Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Uploaded by
Rahul PanwarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Statistics For Management and Economics, 9th Edition Keller ISM PDFDocument869 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, 9th Edition Keller ISM PDFHumaira70% (10)
- Test Bank For Statistics For Management and Economics 11th Edition by KellerDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Statistics For Management and Economics 11th Edition by Kellera16185576650% (2)
- Solution Manual For Statistics For Management and Economics 10th Edition Gerald KellerDocument23 pagesSolution Manual For Statistics For Management and Economics 10th Edition Gerald KellerSrikanthBussa27% (11)
- Statistics SymbolsDocument7 pagesStatistics Symbolsapi-3857574100% (4)
- (Turn In) Homework 3 EconometricsDocument3 pages(Turn In) Homework 3 EconometricsSiti Maghfirotul UlyahNo ratings yet
- Control Chart ProblemsDocument10 pagesControl Chart ProblemsKhalidNo ratings yet
- Supplement Chapter 5 DT AnswersDocument11 pagesSupplement Chapter 5 DT AnswersJea BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Project Title:: Checklist For PlasteringDocument2 pagesProject Title:: Checklist For Plasteringalfie100% (6)
- Stats Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesStats Cheat Sheetkaungwaiphyo89No ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics 9th Edition Gerald Keller Test Bank PDFDocument7 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics 9th Edition Gerald Keller Test Bank PDFa852314876No ratings yet
- Time SeriesDocument19 pagesTime SeriesRahul Dudhoria100% (1)
- Application of Calculas in EconomicsDocument3 pagesApplication of Calculas in EconomicsTalha Ahmed Siddiqui50% (2)
- Chapter 6Document29 pagesChapter 6Bereket DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Introductory Econometrics For Finance Chris Brooks Solutions To Review - Chapter 3Document7 pagesIntroductory Econometrics For Finance Chris Brooks Solutions To Review - Chapter 3Bill Ramos100% (2)
- Cost Revenue Profit FunctionDocument19 pagesCost Revenue Profit FunctionKevin Dauz Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Geometric Mean and Harmonic Mean VTDocument24 pagesGeometric Mean and Harmonic Mean VTTushar AroraNo ratings yet
- DispersionDocument58 pagesDispersionYash Juneja50% (2)
- AutocorrelationDocument49 pagesAutocorrelationManal Rahman0% (1)
- Chapter 09 - Dummy VariablesDocument21 pagesChapter 09 - Dummy VariablesClaudio AballayNo ratings yet
- Multicollinearity Among The Regressors Included in The Regression ModelDocument13 pagesMulticollinearity Among The Regressors Included in The Regression ModelNavyashree B MNo ratings yet
- Chi SquaredDocument15 pagesChi SquaredArlenie Manog MadeloNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Preference As Behavior Towards Risk Review of Economic StudiesDocument23 pagesLiquidity Preference As Behavior Towards Risk Review of Economic StudiesCuenta EliminadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document38 pagesChapter 7Mian Muhammad Rizwan33% (3)
- Nature of Regression AnalysisDocument22 pagesNature of Regression Analysiswhoosh2008No ratings yet
- Minitab Multiple Regression Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesMinitab Multiple Regression Analysis PDFBen GuhmanNo ratings yet
- Index NumbersDocument45 pagesIndex NumbersPranav Khanna50% (2)
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition FormulasDocument11 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition Formulaskumar030290No ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasDocument15 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasMOHAMMED FOUZANNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet伍志棠No ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument5 pagesEquation SheetArisha BasheerNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSwarnabha RayNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument11 pagesFormulae Sheetthyanh.vuNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityKent BrouwerNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Final ExamDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet Final Examanushad.freeNo ratings yet
- Mca4020 SLM Unit 07Document22 pagesMca4020 SLM Unit 07AppTest PINo ratings yet
- 0 MathReviewDocument18 pages0 MathReviewDhananjay ChopadeNo ratings yet
- Stats FormulaDocument2 pagesStats FormulaNam TranNo ratings yet
- EGR 601 Formulas (v2)Document11 pagesEGR 601 Formulas (v2)Kawser AhmedNo ratings yet
- Econ 140 (Spring 2018) - Section 1: 1 Random Variable (RV)Document7 pagesEcon 140 (Spring 2018) - Section 1: 1 Random Variable (RV)Mashiat MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Probability 2 1Document3 pagesSummary of Probability 2 1PeArL PiNkNo ratings yet
- S289-231formula Sheet m2Document2 pagesS289-231formula Sheet m2Sania SamiNo ratings yet
- OCR A Level Mathematics Sample Question PaperDocument40 pagesOCR A Level Mathematics Sample Question PaperANo ratings yet
- Statistics BI: Models of Random Outcomes. What Is A Model?Document22 pagesStatistics BI: Models of Random Outcomes. What Is A Model?Pedro GouvNo ratings yet
- H1 Math Statistics For A LevelDocument6 pagesH1 Math Statistics For A Levelemilychan9639No ratings yet
- Quadratic FormsDocument5 pagesQuadratic FormsMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Formula PDFDocument7 pagesFormula PDFPramit BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Qm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dDocument13 pagesQm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dJan BorowskiNo ratings yet
- Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesStatistics FormulasJayson S. Verdeflor100% (1)
- Probability and Statistics Symbols TableDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Symbols TableChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghNo ratings yet
- Materials SB: N) K X XDocument11 pagesMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument21 pagesFormulasSamantha Marie RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Econ2280 Tutorial 1 Review Notes PDFDocument4 pagesEcon2280 Tutorial 1 Review Notes PDFKelvin ChanNo ratings yet
- Statistiške Formule Za Menadžment I Ekonomiju Statistics For Management and Economics FormulasDocument12 pagesStatistiške Formule Za Menadžment I Ekonomiju Statistics For Management and Economics FormulasalNo ratings yet
- Sept 2017 - Final - With MemoDocument5 pagesSept 2017 - Final - With MemoBrian ZambeziNo ratings yet
- Fe Engineering Probability StatisticsDocument9 pagesFe Engineering Probability Statisticsvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Midterm Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm Formula SheetShahd AlhamaydaNo ratings yet
- Expectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition ExampleDocument2 pagesExpectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition Examplerijalul fikriNo ratings yet
- Linear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SDocument2 pagesLinear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SmichaelNo ratings yet
- 03 ESCh4 Part1newDocument86 pages03 ESCh4 Part1new何謹成No ratings yet
- Open BookDocument22 pagesOpen Bookabhishekrai11111990No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Teixeira 2016Document13 pagesTeixeira 2016Abdul RaufNo ratings yet
- CertificateOfInsurance - GeminiDocument1 pageCertificateOfInsurance - Geminiganesh gaddeNo ratings yet
- 1e0001 - Steel - Heat Treated Cold Finished BarDocument3 pages1e0001 - Steel - Heat Treated Cold Finished BarPuneet EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- Aug 2022Document24 pagesAug 2022Amar JeetNo ratings yet
- WSG7 Dec02Document77 pagesWSG7 Dec02adelNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1vanita kunnoNo ratings yet
- Sales Quiz 1Document3 pagesSales Quiz 1Roldan Cejuela CañadaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economic Survey - 2020-21Document19 pagesPakistan Economic Survey - 2020-21ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS Licensing and Registration General Guidelines (English Version - As at 1 June 2017)Document41 pagesPETRONAS Licensing and Registration General Guidelines (English Version - As at 1 June 2017)Adilah AzamiNo ratings yet
- Indian Partnership Act - Paper 50 MarksDocument2 pagesIndian Partnership Act - Paper 50 Markstherealbeetch99No ratings yet
- Approved Drawing of Boundary WallDocument1 pageApproved Drawing of Boundary WallAnup Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- How To Characterize Organizations Version ComplétéeDocument1 pageHow To Characterize Organizations Version ComplétéeClaraNo ratings yet
- Mid Bing Kls XI SMT 2 2223Document4 pagesMid Bing Kls XI SMT 2 2223hennyNo ratings yet
- College of Physicians & Surgeons Pakistan: Online Application Form (FCPS-I) ExaminationDocument2 pagesCollege of Physicians & Surgeons Pakistan: Online Application Form (FCPS-I) ExaminationUsama BilalNo ratings yet
- Standard: APA Citation BasicsDocument3 pagesStandard: APA Citation BasicsAmhara AammhhaarraaNo ratings yet
- Data Buyer 24 Oktober 22Document37 pagesData Buyer 24 Oktober 22tazkiyaNo ratings yet
- Report 4Document32 pagesReport 4BILENGE MALILONo ratings yet
- Chapter PDFDocument55 pagesChapter PDFWonde BiruNo ratings yet
- 辽宁维航基业科技有限公司 Vh-Marinetech Co.,LtdDocument21 pages辽宁维航基业科技有限公司 Vh-Marinetech Co.,Ltdding liuNo ratings yet
- ThoughtWorks SampleDocument4 pagesThoughtWorks SampleAbhijit ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- R. D. S. O.: Rdso/b - 10408/6Document1 pageR. D. S. O.: Rdso/b - 10408/6MUTHU PANDINo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument4 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceRAKESH VASANINo ratings yet
- TANAPatrika August 2022Document64 pagesTANAPatrika August 2022anushaNo ratings yet
- PT Menolak Rugi Jurnal ZeovDocument68 pagesPT Menolak Rugi Jurnal Zeovtarakannnn364No ratings yet
- The Impact of Earnings Management On The Value Relevance of EarningsDocument25 pagesThe Impact of Earnings Management On The Value Relevance of Earningsanubha srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theory of Factor Pricing or Theory of DistributionDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Theory of Factor Pricing or Theory of DistributionCorolla SedanNo ratings yet
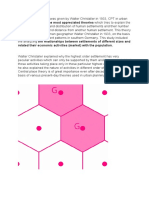
- Central Place TheoryDocument10 pagesCentral Place Theoryतरुण पन्तNo ratings yet
- Brief Intro of IsraelDocument28 pagesBrief Intro of Israel王郁妘No ratings yet
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Uploaded by
Rahul PanwarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Statistics For Management and Economics, Seventh Edition Formulas
Uploaded by
Rahul PanwarCopyright:
Available Formats
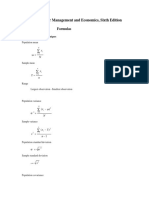
Statistics for management and Economics, Seventh Edition
Formulas
Numerical Descriptive techniques
Population mean
=
N
x
N
i
i
1
Sample mean
n
x
x
n
i
i
1
Range
Largest observation - Smallest observation
Population variance
2
=
N
) x (
N
i
i
1
2
Sample variance
2
s =
1
) (
1
2
n
x x
n
i
i
Population standard deviation
=
2
Sample standard deviation
s =
2
s
Population covariance
N
) y )( x (
N
i
y i x i
xy
Sample covariance
1
1
n
) y y )( x x (
s
n
i
i i
xy
Population coefficient of correlation
y x
xy
Sample coefficient of correlation
y x
xy
s s
s
r
Slope coefficient
2
1
x
s
) y , x cov(
b
y-intercept
x b y b
1 0
Probability
Conditional probability
P(A|B) = P(A and B)/P(B)
Complement rule
P(
C
A
) = 1 P(A)
Multiplication rule
P(A and B) = P(A|B)P(B)
Addition rule
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
Bayes Law Formula
) A | B ( P ) A ( P . . . ) A | B ( P ) A ( P ) A | B ( P ) A ( P
) A | B ( P ) A ( P
) B | A ( P
k k 2 2 1 1
i i
i
+ + +
Random Variables and Discrete Probability Distributions
Expected value (mean)
E(X) =
x all
) x ( xP
Variance
V(x) =
x all
) x ( P ) x (
2 2
Standard deviation
2
Covariance
COV(X, Y) =
) y , x ( P ) y )( x (
y x
Coefficient of Correlation
y x
) Y , X ( COV
Laws of expected value
1. E(c) = c
2. E(X + c) = E(X) + c
3. E(cX) = cE(X)
Laws of variance
1.V(c) = 0
2. V(X + c) = V(X)
3. V(cX) =
2
c
V(X)
Laws of expected value and variance of the sum of two variables
1. E(X + Y) = E(X) + E(Y)
2. V(X + Y) = V(X) + V(Y) + 2COV(X, Y)
Laws of expected value and variance for the sum of more than two variables
1.
k
i
i
k
i
i
X E X E
1 1
) ( ) (
2.
k
i
i
k
i
i
X V X V
1 1
) ( ) ( if the variables are independent
Mean and variance of a portfolio of two stocks
E(Rp) = w1E(R1) + w2E(R2)
V(Rp) =
2
1
w V(R1) +
2
2
w V(R2) + 2
1
w
2
w COV(R1, R2)
=
2
1
w
2
1
+
2
2
w
2
2
+ 2
1
w
2
w
1
Mean and variance of a portfolio of k stocks
E(Rp) =
k
i
i i
R E w
1
) (
V(Rp) =
+
+
k
i
k
i j
j i j i
k
i
i i
R R COV w w w
1 1 1
2 2
) , ( 2
Binomial probability
P(X = x) =
)! x n ( ! x
! n
x n x
) p ( p
1
np
) p ( np 1
2
) p ( np 1
Poisson probability
P(X = x) =
! x
e
x
Continuous Probability Distributions
Standard normal random variable
X
Z
Exponential distribution
/ 1
x
e ) x X ( P
>
x
e 1 ) x X ( P
<
2 1
x x
1 2 2 1
e e ) x X ( P ) x X ( P ) x X x ( P
< < < <
F distribution
2 1
, , 1 A
F
=
1 2
, ,
1
A
F
Sampling Distributions
Expected value of the sample mean
) (X E
x
Variance of the sample mean
) (X V
n
x
2
2
Standard error of the sample mean
n
x
Standardizing the sample mean
n
X
Z
/
Expected value of the sample proportion
)
(P E
p
p
Variance of the sample proportion
n
p p
P V
p
) 1 (
)
(
2
Standard error of the sample proportion
n
p p
p
) 1 (
Standardizing the sample proportion
n p p
p P
Z
) 1 (
Expected value of the difference between two means
) (
2 1
X X E 2 1
2 1
x x
Variance of the difference between two means
2
2
2
1
2
1 2
2 1
2 1
) (
n n
X X V
x x
+
Standard error of the difference between two means
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 1
n n
x x
+
Standardizing the difference between two sample means
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 1 2 1
) ( ) (
n n
X X
Z
Introduction to Estimation
Confidence interval estimator of
n
z x
/
2
t
Sample size to estimate
2
2
,
_
W
z
n
/
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
Test statistic for
n /
x
z
Inference about One Population
Test statistic for
n / s
x
t
Confidence interval estimator of
n
s
t x
/ 2
t
Test statistic for
2
2
2
2
1
s ) n (
Confidence interval Estimator of
2
LCL =
2
2
2
1
/
s ) n (
UCL =
2
2 1
2
1
/
s ) n (
Test statistic for p
n / ) p ( p
p p
z
1
Confidence interval estimator of p
n / ) p ( p z p
/
t 1
2
Sample size to estimate p
2
2
1
,
_
W
) p ( p z
n
/
Confidence interval estimator of the total of a large finite population
1
]
1
t
n
s
t x N
/ 2
Confidence interval estimator of the total number of successes in a large finite population
1
1
]
1
t
n
p ( p
z p N
/
1
2
Confidence interval estimator of
when the population is small
1
2
t
N
n N
n
s
t x
/
Confidence interval estimator of the total in a small population
,
_
t
1
2
N
n N
n
s
t x N
/
Confidence interval estimator of p when the population is small
1
1
2
t
N
n N
n
) p ( p
z p
/
Confidence interval estimator of the total number of successes in a small population
,
_
t
1
1
2
N
n N
n
) p ( p
z p N
/
Inference About Two Populations
Equal-variances t-test of
2 1
,
_
2 1
2
2 1 2 1
1 1
n n
s
) ( ) x x (
t
p
2
2 1
+ n n
Equal-variances interval estimator of
2 1
,
_
+ t
2 1
2
2 2 1
1 1
n n
s t ) x x (
p /
2
2 1
+ n n
Unequal-variances t-test of
2 1
,
_
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 1 2 1
n
s
n
s
) ( ) x x (
t
1 1
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
2
2 1
2
1
n
) n / s (
n
) n / s (
) n / s n / s (
Unequal-variances interval estimator of
2 1
2
2
2
1
2
1
2 2 1
n
s
n
s
t ) x x (
/
+ t
1 1
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
2
2 1
2
1
n
) n / s (
n
) n / s (
) n / s n / s (
t-Test of
D
D D
D D
n / s
x
t
1
D
n
t-Estimator of
D
D
D
/ D
n
s
t x
2
t
1
D
n
F-test of
2
2
2
1
/
F =
2
2
2
1
s
s
1
1 1
n and 1
2 2
n
F-Estimator of
2
2
2
1
/
LCL =
2 1
2
2
2
2
1
1
, , /
F
s
s
,
_
UCL =
1 2
2
2
2
2
1
, , /
F
s
s
,
_
z-Test and estimator of
2 1
p p
Case 1:
,
_
2 1
2 1
1 1
1
n n
) p ( p
) p p (
z
Case 2:
2
2 2
1
1 1
2 1 2 1
1 1
n
) p ( p
n
) p ( p
) p p ( ) p p (
z
z-estimator of
2 1
p p
2
2 2
1
1 1
2 2 1
1 1
n
) p ( p
n
) p ( p
z ) p p (
/
+
t
Analysis of Variance
One-way analysis of variance
SST =
k
j
j j
) x x ( n
1
2
SSE =
j
n
i
j ij
k
j
) x x (
1
2
1
MST =
1 k
SST
MSE =
k n
SSE
F =
MSE
MST
Two-way analysis of variance (randomized block design of experiment)
SS(Total) =
b
i
ij
k
j
) x x (
1
2
1
SST =
k
i
j
) x ] T [ x ( b
1
2
SSB =
b
i
i
) x ] B [ x ( k
1
2
SSE =
+
b
i
i j ij
k
j
) x ] B [ x ] T [ x x (
1
2
1
MST =
1 k
SST
MSB =
1 b
SSB
MSE =
1 b k n
SSE
+
F =
MSE
MST
F=
MSE
MSB
Two-factor experiment
SS(Total) =
a
i
b
j
r
k
ijk
) x x (
1 1 1
2
SS(A) =
a
i
i
) x ] A [ x ( rb
1
2
SS(B) =
b
j
j
) x ] B [ x ( ra
1
2
SS(AB) =
+
a
i
b
j
j i ij
) x ] B [ x ] A [ x ] AB [ x ( r
1 1
2
SSE =
a
i
b
j
r
k
ij ijk
) ] AB [ x x (
1 1 1
2
F =
MSE
) A ( MS
F =
MSE
) B ( MS
F =
MSE
) AB ( MS
Least Significant Difference Comparison Method
LSD =
,
_
+
j i
/
n n
MSE t
1 1
2
Tukeys multiple comparison method
g
n
MSE
) , k ( q
Chi-Squared Tests
Test statistic for all procedures
k
1 i
i
2
i i 2
e
) e f (
Simple Linear Regression
Sample slope
2
1
x
xy
s
s
b
Sample y-intercept
x b y b
1 0
Sum of squares for error
SSE =
n
i
i i
) y y (
1
2
Standard error of estimate
2
n
SSE
s
Test statistic for the slope
1
1 1
b
s
b
t
Standard error of
1
b
2
1
1
x
b
s ) n (
s
s
Coefficient of determination
2 2
2
2
y x
xy
s s
s
R
2
1
) y y (
SSE
i
Prediction interval
2
2
2 2
1
1
1
x
g
n , /
s ) n (
) x x (
n
s t y
+ + t
Confidence interval estimator of the expected value of y
2
2
2 2
1
1
x
g
n , /
s ) n (
) x x (
n
s t y
+ t
Sample coefficient of correlation
y x
xy
s s
s
r
Test statistic for testing
= 0
2
1
2
r
n
r t
Multiple Regression
Standard Error of Estimate
1
k n
SSE
s
Test statistic for
i
i
b
i i
s
b
t
Coefficient of Determination
2 2
2
2
y x
xy
s s
s
R
2
1
) y y (
SSE
i
Adjusted Coefficient of Determination
Adjusted
) n /( ) y y (
) k n /( SSE
R
i
1
1
1
2
2
Mean Square for Error
MSE = SSE/k
Mean Square for Regression
MSR = SSR/(n-k-1)
F-statistic
F = MSR/MSE
Durbin-Watson statistic
n
i
i
n
i
i i
e
) e e (
d
1
2
2
2
1
Time Series Analysis and Forecasting
Exponential smoothing
1
) 1 (
+
t t t
S w wy S
Nonparametric Statistical techniques
Wilcoxon rank sum test statistic
1
T T
E(T) =
2
1
2 1 1
) n n ( n + +
12
1
2 1 2 1
) n n ( n n
T
+ +
T
) T ( E T
z
Sign test statistic
x = number of positive differences
n .
n . x
z
5
5
Wilcoxon signed rank sum test statistic
+
T T
E(T) =
4
1) n ( n +
24
1 2 1 ) n )( n ( n
T
+ +
T
) T ( E T
z
Kruskal-Wallis Test
) n (
n
T
) n ( n
H
k
j
j
j
1 3
1
12
1
2
+
1
1
]
1
Friedman Test
) k ( b T
) k )( k ( b
F
k
j
j r
1 3
1
12
1
2
+
1
1
]
1
Spearman rank correlation coefficient
b a
ab
S
s s
s
r
Spearman Test statistic for n > 30
1 n r z
S
Statistical Process Control
Centerline and control limits for x chart using S
Centerline = x
Lower control limit =
n
S
x 3
Upper control limit =
n
S
x 3 +
Centerline and control limits for the p chart
Centerline =
p
Lower control limit =
n
) p ( p
p
1
3
Upper control limit =
n
) p ( p
p
+
1
3
Decision Analysis
Expected Value of perfect Information
EVPI = EPPI - EMV*
Expected Value of Sample Information
EVSI = EMV' - EMV*
You might also like
- Statistics For Management and Economics, 9th Edition Keller ISM PDFDocument869 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, 9th Edition Keller ISM PDFHumaira70% (10)
- Test Bank For Statistics For Management and Economics 11th Edition by KellerDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Statistics For Management and Economics 11th Edition by Kellera16185576650% (2)
- Solution Manual For Statistics For Management and Economics 10th Edition Gerald KellerDocument23 pagesSolution Manual For Statistics For Management and Economics 10th Edition Gerald KellerSrikanthBussa27% (11)
- Statistics SymbolsDocument7 pagesStatistics Symbolsapi-3857574100% (4)
- (Turn In) Homework 3 EconometricsDocument3 pages(Turn In) Homework 3 EconometricsSiti Maghfirotul UlyahNo ratings yet
- Control Chart ProblemsDocument10 pagesControl Chart ProblemsKhalidNo ratings yet
- Supplement Chapter 5 DT AnswersDocument11 pagesSupplement Chapter 5 DT AnswersJea BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Project Title:: Checklist For PlasteringDocument2 pagesProject Title:: Checklist For Plasteringalfie100% (6)
- Stats Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesStats Cheat Sheetkaungwaiphyo89No ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics 9th Edition Gerald Keller Test Bank PDFDocument7 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics 9th Edition Gerald Keller Test Bank PDFa852314876No ratings yet
- Time SeriesDocument19 pagesTime SeriesRahul Dudhoria100% (1)
- Application of Calculas in EconomicsDocument3 pagesApplication of Calculas in EconomicsTalha Ahmed Siddiqui50% (2)
- Chapter 6Document29 pagesChapter 6Bereket DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Introductory Econometrics For Finance Chris Brooks Solutions To Review - Chapter 3Document7 pagesIntroductory Econometrics For Finance Chris Brooks Solutions To Review - Chapter 3Bill Ramos100% (2)
- Cost Revenue Profit FunctionDocument19 pagesCost Revenue Profit FunctionKevin Dauz Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Geometric Mean and Harmonic Mean VTDocument24 pagesGeometric Mean and Harmonic Mean VTTushar AroraNo ratings yet
- DispersionDocument58 pagesDispersionYash Juneja50% (2)
- AutocorrelationDocument49 pagesAutocorrelationManal Rahman0% (1)
- Chapter 09 - Dummy VariablesDocument21 pagesChapter 09 - Dummy VariablesClaudio AballayNo ratings yet
- Multicollinearity Among The Regressors Included in The Regression ModelDocument13 pagesMulticollinearity Among The Regressors Included in The Regression ModelNavyashree B MNo ratings yet
- Chi SquaredDocument15 pagesChi SquaredArlenie Manog MadeloNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Preference As Behavior Towards Risk Review of Economic StudiesDocument23 pagesLiquidity Preference As Behavior Towards Risk Review of Economic StudiesCuenta EliminadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document38 pagesChapter 7Mian Muhammad Rizwan33% (3)
- Nature of Regression AnalysisDocument22 pagesNature of Regression Analysiswhoosh2008No ratings yet
- Minitab Multiple Regression Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesMinitab Multiple Regression Analysis PDFBen GuhmanNo ratings yet
- Index NumbersDocument45 pagesIndex NumbersPranav Khanna50% (2)
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition FormulasDocument11 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Tenth Edition Formulaskumar030290No ratings yet
- Statistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasDocument15 pagesStatistics For Management and Economics, Sixth Edition: FormulasMOHAMMED FOUZANNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet: B P B A PRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet伍志棠No ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument5 pagesEquation SheetArisha BasheerNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSwarnabha RayNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument11 pagesFormulae Sheetthyanh.vuNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityKent BrouwerNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Final ExamDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet Final Examanushad.freeNo ratings yet
- Mca4020 SLM Unit 07Document22 pagesMca4020 SLM Unit 07AppTest PINo ratings yet
- 0 MathReviewDocument18 pages0 MathReviewDhananjay ChopadeNo ratings yet
- Stats FormulaDocument2 pagesStats FormulaNam TranNo ratings yet
- EGR 601 Formulas (v2)Document11 pagesEGR 601 Formulas (v2)Kawser AhmedNo ratings yet
- Econ 140 (Spring 2018) - Section 1: 1 Random Variable (RV)Document7 pagesEcon 140 (Spring 2018) - Section 1: 1 Random Variable (RV)Mashiat MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Probability 2 1Document3 pagesSummary of Probability 2 1PeArL PiNkNo ratings yet
- S289-231formula Sheet m2Document2 pagesS289-231formula Sheet m2Sania SamiNo ratings yet
- OCR A Level Mathematics Sample Question PaperDocument40 pagesOCR A Level Mathematics Sample Question PaperANo ratings yet
- Statistics BI: Models of Random Outcomes. What Is A Model?Document22 pagesStatistics BI: Models of Random Outcomes. What Is A Model?Pedro GouvNo ratings yet
- H1 Math Statistics For A LevelDocument6 pagesH1 Math Statistics For A Levelemilychan9639No ratings yet
- Quadratic FormsDocument5 pagesQuadratic FormsMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Formula PDFDocument7 pagesFormula PDFPramit BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Qm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dDocument13 pagesQm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dJan BorowskiNo ratings yet
- Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesStatistics FormulasJayson S. Verdeflor100% (1)
- Probability and Statistics Symbols TableDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Symbols TableChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghNo ratings yet
- Materials SB: N) K X XDocument11 pagesMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument21 pagesFormulasSamantha Marie RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Econ2280 Tutorial 1 Review Notes PDFDocument4 pagesEcon2280 Tutorial 1 Review Notes PDFKelvin ChanNo ratings yet
- Statistiške Formule Za Menadžment I Ekonomiju Statistics For Management and Economics FormulasDocument12 pagesStatistiške Formule Za Menadžment I Ekonomiju Statistics For Management and Economics FormulasalNo ratings yet
- Sept 2017 - Final - With MemoDocument5 pagesSept 2017 - Final - With MemoBrian ZambeziNo ratings yet
- Fe Engineering Probability StatisticsDocument9 pagesFe Engineering Probability Statisticsvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Midterm Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm Formula SheetShahd AlhamaydaNo ratings yet
- Expectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition ExampleDocument2 pagesExpectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition Examplerijalul fikriNo ratings yet
- Linear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SDocument2 pagesLinear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SmichaelNo ratings yet
- 03 ESCh4 Part1newDocument86 pages03 ESCh4 Part1new何謹成No ratings yet
- Open BookDocument22 pagesOpen Bookabhishekrai11111990No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Teixeira 2016Document13 pagesTeixeira 2016Abdul RaufNo ratings yet
- CertificateOfInsurance - GeminiDocument1 pageCertificateOfInsurance - Geminiganesh gaddeNo ratings yet
- 1e0001 - Steel - Heat Treated Cold Finished BarDocument3 pages1e0001 - Steel - Heat Treated Cold Finished BarPuneet EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- Aug 2022Document24 pagesAug 2022Amar JeetNo ratings yet
- WSG7 Dec02Document77 pagesWSG7 Dec02adelNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1vanita kunnoNo ratings yet
- Sales Quiz 1Document3 pagesSales Quiz 1Roldan Cejuela CañadaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Economic Survey - 2020-21Document19 pagesPakistan Economic Survey - 2020-21ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS Licensing and Registration General Guidelines (English Version - As at 1 June 2017)Document41 pagesPETRONAS Licensing and Registration General Guidelines (English Version - As at 1 June 2017)Adilah AzamiNo ratings yet
- Indian Partnership Act - Paper 50 MarksDocument2 pagesIndian Partnership Act - Paper 50 Markstherealbeetch99No ratings yet
- Approved Drawing of Boundary WallDocument1 pageApproved Drawing of Boundary WallAnup Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- How To Characterize Organizations Version ComplétéeDocument1 pageHow To Characterize Organizations Version ComplétéeClaraNo ratings yet
- Mid Bing Kls XI SMT 2 2223Document4 pagesMid Bing Kls XI SMT 2 2223hennyNo ratings yet
- College of Physicians & Surgeons Pakistan: Online Application Form (FCPS-I) ExaminationDocument2 pagesCollege of Physicians & Surgeons Pakistan: Online Application Form (FCPS-I) ExaminationUsama BilalNo ratings yet
- Standard: APA Citation BasicsDocument3 pagesStandard: APA Citation BasicsAmhara AammhhaarraaNo ratings yet
- Data Buyer 24 Oktober 22Document37 pagesData Buyer 24 Oktober 22tazkiyaNo ratings yet
- Report 4Document32 pagesReport 4BILENGE MALILONo ratings yet
- Chapter PDFDocument55 pagesChapter PDFWonde BiruNo ratings yet
- 辽宁维航基业科技有限公司 Vh-Marinetech Co.,LtdDocument21 pages辽宁维航基业科技有限公司 Vh-Marinetech Co.,Ltdding liuNo ratings yet
- ThoughtWorks SampleDocument4 pagesThoughtWorks SampleAbhijit ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- R. D. S. O.: Rdso/b - 10408/6Document1 pageR. D. S. O.: Rdso/b - 10408/6MUTHU PANDINo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument4 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceRAKESH VASANINo ratings yet
- TANAPatrika August 2022Document64 pagesTANAPatrika August 2022anushaNo ratings yet
- PT Menolak Rugi Jurnal ZeovDocument68 pagesPT Menolak Rugi Jurnal Zeovtarakannnn364No ratings yet
- The Impact of Earnings Management On The Value Relevance of EarningsDocument25 pagesThe Impact of Earnings Management On The Value Relevance of Earningsanubha srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theory of Factor Pricing or Theory of DistributionDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Theory of Factor Pricing or Theory of DistributionCorolla SedanNo ratings yet
- Central Place TheoryDocument10 pagesCentral Place Theoryतरुण पन्तNo ratings yet
- Brief Intro of IsraelDocument28 pagesBrief Intro of Israel王郁妘No ratings yet