Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Raft
Raft
Uploaded by
Anonymous nwByj9LOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Raft
Raft
Uploaded by
Anonymous nwByj9LCopyright:
Available Formats
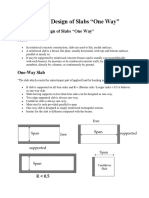
Some tips: - Thickness T is determined from two-way shear (punching shear); - Typical mat thickness T: Stories <5 5 - 10 10 - 20 B=45'
24" 35" 59" B=90' 31" 47" 78" B=120' 39" 59" 98"
Another simple rule of thumb is: 80-100mm per story height. Example : for 10 story building-thickness of raft is 800mm to 1000mm. - Mats should not have L > 90 to 120' without construction joints; - The mat area should be regular, avoiding acute corners and narrow corridors. Keep the column spacing regular and loads within 50% of each other; -When the building. has very dissimilar loadings, use separate mats with joints; - Typical reinforcing is from 1.4 to 2; Use #4( 1/2"=12mmdia), spaced greater than 4 c-c; - Cast a 4" to 8" mud mat to lay out the steel in a level and clean environment; - Attempt a single pour for the entire mat to avoid joints, which have a low or zero
shear; the thicker T, the greater number of hydration cracks (must control the heat). In addition to the information furnished by Er.Vivek Abhyankar you should be knowing that there are various types of RAFT which are: 1.Raft slab only carrying the vertical columns. 2.Raft with the column pedestal +column. 3.Raft with the slab + thickened at the slab bottom directly under column location. 4.Raft with inverted beams in both directions. 6.Raft with the above with a top slab. 7.raft designed with pile supports. So in any one of them you have to consider the column footing (bottom) moment due to DL+LL in addition to the DL+LL or the critical one you get from analysis. What ever the forces there are two means to design- one is as a rigid and the another beams on elastic supports. If you are interested to learn more the following reference books may be useful. 1.RAFT FOUNDATIONS DESIGN & ANALYSIS WITH A PRACTICAL APPROACH by SHARAT CHANDRA GUPTA List Price: Rs. 500.00
2.DESIGN APPLICATION OF RAFT FOUNDATION BY J.A.HEMSLEY. T.Rangarajan
You might also like
- Cabins & Cottages, Revised & Expanded Edition: The Basics of Building a Getaway Retreat for Hunting, Camping, and Rustic LivingFrom EverandCabins & Cottages, Revised & Expanded Edition: The Basics of Building a Getaway Retreat for Hunting, Camping, and Rustic LivingNo ratings yet
- Roof Truss DesignDocument17 pagesRoof Truss Designakgupta7337790% (1)
- Carport - Free Standing, Flat Roof PDFDocument6 pagesCarport - Free Standing, Flat Roof PDFDaniel LourençoNo ratings yet
- Carport - Free Standing, Flat Roof PDFDocument6 pagesCarport - Free Standing, Flat Roof PDFDaniel LourençoNo ratings yet
- Thumb Rules For Structural DesignDocument3 pagesThumb Rules For Structural DesignRajesh Mary75% (4)
- Analysis and Design of Cantilever SlabDocument9 pagesAnalysis and Design of Cantilever SlabOscarKonzultNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro-Open ChannelDocument5 pagesStaad Pro-Open ChannelAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro-Open ChannelDocument5 pagesStaad Pro-Open ChannelAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Slabs Analysis and Design of Concrete Slabs: Lecture-6Document22 pagesSlabs Analysis and Design of Concrete Slabs: Lecture-6Rubab ZahraNo ratings yet
- Module 6- Floor System (One-Way Slab)Document6 pagesModule 6- Floor System (One-Way Slab)RommelNo ratings yet
- Grid Floors STRDocument26 pagesGrid Floors STRVAIDEHI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of SlabsDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Design of SlabsKulal SwapnilNo ratings yet
- Skandhanshi Infra Projects (I) PVT LTD: Qa/Qc DepartmentDocument42 pagesSkandhanshi Infra Projects (I) PVT LTD: Qa/Qc DepartmentVinod MasaniNo ratings yet
- Safety in Formwork and CenteringDocument5 pagesSafety in Formwork and CenteringKrish VetriselvamNo ratings yet
- Structural TipsDocument7 pagesStructural Tipsbalacr3No ratings yet
- Building As Human Shelter: King Post Top Chord Web MembersDocument4 pagesBuilding As Human Shelter: King Post Top Chord Web MembersKristin Brienne Leander-RenomeronNo ratings yet
- Do's and Dont's in Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesDo's and Dont's in Civil EngineeringRam1028100% (1)
- On RCC DetailingDocument22 pagesOn RCC DetailingjadeaachiNo ratings yet
- Beam Rebar ArrangementDocument10 pagesBeam Rebar Arrangementme_decent28457100% (2)
- RCC Thumb RuleDocument7 pagesRCC Thumb RuleRahat ullah100% (6)
- Rebars Arrangement For Concrete ReinforcementsDocument5 pagesRebars Arrangement For Concrete ReinforcementsAntónio Fontes100% (1)
- Another Simple Rule of Thumb Is: 80-100mm Per Story Height. Example: For 10 Story Building-Thickness of Raft Is 800mm To 1000mmDocument1 pageAnother Simple Rule of Thumb Is: 80-100mm Per Story Height. Example: For 10 Story Building-Thickness of Raft Is 800mm To 1000mmMustafa AhmedNo ratings yet
- 05a2. TUV - COSH Scaffolding SafetyDocument33 pages05a2. TUV - COSH Scaffolding SafetyjeromeNo ratings yet
- ACI 318 14 Changes PCI JournalDocument11 pagesACI 318 14 Changes PCI Journalhakim2020No ratings yet
- Design Principles For Roof Steel TrussDocument17 pagesDesign Principles For Roof Steel Trussvprakash7972100% (1)
- Structural Tips / Thumb RulesDocument7 pagesStructural Tips / Thumb Ruleswindspace3No ratings yet
- RCC Design TipsDocument9 pagesRCC Design Tipssatoni12No ratings yet
- RereindetailingDocument47 pagesRereindetailingroseselectorNo ratings yet
- RCC Member Design TipsDocument9 pagesRCC Member Design TipsNaren ViratNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document12 pagesLesson 5MIKE ARTHUR DAVID100% (1)
- RCC Member Design TipsDocument8 pagesRCC Member Design TipsAbhishek ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Sharjah Civil Engineering NotesDocument30 pagesSharjah Civil Engineering NotesSUNDARNo ratings yet
- Thumb RuleDocument6 pagesThumb RuleShafique AhmedNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 4 ADocument32 pagesTOPIC 4 ARomel DumagpiNo ratings yet
- Detailing of Beam Columns and SlabDocument48 pagesDetailing of Beam Columns and Slabsalmantop1100% (2)
- Concrete Rules of ThumbDocument8 pagesConcrete Rules of Thumbdeekchik121No ratings yet
- Reinforcement DetailingDocument47 pagesReinforcement Detailingsomumallidi100% (2)
- Mechanism of RollingDocument4 pagesMechanism of RollingGanesh Kotipalli100% (1)
- Practical Aspects On Detailing of RCC Members in Building Construction BY V.M.Rajan Ce/Civil/MtppDocument21 pagesPractical Aspects On Detailing of RCC Members in Building Construction BY V.M.Rajan Ce/Civil/MtppAnonymous nwByj9L100% (1)
- Reinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented byDocument47 pagesReinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented byMohd ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented byDocument47 pagesReinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented bydr testNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented byDocument47 pagesReinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented byMani DeepNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented byDocument47 pagesReinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Members: Presented byanmoljassalNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Effective Depth of The SlabDocument9 pagesCalculate The Effective Depth of The Slabtapan kumar bhanjoNo ratings yet
- Tex-447-A, Making and Curing Concrete Test SpecimensDocument12 pagesTex-447-A, Making and Curing Concrete Test SpecimensjulsNo ratings yet
- Technical Note For ConstructionDocument44 pagesTechnical Note For ConstructionDanie RoyNo ratings yet
- Thumb Rules For Structural Design - RCC Structures: Minimum Cross-Sectional Dimension For A ColumnDocument3 pagesThumb Rules For Structural Design - RCC Structures: Minimum Cross-Sectional Dimension For A Columnjames conerNo ratings yet
- Thumb Rules For Steel&Concrete DesignDocument11 pagesThumb Rules For Steel&Concrete DesigngvgbabuNo ratings yet
- Flat SlabsDocument21 pagesFlat Slabsnazish AbidNo ratings yet
- InstallationDocument17 pagesInstallationMatthew RokasNo ratings yet
- Multistoreyed Building 3 PDF FreeDocument26 pagesMultistoreyed Building 3 PDF FreeHbk xboyNo ratings yet
- Boiler Making for Boiler Makers - A Practical Treatise on Work in the ShopFrom EverandBoiler Making for Boiler Makers - A Practical Treatise on Work in the ShopRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168No ratings yet
- Stair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareFrom EverandStair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareNo ratings yet
- Strength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionFrom EverandStrength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Linotype Manual: Giving Detailed Instructions of the Proper Adjustment and Care of the LinotypeFrom EverandLinotype Manual: Giving Detailed Instructions of the Proper Adjustment and Care of the LinotypeNo ratings yet
- How to Build a Children's Swing, Slide, Roundabout and Toboggan for the Garden - An Illustrated GuideFrom EverandHow to Build a Children's Swing, Slide, Roundabout and Toboggan for the Garden - An Illustrated GuideNo ratings yet
- Staad Auto Load CombinationDocument1 pageStaad Auto Load CombinationAnonymous 48jYxR1CNo ratings yet
- Pushover CE&CRDocument9 pagesPushover CE&CRAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Planwin / RCDC Is A Total End To End Solution For RCC Building Design and Drawing. It Offers FollowingDocument4 pagesPlanwin / RCDC Is A Total End To End Solution For RCC Building Design and Drawing. It Offers FollowingAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Continuous Beam 2Document6 pagesContinuous Beam 2Anonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro NotesDocument134 pagesStaad Pro NotesAnonymous nwByj9L100% (31)
- Etabs: Extended Three Dimensional Analysis For Building System Example 1Document41 pagesEtabs: Extended Three Dimensional Analysis For Building System Example 1Anonymous nwByj9L100% (2)
- Practical Aspects On Detailing of RCC Members in Building Construction BY V.M.Rajan Ce/Civil/MtppDocument21 pagesPractical Aspects On Detailing of RCC Members in Building Construction BY V.M.Rajan Ce/Civil/MtppAnonymous nwByj9L100% (1)
- Schematic Layout of Bazaar Road SSDocument1 pageSchematic Layout of Bazaar Road SSAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- WindDocument139 pagesWindAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Section IDocument37 pagesSection IAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Fire Barrier Wall: Cable TrenchDocument1 pageFire Barrier Wall: Cable TrenchAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Etabs G+4Document69 pagesEtabs G+4Anonymous nwByj9L100% (7)
- 8 7 Battery Room: S C A D A RTCCDocument1 page8 7 Battery Room: S C A D A RTCCAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- Staad FoundationDocument25 pagesStaad FoundationAnonymous nwByj9L100% (2)
- Seismic Analysis Using Reference Load DT 5.9.13Document32 pagesSeismic Analysis Using Reference Load DT 5.9.13Anonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- ETABS ExampleDocument65 pagesETABS Examplevish5610100% (2)
- Etabs G+4Document69 pagesEtabs G+4Anonymous nwByj9L100% (7)
- DG Building: North Chennai Thermal Power StationDocument22 pagesDG Building: North Chennai Thermal Power StationAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- 3 Storey RC Row Houses EtabsDocument60 pages3 Storey RC Row Houses EtabsRian Ibayan100% (1)
- Pile DesignDocument5 pagesPile DesignAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet