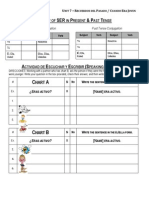
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verbos Reflexivos Explanation
Verbos Reflexivos Explanation
Uploaded by
amn628Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verbos Reflexivos Explanation
Verbos Reflexivos Explanation
Uploaded by
amn628Copyright:
Available Formats
Verbos Reflexivos
(Reflexive Verbs)
Reflexive verbs are verbs which are accompanied by a pronoun, called a
reflexive pronoun, that serves “to reflect” the action of the verb back to the
subject.
He cut himself with the razor.
Reflexive pronouns end with –self in the singular and –selves in the plural.
As the subject (yo, tú, etc.) changes, so does the reflexive pronoun , because
they both refer to the same person or object.
The reflexive pronouns are: me nos
te os
se se
In the infinitive form, reflexive verbs all have se as their reflexive pronoun
(lavarse, peinarse, ducharse, etc.)
**In the dictionary, reflexive verbs are listed under the regular verb. For example,
under dormir you’ll find dormirse. The meaning of the reflexive verb versus the
non reflexive verb varies slightly due to the fact that the action is being done by
and to the same person. (dormir = to sleep, dormirse= to go to sleep)
The reflexive pronoun comes BEFORE the verb when it is conjugated:
Despertarse Me despierto, te despiertas, se despierta
The reflexive pronoun is attached to the end of the infinitive when it is not
conjugated:
Voy a despertarme a las ocho de la mañana.
A reflexive verb is conjugated as normal, in any tense, and is accompanied by
the appropriate pronoun:
PEINARSE
me peino nos penamos
te peinas os penáis
se peina se peinan
**Reflexive verbs are also used to show reciprocal action; when people do the
same action to each other:
Raúl y María se besan. = Raúl and Maria kiss each other.
Las chicas se miran. = The girls look at each other.
You might also like
- Spanish 3 Lesson, Rap Song Using Ser and EstarDocument5 pagesSpanish 3 Lesson, Rap Song Using Ser and Estarvbevans1100% (1)
- True Cognates: Spanish Cognate Rule 1Document4 pagesTrue Cognates: Spanish Cognate Rule 1Edwin AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Present Tense - Regular VerbsDocument3 pagesPresent Tense - Regular VerbsAngeles Fernández100% (2)
- LESO Por Vs paraDocument46 pagesLESO Por Vs paraLearnenglishspanishonline Thelanguagetutors100% (1)
- Spanish Adjective Placement-Adjectives That Go Before The NounDocument5 pagesSpanish Adjective Placement-Adjectives That Go Before The Nounswatson033No ratings yet
- 10 Spanish Notes Preterite Vs ImperfectDocument3 pages10 Spanish Notes Preterite Vs ImperfectMelinda100% (3)
- La Familia ChoiceboardDocument1 pageLa Familia Choiceboardapi-235730203No ratings yet
- Spanish Future TenseDocument2 pagesSpanish Future TenseEvelyn Leong100% (1)
- Spanish Verb Conjugation and Tenses Practice Volume IV: Learn Spanish Verb Conjugation with Step by Step Spanish Examples Quick and Easy in Your Car Lesson by LessonFrom EverandSpanish Verb Conjugation and Tenses Practice Volume IV: Learn Spanish Verb Conjugation with Step by Step Spanish Examples Quick and Easy in Your Car Lesson by LessonNo ratings yet
- Spanish Verb Conjugation and Tenses Practice Volume VI: Learn Spanish Verb Conjugation with Step by Step Spanish Examples Quick and Easy in Your Car Lesson by LessonFrom EverandSpanish Verb Conjugation and Tenses Practice Volume VI: Learn Spanish Verb Conjugation with Step by Step Spanish Examples Quick and Easy in Your Car Lesson by LessonNo ratings yet
- Spanish Conjugations-Imperfect TenseDocument3 pagesSpanish Conjugations-Imperfect TenseHinatardNo ratings yet
- Regular AR VerbsDocument5 pagesRegular AR Verbsswatson033No ratings yet
