Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
423 viewsCornell Notes Ecology
Cornell Notes Ecology
Uploaded by
Melodee PetersThe document summarizes key roles in ecosystems:
1. Producers such as plants and microorganisms produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, converting raw materials like water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into glucose. They are the base of the food chain.
2. Consumers eat producers or other organisms. Herbivores eat plants directly, carnivores eat herbivores, omnivores eat plants and animals, and scavengers eat dead organisms.
3. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter and cycle nutrients in the ecosystem.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ELL - EXP The White Umbrella - Gish JenDocument9 pagesELL - EXP The White Umbrella - Gish JenMelodee Peters100% (1)
- C. Chapter 9 Lesson 9.3-Interactions and Relationships in An EcosystemDocument13 pagesC. Chapter 9 Lesson 9.3-Interactions and Relationships in An EcosystemAnaliza SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Ecology DiscussionDocument31 pagesEcology DiscussionAl Marjorie Abrasaldo TatingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 35Document3 pagesLecture 35Tzuyu TchaikovskyNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow Through Ecosystems: Science 9 2019Document20 pagesEnergy Flow Through Ecosystems: Science 9 2019Rene RamiloNo ratings yet
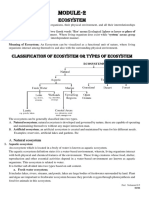
- EVS Module No - 2 Ecosystem New 2023Document11 pagesEVS Module No - 2 Ecosystem New 2023prakashnisha9741No ratings yet
- Unit 1-EcosystemsDocument60 pagesUnit 1-EcosystemsRidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 MSTDocument16 pagesLesson 2 MSTcornejababylynneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 EcosystemDocument19 pagesLecture 2 EcosystemParva PatelNo ratings yet
- 11-1 The Science of EcologyDocument14 pages11-1 The Science of Ecologyapi-265907602No ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Biotic Components of An EcosystemDocument3 pagesLesson 9 - Biotic Components of An EcosystemAbegail HernandezNo ratings yet
- Science of EcologyDocument2 pagesScience of Ecologyhomamunfat100% (1)
- Environmental Sciences Unit-IIIDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Sciences Unit-IIIpavansvgp2003No ratings yet
- ES UNIT - 2: EcosystemsDocument18 pagesES UNIT - 2: Ecosystemsxijiwo8667No ratings yet
- EcologyDocument8 pagesEcologytnkele73No ratings yet
- HWDocument6 pagesHWabm12diamond.lozada.quineNo ratings yet
- Gee2 ReviewerDocument29 pagesGee2 ReviewerFrances Samson GianNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering Module 1Document8 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering Module 1Pamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument46 pagesEcosystemShrawani DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Interactions in The Biosphere (Biotic Factors)Document7 pagesInteractions in The Biosphere (Biotic Factors)Jonel Racuya BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Our EnvironmentDocument9 pagesOur Environmentraimaali220077No ratings yet
- 2 Term: Our EnvironmentDocument15 pages2 Term: Our EnvironmentdharmeshdalalNo ratings yet
- Unit III - ENVIRONMENT STUDIES Sem IIDocument17 pagesUnit III - ENVIRONMENT STUDIES Sem IIsurajkumar436No ratings yet
- Evs Unit-3 Short NotesDocument14 pagesEvs Unit-3 Short NotesMohammed SiddiqNo ratings yet
- 10th Science Our EnvironmentDocument10 pages10th Science Our EnvironmentLe TensaiNo ratings yet
- The Major Components of An EcosystemDocument6 pagesThe Major Components of An EcosystemCrisha Joy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Enviromental StudiesDocument86 pagesEcosystem Enviromental StudiesMridul SondhiNo ratings yet
- Handout ECOSYSTEMDocument3 pagesHandout ECOSYSTEMHubert BernardNo ratings yet
- 13.3 Energy in EcosystemsDocument2 pages13.3 Energy in EcosystemsOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PDFDocument32 pagesEcosystem PDFYuvashreeNo ratings yet
- Study of Ecosystems: Is The Study of Interactions Among Organisms Group of Organisms With The EnvironmentDocument44 pagesStudy of Ecosystems: Is The Study of Interactions Among Organisms Group of Organisms With The Environmentleela777No ratings yet
- Exploring Ecosystems A Journey Into Natures MarvelsDocument10 pagesExploring Ecosystems A Journey Into Natures Marvelstejaswaniverma289No ratings yet
- Ecosystems IntroDocument7 pagesEcosystems IntroNidhi PNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Its Components: February 2008Document7 pagesEcosystem and Its Components: February 2008aufaaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EcosystemsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EcosystemsKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Ge 2021 16 Marks Q@aDocument60 pagesGe 2021 16 Marks Q@aSasi RekhaNo ratings yet
- Environment - Sunya Prelims Notes 2024 - 240208 - 180522Document221 pagesEnvironment - Sunya Prelims Notes 2024 - 240208 - 180522rameshpradhansaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Energy & Environmental Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument24 pagesUnit 2 - Energy & Environmental Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inHarshal BordiaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem: Unit 2Document36 pagesEcosystem: Unit 2Dominador MasiragNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM PPT Final PGDocument56 pagesECOSYSTEM PPT Final PGShovana DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1Vim EnobioNo ratings yet
- I. Preparation: Lesson 2 Concept of Ecosystem Intended Learning OutcomeDocument17 pagesI. Preparation: Lesson 2 Concept of Ecosystem Intended Learning OutcomeLeslie ObisoNo ratings yet
- Our Environment: Chapter - 15Document10 pagesOur Environment: Chapter - 15IshvaryaNo ratings yet
- GE 302 - Industry and The EnvironmentDocument18 pagesGE 302 - Industry and The EnvironmenthassanNo ratings yet
- Group II: - Ecosystem - Ecological ChainDocument33 pagesGroup II: - Ecosystem - Ecological ChainSariah MirandaNo ratings yet
- Evs NotesDocument36 pagesEvs NotesPUSHPA RAAJNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDocument7 pagesEcosystem and Its Componentsনিঃসঙ্গ পথিকNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and BiodiversityDocument25 pagesEcosystems and BiodiversityRahul67% (3)
- Environment and DevelopmentDocument122 pagesEnvironment and DevelopmentSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem NotesDocument11 pagesEcosystem Notesluciferx187No ratings yet
- Ecosystem Prac1Document2 pagesEcosystem Prac1athilasyakura86No ratings yet
- Ecosystem (Part-I) : Mr. Tarun ChauhanDocument17 pagesEcosystem (Part-I) : Mr. Tarun ChauhanNEHA BANSALNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Notes PDFDocument17 pagesEcosystem Notes PDFNEHA BANSALNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document11 pagesUnit 2bádshãh raiNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem New 2017Document20 pagesEcosystem New 2017raniNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Introduction PDFDocument84 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Introduction PDFChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Evs Unit - 3Document20 pagesLecture Notes - Evs Unit - 3Nambi RajanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Ecosystems: Environmental Science Notes (Yogesh R. Kadam M.Sc. Environmental Science, SPPU, Pune.)Document26 pagesUnit 2: Ecosystems: Environmental Science Notes (Yogesh R. Kadam M.Sc. Environmental Science, SPPU, Pune.)ankit kaleNo ratings yet
- People and The Earths Ecosystem CoverageDocument49 pagesPeople and The Earths Ecosystem CoverageChristen Honely DadangNo ratings yet
- 3 EcosystemDocument21 pages3 EcosystemKishore KNo ratings yet
- Exploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandExploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms Review SheetDocument2 pagesLiterary Terms Review SheetMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Cheeseburger ChemistryDocument3 pagesCheeseburger ChemistryMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- GO For notesTHE ANATOMY OF A REVOLUTIONDocument1 pageGO For notesTHE ANATOMY OF A REVOLUTIONMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Choiceboard Feb22Document3 pagesChoiceboard Feb22Melodee PetersNo ratings yet
- "Charles" Literature Groups WorksheetDocument2 pages"Charles" Literature Groups WorksheetMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Note-Making RubricDocument1 pageNote-Making RubricMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- VoiceThread RubricDocument2 pagesVoiceThread RubricMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Geometry Study GuideDocument6 pagesGeometry Study GuideMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- STATION 1A: Science STATION 1B: Science STATION 2: Social StudiesDocument3 pagesSTATION 1A: Science STATION 1B: Science STATION 2: Social StudiesMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of BileDocument2 pagesBehaviour of BileMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Coming Up With A Research Question 2012Document1 pageComing Up With A Research Question 2012Melodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Flow ChartDocument2 pagesDigestive System Flow ChartMelodee Peters79% (24)
Cornell Notes Ecology
Cornell Notes Ecology
Uploaded by
Melodee Peters0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
423 views1 pageThe document summarizes key roles in ecosystems:
1. Producers such as plants and microorganisms produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, converting raw materials like water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into glucose. They are the base of the food chain.
2. Consumers eat producers or other organisms. Herbivores eat plants directly, carnivores eat herbivores, omnivores eat plants and animals, and scavengers eat dead organisms.
3. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter and cycle nutrients in the ecosystem.
Original Description:
Example of how to make notes from textbook
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key roles in ecosystems:
1. Producers such as plants and microorganisms produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, converting raw materials like water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into glucose. They are the base of the food chain.
2. Consumers eat producers or other organisms. Herbivores eat plants directly, carnivores eat herbivores, omnivores eat plants and animals, and scavengers eat dead organisms.
3. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter and cycle nutrients in the ecosystem.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
423 views1 pageCornell Notes Ecology
Cornell Notes Ecology
Uploaded by
Melodee PetersThe document summarizes key roles in ecosystems:
1. Producers such as plants and microorganisms produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, converting raw materials like water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into glucose. They are the base of the food chain.
2. Consumers eat producers or other organisms. Herbivores eat plants directly, carnivores eat herbivores, omnivores eat plants and animals, and scavengers eat dead organisms.
3. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter and cycle nutrients in the ecosystem.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Notes from Ecology Textbook pp.
18-22
Roles of Organisms in an Ecosystem
26 April 2013 FOOD AND ENERGY IN THE ENVIRONMENT
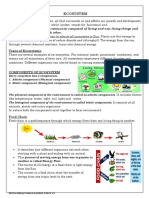
1. PRODUCERS Make their own food, e.g. plants & certain microorganisms Use energy to convert raw materials into food, e.g. plants use sunlight to turn H2O and CO2 into food (glucose) IMPORTANT: producers are the source of ALL the FOOD in an ecosystem 2. CONSUMERS Consumes producers directly: herbivores (grasshoppers, goats) that eat plants Consumes producers indirectly: - carnivores eat herbivores, e.g spider eats grasshopper, lion eats goat; - omnivores eat plants and animals, e.g. humans, bears; - scavengers eat dead organisms, e.g. vultures (aasvoel), certain crabs, and hyenas 3. DECOMPOSERS
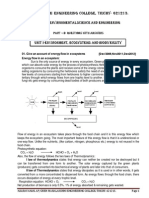
Food Chains & Feeding Levels Food Webs Review Questions 1. Explain how producers, consumers, and decomposers interact. For each energy role, give 2 examples of organisms that perform that role in their ecosystem. 2. What is the relationship between feeding levels and amount of available energy? 3. How does energy flow through an ecosystem? Critical Thinking Evaluating Diagrams Why are decomposers left out of most diagrams of food chains and webs? Is this good practice? Explain.
You might also like
- ELL - EXP The White Umbrella - Gish JenDocument9 pagesELL - EXP The White Umbrella - Gish JenMelodee Peters100% (1)
- C. Chapter 9 Lesson 9.3-Interactions and Relationships in An EcosystemDocument13 pagesC. Chapter 9 Lesson 9.3-Interactions and Relationships in An EcosystemAnaliza SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Ecology DiscussionDocument31 pagesEcology DiscussionAl Marjorie Abrasaldo TatingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 35Document3 pagesLecture 35Tzuyu TchaikovskyNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow Through Ecosystems: Science 9 2019Document20 pagesEnergy Flow Through Ecosystems: Science 9 2019Rene RamiloNo ratings yet
- EVS Module No - 2 Ecosystem New 2023Document11 pagesEVS Module No - 2 Ecosystem New 2023prakashnisha9741No ratings yet
- Unit 1-EcosystemsDocument60 pagesUnit 1-EcosystemsRidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 MSTDocument16 pagesLesson 2 MSTcornejababylynneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 EcosystemDocument19 pagesLecture 2 EcosystemParva PatelNo ratings yet
- 11-1 The Science of EcologyDocument14 pages11-1 The Science of Ecologyapi-265907602No ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Biotic Components of An EcosystemDocument3 pagesLesson 9 - Biotic Components of An EcosystemAbegail HernandezNo ratings yet
- Science of EcologyDocument2 pagesScience of Ecologyhomamunfat100% (1)
- Environmental Sciences Unit-IIIDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Sciences Unit-IIIpavansvgp2003No ratings yet
- ES UNIT - 2: EcosystemsDocument18 pagesES UNIT - 2: Ecosystemsxijiwo8667No ratings yet
- EcologyDocument8 pagesEcologytnkele73No ratings yet
- HWDocument6 pagesHWabm12diamond.lozada.quineNo ratings yet
- Gee2 ReviewerDocument29 pagesGee2 ReviewerFrances Samson GianNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering Module 1Document8 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering Module 1Pamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument46 pagesEcosystemShrawani DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Interactions in The Biosphere (Biotic Factors)Document7 pagesInteractions in The Biosphere (Biotic Factors)Jonel Racuya BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Our EnvironmentDocument9 pagesOur Environmentraimaali220077No ratings yet
- 2 Term: Our EnvironmentDocument15 pages2 Term: Our EnvironmentdharmeshdalalNo ratings yet
- Unit III - ENVIRONMENT STUDIES Sem IIDocument17 pagesUnit III - ENVIRONMENT STUDIES Sem IIsurajkumar436No ratings yet
- Evs Unit-3 Short NotesDocument14 pagesEvs Unit-3 Short NotesMohammed SiddiqNo ratings yet
- 10th Science Our EnvironmentDocument10 pages10th Science Our EnvironmentLe TensaiNo ratings yet
- The Major Components of An EcosystemDocument6 pagesThe Major Components of An EcosystemCrisha Joy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Enviromental StudiesDocument86 pagesEcosystem Enviromental StudiesMridul SondhiNo ratings yet
- Handout ECOSYSTEMDocument3 pagesHandout ECOSYSTEMHubert BernardNo ratings yet
- 13.3 Energy in EcosystemsDocument2 pages13.3 Energy in EcosystemsOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PDFDocument32 pagesEcosystem PDFYuvashreeNo ratings yet
- Study of Ecosystems: Is The Study of Interactions Among Organisms Group of Organisms With The EnvironmentDocument44 pagesStudy of Ecosystems: Is The Study of Interactions Among Organisms Group of Organisms With The Environmentleela777No ratings yet
- Exploring Ecosystems A Journey Into Natures MarvelsDocument10 pagesExploring Ecosystems A Journey Into Natures Marvelstejaswaniverma289No ratings yet
- Ecosystems IntroDocument7 pagesEcosystems IntroNidhi PNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Its Components: February 2008Document7 pagesEcosystem and Its Components: February 2008aufaaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EcosystemsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EcosystemsKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Ge 2021 16 Marks Q@aDocument60 pagesGe 2021 16 Marks Q@aSasi RekhaNo ratings yet
- Environment - Sunya Prelims Notes 2024 - 240208 - 180522Document221 pagesEnvironment - Sunya Prelims Notes 2024 - 240208 - 180522rameshpradhansaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Energy & Environmental Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument24 pagesUnit 2 - Energy & Environmental Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inHarshal BordiaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem: Unit 2Document36 pagesEcosystem: Unit 2Dominador MasiragNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM PPT Final PGDocument56 pagesECOSYSTEM PPT Final PGShovana DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1Vim EnobioNo ratings yet
- I. Preparation: Lesson 2 Concept of Ecosystem Intended Learning OutcomeDocument17 pagesI. Preparation: Lesson 2 Concept of Ecosystem Intended Learning OutcomeLeslie ObisoNo ratings yet
- Our Environment: Chapter - 15Document10 pagesOur Environment: Chapter - 15IshvaryaNo ratings yet
- GE 302 - Industry and The EnvironmentDocument18 pagesGE 302 - Industry and The EnvironmenthassanNo ratings yet
- Group II: - Ecosystem - Ecological ChainDocument33 pagesGroup II: - Ecosystem - Ecological ChainSariah MirandaNo ratings yet
- Evs NotesDocument36 pagesEvs NotesPUSHPA RAAJNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDocument7 pagesEcosystem and Its Componentsনিঃসঙ্গ পথিকNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and BiodiversityDocument25 pagesEcosystems and BiodiversityRahul67% (3)
- Environment and DevelopmentDocument122 pagesEnvironment and DevelopmentSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem NotesDocument11 pagesEcosystem Notesluciferx187No ratings yet
- Ecosystem Prac1Document2 pagesEcosystem Prac1athilasyakura86No ratings yet
- Ecosystem (Part-I) : Mr. Tarun ChauhanDocument17 pagesEcosystem (Part-I) : Mr. Tarun ChauhanNEHA BANSALNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Notes PDFDocument17 pagesEcosystem Notes PDFNEHA BANSALNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document11 pagesUnit 2bádshãh raiNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem New 2017Document20 pagesEcosystem New 2017raniNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Introduction PDFDocument84 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Introduction PDFChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Evs Unit - 3Document20 pagesLecture Notes - Evs Unit - 3Nambi RajanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Ecosystems: Environmental Science Notes (Yogesh R. Kadam M.Sc. Environmental Science, SPPU, Pune.)Document26 pagesUnit 2: Ecosystems: Environmental Science Notes (Yogesh R. Kadam M.Sc. Environmental Science, SPPU, Pune.)ankit kaleNo ratings yet
- People and The Earths Ecosystem CoverageDocument49 pagesPeople and The Earths Ecosystem CoverageChristen Honely DadangNo ratings yet
- 3 EcosystemDocument21 pages3 EcosystemKishore KNo ratings yet
- Exploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandExploring Ecosystems with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Literary Terms Review SheetDocument2 pagesLiterary Terms Review SheetMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Cheeseburger ChemistryDocument3 pagesCheeseburger ChemistryMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- GO For notesTHE ANATOMY OF A REVOLUTIONDocument1 pageGO For notesTHE ANATOMY OF A REVOLUTIONMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Choiceboard Feb22Document3 pagesChoiceboard Feb22Melodee PetersNo ratings yet
- "Charles" Literature Groups WorksheetDocument2 pages"Charles" Literature Groups WorksheetMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Note-Making RubricDocument1 pageNote-Making RubricMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- VoiceThread RubricDocument2 pagesVoiceThread RubricMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Geometry Study GuideDocument6 pagesGeometry Study GuideMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- STATION 1A: Science STATION 1B: Science STATION 2: Social StudiesDocument3 pagesSTATION 1A: Science STATION 1B: Science STATION 2: Social StudiesMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of BileDocument2 pagesBehaviour of BileMelodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Coming Up With A Research Question 2012Document1 pageComing Up With A Research Question 2012Melodee PetersNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Flow ChartDocument2 pagesDigestive System Flow ChartMelodee Peters79% (24)