Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsSensory Powerpoint
Sensory Powerpoint
Uploaded by
api-202513022The eye contributes to vision. Ears contribute to hearing skin contributes to touch tongue contributes to taste nose contributes to smell Do you think that you hear sounds with your ear, smell with your nose and taste with your tongue? 29. The Senses the primary sensory cortex This is part of the brain that receives information about your sense of touch from different parts of your body.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Science Form 2Document29 pagesChapter 1 Science Form 2Minh HayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Stimuli and ResponseDocument84 pagesChapter 1 Stimuli and Responseg-37211406No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesMichelle LambertNo ratings yet
- Sensation: Prepared and Compiled by Dipesh UpadhyayDocument43 pagesSensation: Prepared and Compiled by Dipesh UpadhyayBhuwan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3Document6 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3Kirstelle Sarabillo86% (14)
- The World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter OneDocument10 pagesThe World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter Onegan tong hock a.k.a ganosNo ratings yet
- 01 Amali Sci F2Document34 pages01 Amali Sci F2Nur Dalila YusofNo ratings yet
- The World Through Our SensesDocument12 pagesThe World Through Our SenseskokondosNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3Document6 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3DUNGOG AYESSANo ratings yet
- Science Folio Form 2: The World Through Our SensesDocument19 pagesScience Folio Form 2: The World Through Our Sensesfikery100% (1)
- SCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Document49 pagesSCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Nurul NasaruddinNo ratings yet
- Evs 1 BrianDocument3 pagesEvs 1 Briangeorge baruahNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2: The World Through Our SensesDocument13 pagesScience Form 2: The World Through Our Sensesburn8464No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Receptors SensorsDocument32 pagesLecture 2 Receptors Sensorsshubham GautamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The World Through Our Senses: 1.1 Sensory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument14 pagesChapter 1: The World Through Our Senses: 1.1 Sensory Organs and Their FunctionsChai WanzhenNo ratings yet
- Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems: Bio 137 Antomy & Physiology IDocument31 pagesSensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems: Bio 137 Antomy & Physiology INarinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Form 2-Chapter 1-The World Through Our SensesDocument8 pagesForm 2-Chapter 1-The World Through Our SensesMathew Hon Jun YoonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document21 pagesLecture 7Rishi GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sensory ProcessDocument18 pagesSensory ProcessIrfan Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Sense of TouchDocument10 pages1.2 Sense of TouchDayangNo ratings yet
- GenpsyDocument27 pagesGenpsyGerlyn BrionesNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception Attention EmotionDocument15 pagesSensation and Perception Attention EmotionphanishashidharNo ratings yet
- S2 Senses NotesDocument7 pagesS2 Senses NotesDIONYSUSNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Sensation and PerceptionDocument235 pagesUnit 3: Sensation and PerceptionShanti DumreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Science (Form 2)Document128 pagesChapter 1-Science (Form 2)Yeoh Hui KoonNo ratings yet
- Unit Three Sensation and Perception: Learning ObjectivesDocument65 pagesUnit Three Sensation and Perception: Learning ObjectivesAnonymous Y2J3QRfdNo ratings yet
- Sensory Receptors LabDocument5 pagesSensory Receptors Labapi-290419496No ratings yet
- Is Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesDocument11 pagesIs Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesHafizah Ghany HayudinnaNo ratings yet
- Sensation ProcessesDocument19 pagesSensation Processesehtasham asifNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Jurnal - Facebook Profiles Reflect Actual Personality, Not Self-IdealizationDocument6 pagesIdentifikasi Jurnal - Facebook Profiles Reflect Actual Personality, Not Self-IdealizationFika_nNo ratings yet
- 2 HVCDocument18 pages2 HVCjadhavjaysurya3No ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception: Psychology 1Document28 pagesSensation and Perception: Psychology 1Vincent OrianaNo ratings yet
- General PhysiologyDocument18 pagesGeneral PhysiologyNerizza Shane ErmitaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Sensors and Comparing Them With Those in A Robot (50 MINUTES)Document28 pagesUnderstanding Human Sensors and Comparing Them With Those in A Robot (50 MINUTES)Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionNoralizah IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesNurul Ain RazaliNo ratings yet
- 4as Lesson PlanDocument8 pages4as Lesson PlanDUNGOG AYESSANo ratings yet
- The Senses Detect The Internal and External Environments.: Key ConceptDocument6 pagesThe Senses Detect The Internal and External Environments.: Key ConceptEman ShirriNo ratings yet
- The SensesDocument46 pagesThe SensesRizqi Putra ZaraNo ratings yet
- Sensation BBA 1st LectureDocument37 pagesSensation BBA 1st Lecture52wtq8v288No ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionReduan Ibrahim100% (3)
- Biology 12 Chapter 29.3 The SensesDocument11 pagesBiology 12 Chapter 29.3 The Sensesismail gamalNo ratings yet
- Psychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Document5 pagesPsychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Lyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Skin Receptors, Taste and Smell Nov 4th 2016Document23 pagesAnatomy Skin Receptors, Taste and Smell Nov 4th 2016HollyNo ratings yet
- Five SensesDocument41 pagesFive SensesJobel Sibal CapunfuerzaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document26 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- 9 ASensory Intro ChemoDocument38 pages9 ASensory Intro ChemoLorsa HughesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Sensation and PerceptionDocument49 pagesLecture 3 Sensation and PerceptionNURUL FARHANA BINTI IMRAN -No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Sensory OrgansDocument76 pagesChapter 1 Sensory OrgansNadia Mohamad YusofNo ratings yet
- BI 232 Lab 10Document11 pagesBI 232 Lab 10Cj LinceNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception 3: Jason Bell Perception Lecture May 6Document16 pagesSensation and Perception 3: Jason Bell Perception Lecture May 6Billy TherionNo ratings yet
- SensationDocument6 pagesSensationIzhar KhanNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Skin Lab-Tactile ReceptorsDocument1 page5.4 Skin Lab-Tactile Receptorsmilnertonward.ldsNo ratings yet
- Sense Lab - Taste and Touch 2024Document5 pagesSense Lab - Taste and Touch 2024Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- A Tour of the Senses: How Your Brain Interprets the WorldFrom EverandA Tour of the Senses: How Your Brain Interprets the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- I Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandI Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Applied Psychology: Making Your Own World: Being the Second of a Series of Twelve Volumes on the / Applications of Psychology to the Problems of Personal and / Business EfficiencyFrom EverandApplied Psychology: Making Your Own World: Being the Second of a Series of Twelve Volumes on the / Applications of Psychology to the Problems of Personal and / Business EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- LR 3 How To Write An IntroductionDocument4 pagesLR 3 How To Write An Introductionapi-202513022No ratings yet
- The Immune System 2013Document31 pagesThe Immune System 2013api-202513022No ratings yet
- Good Kid PresentationDocument7 pagesGood Kid Presentationapi-202513022No ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesThe Digestive Systemianpoblete13No ratings yet
- 8 Electrostatic SituationsDocument8 pages8 Electrostatic Situationsapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Skeletalsystemmenuboardrosen 1Document3 pagesSkeletalsystemmenuboardrosen 1api-202513022No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument51 pagesCirculatory SystemTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Winter Formal PPDocument4 pagesWinter Formal PPapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Momentum DemonstrationDocument16 pagesMomentum Demonstrationapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Biology Slide 1Document8 pagesBiology Slide 1api-202513022No ratings yet
- My Action Research PresentationDocument31 pagesMy Action Research Presentationapi-202513022No ratings yet
- The Nervous System by MR RosenDocument10 pagesThe Nervous System by MR Rosenapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Habitats For Plants and AnimalsDocument38 pagesHabitats For Plants and Animalsapi-202513022100% (1)
- Living in Cold Places1Document8 pagesLiving in Cold Places1api-202513022No ratings yet
- Chordata MammaliaDocument9 pagesChordata Mammaliaapi-202513022No ratings yet
Sensory Powerpoint
Sensory Powerpoint
Uploaded by
api-2025130220 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesThe eye contributes to vision. Ears contribute to hearing skin contributes to touch tongue contributes to taste nose contributes to smell Do you think that you hear sounds with your ear, smell with your nose and taste with your tongue? 29. The Senses the primary sensory cortex This is part of the brain that receives information about your sense of touch from different parts of your body.
Original Description:
Original Title
sensory powerpoint
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe eye contributes to vision. Ears contribute to hearing skin contributes to touch tongue contributes to taste nose contributes to smell Do you think that you hear sounds with your ear, smell with your nose and taste with your tongue? 29. The Senses the primary sensory cortex This is part of the brain that receives information about your sense of touch from different parts of your body.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesSensory Powerpoint
Sensory Powerpoint
Uploaded by
api-202513022The eye contributes to vision. Ears contribute to hearing skin contributes to touch tongue contributes to taste nose contributes to smell Do you think that you hear sounds with your ear, smell with your nose and taste with your tongue? 29. The Senses the primary sensory cortex This is part of the brain that receives information about your sense of touch from different parts of your body.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
29.
3 The Senses
The senses detect physical and chemical stimuli.
The eye contributes to vision. Ears contribute to hearing Skin contributes to touch Tongue contributes to taste Nose contributes to smell
Do you think that you hear sounds with your ear, smell with your nose and taste with your tongue?
29.3 The Senses
29.3 The Senses
We humans only see within a certain range of the electromagnetic spectrum
Birds can also see in the Ultraviolet range
What are some things we cannot see but we know are out there?
29.3 The Senses
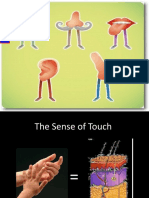
The skin senses touch. Mechanoreceptors detect pressure. Pain receptors detect damaged tissue. Thermoreceptors detect temperature.
pain receptor light pressure receptor hair follicle heavy pressure receptor
29.3 The Senses
The Primary Sensory Cortex This is part of the brain that receives information about your sense of touch from different parts of your body. Each body part sends information to a different place in your primary sensory cortex. Question: Does your finger or your forearm have more space devoted to it in the primary sensory cortex?
1) Have your partner close his or her eyes. Gently, touch the tip of your partners index finger with the tip(s) of 1, 2, or 3 Q-Tips at the same time. 2) Ask your partner how many points he or she feels. Repeat a couple more times, varying the number of toothpicks used. 3) Repeat steps 1 and 2 on your partners forearm. Did your partners finger or forearm receive more sensory information? Which are likely has more space in the primary sensory cortex?
You might also like
- Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesRespiratory Systemapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Science Form 2Document29 pagesChapter 1 Science Form 2Minh HayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Stimuli and ResponseDocument84 pagesChapter 1 Stimuli and Responseg-37211406No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesMichelle LambertNo ratings yet
- Sensation: Prepared and Compiled by Dipesh UpadhyayDocument43 pagesSensation: Prepared and Compiled by Dipesh UpadhyayBhuwan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3Document6 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3Kirstelle Sarabillo86% (14)
- The World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter OneDocument10 pagesThe World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter Onegan tong hock a.k.a ganosNo ratings yet
- 01 Amali Sci F2Document34 pages01 Amali Sci F2Nur Dalila YusofNo ratings yet
- The World Through Our SensesDocument12 pagesThe World Through Our SenseskokondosNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3Document6 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan Science 3DUNGOG AYESSANo ratings yet
- Science Folio Form 2: The World Through Our SensesDocument19 pagesScience Folio Form 2: The World Through Our Sensesfikery100% (1)
- SCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Document49 pagesSCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Nurul NasaruddinNo ratings yet
- Evs 1 BrianDocument3 pagesEvs 1 Briangeorge baruahNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2: The World Through Our SensesDocument13 pagesScience Form 2: The World Through Our Sensesburn8464No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Receptors SensorsDocument32 pagesLecture 2 Receptors Sensorsshubham GautamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The World Through Our Senses: 1.1 Sensory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument14 pagesChapter 1: The World Through Our Senses: 1.1 Sensory Organs and Their FunctionsChai WanzhenNo ratings yet
- Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems: Bio 137 Antomy & Physiology IDocument31 pagesSensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems: Bio 137 Antomy & Physiology INarinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Form 2-Chapter 1-The World Through Our SensesDocument8 pagesForm 2-Chapter 1-The World Through Our SensesMathew Hon Jun YoonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document21 pagesLecture 7Rishi GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sensory ProcessDocument18 pagesSensory ProcessIrfan Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Sense of TouchDocument10 pages1.2 Sense of TouchDayangNo ratings yet
- GenpsyDocument27 pagesGenpsyGerlyn BrionesNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception Attention EmotionDocument15 pagesSensation and Perception Attention EmotionphanishashidharNo ratings yet
- S2 Senses NotesDocument7 pagesS2 Senses NotesDIONYSUSNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Sensation and PerceptionDocument235 pagesUnit 3: Sensation and PerceptionShanti DumreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Science (Form 2)Document128 pagesChapter 1-Science (Form 2)Yeoh Hui KoonNo ratings yet
- Unit Three Sensation and Perception: Learning ObjectivesDocument65 pagesUnit Three Sensation and Perception: Learning ObjectivesAnonymous Y2J3QRfdNo ratings yet
- Sensory Receptors LabDocument5 pagesSensory Receptors Labapi-290419496No ratings yet
- Is Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesDocument11 pagesIs Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesHafizah Ghany HayudinnaNo ratings yet
- Sensation ProcessesDocument19 pagesSensation Processesehtasham asifNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Jurnal - Facebook Profiles Reflect Actual Personality, Not Self-IdealizationDocument6 pagesIdentifikasi Jurnal - Facebook Profiles Reflect Actual Personality, Not Self-IdealizationFika_nNo ratings yet
- 2 HVCDocument18 pages2 HVCjadhavjaysurya3No ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception: Psychology 1Document28 pagesSensation and Perception: Psychology 1Vincent OrianaNo ratings yet
- General PhysiologyDocument18 pagesGeneral PhysiologyNerizza Shane ErmitaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Sensors and Comparing Them With Those in A Robot (50 MINUTES)Document28 pagesUnderstanding Human Sensors and Comparing Them With Those in A Robot (50 MINUTES)Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionNoralizah IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesNurul Ain RazaliNo ratings yet
- 4as Lesson PlanDocument8 pages4as Lesson PlanDUNGOG AYESSANo ratings yet
- The Senses Detect The Internal and External Environments.: Key ConceptDocument6 pagesThe Senses Detect The Internal and External Environments.: Key ConceptEman ShirriNo ratings yet
- The SensesDocument46 pagesThe SensesRizqi Putra ZaraNo ratings yet
- Sensation BBA 1st LectureDocument37 pagesSensation BBA 1st Lecture52wtq8v288No ratings yet
- 1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionDocument20 pages1.1 Sense Organ and Their FunctionReduan Ibrahim100% (3)
- Biology 12 Chapter 29.3 The SensesDocument11 pagesBiology 12 Chapter 29.3 The Sensesismail gamalNo ratings yet
- Psychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Document5 pagesPsychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Lyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Skin Receptors, Taste and Smell Nov 4th 2016Document23 pagesAnatomy Skin Receptors, Taste and Smell Nov 4th 2016HollyNo ratings yet
- Five SensesDocument41 pagesFive SensesJobel Sibal CapunfuerzaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document26 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- 9 ASensory Intro ChemoDocument38 pages9 ASensory Intro ChemoLorsa HughesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Sensation and PerceptionDocument49 pagesLecture 3 Sensation and PerceptionNURUL FARHANA BINTI IMRAN -No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Sensory OrgansDocument76 pagesChapter 1 Sensory OrgansNadia Mohamad YusofNo ratings yet
- BI 232 Lab 10Document11 pagesBI 232 Lab 10Cj LinceNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception 3: Jason Bell Perception Lecture May 6Document16 pagesSensation and Perception 3: Jason Bell Perception Lecture May 6Billy TherionNo ratings yet
- SensationDocument6 pagesSensationIzhar KhanNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Skin Lab-Tactile ReceptorsDocument1 page5.4 Skin Lab-Tactile Receptorsmilnertonward.ldsNo ratings yet
- Sense Lab - Taste and Touch 2024Document5 pagesSense Lab - Taste and Touch 2024Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- A Tour of the Senses: How Your Brain Interprets the WorldFrom EverandA Tour of the Senses: How Your Brain Interprets the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- I Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandI Can Hear, See, Taste, Smell and Feel! Senses Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Applied Psychology: Making Your Own World: Being the Second of a Series of Twelve Volumes on the / Applications of Psychology to the Problems of Personal and / Business EfficiencyFrom EverandApplied Psychology: Making Your Own World: Being the Second of a Series of Twelve Volumes on the / Applications of Psychology to the Problems of Personal and / Business EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- LR 3 How To Write An IntroductionDocument4 pagesLR 3 How To Write An Introductionapi-202513022No ratings yet
- The Immune System 2013Document31 pagesThe Immune System 2013api-202513022No ratings yet
- Good Kid PresentationDocument7 pagesGood Kid Presentationapi-202513022No ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesThe Digestive Systemianpoblete13No ratings yet
- 8 Electrostatic SituationsDocument8 pages8 Electrostatic Situationsapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Skeletalsystemmenuboardrosen 1Document3 pagesSkeletalsystemmenuboardrosen 1api-202513022No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument51 pagesCirculatory SystemTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Winter Formal PPDocument4 pagesWinter Formal PPapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Momentum DemonstrationDocument16 pagesMomentum Demonstrationapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Biology Slide 1Document8 pagesBiology Slide 1api-202513022No ratings yet
- My Action Research PresentationDocument31 pagesMy Action Research Presentationapi-202513022No ratings yet
- The Nervous System by MR RosenDocument10 pagesThe Nervous System by MR Rosenapi-202513022No ratings yet
- Habitats For Plants and AnimalsDocument38 pagesHabitats For Plants and Animalsapi-202513022100% (1)
- Living in Cold Places1Document8 pagesLiving in Cold Places1api-202513022No ratings yet
- Chordata MammaliaDocument9 pagesChordata Mammaliaapi-202513022No ratings yet