Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Rio
Formula Rio
Uploaded by
alfonsojimenesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Rio
Formula Rio
Uploaded by
alfonsojimenesCopyright:
Available Formats
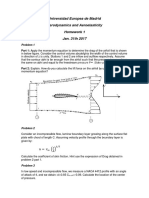
Prueba Build up
Step 1. Plot pws vs. (tp+t)/t on a semilog scale as shown in Figure. Step 2. Identify the correct straight-line portion of the curve and determine the slope m: Step 3. Calculate the average permeability by using Equation
Step 4. Determine pwf after 1 hour from the straight-line portion of the curve:
Step 5. Calculate the skin factor by applying Equation
Step 6. Calculate the additional pressure drop by using:
The selected shut-in times satisfy t1 < t2 < t3. The slope of the pseudosteadystate straight-line mpss is then approximated by:
The well drainage area can be calculated from Equation
where: mpss or m\ = slope of straight line during the pseudosteady-state flow, psi/hr Qo = flow rate, bbl/day A = well drainage area, ft2
Prueba Buildup FALLA
Step 1. Calculate total production time t
Step 2. Plot pws vs. (tp+t)/ t The plot clearly shows two straight lines with the rst slope of 650 psi/cycle and the second with 1300 psi/cycle. Notice that the second slope is twice that of the rst slope indicating the existence of the sealing fault. Step 3. Using the value of the rst slope, calculate the permeability k:
Step 4. Determine the value of Horners time ratio at the intersection of the two semilog straight lines shown in Figure 1.96, to give:
Step 5. Calculate the distance L from the well to the fault by applying Equation:
You might also like
- Oupa Nhambe - Control Project Part 2Document19 pagesOupa Nhambe - Control Project Part 2Oupa100% (4)
- CH - 2 Pressure Buildup Tests PDFDocument68 pagesCH - 2 Pressure Buildup Tests PDFMohannad Abdulrahman75% (4)
- 14 Jet Bit Nozzle Size SelectionDocument46 pages14 Jet Bit Nozzle Size Selectiontotos20100% (2)
- Gas Well Testing Field Case StudiesDocument26 pagesGas Well Testing Field Case Studies77bgfaNo ratings yet
- Circular Channel ExampleDocument6 pagesCircular Channel ExampleNoel MontanaNo ratings yet
- Osterhuis Ühler Ilcox Van Der EERDocument5 pagesOsterhuis Ühler Ilcox Van Der EERmhdmkNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Malaysia: Title of ExperimentDocument20 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Malaysia: Title of ExperimentKhairil IkramNo ratings yet
- Pan System Report 2014Document12 pagesPan System Report 2014Inam Ali AwanNo ratings yet
- Kailash WT Perf AnalysisDocument20 pagesKailash WT Perf AnalysisNahas NazarNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Multirate Test by Tue Pressure Derivative Oil ReservoirsDocument12 pagesInterpretation of Multirate Test by Tue Pressure Derivative Oil ReservoirsLuis RuizNo ratings yet
- ME2109 Fluid May2012Document7 pagesME2109 Fluid May2012Hafsa KhanNo ratings yet
- Design of An AqueductDocument7 pagesDesign of An Aqueduct4gen_5No ratings yet
- Cee5324 hw3 sp12 PDFDocument2 pagesCee5324 hw3 sp12 PDFabimanaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Fluid FlowDocument13 pagesMeasurement of Fluid FlowDahiru Muhammed DanbarebariNo ratings yet
- HG Assignement - 2013x PDFDocument16 pagesHG Assignement - 2013x PDFRatha PhokNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Laboratory: Lab Report SKTG 2741Document20 pagesFluid Mechanics Laboratory: Lab Report SKTG 2741madworldNo ratings yet
- Determination Peak RunoffDocument6 pagesDetermination Peak RunoffNhan DoNo ratings yet
- Session4 E1 E2 Runoff Hydrograph TransformationDocument3 pagesSession4 E1 E2 Runoff Hydrograph TransformationTiên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Exam2010 SolutionsDocument5 pagesExam2010 SolutionsAmin GillaniNo ratings yet
- Pitot Tube Fluids EssayDocument12 pagesPitot Tube Fluids EssaysceroxNo ratings yet
- Graphical Peak Discharge MethodDocument7 pagesGraphical Peak Discharge MethodNhan DoNo ratings yet
- 3 Flow Rates and Pressure MeasurementsDocument20 pages3 Flow Rates and Pressure MeasurementsRiswan RiswanNo ratings yet
- 2D Jet Experiment: AE - 611 Laboratory ReportDocument13 pages2D Jet Experiment: AE - 611 Laboratory ReportAbhishek KanthedNo ratings yet
- (ENG) Compressive Flow ReportDocument12 pages(ENG) Compressive Flow ReportMónica Martínez PoloNo ratings yet
- Design Flood EstimationDocument18 pagesDesign Flood Estimationrajesh005No ratings yet
- Homework 1Document2 pagesHomework 1Fernando AguayoNo ratings yet
- Example and AssignmentDocument6 pagesExample and Assignmentzemen TadesseNo ratings yet
- Experiment (1) : Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface: ObjectivesDocument25 pagesExperiment (1) : Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface: ObjectivesBatool Al-kharabshehNo ratings yet
- SPE 132475 Using Second Derivative of Transient Pressure in Welltest Analysis of Low Permeability Gas ReservoirsDocument9 pagesSPE 132475 Using Second Derivative of Transient Pressure in Welltest Analysis of Low Permeability Gas ReservoirsFajar MariyuadiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: University of LeedsDocument16 pagesFluid Mechanics: University of LeedsHasitha MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Interference Well TestDocument6 pagesInterference Well TestParitosh DoshiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5: Linear Momentum Experiments PurposeDocument5 pagesLab 5: Linear Momentum Experiments Purposenil_008No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Research PaperDocument8 pagesHydraulics Research PaperKashika KheraNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Liquid Flow Aug 2012Document12 pagesExp 3 Liquid Flow Aug 2012Himanshu ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE 5.2-1: Filling A Watering Tank: Table 1: Data From The Manufacturer's Pump CurveDocument4 pagesEXAMPLE 5.2-1: Filling A Watering Tank: Table 1: Data From The Manufacturer's Pump CurveRohit Gadekar100% (1)
- Station KeepingDocument67 pagesStation KeepingSagar MhatreNo ratings yet
- Masterclass - Ducting - Equal Friction Method Part 30Document11 pagesMasterclass - Ducting - Equal Friction Method Part 30T Satheesh Kumar100% (1)
- Triaxial Permeability 2023Document3 pagesTriaxial Permeability 2023Kim Yuen WongNo ratings yet
- P 303 AnsDocument4 pagesP 303 AnsDiptoNo ratings yet
- Active Control of Rotating Stall in Axial CompressorsDocument4 pagesActive Control of Rotating Stall in Axial Compressorsinam vfNo ratings yet
- 1 Orifice MeterDocument7 pages1 Orifice MeterFlorin EneNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drawdown TestDocument33 pagesPressure Drawdown TestAmy Nur Syafiqah100% (1)
- Draft For Distillation ColumnDocument9 pagesDraft For Distillation ColumnsamarthbhandNo ratings yet
- Methods: Full Size ImageDocument6 pagesMethods: Full Size ImageArronNo ratings yet
- Injection Well Transient Testing and AnalysisDocument82 pagesInjection Well Transient Testing and AnalysisBarbara_LFC100% (1)
- Impact of A Water JetDocument5 pagesImpact of A Water JetAnirban SardarNo ratings yet
- PCB3013-Well Test Analysis HW# 8 Prof. Dr. Mustafa Onur, UTP, September 2013Document3 pagesPCB3013-Well Test Analysis HW# 8 Prof. Dr. Mustafa Onur, UTP, September 2013Chai CwsNo ratings yet
- Determining Flow VelocityDocument19 pagesDetermining Flow VelocityFauzi AbasNo ratings yet
- 1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project AssignmentDocument4 pages1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project Assignmentazeem sheikhNo ratings yet
- 0207 Sin 2Document5 pages0207 Sin 2bogodavidNo ratings yet
- AE1256 AerodynamicslabmanualsDocument48 pagesAE1256 AerodynamicslabmanualsSenthil ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Air Leakage in Vacuum VesselsDocument2 pagesAir Leakage in Vacuum VesselsAccio_thebest100% (5)
- Agrohydrology ManualDocument113 pagesAgrohydrology Manualjoverevocal50% (2)
- Supercritical Airfoil and CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesSupercritical Airfoil and CharacteristicsABHISHEK MANI TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- PCB3013 HW#5 SolutionDocument5 pagesPCB3013 HW#5 SolutionChai CwsNo ratings yet
- Hydro Turbine Model For System Dynamic StudiesDocument7 pagesHydro Turbine Model For System Dynamic StudiesAbraham Barron GarciaNo ratings yet
- Design of An Aqueduct - CompressDocument5 pagesDesign of An Aqueduct - CompressMursaleen BawarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods for Simulation and Optimization of Piecewise Deterministic Markov Processes: Application to ReliabilityFrom EverandNumerical Methods for Simulation and Optimization of Piecewise Deterministic Markov Processes: Application to ReliabilityNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet