Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 1 Ed
Assignment 1 Ed
Uploaded by
Mohamad HasyimiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 1 Ed
Assignment 1 Ed
Uploaded by
Mohamad HasyimiCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1.0: KINEMATIC OF PARTICLES 1.
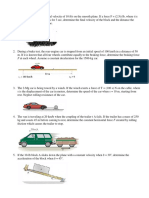
A train which is travelling at 130 km/h applies its brakes as it reaches point A and slows down with a constant deceleration. Its decreased velocity is observed to be 96 km/h as it passes a point 0.8 km beyond A. A car moving at 80 km/h passes point B at the same instant that the train reaches point A. In an unwise effort to beat the train to the crossing, the driver steps on the gas. Calculate the constant acceleration that the car must have in order to beat the train to the crossing by 4 seconds and find the velocity of the car as it reaches the crossing.
2. The muzzle velocity of a long-range rifleat A is u = 400 m/s. Determine the two angles of elevation which will permit the projectile to hit the mountain target B. Ans: 1 = 26.1o , 2 = 80.6o
3. The pin P is constrained to move in the slotted guides which move at right angles to one another. At the instant represented, A has a velocity to the right of 0.2 m/s which is decreasing at the rate of 0.75 m/s each second. At the same time, B is moving down with a velocity of 0.15 m/s which is decreasing at the rate of 0.5 m/s each second. For this instant determine the radius of curvature of the path followed by P. Is it possible to determine also the time rate of change of ? Ans: = 1.25 m
4. The slider P can be moved inward by means of the string S as the bar OA rotates about the pivot O. The angular position of the bar is given by = 0.4 + 0.12t + 0.06t3, where is in radians and t is in seconds. The position of the slider is given by r = 0.8 0.1t 0.05t2. where r is in meters and t is in seconds. Determine and sketch the velocity and acceleration of the slider at time t = 2 s. Find the angles and which v and a make with the positive x-axis. Ans: = 195.9o , = -86.4o
5. Car A negotiates a curve of 60 m radius at a constant speed of 50 km/h. When A passes the position shown, car B is 30 m from the intersection and is accelerating south toward the intersection at the rate of 1.5 m/s2. Determine the acceleration which A appears to have when observed by an occupant of B at this instant. Ans: A/B = 4.58 m/s2, = 20.6o west of north
CHAPTER 2.0: KINETIC OF PARTICLES 1. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the 20 kg block A and the 100 kg cart B are both essentially the same value of 0.50, determine the acceleration of each part for (a) P = 60 N and (b) P = 40 N. Ans: (a) A = 1.095 m/s2 , B = 0.981 m/s2 (b) A = B = 0.667 m/s2
2. Beginning from rest when = 20o, a 35 kg child slides with negligible friction down the sliding board which is in the shape of a 2.5 m circular arc. Determine the tangential acceleration and speed of the child, and the normal force exerted on her (a) when = 30o and (b) when = 90o. Ans: (a) t = 8.50 m/s2 , v = 2.78 m/s, N = 280 N (b) t = 0, v = 5.68 m/s, N = 795 N
3. The 0.8 kg collar slides freely on the fixed circular rod. Calculate the velocity v of the collar as it hits the stop at B if it is elevated fro rest at A by the action of the constant 40 N force in the cord. The cord is guided by he small fixed pulleys.
4. In the selection of the ram of a pile driver, it is desired that the ram lose all of its kinetic energy at each blow. Hence, the velocity of the ram is zero immediately after impact. The mass of each pile to be driven is 300 kg, and experience has shown that a coefficient of restitution of 0.3 can be expected. What should be the mass m of the ram? Compute the velocity v of the pile immediately after impact if the ram is dropped from a height of 4 m onto the pile. Also compute the energy loss E due to impact at each blow. Ans: m = 90 kg, v = 2.66 m/s, E = 2470 J
5. During a pregame warmup period, two basketballs collide above the hoop when in the positions shown. Just before impact, ball 1 has a velocity v1 which makes a 300 angle with the horizontal. If the velocity v2 of ball 2 just before impact has the same magnitude as velocity v1, determine the two possible values of the angle , measured from the horizontal, which will cause ball 1 to go directly through the center of the basket. The coefficient of restitution is e = 0.8. Ans: = 82.3o or = -22.3o
You might also like
- Lesson Plan in KinematicsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in KinematicsEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- MD 4Document37 pagesMD 4martex_37No ratings yet
- Ozito Cordless Drill-Driver 14-4V - OZCD144V2BK PDFDocument14 pagesOzito Cordless Drill-Driver 14-4V - OZCD144V2BK PDFtradosevic4091No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument46 pagesHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake Rodriguez0% (1)
- Module 6 Exercises Problem No. 3Document2 pagesModule 6 Exercises Problem No. 3Ariel GamboaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 1 ClassifiedDocument235 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 1 Classifiedlozzzzz79% (58)
- M&M Catapult ProjectDocument5 pagesM&M Catapult ProjectJessica BrtvaNo ratings yet
- MD Board - Exam - 2022Document21 pagesMD Board - Exam - 2022Niño Gerard JabagatNo ratings yet
- ME198D Design ElemetsDocument2 pagesME198D Design ElemetsChloe OlazoNo ratings yet
- 1 Chapter 1 StrenghtDocument37 pages1 Chapter 1 Strenghttest 2No ratings yet
- Section 16Document97 pagesSection 16Carolina FerrerNo ratings yet
- Mikee EncodedDocument2 pagesMikee EncodedjaysonNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONDocument11 pagesSOLUTIONKim Howard CastilloNo ratings yet
- Hea RansferDocument40 pagesHea RansferHikki KunNo ratings yet
- ME463 - Lab Exercise 1: Design of Flat BeltDocument4 pagesME463 - Lab Exercise 1: Design of Flat BeltJoshua OliverNo ratings yet
- Sample ProblemsDocument8 pagesSample ProblemsKenn Earl Bringino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Gecolea, ME143-2 Sample QuestionsDocument25 pagesGecolea, ME143-2 Sample QuestionsJazztine Andrei GecoleaNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Thermo MekfluDocument31 pagesPrinsip Thermo MekfluGhany RadifanNo ratings yet
- Chap 08 Soln PDFDocument26 pagesChap 08 Soln PDFsoma sundaramNo ratings yet
- Basic ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageBasic ThermodynamicsJim Albert De Asis100% (1)
- Exam Set 09Document1 pageExam Set 09allovidNo ratings yet
- Section 16 PDFDocument97 pagesSection 16 PDFherrerafaridNo ratings yet
- StressDocument13 pagesStressLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- 1 FansDocument20 pages1 FansEasy WriteNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument70 pagesCombinepdfniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document14 pagesChapter 02stephen jamesNo ratings yet
- Anto ME463 Plate No. 3Document18 pagesAnto ME463 Plate No. 3Eman Lampago AntoNo ratings yet
- Coaching Machine DesgnDocument4 pagesCoaching Machine DesgnJerome Isaac KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFDocument118 pagesChapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFsindyNo ratings yet
- Plate No RaDocument5 pagesPlate No RaEdelleNo ratings yet
- Question Number 1Document82 pagesQuestion Number 1Ryan Llona FernandezNo ratings yet
- Homework No.13: Aaron Enrique M. Magsino ME-5301Document5 pagesHomework No.13: Aaron Enrique M. Magsino ME-5301Adrian Kim MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Mecorrel3 - Quiz3Document3 pagesMecorrel3 - Quiz3John Paul EspañoNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTsolved6 9Document13 pagesASSIGNMENTsolved6 9Samyabrata ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Exercises Problem No. 4Document3 pagesModule 6 Exercises Problem No. 4Ariel GamboaNo ratings yet
- A. B. 0.99 M /KG 0.79 M /KG 0.89 M /KG 0.69m /KGDocument143 pagesA. B. 0.99 M /KG 0.79 M /KG 0.89 M /KG 0.69m /KGRyan Togonon100% (1)
- Machine Elements Quiz 1Document17 pagesMachine Elements Quiz 1Quen CuestaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document5 pagesChapter 04stephen jamesNo ratings yet
- Theory of MecanicalDocument31 pagesTheory of MecanicalHhH MmmNo ratings yet
- Nit Mtech Course 1.1Document61 pagesNit Mtech Course 1.1AbhishekVermaNo ratings yet
- Machine Design/Shop Practice Trivia: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMachine Design/Shop Practice Trivia: Multiple Choice QuestionsPaul EdwardNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Heat TransferDocument12 pagesReviewer in Heat TransferKristian Allen B. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics - QuestionsHermione GrangerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document11 pagesChapter 3bernabasNo ratings yet
- Fans & Blowers PDFDocument9 pagesFans & Blowers PDFnaveedsidhu100% (1)
- CO Assign#2 BSEE-2ADocument3 pagesCO Assign#2 BSEE-2AEisen JaylordNo ratings yet
- 7 - FANS (Formulas & Solution To Problems) - by ENGR ROBLESDocument25 pages7 - FANS (Formulas & Solution To Problems) - by ENGR ROBLESandradajc7No ratings yet
- Conduction Heat Transfer Part 1Document8 pagesConduction Heat Transfer Part 1Ali Aimran0% (1)
- Pipe 4Document19 pagesPipe 4Mark AllenNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRA Worded ProblemDocument2 pagesALGEBRA Worded ProblemanthonyNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Thermodynamics Part 7 ECE Board ExamDocument13 pagesMCQ in Thermodynamics Part 7 ECE Board ExamAlexter de GalaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Cascade Refrigeration SystemsDocument6 pagesTopic 7 Cascade Refrigeration SystemsJanelle D. Puti-anNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1Von A. Damirez0% (1)
- Ideal Gas Law Simulation: PV NRTDocument3 pagesIdeal Gas Law Simulation: PV NRTElla GreenNo ratings yet
- Power and Industrial Plant Engineering: INTRUCTION: Solve The Following Very Important ProblemsDocument2 pagesPower and Industrial Plant Engineering: INTRUCTION: Solve The Following Very Important ProblemsAnonymous zF4syKOrJNo ratings yet
- ARAÑA MECC486 P2 M4AssignmentDocument15 pagesARAÑA MECC486 P2 M4AssignmentKent LabajoNo ratings yet
- RankineDocument12 pagesRankineMeej AustriaNo ratings yet
- Gas Compressor ProblemsDocument2 pagesGas Compressor Problemskim dianon0% (1)
- Common Mechanical Engineering Conversion FactorsDocument1 pageCommon Mechanical Engineering Conversion FactorspronckNo ratings yet
- Problem Set For DynamicsDocument4 pagesProblem Set For DynamicsSayan KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - WorksheetDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - WorksheetHenokNo ratings yet
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarDocument12 pagesF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarAndre BocoNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion ProblemsDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion Problemsomar_oj_4No ratings yet
- Mech-Iv-Kinematics of Machines (10me44) - Notes PDFDocument196 pagesMech-Iv-Kinematics of Machines (10me44) - Notes PDFgopalNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument19 pagesMATHEMATICSsmpopadeNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document14 pagesGrade 8Dandan Ostria100% (1)
- No Found Discrepancies/Good Condition: C08 CHK PK-CLQ PK-CLQDocument7 pagesNo Found Discrepancies/Good Condition: C08 CHK PK-CLQ PK-CLQMario EdiNo ratings yet
- Cape Physics U1 P1 2013Document11 pagesCape Physics U1 P1 2013C.No ratings yet
- 5.torsional Stiffness of The Shaft and Mass Momentof Inertia of Disc Assembly by AccelerationDocument5 pages5.torsional Stiffness of The Shaft and Mass Momentof Inertia of Disc Assembly by AccelerationMuhammed Shameem N EdavannapparaNo ratings yet
- Week01 - Course Module - Scalar and Vector QuantityDocument5 pagesWeek01 - Course Module - Scalar and Vector QuantityJuan Carlo Tan BisdaNo ratings yet
- Limpopo Physical Science Grade 10 June 2022 QP and MemoDocument19 pagesLimpopo Physical Science Grade 10 June 2022 QP and MemoThando MahlanguNo ratings yet
- GP1 Long QuizDocument2 pagesGP1 Long QuizFrancis JaenNo ratings yet
- PhySci GR 12 Physics Revision Book ENG 2024Document133 pagesPhySci GR 12 Physics Revision Book ENG 2024mkhongelomkansi369No ratings yet
- 1.11 Momentum Note ReadingDocument2 pages1.11 Momentum Note ReadingT. Danielle DockeryNo ratings yet
- Lewain Signature Assignment 1210Document4 pagesLewain Signature Assignment 1210api-558954405No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics SoloutionDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Physics Soloution8310032914No ratings yet
- WAEC Syllabus For PhysicsDocument32 pagesWAEC Syllabus For Physicstrustphli73No ratings yet
- Physics: (Syllabus 6091)Document33 pagesPhysics: (Syllabus 6091)The ExistingNo ratings yet
- KOM Lect13Document24 pagesKOM Lect13Pranav C PNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Rotational KinematicsDocument1 pageAssignment - Rotational Kinematicsarqam SaadNo ratings yet
- 8th (0) Physics 9 Weeks DivisionDocument3 pages8th (0) Physics 9 Weeks Divisionusama nisarNo ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedDocument20 pagesApplied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedYoukesh GautamNo ratings yet
- Part 01 Theory (389 - 403)Document16 pagesPart 01 Theory (389 - 403)Vansh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Draw Inlet Vector DiagramDocument8 pagesDraw Inlet Vector DiagramJack HaamboteNo ratings yet
- Vectors MCQDocument1 pageVectors MCQashrafrazi100% (7)
- Ques - Holiday Homework IX FINALDocument5 pagesQues - Holiday Homework IX FINALPurvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- II B.tech I Sem Question Bank For r18Document30 pagesII B.tech I Sem Question Bank For r18saiharish634No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - KinematicsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - KinematicsĐức Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument11 pagesNewton's Second Law of MotionKerwin MarasiganNo ratings yet