Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Synaptic Communication With Catecholamines
Synaptic Communication With Catecholamines
Uploaded by
kep1313Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Synaptic Communication With Catecholamines
Synaptic Communication With Catecholamines
Uploaded by
kep1313Copyright:
Available Formats
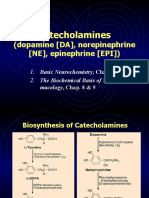
Synaptic Communication with Catecholamines (CA) April 5, 2010 1. Outline the biosynthesis, storage, release, and metabolism of CA.
a. BIOSYNTHESIS
CA Phenylalanine tyrosine Enzyme Phenylalanine hydroxylase Clinical significance PKU: deficiency in enzyme; build up of Phe (toxic to brain) Alpha-methyltyrosine, iron chelators, and lead: inhibit TH Additional info Majority of tyrosine is obtained from eating highprotein foods Regulation of TH: short-term: phosphorylation & dephosphorylation long-term: transcription (stimulated by neurotransmitters, hormones, caffeine, and nicotine)
Tyrosine LDopa
Tyrosine hydroxylase
L-Dopa dopamine
DOPA decarboxylase (also AAADC, which produces 2PEA) Dopamine betahydroxylase
AAADC activity increased in schizophrenia; stimulated by amphetamines, LSD NE is target for treating depression, anxiety, etc NE function: sleep, arousal, attention, vigilance, learning
DA Norepinephrine
NE Epinephrine
Phenylethylamine -N-methyl transferase
Epi functions: increased sympathetic activity
b. CATABOLISM i. Enzymes: 1. Monoamine oxidases MAO (types A and B) a. Genes: X chromosome b. Inhibitors i. MAO-A: gene mutation causes abnormal and violent behavior
ii. MAO-B: 1-Deprenyl, smoking (nicotine facilitates DA release) iii. *Pargyline: inhibitor of MAO 2. CA-O-methyltransferases (COMT) a. Inhibitors used to treat Parkinsons ii. Products: 1. DA homovanillic acid (HVA) 2. NE 3-methyl-4-hydroxyphenol-glycol (MHPG) 2. Discuss possible abnormalities in CA metabolism a. See #1
3. Discuss the CA receptors and their regulation
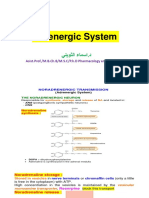
CA Dopamine Release Released from synaptic vesicles after Ca2+ permeability increases Receptor 5 major types; G-coupled 1&5: activate cAMP synthesis 2-4: inhibit synthesis Reuptake DA transporter (DAT): reuptake of DA by presynaptic neuron **Inhibited by cocaine (more DA in the cleft) and amphetamines (release DA and block its reuptake)
Norepinephri ne/ epinephrine
Released from postsynaptic adrenergic neurons
Alpha1, alpha 2 Beta: agonists used to treat asthma; antagonists used to treat social phobias/stage fright (e.g. propranolol)
4. Discuss how the Human Genome Project will help to choose pharmacological treatment options based on exact science a. Intrastriatal injection of an adenoviral vector expressing glial-cell-linederived neurotrophic factor prevents dopaminergic neuron degeneration and behavioral impairment in a rat model of Parkinson disease
You might also like
- Antidepressant and AntimanicDocument60 pagesAntidepressant and Antimanictbuyinza21apNo ratings yet
- Stimulant DrugsDocument4 pagesStimulant Drugskep1313No ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To CNS Pharmacology PDFDocument3 pages01 Introduction To CNS Pharmacology PDFjackNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument52 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's Diseasebhagyashri chaudhariNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect Parkinson DiseaseDocument12 pagesDrugs That Affect Parkinson Diseaserichardmd2No ratings yet
- Catecholamines: (Dopamine (DA), Norepinephrine (NE), Epinephrine (EPI) )Document30 pagesCatecholamines: (Dopamine (DA), Norepinephrine (NE), Epinephrine (EPI) )Imrana AamirNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument52 pagesDrugs For Parkinson's DiseaseKAMALNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Ns (Adrenergic) Parasympa NS (Cholinergic)Document6 pagesSympathetic Ns (Adrenergic) Parasympa NS (Cholinergic)Jov May DimcoNo ratings yet
- NP3 PDFDocument30 pagesNP3 PDFRajat AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Faktor Neurobiologi: Qara Syifa Fachrani 1610211039Document22 pagesFaktor Neurobiologi: Qara Syifa Fachrani 1610211039Qara Syifa FNo ratings yet
- K10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For ParkinsonDocument41 pagesK10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For Parkinsonali100% (1)
- CatecholaminesDocument30 pagesCatecholaminesashutoshkafle100% (1)
- CNS NeurotransmittersDocument30 pagesCNS Neurotransmittersdevanshi_582262183100% (1)
- 14 CatecholamineDocument5 pages14 CatecholamineZiedTrikiNo ratings yet
- 2018 Zambrana Infantes E Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 166 1-12Document12 pages2018 Zambrana Infantes E Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 166 1-12Eduardo Blanco CalvoNo ratings yet
- 1996 Role of NTs in Alcohol DependenceDocument4 pages1996 Role of NTs in Alcohol DependenceMuhammad Sona KhanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Medicinal Plants and Natural ProductsDocument116 pagesPharmacology of Medicinal Plants and Natural ProductsMichael MasengiNo ratings yet
- Naidoo Lecture NoteDocument10 pagesNaidoo Lecture NoteDanny LeeNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Biochemistry Assignment 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: Biochemistry Assignment 1Fredrick LiyengaNo ratings yet
- 10-Antiparkinsonian and Spasmolytic AgentsDocument32 pages10-Antiparkinsonian and Spasmolytic Agentszeynep özdalNo ratings yet
- Dopamine, Serotonine, Epinephrine, and NorephinephrineDocument28 pagesDopamine, Serotonine, Epinephrine, and Norephinephrinehafshah100% (1)
- DopamineDocument17 pagesDopamineRajan BalavendranNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsons DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinsons Drugs39 Nayan BhagatNo ratings yet
- Antidepreesent AgentsDocument34 pagesAntidepreesent Agentsmaryamkefahn2003No ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian Drugs: Dr. Jahid Senior Lecturer KuinDocument51 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugs: Dr. Jahid Senior Lecturer KuinfahmiNo ratings yet
- Capsicum Protects Against Rotenoneinduced Toxicity in Mice Brain Via Reduced Oxidative Stress and 5lipoxygenase Activationp PDFDocument18 pagesCapsicum Protects Against Rotenoneinduced Toxicity in Mice Brain Via Reduced Oxidative Stress and 5lipoxygenase Activationp PDFFortune JournalsNo ratings yet
- BMS1 - K14 - Pharmacotherapy For ParkinsonDocument51 pagesBMS1 - K14 - Pharmacotherapy For ParkinsonAndreNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Serotonergic and Central Adrenergic Neurotransmission-Week 6Document46 pagesPharmacology of Serotonergic and Central Adrenergic Neurotransmission-Week 6boboNo ratings yet
- GFDGFDGFDGDocument11 pagesGFDGFDGFDGلو ترىNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument21 pagesNeurotransmittersYannie GomezNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument9 pagesParkinson's Diseaselucia desantisNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument52 pagesAntiparkinsonian DrugsRENTI NOVITANo ratings yet
- Pharm Parkinsons HandoutDocument9 pagesPharm Parkinsons HandoutDavidNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetics (Catecholamines & Non Catecholamines)Document99 pagesSympathomimetics (Catecholamines & Non Catecholamines)Raheel JavaidNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UDocument24 pagesDrugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UtemitopeNo ratings yet
- Pharm Final Study GuideDocument27 pagesPharm Final Study GuideangelNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids Derived From TyrosineDocument3 pagesAlkaloids Derived From TyrosineMark KuaNo ratings yet
- Activity of Selected Aromatic Amino Acids in Biological SystemsDocument6 pagesActivity of Selected Aromatic Amino Acids in Biological SystemsEduardo Lopez MedranoNo ratings yet
- Departement of Neurology Christian University of Indonesia Medical FacultyDocument39 pagesDepartement of Neurology Christian University of Indonesia Medical FacultySandra Anastasia Gultom100% (1)
- Levodopa Seminar - Adi CohenDocument8 pagesLevodopa Seminar - Adi Cohenעדי כהןNo ratings yet
- Right-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichDocument47 pagesRight-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Drugs of Abuse Is: Metabolized by The Liver Enzyme CYP2D6, So CYP2D6 Inhibitors Will Prolong TheDocument3 pagesDrugs of Abuse Is: Metabolized by The Liver Enzyme CYP2D6, So CYP2D6 Inhibitors Will Prolong TheCattrainuhNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Pharmacology of Cns 29022024 031838pmDocument51 pagesIntroduction of Pharmacology of Cns 29022024 031838pmaz.rah.e.khudiNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter (Dr. Devi) - 2Document71 pagesNeurotransmitter (Dr. Devi) - 2nazyaNo ratings yet
- Neurology AL QUDS Part 2Document73 pagesNeurology AL QUDS Part 2reem natshehNo ratings yet
- Cns Stimulants: Convulsants - Analeptics - PsychostimulantsDocument4 pagesCns Stimulants: Convulsants - Analeptics - Psychostimulantss.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- 4 Adrenergic AgonistsDocument46 pages4 Adrenergic Agonistsmatchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- Parkinson in MonkeysDocument16 pagesParkinson in MonkeysSergeyNo ratings yet
- Anti-Parkinsonism DrugDocument15 pagesAnti-Parkinsonism Drugsaihjad pramaniNo ratings yet
- Toxicity of Amphetamines: An UpdateDocument65 pagesToxicity of Amphetamines: An UpdateMariana MadiaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusDocument5 pagesDrugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsDocument35 pagesLecture 8 Central Nervous System CnsakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- AntiepilepticsDocument16 pagesAntiepilepticsDivyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in Developing BrainsDocument38 pagesPharmacology in Developing Brainsjamsterman5No ratings yet
- Herbal Treatment of Parkinsonism A ReviewDocument7 pagesHerbal Treatment of Parkinsonism A ReviewKartika BorraNo ratings yet
- Dopaminergics 23mars10Document24 pagesDopaminergics 23mars10safemindNo ratings yet
- Continum ParkinsonDocument14 pagesContinum Parkinsonfernando gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Advances in Dopamine Research: Proceeding of a Satellite Symposium to the 8th International Congress of Pharmacology, Okayama, Japan, July 1981From EverandAdvances in Dopamine Research: Proceeding of a Satellite Symposium to the 8th International Congress of Pharmacology, Okayama, Japan, July 1981M. KohsakaNo ratings yet
- Case Studies 5Document4 pagesCase Studies 5kep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- Case Studies 4Document4 pagesCase Studies 4kep1313No ratings yet
- Psychiatry - BSDocument15 pagesPsychiatry - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Physiology - BSDocument14 pagesPhysiology - BSkep1313No ratings yet
- Anemia DifferentialDocument1 pageAnemia Differentialkep1313No ratings yet
- Biochem MedicineDocument27 pagesBiochem Medicinekep1313No ratings yet
- 2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune DisordersDocument2 pages2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- 2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative DisordersDocument7 pages2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative Disorderskep1313No ratings yet
- 2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV DiseaseDocument2 pages2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV Diseasekep1313No ratings yet
- 2-3-10 Hive-1 Basic Virology and PathobiologyDocument3 pages2-3-10 Hive-1 Basic Virology and Pathobiologykep1313No ratings yet