawanNo ratings yet
- Answers Paper AIEEEDocument17 pagesAnswers Paper AIEEESuyash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The Three-Dimensional Coordinate System PDFDocument16 pagesThe Three-Dimensional Coordinate System PDFResty BalinasNo ratings yet
- Relations, Functions - ITF SolutionsDocument76 pagesRelations, Functions - ITF SolutionsDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Test Zbi 2013Document144 pagesTest Zbi 2013lformula6429No ratings yet
- Mathematics FormulasDocument2 pagesMathematics FormulasgopalmyneniNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture: Tutorial 6Document22 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture: Tutorial 6John DoeNo ratings yet
- 2010 Revision Solution - StudentDocument12 pages2010 Revision Solution - StudentmosesNo ratings yet
- PT-2 QP 2021-22 Set-QDocument5 pagesPT-2 QP 2021-22 Set-QGunjan MeshramNo ratings yet
- Nishant Math AssingmentDocument15 pagesNishant Math AssingmentNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- QM Problem Set 1Document9 pagesQM Problem Set 1Aniruddha GhoshNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier-2 2010 Maths by CrackuDocument42 pagesSSC CGL Tier-2 2010 Maths by CrackuRohit BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 1: B1 + TB1 Statistics For Engineers (Mat-2001) Prof. Kalaivani KDocument9 pagesDigital Assignment 1: B1 + TB1 Statistics For Engineers (Mat-2001) Prof. Kalaivani KHappy AsiamNo ratings yet
- Resume Vector 3 Dimension Multiple Variable CalculusDocument9 pagesResume Vector 3 Dimension Multiple Variable CalculusRendy B. SuharsonoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Algebra Lineal 1Document52 pagesEjercicios de Algebra Lineal 1Ruben Dario RamirezNo ratings yet
- Periodic Solutions For Non-Linear Systems of Integral EquationsDocument16 pagesPeriodic Solutions For Non-Linear Systems of Integral EquationsInternational Journal of Engineering Inventions (IJEI)No ratings yet
- hw1 Math3410 S23solutionsDocument5 pageshw1 Math3410 S23solutionstaxin90604No ratings yet
- Ichiro 30 Nov 2023Document8 pagesIchiro 30 Nov 2023wisnuNo ratings yet
- DM E Class 1 Group E Assignment 1Document8 pagesDM E Class 1 Group E Assignment 1EkaNo ratings yet
- Shadow FunctionsDocument14 pagesShadow FunctionsAngus 鄧雋杰 TangNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 March 18 Question Paper With Solutions by R - dxUKhGJDocument69 pagesJEE Main 2021 March 18 Question Paper With Solutions by R - dxUKhGJhari kishoreNo ratings yet
- Mat1503 A04Document20 pagesMat1503 A04Duncan Jäger DMninetynineNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Answer & SolutionDocument5 pagesMathematics: Answer & SolutionBhupatrai FalduNo ratings yet
- Ipvive ChallengeDocument8 pagesIpvive ChallengeTrung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument8 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- Math Sample Paper-1 (With Solutions)Document21 pagesMath Sample Paper-1 (With Solutions)Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2011: Mathematics Paper IIDocument9 pagesIIT JEE 2011: Mathematics Paper IIkapilNo ratings yet
- Eko Budi Hartanto 41121110087 (Analisa Struktur 3)Document4 pagesEko Budi Hartanto 41121110087 (Analisa Struktur 3)Eko Budi HartantoNo ratings yet
- STA 421 LNoteDocument20 pagesSTA 421 LNotesanusi bello bakuraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document76 pagesLecture 2mjiabir12007No ratings yet
- Example 1:: 3.examples of SVMDocument4 pagesExample 1:: 3.examples of SVMDeadNo ratings yet
- Matemáticas II: Tarea Semanal # 1 Unidad # 1Document7 pagesMatemáticas II: Tarea Semanal # 1 Unidad # 1Nani brockNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument36 pagesVectorstizzy768020No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MDocument18 pagesAssignment 2 MabadittadesseNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Video y ForoDocument2 pagesEjercicios Video y ForoJackeline posada barreraNo ratings yet
- 18th March Shift-1 Mathematics (Crackjee - Xyz)Document12 pages18th March Shift-1 Mathematics (Crackjee - Xyz)StockPlusIndiaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandComplex Numbers (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design: Circuits & LayoutDocument48 pagesVLSI Design: Circuits & LayoutVel Murugan KTNo ratings yet
- LICDocument89 pagesLICBala913No ratings yet
- DSP Lab Sample Viva QuestionsDocument5 pagesDSP Lab Sample Viva QuestionsVel Murugan KTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Write VHDL Code For Realize All Logic Gates.Document65 pagesExperiment 1: Write VHDL Code For Realize All Logic Gates.sudharsan79% (43)