Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photo Voltaic Cell
Photo Voltaic Cell
Uploaded by
Sarath YarramalliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Welcome To Rogers: Vishn VardhanDocument8 pagesWelcome To Rogers: Vishn VardhanSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- EXP-01 Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleDocument6 pagesEXP-01 Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModulevincentNo ratings yet
- Light Electricity Photovoltaic EffectDocument1 pageLight Electricity Photovoltaic EffectSindhu SundaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell 1Document1 pageSolar Cell 1Samira Kumar beheraNo ratings yet
- TEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuideDocument2 pagesTEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuidenhstechnologyNo ratings yet
- Solar CellDocument1 pageSolar CellDinesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic ModuleDocument3 pagesPhotovoltaic ModuleAung MyatNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell A Solar Cell, or Photovoltaic Cell, Is An Electrical Device That Converts The Energy of Light Directly IntoDocument2 pagesSolar Cell A Solar Cell, or Photovoltaic Cell, Is An Electrical Device That Converts The Energy of Light Directly IntoET163018 Khaled ArjuNo ratings yet
- CO4 Material 1Document5 pagesCO4 Material 1SAI MNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell Working PrincipleDocument9 pagesSolar Cell Working PrincipleWinry Rockbell0% (1)
- Solar Energy ReportDocument13 pagesSolar Energy ReportScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- What Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellDocument9 pagesWhat Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellrishabhNo ratings yet
- Examen Final de Práctica 2 - How Does Photovoltaics WorkDocument2 pagesExamen Final de Práctica 2 - How Does Photovoltaics Workdaniela BroccardoNo ratings yet
- Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleDocument6 pagesCurrent-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleKzandra KatigbakNo ratings yet
- OptoelectonicsDocument1 pageOptoelectonicswalbrobatNo ratings yet
- Uasenglishc431 20 0099muhamadnasfaalfiDocument1 pageUasenglishc431 20 0099muhamadnasfaalfinasfaalfiNo ratings yet
- A Solar CellDocument22 pagesA Solar CellSejal andraskarNo ratings yet
- Solar LunaaDocument36 pagesSolar Lunaasuraj choudhuryNo ratings yet
- Photo Voltaic CellsDocument2 pagesPhoto Voltaic CellsRomina NitaNo ratings yet
- Solar Cells and The PhotoDocument4 pagesSolar Cells and The PhotoLud EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurDocument29 pagesSolar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurHinduja KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3digiy40095No ratings yet
- What Is Solar Power and Solar Power PlantDocument4 pagesWhat Is Solar Power and Solar Power PlantKHILY SAXENANo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument7 pagesSolar SystemPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Group3-SECT W.answersDocument44 pagesGroup3-SECT W.answersJustino BalaneNo ratings yet
- SOLARDocument5 pagesSOLARKim CanilloNo ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument19 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerShibu100% (1)
- Solar PowerDocument6 pagesSolar PowerkusumchitikaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic CellDocument12 pagesPhotovoltaic CellChristopher WalkerNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity: Electronics Engineering DepartmentDocument50 pagesBasic Electricity: Electronics Engineering DepartmentMartin John RamirezNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On SolarmobilechargerDocument25 pagesSeminar Report On SolarmobilechargerSujana Suji100% (1)
- Solar Energy L M - U N 4 - Session 15 16Document12 pagesSolar Energy L M - U N 4 - Session 15 16DHANANJAY POPAT MANENo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Cells EssayDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Cells EssayIulia NeaguNo ratings yet
- Solar AssignmentDocument52 pagesSolar AssignmentshehzadchoudhryNo ratings yet
- Cell, Module, Panel, ArrayDocument2 pagesCell, Module, Panel, ArrayPNo ratings yet
- SOLAR CELLS (Photovoltaic Cell) : PV GeneratorDocument3 pagesSOLAR CELLS (Photovoltaic Cell) : PV GeneratorAyush JainNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy - Energy From The SunDocument4 pagesSolar Energy - Energy From The SunAntony RatheeshNo ratings yet
- PV Technology - LatestDocument21 pagesPV Technology - LatestZaferullah KhanNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON: Submitted By:-Renu MeenaDocument10 pagesA Presentation ON: Submitted By:-Renu MeenaDinesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction of Photovoltaic CellDocument48 pagesChapter-1 Introduction of Photovoltaic Cellkalyan kingNo ratings yet
- Solar Power PlantDocument65 pagesSolar Power PlantHil GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument9 pagesSolar Energysayyohabba2021No ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument21 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerPrabir Kumar Pati33% (3)
- Photovoltaic System: How Do These Systems Work?Document1 pagePhotovoltaic System: How Do These Systems Work?SumiNo ratings yet
- Artice For Magazine Solar Energy by Naman Pandey B.Tech 2nd YearDocument9 pagesArtice For Magazine Solar Energy by Naman Pandey B.Tech 2nd YearNaman PandeyNo ratings yet
- Vishal Dagade Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesVishal Dagade Seminar ReportVishal DagadeNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy It Is Energy: Direct Indirect (PV)Document1 pageSolar Energy It Is Energy: Direct Indirect (PV)Katrina CaveNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy SubjectDocument1 pageSolar Energy SubjectKatrina CaveNo ratings yet
- TOP8Document22 pagesTOP8befikehalexNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportNishkarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy and Solar Panels (Pratham)Document7 pagesSolar Energy and Solar Panels (Pratham)Aayush LandgeNo ratings yet
- Bypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysDocument11 pagesBypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysAyanda MhlangaNo ratings yet
- RW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Document4 pagesRW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Olawale John AdeotiNo ratings yet
- Ganesh SeminarDocument19 pagesGanesh SeminarRohithNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Cell: Solar Energy Can Be Converted To Thermal (Or Heat) Energy and Used ToDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Cell: Solar Energy Can Be Converted To Thermal (Or Heat) Energy and Used To123nilNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Solar Powered Streetlight SystemDocument7 pagesDesign and Construction of A Solar Powered Streetlight Systemsamuel mechNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic System: Camilo Peñaranda Rincon 1092156401Document3 pagesPhotovoltaic System: Camilo Peñaranda Rincon 1092156401Camilo PeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Report TextDocument2 pagesReport TextFadlillah IhsanNo ratings yet
- How to Install & Design Solar Panels Like a ProfessionalFrom EverandHow to Install & Design Solar Panels Like a ProfessionalNo ratings yet
- Title Daily Current Affairs CapsuleDocument8 pagesTitle Daily Current Affairs CapsuleSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Englisb VocabDocument1 pageEnglisb VocabSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- MAG ZNE TelegramDocument38 pagesMAG ZNE TelegramSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Adda247 50 PuzzlesDocument1 pageAdda247 50 PuzzlesSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs - Capsule: Exclusive For IBPS PO MAINS AspirantsDocument12 pagesCurrent Affairs - Capsule: Exclusive For IBPS PO MAINS AspirantsSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- MoneyGram - Thank YouDocument1 pageMoneyGram - Thank YouSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Effective Report Writing KRUSHANTDocument38 pagesEffective Report Writing KRUSHANTSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Carrer Planning: by Abhilash RudrasamudramDocument6 pagesCarrer Planning: by Abhilash RudrasamudramSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Bhasker ReddyDocument19 pagesBhasker ReddySarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Incentive PayDocument22 pagesPros and Cons of Incentive PaySarath Yarramalli100% (1)
- Cliff AssignmentsDocument19 pagesCliff AssignmentsSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Case 2 PDFDocument6 pagesCase 2 PDFSarath Yarramalli100% (1)
- Volkswagen: BY Sai SarathDocument10 pagesVolkswagen: BY Sai SarathSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- BUS 340 Strategic Planning Syllabus Canadore@StanfordDocument1 pageBUS 340 Strategic Planning Syllabus Canadore@StanfordSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Changing Course atDocument17 pagesChanging Course atSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
Photo Voltaic Cell
Photo Voltaic Cell
Uploaded by
Sarath YarramalliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photo Voltaic Cell
Photo Voltaic Cell
Uploaded by
Sarath YarramalliCopyright:
Available Formats
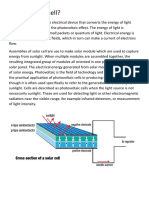
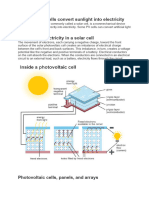
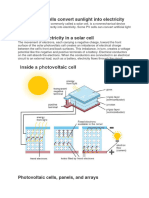
A solar cell (also called a photovoltaic cell) is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into
electricity by the photovoltaic effect. It is a form of photoelectric cell (in that its electrical characteristicse.g. current, voltage, or resistancevary when light is incident upon it) which, when exposed to light, can generate and support an electric current without being attached to any external voltage source. Photovoltaics is the field of technology and research related to the practical application of photovoltaic cells in producing electricity from light, though it is often used specifically to refer to the generation of electricity from sunlight. Cells can be described as photovoltaic even when the light source is not necessarily sunlight (lamplight, artificial light, etc.). In such cases the cell is sometimes used as a photodetector (for example infrared detectors), detecting light or other electromagnetic radiation near the visible range, or measuring light intensity. The operation of a photovoltaic (PV) cell requires 3 basic attributes:
1. 2.
The absorption of light, generating either electron-hole pairs or excitons. The separation of charge carriers of opposite types.
3. The separate extraction of those carriers to an external circuit. Assemblies of photovoltaic cells are used to make solar modules which generate electrical power from sunlight. Multiple cells in an integrated group, all oriented in one plane, constitute a solar photovoltaic panel or "solar photovoltaic module," as distinguished from a "solar thermal module" or "solar hot water panel." The electrical energy generated from solar modules, referred to as solar power, is an example of solar energy. A group of connected solar modules (such as prior to installation on a pole-mounted tracker system) is called an "array."
You might also like
- Welcome To Rogers: Vishn VardhanDocument8 pagesWelcome To Rogers: Vishn VardhanSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- EXP-01 Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleDocument6 pagesEXP-01 Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModulevincentNo ratings yet
- Light Electricity Photovoltaic EffectDocument1 pageLight Electricity Photovoltaic EffectSindhu SundaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell 1Document1 pageSolar Cell 1Samira Kumar beheraNo ratings yet
- TEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuideDocument2 pagesTEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuidenhstechnologyNo ratings yet
- Solar CellDocument1 pageSolar CellDinesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic ModuleDocument3 pagesPhotovoltaic ModuleAung MyatNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell A Solar Cell, or Photovoltaic Cell, Is An Electrical Device That Converts The Energy of Light Directly IntoDocument2 pagesSolar Cell A Solar Cell, or Photovoltaic Cell, Is An Electrical Device That Converts The Energy of Light Directly IntoET163018 Khaled ArjuNo ratings yet
- CO4 Material 1Document5 pagesCO4 Material 1SAI MNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell Working PrincipleDocument9 pagesSolar Cell Working PrincipleWinry Rockbell0% (1)
- Solar Energy ReportDocument13 pagesSolar Energy ReportScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- What Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellDocument9 pagesWhat Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellrishabhNo ratings yet
- Examen Final de Práctica 2 - How Does Photovoltaics WorkDocument2 pagesExamen Final de Práctica 2 - How Does Photovoltaics Workdaniela BroccardoNo ratings yet
- Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleDocument6 pagesCurrent-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleKzandra KatigbakNo ratings yet
- OptoelectonicsDocument1 pageOptoelectonicswalbrobatNo ratings yet
- Uasenglishc431 20 0099muhamadnasfaalfiDocument1 pageUasenglishc431 20 0099muhamadnasfaalfinasfaalfiNo ratings yet
- A Solar CellDocument22 pagesA Solar CellSejal andraskarNo ratings yet
- Solar LunaaDocument36 pagesSolar Lunaasuraj choudhuryNo ratings yet
- Photo Voltaic CellsDocument2 pagesPhoto Voltaic CellsRomina NitaNo ratings yet
- Solar Cells and The PhotoDocument4 pagesSolar Cells and The PhotoLud EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurDocument29 pagesSolar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurHinduja KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3digiy40095No ratings yet
- What Is Solar Power and Solar Power PlantDocument4 pagesWhat Is Solar Power and Solar Power PlantKHILY SAXENANo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument7 pagesSolar SystemPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Group3-SECT W.answersDocument44 pagesGroup3-SECT W.answersJustino BalaneNo ratings yet
- SOLARDocument5 pagesSOLARKim CanilloNo ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument19 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerShibu100% (1)
- Solar PowerDocument6 pagesSolar PowerkusumchitikaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic CellDocument12 pagesPhotovoltaic CellChristopher WalkerNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity: Electronics Engineering DepartmentDocument50 pagesBasic Electricity: Electronics Engineering DepartmentMartin John RamirezNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On SolarmobilechargerDocument25 pagesSeminar Report On SolarmobilechargerSujana Suji100% (1)
- Solar Energy L M - U N 4 - Session 15 16Document12 pagesSolar Energy L M - U N 4 - Session 15 16DHANANJAY POPAT MANENo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Cells EssayDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Cells EssayIulia NeaguNo ratings yet
- Solar AssignmentDocument52 pagesSolar AssignmentshehzadchoudhryNo ratings yet
- Cell, Module, Panel, ArrayDocument2 pagesCell, Module, Panel, ArrayPNo ratings yet
- SOLAR CELLS (Photovoltaic Cell) : PV GeneratorDocument3 pagesSOLAR CELLS (Photovoltaic Cell) : PV GeneratorAyush JainNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy - Energy From The SunDocument4 pagesSolar Energy - Energy From The SunAntony RatheeshNo ratings yet
- PV Technology - LatestDocument21 pagesPV Technology - LatestZaferullah KhanNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON: Submitted By:-Renu MeenaDocument10 pagesA Presentation ON: Submitted By:-Renu MeenaDinesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction of Photovoltaic CellDocument48 pagesChapter-1 Introduction of Photovoltaic Cellkalyan kingNo ratings yet
- Solar Power PlantDocument65 pagesSolar Power PlantHil GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument9 pagesSolar Energysayyohabba2021No ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument21 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerPrabir Kumar Pati33% (3)
- Photovoltaic System: How Do These Systems Work?Document1 pagePhotovoltaic System: How Do These Systems Work?SumiNo ratings yet
- Artice For Magazine Solar Energy by Naman Pandey B.Tech 2nd YearDocument9 pagesArtice For Magazine Solar Energy by Naman Pandey B.Tech 2nd YearNaman PandeyNo ratings yet
- Vishal Dagade Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesVishal Dagade Seminar ReportVishal DagadeNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy It Is Energy: Direct Indirect (PV)Document1 pageSolar Energy It Is Energy: Direct Indirect (PV)Katrina CaveNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy SubjectDocument1 pageSolar Energy SubjectKatrina CaveNo ratings yet
- TOP8Document22 pagesTOP8befikehalexNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportNishkarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy and Solar Panels (Pratham)Document7 pagesSolar Energy and Solar Panels (Pratham)Aayush LandgeNo ratings yet
- Bypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysDocument11 pagesBypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysAyanda MhlangaNo ratings yet
- RW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Document4 pagesRW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Olawale John AdeotiNo ratings yet
- Ganesh SeminarDocument19 pagesGanesh SeminarRohithNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Cell: Solar Energy Can Be Converted To Thermal (Or Heat) Energy and Used ToDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Cell: Solar Energy Can Be Converted To Thermal (Or Heat) Energy and Used To123nilNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Solar Powered Streetlight SystemDocument7 pagesDesign and Construction of A Solar Powered Streetlight Systemsamuel mechNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic System: Camilo Peñaranda Rincon 1092156401Document3 pagesPhotovoltaic System: Camilo Peñaranda Rincon 1092156401Camilo PeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Report TextDocument2 pagesReport TextFadlillah IhsanNo ratings yet
- How to Install & Design Solar Panels Like a ProfessionalFrom EverandHow to Install & Design Solar Panels Like a ProfessionalNo ratings yet
- Title Daily Current Affairs CapsuleDocument8 pagesTitle Daily Current Affairs CapsuleSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Englisb VocabDocument1 pageEnglisb VocabSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- MAG ZNE TelegramDocument38 pagesMAG ZNE TelegramSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Adda247 50 PuzzlesDocument1 pageAdda247 50 PuzzlesSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs - Capsule: Exclusive For IBPS PO MAINS AspirantsDocument12 pagesCurrent Affairs - Capsule: Exclusive For IBPS PO MAINS AspirantsSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- MoneyGram - Thank YouDocument1 pageMoneyGram - Thank YouSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Effective Report Writing KRUSHANTDocument38 pagesEffective Report Writing KRUSHANTSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Carrer Planning: by Abhilash RudrasamudramDocument6 pagesCarrer Planning: by Abhilash RudrasamudramSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Bhasker ReddyDocument19 pagesBhasker ReddySarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Incentive PayDocument22 pagesPros and Cons of Incentive PaySarath Yarramalli100% (1)
- Cliff AssignmentsDocument19 pagesCliff AssignmentsSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Case 2 PDFDocument6 pagesCase 2 PDFSarath Yarramalli100% (1)
- Volkswagen: BY Sai SarathDocument10 pagesVolkswagen: BY Sai SarathSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- BUS 340 Strategic Planning Syllabus Canadore@StanfordDocument1 pageBUS 340 Strategic Planning Syllabus Canadore@StanfordSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Changing Course atDocument17 pagesChanging Course atSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet