Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Derivative Rules
Derivative Rules
Uploaded by
superchawaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Derivative Rules
Derivative Rules
Uploaded by
superchawaCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Derivative Rules
Spring 2012
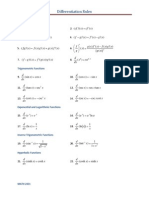
General Derivative Rules
d [c ] = 0 dx d [cf (x )] = cf (x ) dx d [f (x ) + g (x )] = f (x ) + g (x ) dx d [f (x ) g (x )] = f (x ) g (x ) dx d [f (x )g (x )] = f (x )g (x ) + f (x )g (x ) dx d dx f (x ) g (x )f (x ) f (x )g (x ) = 2 g (x ) [g (x )]
1. Constant Rule 2. Constant Multiple Rule 3. Sum Rule 4. Dierence Rule 5. Product Rule 6. Quotient Rule
7. Chain Rule
d [f (g (x ))] = f (g (x ))g (x ) dx
Derivative Rules for Particular Functions
Basic Rule Chain Rule Form
1. Powers 2. Sine 3. Cosine 4. Tangent 5. Secant 6. Cosecant 7. Cotangent 8. Exponential (base e ) 9. Exponential (base a) 10. Natural Logarithm
d n [x ] = nx n1 dx d [sin x ] = cos x dx d [cos x ] = sin x dx d [tan x ] = sec2 x dx d [sec x ] = sec x tan x dx d [csc x ] = csc x cot x dx d [cot x ] = csc2 x dx d x [e ] = e x dx d x [a ] = ax ln a dx d 1 [ln x ] = dx x d 1 [loga x ] = dx x ln a
d [(f (x ))n ] = n(f (x ))n1 f (x ) dx d [sin (f (x ))] = cos (f (x ))f (x ) dx d [cos (f (x ))] = sin (f (x ))f (x ) dx d [tan (f (x ))] = sec2 (f (x ))f (x ) dx d [sec (f (x ))] = sec (f (x )) tan (f (x ))f (x ) dx d [csc (f (x ))] = csc (f (x )) cot (f (x ))f (x ) dx d [cot (f (x ))] = csc2 (f (x ))f (x ) dx d e (f (x )) = e (f (x )) f (x ) dx d a(f (x )) = a(f (x )) ln af (x ) dx d 1 [ln f (x )] = f (x ) dx f (x ) d 1 [loga f (x )] = f (x ) dx f (x ) ln a
11. Logarithm (base a)
p. 1 of 2
Summary of Derivative Rules
Spring 2012
General Antiderivative Rules
Let F (x ) be any antiderivative of f (x ). That is, F (x ) = f (x ). The most general antiderivative of f (x ) is then F (x ) + C . Original Function 1. Constant Rule 2. Constant Multiple Rule 3. Sum Rule 4. Dierence Rule General Antiderivative
c (a constant) cf (x ) f (x ) + g (x ) f (x ) g (x )
cx + C cF (x ) + C F (x ) + G (x ) + C F (x ) G (x ) + C
Antiderivative Rules for Particular Functions
Original Function General Antiderivative
1. Powers (n = 1) 2. Powers (n = 1) 3. Sine 4. Cosine 5. Secant squared 6. Secant times tangent 7. Cosecant times cotangent 8. Cosecant squared 9. Exponential (base e ) 10. Exponential (base a)
xn
1 x sin x cos x sec2 x sec x tan x csc x cot x csc2 x
x n+1 +C n+1
ln |x | + C cos x + C sin x + C tan x + C sec x + C csc x + C cot x + C
ex ax
ex + C ax +C ln a
p. 2 of 2
You might also like
- DifferentiationDocument1 pageDifferentiationVarun Krishna33% (3)
- Integral CalculusDocument120 pagesIntegral CalculusBernadette Boncolmo100% (3)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument5 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralsapi-322359712No ratings yet
- 1 General Derivative Rules: Mon Mar 2 2009Document2 pages1 General Derivative Rules: Mon Mar 2 2009brandon999No ratings yet
- Derivative Rules 2Document2 pagesDerivative Rules 2Anonymous CKg2M9SnNo ratings yet
- 1 General Derivative Rules: Wed May 19 2010Document2 pages1 General Derivative Rules: Wed May 19 2010stopeatingthatNo ratings yet
- Pravila Derivacije I IntegracijeDocument2 pagesPravila Derivacije I IntegracijeSasa UscumlicNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryZainariah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-O.D.E. New VersionDocument100 pagesChapter 5-O.D.E. New VersionJohn Niko Alvarez AmaroNo ratings yet
- Derivatives FormulasDocument5 pagesDerivatives Formulas007phantomNo ratings yet
- TABELA de Diretivas de Derivadas e IntegraisDocument1 pageTABELA de Diretivas de Derivadas e IntegraispablomuroNo ratings yet
- Some Basic DerivativesDocument2 pagesSome Basic DerivativesMuhammad Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation FormulasDocument1 pageDifferentiation Formulasslipper_crazy5335No ratings yet
- Math Formulas: Common Derivatives: Basic Properties of DerivativesDocument2 pagesMath Formulas: Common Derivatives: Basic Properties of DerivativesPranav SaihgalNo ratings yet
- (A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Document15 pages(A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Heather JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Integrals FormulasDocument10 pagesIntegrals Formulas007phantomNo ratings yet
- Limits and Derivatives FormulasDocument2 pagesLimits and Derivatives FormulasSwapnil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument6 pagesMathsshahmeer sultanNo ratings yet
- Formulae For CalculusDocument2 pagesFormulae For CalculusDeLamooreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Numerical Integration: CVEN 302 July 16, 2001Document46 pagesLecture 19 - Numerical Integration: CVEN 302 July 16, 2001Vaibhav VermaNo ratings yet
- Formulario IntegraliDocument1 pageFormulario IntegraliAlessandro CaiazzoNo ratings yet
- Rumus Matematika Sma InterDocument19 pagesRumus Matematika Sma InterAde JayusNo ratings yet
- Numerical Integration TechniquesDocument60 pagesNumerical Integration TechniquesImran ParvezNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 List of ExercisesDocument8 pagesCalculus 1 List of Exercisesp1tru1mariusNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 7 Solutions PDFDocument33 pagesProblem Set 7 Solutions PDFfrancis_tsk1No ratings yet
- Antiderivatives: X F X FDocument1 pageAntiderivatives: X F X FxbloodyfeetxNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Rules: KF X DX K F X DXDocument2 pagesBasic Integration Rules: KF X DX K F X DXElizabeth HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Limits: Calculus Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesLimits: Calculus Cheat SheetPratiksh PatelNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CalculusDocument11 pagesMathematics CalculusAnish NaniNo ratings yet
- Calculus Notes: 1 DifferentiationDocument6 pagesCalculus Notes: 1 DifferentiationsdrakosNo ratings yet
- Prop DerivDocument1 pageProp DerivEloi Rubio GarciaNo ratings yet
- Guia 4luis PDFDocument3 pagesGuia 4luis PDFjmch_dark9832No ratings yet
- Differentiation Techniques SummaryDocument3 pagesDifferentiation Techniques SummaryFaisal RaoNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Differntiation & Integration Formulae.Document1 pageClass Xii - Differntiation & Integration Formulae.Mandeep Singh Plaha59% (22)
- Find Derivatives by Using Differentiation RulesDocument2 pagesFind Derivatives by Using Differentiation RulesSumit PolNo ratings yet
- Knf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeDocument37 pagesKnf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeSyura PisyuNo ratings yet
- Basic Differentiation FormulasDocument6 pagesBasic Differentiation FormulasRevathi AnbunesanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboNo ratings yet
- TABELA: Derivadas, Integrais e Identidades TrigonométricasDocument1 pageTABELA: Derivadas, Integrais e Identidades TrigonométricasBruno QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Interpolation Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation: J J J J JDocument2 pagesPolynomial Interpolation Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation: J J J J JPH2303327No ratings yet
- C CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesDocument10 pagesC CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesFolk NarongritNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio CNDocument7 pagesFormula Rio CNJoana Alves QuitérioNo ratings yet
- List of Derivative RulesDocument1 pageList of Derivative RulesEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Integrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofDocument5 pagesIntegrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofuditagarwal1997No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet