Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matrices: Matrix: An Arrangement of Number in To Rows and Columns Is Called A "Matrix"
Matrices: Matrix: An Arrangement of Number in To Rows and Columns Is Called A "Matrix"
Uploaded by
Komanduri Murali SrinivasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Matrices: Matrix: An Arrangement of Number in To Rows and Columns Is Called A "Matrix"
Matrices: Matrix: An Arrangement of Number in To Rows and Columns Is Called A "Matrix"
Uploaded by
Komanduri Murali SrinivasCopyright:
Available Formats
This chapter comes under Paper-II.
It is easiest chapter in all and also have lot of
weightage. From this chapter 2 Long answer type questions (24 = 8M), 2 short answer type
questions (22 = 4M) and 2 very short answer type questions (21 = 2M), and 6 objective
bits (61/2 = 3M) altogether 17 marks very easily can be scored. The following material will
help the students very much in the S.S.C public exams.
Matrix: An arrangement of number in to rows and columns is called a "matrix".
Concept of matrices was introduced by "Sir Arthurcayley".
The name "matrix" was given by "J.J. Sylvestor".
The symbol of matrix is "[ ]" or "( )".
If a matrix has 'm' rows and 'n' columns then "m
n" is called "order of matrix".
Addition and subtraction of matrices is possible if and only if they are of the same order.
Multiplication of matrices is possible if the number of columns of first matrix is equals to
number of rows of second matrix. i.e. A
mn
B
np
= AB
mp
.
If A
T
= A or A
T
A = 0 or A A
T
= 0 then A is called symmetric matrix.
If A
T
= A or A
T
+ A = 0 then 'A' is called skew-symmetric matrix.
A square matrix in which principle diagonal elements are equal is called "scalar matrix".
Eg: is a scalar matrix.
If is a scalar matrix then = _____ (Ans: 3)
If then t = ______ (Ans: 4)
Problem: 1
Find x and y if
Sol:
[ ] [ ]
2 3
x y 6 10
0 1
, ]
, ]
]
[ ] [ ]
2 3
x y 6 10
0 1
, ]
, ]
]
t
4 3
4 3
2 16
2 2
, ] , ]
, ]
, ]
]
]
[ ] ( ) [ ]
( )
, ]
+
, ]
]
, ]
, ]
]
x
A 5 2 B then i AB 5x 2y
y
5x 2x
ii BA
5y 2y
3 0
0
, ]
, ]
]
7 0
A
0 7
, ]
, ]
]
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
MATRICES
[ ] [ ]
2x 0 3x y 6 10 + +
3x + y = 10
3(3) + y = 10
9 + y = 10
y = 10 9
x = 3, y = 1
Problem: 2
find m if AB = BA.
Sol:
2 0 8 m
1
0 0 0
2
+ , ]
, ]
, ]
+ +
]
1 4
2 m
BA
1
0 1
0
2
, ]
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
]
, ]
]
( )
2 m 2
____ 1
1
0
2
, ]
, ]
, ]
]
2 0 m 4 + +
2
1
2
1
1
0 0 0 1
2
, ]
j \
, ] , (
, ] , (
, (
, ]
( ,
, ]
j \
, ]
+ +
, (
, ]
( ,
]
2 m
1 4
AB
1
0 1 0
2
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
]
]
2 m
1 4
A B
1
0 1 0
2
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
]
]
2 m
1 4
A B ,
1
0 1 0
2
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
]
]
y 1
x 3
2
1
x 6
3
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
Given that AB = BA
From (1) & (2)
m 2 = 8 m
m + m = 8 + 2
Problem: 3
then show that A
2
(a + d) A = (bc ad)I
Sol:
L.H.S
A
2
(a + d)A
= A A (a + d)A
( )
1 0
bc ad
0 1
, ]
, ]
]
bc ad 0
0 bc ad
, ]
, ]
]
2
a
2
bc a + ad ab bd + ab bd
ca dc + ac dc
2
cb d +
2
ad d
, ]
, ]
, ]
]
2 2
2 2
a bc ab bd a ad ab bd
ca dc cb d ac dc ad d
, ] , ]
+ + + +
, ] , ]
+ + + + , ] , ]
] ]
( )
a b a b a b
a d
c d c d c d
, ] , ] , ]
+
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
I
a b 1 0
A
c d 0 1
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
I
a b 1 0
A
c d 0 1
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
m 5
2
1
m 10
5
( )
2 8 m
____ 2
1
0
2
, ]
, ]
, ]
]
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
2 m 2 2 8 m
1 1
0 0
2 2
, ] , ]
, ] ,
, ] ,
] ]
= (bc ad) I
R.H.S.
Determinant of square matrix:
Then ad bc is called determinant of A and it is denoted by |A| ie |A| = ad bc
Eg:
Eg:
Note: A matrix whose determinant is zero is called "singular matrix".
A matrix whose determinant is not equals to zero is called "non singular matrix".
Multiplicative inverse of a square matrix:
A & B are any two non-singular matrices and AB = BA = I then each is called multiplicative
inverse of other ie A
1
= B and B
1
= A.
Problem: 4
and A doesn't have multiplicative inverse then find x.
Sol:
A doesn't have multiplicative inverse
A is singular matrix
|A| = 0
(4 9) (x x) = 0
36 x
2
= 0
x
2
= 36
x = 6
Problem: 5
If show that 'P' is it's own inverse.
1 4
P ,
0 1
, ]
, ]
]
4 x
0
x 9
4 x
A
x 9
, ]
, ]
]
4 x
A
x 9
, ]
, ]
]
1
a b d b
1
A A
ad bc c d c a
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
( )
1 2
____ Ans : 10
3 4
( )
2 3
____ Ans : 0
6 9
a b
If A
c d
, ]
, ]
]
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
Proof:
= P
Here P
1
= P
P is it's own inverse
Problem: 6
If then show that B + B
1
= 4I
Sol:
3 2
1 1
, ]
, ]
]
3 2
1
1 1 1
, ]
, ]
]
3 2
1
3 2 1 1
, ]
, ]
]
( ) ( )
1
1 2 3 2
1
B B
1 3 1 2 1 3 1 1
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
1
a b d b
1
A A
ad bc c d c a
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
1 2
B
1 3
, ]
, ]
]
1 2
B
1 3
, ]
, ]
]
1 4
0 1
, ]
, ]
]
1 4
1
0 1
, ]
, ]
]
1 4
1
1 0 1
, ]
, ]
]
( ) ( )
1
1 4 1 4
1
P P
1 1 4 0 0 1 0 1
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
1
a b d b
1
A A
ad bc c d c a
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
+
] ]
1 4
P ,
0 1
, ]
, ]
]
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
Consider
L.H.S
= B + B
1
=
= R.H.S
Cramer's method: (Procedure)
ax + by = p
cx + dy = q
Matrix equation form is
AX = B
|A| = ad bc
0
Cramer's rule can be applicable.
Here
Problem: 7
Solve by using Cramer's method.
Sol:
2x = 7 3y 6x + y = 13
2x + 3y = 7
2x + 3y = 7
6x + y = 13
Matrix equation form is
7 3y
x , y 13 6x
2
7 3y
x , y 13 6x
2
1 2
B B
x and y
A A
2 2
a p
B B aq pc
c q
, ]
, ]
]
1 1
p b
B B pd bq
q d
, ]
, ]
]
a b x p
c d y q
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
I
4 0
4
0 4
, ]
, ]
]
1 2 3 2
1 3 1 1
, ] , ]
+
, ] , ]
] ]
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
co-efficient
matrix
variable
matrix
constant
matrix
AX = B
|A| = ad bc
= (2 1) (3 6)
= 2 18
= 1 0
Cramer's rule is applicable.
= 7 39
= 32
= 26 42
= 16
x = 2, y = 1
Matrix inversion method: (Procedure)
ax + by = p
cx + dy = q
Matrix equation form is
AX = B
X = A
1
.B
|A| = ad bc
0
Matrix inversion method is applicable.
X = A
1
.B
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] ,
] ] ]
a b x p
A , X ,B
c d y q
a b x p
c d y q
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
2
B
16
y 1
A 16
1
B
32
x 2
A 16
( ) ( )
2 2
2 7
B B 2 13 7 6
6 13
, ]
, ]
]
( ) ( )
1 1
7 3
B B 7 1 3 13
13 1
, ]
, ]
]
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] ,
] ] ]
2 3 x 7
A , X ,B
6 1 y 13
2 3 x 7
6 1 y 13
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
Problem: 8
Solve 2x 3y + 6 = 0 and
by using matrix inversion method.
Sol:
2x 3y + 6 = 0
2x 3y = 6
Matrix equation form is
AX = B X = A
1
.B
|A| = ad bc
= (2 1) (3 6)
= 2 + 18
= 20 0
Matrix inversion method is applicable.
X = A
1
.B
X = 3/2 , y = 1
Assignment:
1. If find x and y.
3x 2y 6 5 6
2 2x 3y 2 8
+ , ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
30
3
20
2
20
1
20
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
, ]
]
]
30
1
20 20
, ]
, ]
]
6 24
1
20 36 16
, ]
, ]
]
1 3 6
1
20 6 2 8
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
d b p
1
X
ad bc c a q
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
2 3 x 6
A , X ,B
6 1 y 8
2 3 x 6
6 1 y 8
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
8 y
x
6
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
6x = 8 y
6x + y = 8
8 y
x
6
2. then show that A(B+C) = AB + AC.
3.
then show that (AB)
1
= B
1
.A
1
4. Solve by using Cramer's rule.
5. Solve by using 'matrix inversion method'.
Fill in the blanks:
1. If then P = ______
2. AB = K.I where KR, then A
1
= ______
3. then d = ______
4. then a = ______
5. ______
6. then order of A is ______
7. (AB)
T
= ______
8. |A| = 0 then A is ______ matrix
9. ______
10. In AX = B ; the coefficient matrix is ______,
variable matrix is ______,
constant matrix is ______.
1
1 4
P P
2 3
, ]
, ]
]
[ ]
1 1
AX 1 2
0 2
, ]
, ]
]
[ ]
a h x
x y
h b y
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
2a 5
0
6 3
2 4
0
5 d 2
1 3 2 P
0 1 1 1
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
13 y 17 x
x , y
5 5
7 3x
y , x by 10 0
8
2 1 2 0
A B
3 1 5 3
, ] , ]
, ] , ]
] ]
2 4 2 5 1 2
A B C
3 6 6 1 3 0
, ] , ] , ]
, ] , ] , ]
] ] ]
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
You might also like
- Exercise On Base and Derived QuantitiesDocument5 pagesExercise On Base and Derived QuantitiesNong HmNo ratings yet
- Inter Material Istyearem Mathsia 04 - 03 - Multiple - ProductsDocument18 pagesInter Material Istyearem Mathsia 04 - 03 - Multiple - ProductsmohithapanandNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document21 pagesLecture 4Colin LongNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Matrices: Matrix EqualityDocument4 pages2.6 Matrices: Matrix Equalityالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- Solucións 1 Exame 2 Aval 2CDocument2 pagesSolucións 1 Exame 2 Aval 2Canamatesverin1321No ratings yet
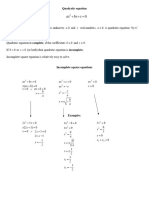
- 1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic EquationDocument8 pages1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic Equationkhrr7brbpcNo ratings yet
- Class-12-Maths-Important Short Answer Type Questions Chapter-3Document14 pagesClass-12-Maths-Important Short Answer Type Questions Chapter-3Hf vgvvv Vg vNo ratings yet
- Zadaci Algebarski - IzraziDocument9 pagesZadaci Algebarski - IzraziJelena ZakicNo ratings yet
- Taller Fundamentos de MatematicasDocument11 pagesTaller Fundamentos de Matematicasandres gomezNo ratings yet
- Inter Material Istyearem Mathsia 04 05 Additional ExerciseDocument27 pagesInter Material Istyearem Mathsia 04 05 Additional ExercisemohithapanandNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solution 10.04.2021Document5 pagesAssignment Solution 10.04.2021Prarthana DubeyNo ratings yet
- 2.2a Quadratic EquationsDocument45 pages2.2a Quadratic EquationsMario VNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Quadraticequations PDFDocument18 pagesChapter2 Quadraticequations PDFcm6699No ratings yet
- Quartic FormulaDocument3 pagesQuartic FormulaShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Further MATHSS2Document25 pagesFurther MATHSS2Samuel BiyamaNo ratings yet
- 2004 State Mathematics Finals: Algebra I Solutions: C C XC X C XDocument5 pages2004 State Mathematics Finals: Algebra I Solutions: C C XC X C XbiswacementNo ratings yet
- Phase-2 A) Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables SolutionsDocument44 pagesPhase-2 A) Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutionspsnarayanan99No ratings yet
- X BX Ax X F B X X F X F X A and B. Also, Find The Other Two Linear Factors of X FDocument18 pagesX BX Ax X F B X X F X F X A and B. Also, Find The Other Two Linear Factors of X FJanaka PriyalalNo ratings yet
- Statics: Edition, Mc-Graw Hill. (/)Document72 pagesStatics: Edition, Mc-Graw Hill. (/)叭叭叭2No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Partial Fractions: X A B X X X XDocument16 pagesChapter 3 Partial Fractions: X A B X X X Xkevin boodramlallNo ratings yet
- Quadratics: KAZIBA StephenDocument11 pagesQuadratics: KAZIBA Stephenkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Linear Eqn Tutorial2Document6 pagesLinear Eqn Tutorial2hemal mitreshNo ratings yet
- SET B Values Activity Lesson 2 With Answer LongDocument5 pagesSET B Values Activity Lesson 2 With Answer LongAnonymous L7XrzMENo ratings yet
- Chap 6Document24 pagesChap 6Dawood MNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pagesQuadratic EquationsSri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Eng Math 501e - 2011 2012 Fall - Week3 - ApplicationsDocument3 pagesEng Math 501e - 2011 2012 Fall - Week3 - ApplicationscherkessNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Kuadratik: MTE1014 Ipg Kampus Darulaman Pn. HJH Saruvari Bt. Badru Duja KhanDocument29 pagesPersamaan Kuadratik: MTE1014 Ipg Kampus Darulaman Pn. HJH Saruvari Bt. Badru Duja KhanElavarasi SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- 18 Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pages18 Quadratic EquationsVinod Kr50% (6)
- bbmp1103 Sem 2Document13 pagesbbmp1103 Sem 2irisardellaNo ratings yet
- ME555 Lecture 2Document58 pagesME555 Lecture 2陆强No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Additonal Algebra - Worked SolutionsDocument60 pagesChapter 4 - Additonal Algebra - Worked SolutionsdharvahetNo ratings yet
- Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2016: Junior Section ImportantDocument6 pagesHanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2016: Junior Section ImportantKinomoto SakuraNo ratings yet
- Applications of Basic Identities S1Document57 pagesApplications of Basic Identities S1KunalNo ratings yet
- Actividad 2 Calculo IntegralDocument5 pagesActividad 2 Calculo IntegralEdmy Lorena JIMENEZ CELYNo ratings yet
- TIFR Question With Solution 2018Document25 pagesTIFR Question With Solution 2018Shiva SahaniNo ratings yet
- Applications+of+basic+identities+ +S1+-+JEE+2023Document78 pagesApplications+of+basic+identities+ +S1+-+JEE+2023SaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- Sin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsDocument10 pagesSin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsChetnaNo ratings yet
- Equations Inequations Systemes 1Document11 pagesEquations Inequations Systemes 1Pape ngor DioufNo ratings yet
- 1.4: Quadratic Equations: Section OutlineDocument4 pages1.4: Quadratic Equations: Section OutlineAHMED ALSHAMMARINo ratings yet
- Board of Intermediate Education: Mathematics - I (A)Document14 pagesBoard of Intermediate Education: Mathematics - I (A)Sriram_VNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - 11th ClassDocument9 pagesMathematics - 11th ClasspaupermNo ratings yet
- Copiumhs Trial23 Solutions-1Document33 pagesCopiumhs Trial23 Solutions-1tedzone9No ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerDocument3 pagesMathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerJames Russel MariNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument98 pagesSolutionsGladiusClarkNo ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions: Problem 1 - SPBDocument19 pagesProblems and Solutions: Problem 1 - SPBgeorgeNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations 4: Polynomial EquationDocument16 pagesQuadratic Equations 4: Polynomial EquationRithin NagarajNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Tangents From External Point 6Document6 pages8.3 Tangents From External Point 6Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaDocument9 pagesLesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaflyleafNo ratings yet
- Algebra Problems and Solutions 09-05-2020Document5 pagesAlgebra Problems and Solutions 09-05-2020caomandanteNo ratings yet
- WIMO Final Training Course S - AlgebraDocument29 pagesWIMO Final Training Course S - AlgebraMicin AnandiNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in Mathematics 9Document14 pagesActivity Sheets in Mathematics 9Loraine TangalinNo ratings yet
- MATHS SA - Msa Revision Package SolutionsDocument7 pagesMATHS SA - Msa Revision Package SolutionsglenlcyNo ratings yet
- STEP Support Programme STEP 2 Trigonometry Questions: SolutionsDocument7 pagesSTEP Support Programme STEP 2 Trigonometry Questions: SolutionsMUHAMMAD ARSLANNo ratings yet
- Arithmatic Operations Revision 2Document1 pageArithmatic Operations Revision 2eemanNo ratings yet
- Teorema 2Document3 pagesTeorema 2Ariana Mitchel Avila ZapataNo ratings yet
- Ans 3Document6 pagesAns 3gcxjx8qgpqNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term s1 MathematicsDocument59 pages2nd Term s1 Mathematicsugobeck111No ratings yet
- 3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareDocument3 pages3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareAanya RalhanNo ratings yet
- Math SummDocument11 pagesMath SummRomario TambunanNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics - DPP 02 - IOQM 2024Document4 pagesBasic Mathematics - DPP 02 - IOQM 2024bandahero875No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MathsDocument2 pagesMathsNarola D HNo ratings yet
- AE01 M1 SolutionsDocument154 pagesAE01 M1 Solutionshemanthindia19No ratings yet
- Linear Discriminant Analysis: Intelligent Data Analysis and Probabilistic InferenceDocument81 pagesLinear Discriminant Analysis: Intelligent Data Analysis and Probabilistic InferenceÂn LêNo ratings yet
- MATH3067 (Coding Theory) 2012: R3 R3-R1 R3 R3-R2Document3 pagesMATH3067 (Coding Theory) 2012: R3 R3-R1 R3 R3-R2Sara OmranNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Scalars: AP Physics CDocument34 pagesVectors and Scalars: AP Physics CFastopioNo ratings yet
- Sistema. Markov Chain - Anton, Rorres - 10.4 (Intro) (Solucao de Sistema)Document10 pagesSistema. Markov Chain - Anton, Rorres - 10.4 (Intro) (Solucao de Sistema)Diego SalazarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Perspec - Ve: How A Moving Camera Reveals Scene Depth and Egomo - On ParametersDocument22 pagesDynamic Perspec - Ve: How A Moving Camera Reveals Scene Depth and Egomo - On ParametersElisée Ndjabu DHNo ratings yet
- 5 6080212603391444015Document119 pages5 6080212603391444015Logeshwer SPNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Chapter 9: 9.1. Basic Solution TechniquesDocument46 pagesSolutions - Chapter 9: 9.1. Basic Solution Techniquesdevilene nayazakoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Question BankDocument4 pagesUnit 1-Question BankSrinathNo ratings yet
- APL 701 Continuum Mechanics Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology DelhiDocument3 pagesAPL 701 Continuum Mechanics Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology DelhiVishal kumarNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Module Description - OMATDocument4 pages2.1 Module Description - OMATbe zeeNo ratings yet
- Vector AssignmentDocument2 pagesVector AssignmentPrince GuriaNo ratings yet
- What Are Magic Squares and How Are They Constructed?: F E D C B ADocument6 pagesWhat Are Magic Squares and How Are They Constructed?: F E D C B AJohanna MaxyneNo ratings yet
- Selected Solutions To Linear Algebra Done WrongDocument21 pagesSelected Solutions To Linear Algebra Done WrongasdfNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matlab2Document26 pagesIntroduction To Matlab2api-3706794No ratings yet
- A First Course in Linear OptimizationDocument196 pagesA First Course in Linear OptimizationGaryNo ratings yet
- CE503 Fall 2020 Midterm1 SolutionsDocument12 pagesCE503 Fall 2020 Midterm1 SolutionsNevzat Can YerlikayaNo ratings yet
- PDF Lectures On Von Neumann Algebras Second Edition Serban Valentin Stratila Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Lectures On Von Neumann Algebras Second Edition Serban Valentin Stratila Ebook Full Chapterlester.jarvis649100% (2)
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvections Examples and Practice ExercisesDocument18 pagesEigenvalues and Eigenvections Examples and Practice Exercisesmcsquared657No ratings yet
- Maths Vector ProjectDocument13 pagesMaths Vector ProjectJunior hero100% (3)
- EGM 5653 Advanced Mechanics of Materials: Theories of Stress and StrainDocument34 pagesEGM 5653 Advanced Mechanics of Materials: Theories of Stress and StrainBrajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- MTH 9857Document56 pagesMTH 9857Sachin RajoriaNo ratings yet
- A1201132722 63869 8 2023 K21MDCA2QSetAllocationDocument12 pagesA1201132722 63869 8 2023 K21MDCA2QSetAllocationHanu VadlamudiNo ratings yet
- BMATS201Document5 pagesBMATS201Nithin GowdruNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants MCQ Suggestion HSC 2024Document9 pagesMatrices and Determinants MCQ Suggestion HSC 2024galaxyspace5360No ratings yet
- Star English Boarding School Bagtar, Colony First Terminal Examination 2076Document4 pagesStar English Boarding School Bagtar, Colony First Terminal Examination 2076Pradhumna AdhikariNo ratings yet
- System of Linear Equations: Ð"unknowns"Ñ BSS BSS ÞÞÞ SS BDocument6 pagesSystem of Linear Equations: Ð"unknowns"Ñ BSS BSS ÞÞÞ SS BGustavo G Borzellino CNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Linear Spaces 1Document4 pages1.2. Linear Spaces 1Muhammad ShoaibNo ratings yet