- Guided Notes Adjective Noun Agreement and The Verb SerDocument4 pagesGuided Notes Adjective Noun Agreement and The Verb Serapi-246261720No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Quiz Review - Stations (Spanish 2)Document2 pagesUnit 5 Quiz Review - Stations (Spanish 2)JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Holiday Vocabulary & Christmas Celebrations in Spanish Speaking WorldDocument2 pagesHoliday Vocabulary & Christmas Celebrations in Spanish Speaking WorldJoaquin100% (1)
- Independent Practice ReflexiveDocument2 pagesIndependent Practice ReflexiveJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Spanish 3 and 4 Reflexive VerbsDocument14 pagesSpanish 3 and 4 Reflexive Verbsapi-262025495100% (1)
- Informal Commands TuDocument2 pagesInformal Commands TuMelissa JeffriesNo ratings yet
- Span I Review Packet IDocument7 pagesSpan I Review Packet IJoaquin100% (1)
- Adverbs / Adverbios: Adverb PlacementDocument8 pagesAdverbs / Adverbios: Adverb PlacementSara E. GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Preterite Vs Imperfect - Part IDocument16 pagesPreterite Vs Imperfect - Part IMerecia SmithNo ratings yet
- Notes On "Ser": The Verb "To Be"Document1 pageNotes On "Ser": The Verb "To Be"Anonymous dRKs83No ratings yet
- Los Adjetivos PosesivosDocument15 pagesLos Adjetivos Posesivosmartivola100% (1)
- Notas Affirmative CommandsDocument2 pagesNotas Affirmative CommandsJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Forming Questions in SpanishDocument10 pagesForming Questions in SpanishMaria FortinoNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Regular Verbs BookletDocument9 pagesPresent Tense Regular Verbs Bookletpetarda12100% (1)
- MINUTO LOCO - Intro SheetDocument2 pagesMINUTO LOCO - Intro SheetolliepraxlodgeNo ratings yet
- Progressive WorksheetDocument3 pagesProgressive Worksheetsw4738100% (2)
- D O C T O R: Apuntes 2.2.2-Ser Versus EstarDocument16 pagesD O C T O R: Apuntes 2.2.2-Ser Versus EstarJoaquin100% (3)
- El Subjuntivo Con EmocionDocument8 pagesEl Subjuntivo Con Emocionapi-246568048No ratings yet
- Para + InfDocument7 pagesPara + InfolliepraxlodgeNo ratings yet
- Spanish Demonstrative AdjectivesDocument8 pagesSpanish Demonstrative AdjectivesPowerPoints Galore100% (1)
- El Verbo: "To Be"Document5 pagesEl Verbo: "To Be"api-293868901No ratings yet
- EstarDocument11 pagesEstarapi-264563508No ratings yet
- Car Gar Zar Notes With AnswersDocument3 pagesCar Gar Zar Notes With Answersapi-246261720100% (1)
- Adjetivos DemostrativosDocument20 pagesAdjetivos Demostrativosjose valverdeNo ratings yet
- Spanish Past Tense AB INITIO OCT 25Document16 pagesSpanish Past Tense AB INITIO OCT 25Osa NilefunNo ratings yet
- Preterito y Imperfecto 9-5 Homework SlidesDocument23 pagesPreterito y Imperfecto 9-5 Homework Slidesapi-261138720No ratings yet
- Rutina Diaria ProjectDocument1 pageRutina Diaria ProjectJoaquinNo ratings yet
- CN Reflexive VerbsDocument6 pagesCN Reflexive VerbsJoaquinNo ratings yet
- Spanish 2 - Preterite Conjugation RacesDocument2 pagesSpanish 2 - Preterite Conjugation RacesJoaquinNo ratings yet
- El Pretérito y El Imperfecto, Juntos: erw1QUDocument18 pagesEl Pretérito y El Imperfecto, Juntos: erw1QUlzeeNo ratings yet
- Preterite Tense Assessment PlanDocument21 pagesPreterite Tense Assessment Planandrewsg23No ratings yet
- Guided Notes - Review of Daily Routine & Chores, Reflexive VerbsDocument4 pagesGuided Notes - Review of Daily Routine & Chores, Reflexive VerbsJoaquin100% (1)
- El Porque de Confusion Entre Preterito Indefinido y ImperfectoDocument17 pagesEl Porque de Confusion Entre Preterito Indefinido y ImperfectodrissechoNo ratings yet
- Preterite Stem-Changing Verbs IIDocument17 pagesPreterite Stem-Changing Verbs IIapi-293988969No ratings yet
- Spanish Class Questionnaire For TPRS/CI ClassesDocument1 pageSpanish Class Questionnaire For TPRS/CI ClassesElizabeth Dentlinger100% (1)
- Ser in Present & Past, The Imperfect TenseDocument10 pagesSer in Present & Past, The Imperfect TenseJoaquin100% (1)
- Spanish 1 - Sample Dialogues & Practice With Writing RubricDocument2 pagesSpanish 1 - Sample Dialogues & Practice With Writing RubricJoaquin50% (2)
- Los Verbos Reflexivos-RubricDocument4 pagesLos Verbos Reflexivos-Rubricamn628No ratings yet
- Spanish Grammar Rules: 7 Tricky Topics and How To Master ThemDocument11 pagesSpanish Grammar Rules: 7 Tricky Topics and How To Master ThemCora GalavísNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Past, Present and Future Tense in SpanishDocument19 pagesTopic 6 - Past, Present and Future Tense in SpanishYahiko100% (1)
- Review For Our UNIT TWO QUIZDocument5 pagesReview For Our UNIT TWO QUIZJoaquin100% (1)
- Spanish Speaking Countries ProjectDocument1 pageSpanish Speaking Countries Projectapi-326210415100% (1)
- LacasachoiceboardDocument2 pagesLacasachoiceboardapi-235730203No ratings yet
- SR Jordan VideosDocument3 pagesSR Jordan Videosapi-233375728No ratings yet
- Accentuation of Spanish WordsDocument2 pagesAccentuation of Spanish WordsManuel100% (2)
- All Preterite Verb ReviewDocument2 pagesAll Preterite Verb ReviewRebecca Robbins100% (1)
- Rules For Accent Marks in SpanishDocument5 pagesRules For Accent Marks in SpanishAna Jaen100% (1)
- Reflexive Verb PROJECTDocument1 pageReflexive Verb PROJECTamn628100% (1)
- Re Exive Verbs: Part II: I Wash MyselfDocument4 pagesRe Exive Verbs: Part II: I Wash Myselfamn628No ratings yet
- Los Verbos Reflexivos-RubricDocument4 pagesLos Verbos Reflexivos-Rubricamn628No ratings yet
- SabconDocument2 pagesSabconamn628No ratings yet
- Pret 1Document2 pagesPret 1amn628No ratings yet
- Reflexive 1Document3 pagesReflexive 1amn628No ratings yet
- PossproDocument3 pagesPossproamn628No ratings yet
- Pret 3Document2 pagesPret 3amn628No ratings yet
- Imp 1Document2 pagesImp 1amn628No ratings yet
- Preterite and Imperfect: Review: Hablar Comer VivirDocument6 pagesPreterite and Imperfect: Review: Hablar Comer Viviramn628100% (1)
- Pretimp 3Document2 pagesPretimp 3amn628No ratings yet
- Indirect Object Pronouns: Part II: He Gives The Book To MaríaDocument4 pagesIndirect Object Pronouns: Part II: He Gives The Book To Maríaamn628No ratings yet
- Direct Object Pronouns: Part I: BallDocument5 pagesDirect Object Pronouns: Part I: Ballamn628No ratings yet
- Indirect Object Pronouns: Part I: He Gives The Book To MaríaDocument4 pagesIndirect Object Pronouns: Part I: He Gives The Book To Maríaamn628No ratings yet
- Indirect Object Pronouns: Part III: He Gives María The BookDocument3 pagesIndirect Object Pronouns: Part III: He Gives María The Bookamn628No ratings yet
- Time Expressions With Hacer: Hace + Time + Que + Present Tense Form of The VerbDocument1 pageTime Expressions With Hacer: Hace + Time + Que + Present Tense Form of The Verbamn628No ratings yet
- FormcommDocument3 pagesFormcommamn628No ratings yet
- Subjunctive: Part II: Yo Form of The Present Indicative. - o EndingDocument5 pagesSubjunctive: Part II: Yo Form of The Present Indicative. - o Endingamn628No ratings yet
- Subjunctive: Part I: Usted Va Al Perú en DiciembreDocument3 pagesSubjunctive: Part I: Usted Va Al Perú en Diciembreamn628No ratings yet
- Subj 7Document2 pagesSubj 7amn628No ratings yet
- Definite and Indefinite Articles: P. 60 Realidades 1Document8 pagesDefinite and Indefinite Articles: P. 60 Realidades 1amn628No ratings yet
- P 110 NounsDocument18 pagesP 110 Nounsamn628No ratings yet