Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Uploaded by
Venu KoonamneniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ServerRaid M5015 User GuideDocument106 pagesServerRaid M5015 User Guidehowy_renshaw35No ratings yet
- Presentation 17 - Buses: PC FundamentalsDocument32 pagesPresentation 17 - Buses: PC Fundamentalsindranijagrati100% (1)
- Parts of MotherboardDocument14 pagesParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Micro Project Report On MotherboardDocument15 pagesMicro Project Report On Motherboardabu100% (14)
- How PCI Works: Hop On The Bus, GusDocument7 pagesHow PCI Works: Hop On The Bus, Gusapi-19737301No ratings yet
- Pci BusDocument17 pagesPci BusA TNo ratings yet
- Third Part CamDocument8 pagesThird Part Camrh_rathodNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PCI AGP and PCI Express Graphics CardsDocument2 pagesDifference Between PCI AGP and PCI Express Graphics CardsRakib AhsanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Component Interconnect (Pci) BusDocument19 pagesPeripheral Component Interconnect (Pci) BusPrince Thomas100% (1)
- Diagram of Bus ControllerDocument7 pagesDiagram of Bus ControllerGhanshyam KashyapNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: Types of Buses in Computer ArchitectureDocument19 pagesUnit-5: Types of Buses in Computer ArchitectureEphrage GurureNo ratings yet
- PC InterfaceDocument50 pagesPC InterfacechiropriyacNo ratings yet
- CW Final Worksheet (Chandigarh University)Document2 pagesCW Final Worksheet (Chandigarh University)Satyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The I/O Buses: Functions of Buses in ComputersDocument12 pagesIntroduction To The I/O Buses: Functions of Buses in ComputersrubinderNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 1Document18 pagesChapter No 1Shreyash JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven Bus and Cards Bus: Processor-Memory Bus (May Be Proprietary)Document10 pagesChapter Seven Bus and Cards Bus: Processor-Memory Bus (May Be Proprietary)minichelNo ratings yet
- Pci eDocument19 pagesPci eapi-3760834No ratings yet
- Chs Assignment 1Document7 pagesChs Assignment 1Kiruba KaranNo ratings yet
- Types of Local Buses: Vesa Bus Pci Bus PCI Express AGPDocument21 pagesTypes of Local Buses: Vesa Bus Pci Bus PCI Express AGPmanibrarNo ratings yet
- 2.sys Bus ArchDocument14 pages2.sys Bus ArchChar MondeNo ratings yet
- Pci Bus Overview: A New StandardDocument4 pagesPci Bus Overview: A New StandardShanayaNo ratings yet
- Pci ExpressDocument43 pagesPci Expresseugen lupuNo ratings yet
- Expansion SlotsDocument9 pagesExpansion SlotsVilmaMiguelHernandezNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit-3Document11 pagesCoa Unit-3singhshiva8082No ratings yet
- Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)Document28 pagesPeripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)rohitsingh2909No ratings yet
- Parallel Bus Device Protocols: Parallel Communication Network Using ISA/EISA PCI/PCI-X Advanced BusesDocument14 pagesParallel Bus Device Protocols: Parallel Communication Network Using ISA/EISA PCI/PCI-X Advanced BusesDarren Neh100% (1)
- Name: Mohamed Hardi Lafou: A Brief DescriptionDocument4 pagesName: Mohamed Hardi Lafou: A Brief DescriptionmohaNo ratings yet
- Pciexpress OverviewDocument46 pagesPciexpress Overvieweugen lupuNo ratings yet
- The PCI Local BusDocument56 pagesThe PCI Local Busatorresh090675No ratings yet
- Serial and Parallel CommunicationDocument21 pagesSerial and Parallel CommunicationHari KrishNo ratings yet
- Computer Buses and InterfacesDocument29 pagesComputer Buses and InterfacesNolduatiga TiNo ratings yet
- Barramento PCI: PDF Generated At: Mon, 29 Apr 2013 11:40:35 UTCDocument50 pagesBarramento PCI: PDF Generated At: Mon, 29 Apr 2013 11:40:35 UTCKay SmithNo ratings yet
- Types of BusesDocument16 pagesTypes of BusesIan Conan JuanicoNo ratings yet
- PCIeDocument5 pagesPCIevijithacvijayanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Input/output Organization Introduction To Bus ArchitectureDocument14 pagesUnit - 6 Input/output Organization Introduction To Bus ArchitectureAyushi SinghNo ratings yet
- SLOTDocument1 pageSLOTmohaNo ratings yet
- Expansion SlotsDocument6 pagesExpansion SlotsMahesh Abnave0% (1)
- Introduction To The I/O Buses Technical and Historical Background For The I/O BusesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To The I/O Buses Technical and Historical Background For The I/O BusesshankyguptaNo ratings yet
- Group 29Document5 pagesGroup 29emanueldakho3No ratings yet
- Lectures 5-8 Types of BusesDocument17 pagesLectures 5-8 Types of BusesaaaaNo ratings yet
- 4 PCI Bus and Memory SystemDocument12 pages4 PCI Bus and Memory Systemrkeditors47No ratings yet
- Form Factor: AT ATX Micro Atx LPX NLX BTXDocument54 pagesForm Factor: AT ATX Micro Atx LPX NLX BTXrh_rathodNo ratings yet
- Standard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"Document10 pagesStandard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"JochumNo ratings yet
- Chapter ModifedDocument107 pagesChapter ModifedgnanaNo ratings yet
- E7520 E7320 Chipsets BriefDocument4 pagesE7520 E7320 Chipsets BriefJhon ErickNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument4 pagesMotherboardMary Ann BalauitanNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Wilmar Jennie V. Motea, MitDocument83 pagesMotherboard: Wilmar Jennie V. Motea, MitGretchen Sarmiento Cabarles AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Its Component: Visit For More Learning ResourcesDocument35 pagesMotherboard and Its Component: Visit For More Learning ResourcesRushikesh TanpureNo ratings yet
- Computer Buses and InterfacesDocument34 pagesComputer Buses and InterfacesSholeh FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- PCI Bus-by-Lauren-Greenfield-Matt-Pozun-Lindsay-Stenger-Olivia-Ting-2004-SpringDocument17 pagesPCI Bus-by-Lauren-Greenfield-Matt-Pozun-Lindsay-Stenger-Olivia-Ting-2004-SpringMahendra MunirathnamNo ratings yet
- Intel Iop333 I/O Processor With Intel Xscale MicroarchitectureDocument4 pagesIntel Iop333 I/O Processor With Intel Xscale Microarchitecturettanand87No ratings yet
- Computer Bus Architecture: Von Neumann Computer ModelDocument19 pagesComputer Bus Architecture: Von Neumann Computer ModelJoshua AyoolaNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument15 pagesComputer ArchitectureAbdul KapiteniNo ratings yet
- How PCI Express WorksDocument11 pagesHow PCI Express WorksNick.mkNo ratings yet
- A+ Certification Core Exam Memory TutorialDocument4 pagesA+ Certification Core Exam Memory Tutorialthesingh_0No ratings yet
- Bus StandardsDocument2 pagesBus Standardsweilong100% (1)
- Pci Local Bus: Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)Document41 pagesPci Local Bus: Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)Nizamuddin Chapatle100% (1)
- Expansion Slots and CardsDocument29 pagesExpansion Slots and CardsJAYME JOSWANo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Bus and CardsDocument7 pagesChapter Seven: Bus and CardsYd ManNo ratings yet
- Bus and Memory TransfersDocument11 pagesBus and Memory TransfersSam-eer Neo-paneyNo ratings yet
- Scale Up Network Availability and Performance With Multi-Port Gigabit AdaptersDocument12 pagesScale Up Network Availability and Performance With Multi-Port Gigabit Adaptersnapoleon_snklNo ratings yet
- Nintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8From EverandNintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8No ratings yet
- Professional Experience:: and Publish Them in Dash Board Using AnswersDocument4 pagesProfessional Experience:: and Publish Them in Dash Board Using AnswersVenu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- AuditDocument3 pagesAuditVenu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- FibreChnnel Apple COmputersDocument10 pagesFibreChnnel Apple COmputersVenu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- AIX 6 System Administration I Implementation Student GuideDocument904 pagesAIX 6 System Administration I Implementation Student Guidetdt8450% (2)
- AN30Document3 pagesAN30Venu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- MB0039 Fall Drive Solved Assignment 2011Document2 pagesMB0039 Fall Drive Solved Assignment 2011Sirish KhNo ratings yet
- Portwell TechnologiesDocument172 pagesPortwell TechnologiesCampiersonNo ratings yet
- Idt Ca91l750 Man 20130619Document337 pagesIdt Ca91l750 Man 20130619karnamsidharNo ratings yet
- 7642v1.0 (G52 76421X1) (890GXM G65)Document110 pages7642v1.0 (G52 76421X1) (890GXM G65)Nicolas BertoaNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Manual: 25 January 2010 Revision N. 3Document32 pagesTechnical Information Manual: 25 January 2010 Revision N. 3elrhysoNo ratings yet
- d1691 PDFDocument34 pagesd1691 PDFAlex CruceruNo ratings yet
- Biostar Mainboard Manual I86GVM4Document67 pagesBiostar Mainboard Manual I86GVM4Victoria KiddNo ratings yet
- Mainboard Foxconn Model-865a01Document44 pagesMainboard Foxconn Model-865a01Nicu LiviuNo ratings yet
- Compal La-5892p r1.0 SchematicsDocument50 pagesCompal La-5892p r1.0 Schematicsadysan73No ratings yet
- ASUS A7v266-C - 100Document100 pagesASUS A7v266-C - 100Radomir ProticNo ratings yet
- 8088Document34 pages8088chandrasekarNo ratings yet
- 1.1-4 Assemble Computer Hardware PDFDocument51 pages1.1-4 Assemble Computer Hardware PDFAyra Zerimar SomarNo ratings yet
- Mainboard 845eiclientDocument35 pagesMainboard 845eiclientHo Thanh Binh100% (1)
- DeckLink ManualDocument75 pagesDeckLink ManualNinoNo ratings yet
- P47G (1.0) - User's GuideDocument41 pagesP47G (1.0) - User's GuideDavid DouglasNo ratings yet
- Chipset Intel 855GMDocument20 pagesChipset Intel 855GMflaviotrabNo ratings yet
- Intel D915gav D915gag D915gev D915gux Productguide EnglishDocument80 pagesIntel D915gav D915gag D915gev D915gux Productguide EnglishgbmelbobNo ratings yet
- C Language Staff ManualDocument153 pagesC Language Staff ManualSRINU PADIGALANo ratings yet
- Megaraid Sas 9260-8I / Megaraid Sas 9260De-8I: Eight-Port 6Gb/S Pci Express Sata and Sas Raid ControllerDocument2 pagesMegaraid Sas 9260-8I / Megaraid Sas 9260De-8I: Eight-Port 6Gb/S Pci Express Sata and Sas Raid ControllerjohnnytvNo ratings yet
- MSI - Megabook PR300 - MSI MS-1313 - Ver1.1 PDFDocument42 pagesMSI - Megabook PR300 - MSI MS-1313 - Ver1.1 PDFDennyTadashiLisboaDaSilvaKatanoNo ratings yet
- Bug ReportDocument37 pagesBug ReportleandroNo ratings yet
- Meu ComputadorDocument268 pagesMeu ComputadortiagogpiresNo ratings yet
- Sahara 3810 Manual EngDocument92 pagesSahara 3810 Manual Engpat98usbNo ratings yet
- Ig31a-M7 Ip31a-A7 Bios 1116Document39 pagesIg31a-M7 Ip31a-A7 Bios 1116silviu_sealNo ratings yet
- Trademarks: Motherboard User's GuideDocument51 pagesTrademarks: Motherboard User's GuidejuanjoticoNo ratings yet
- HP DGS&DDocument35 pagesHP DGS&DsanbarunNo ratings yet
- System Bus Functions and FeaturesDocument21 pagesSystem Bus Functions and FeaturesJerome Salazar CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Dialogic D/120JCT-LS Media Boards by Sangoma: DatasheetDocument7 pagesDialogic D/120JCT-LS Media Boards by Sangoma: DatasheetLarry FailureNo ratings yet
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Uploaded by
Venu KoonamneniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Uploaded by
Venu KoonamneniCopyright:
Available Formats
Peripheral Component Interconnect
The Peripheral Component Interconnect, also known as PCI, has been licensed by Intel in the 1990s. The bus is used as a communication lane to transmit signals and data from your computer system to peripheral devices attached to the computer system. Compared to the earlier VL-bus and ISA, it has a higher performance capacity and avoids any risk of interference with your CPU.
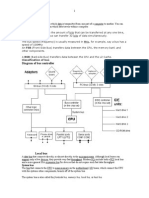
How does it work?
The processor is connected to the other components like the hard drives, the main memory and the PCI slots by the use of a front-side bus. The speed of the front side bus can reach up to 400 Mhz with a system operating at the speed of 800 Mhz. The backside bus usually has a quicker speed than the front-side bus but operates at the same rate as the processor itself. Though it is a detached connection, it ensures the connection between the processor and the Level 2 cache. With time, the level 2 cache was included in the main processor to make them more affordable and easier to use.
Different Bus Types
PCI 32 bits have a bus speed of 33 MHz and operate at 132 MBps PCI 64 bits have a bus speed of 33 MHz and operate at 264 MBps PCI 64 bits have a bus speed of 66 MHz and operate at 512 MBps PCI 64 bits have a bus speed of 66 MHz and operate at 1 GBps.
Advantages of PCI The PCI technology offers a number of advantages compared to the VL-Bus or ISA. 1. You can connect a maximum of five components to the PCI and you can also replace each of them by fixed devices on the motherboard. 2. You an have multiple PCI buses on the same computer 3. The PCI bus will enhance the speed of the transfers from 33MHz to 133 MHz with a transfer rate of 1 gigabyte per second. 4. The PCI can handle devices using a maximum of 5 volts and the pins used can transfer more that one signal through one pin.
You might also like
- ServerRaid M5015 User GuideDocument106 pagesServerRaid M5015 User Guidehowy_renshaw35No ratings yet
- Presentation 17 - Buses: PC FundamentalsDocument32 pagesPresentation 17 - Buses: PC Fundamentalsindranijagrati100% (1)
- Parts of MotherboardDocument14 pagesParts of MotherboardNoelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Micro Project Report On MotherboardDocument15 pagesMicro Project Report On Motherboardabu100% (14)
- How PCI Works: Hop On The Bus, GusDocument7 pagesHow PCI Works: Hop On The Bus, Gusapi-19737301No ratings yet
- Pci BusDocument17 pagesPci BusA TNo ratings yet
- Third Part CamDocument8 pagesThird Part Camrh_rathodNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PCI AGP and PCI Express Graphics CardsDocument2 pagesDifference Between PCI AGP and PCI Express Graphics CardsRakib AhsanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Component Interconnect (Pci) BusDocument19 pagesPeripheral Component Interconnect (Pci) BusPrince Thomas100% (1)
- Diagram of Bus ControllerDocument7 pagesDiagram of Bus ControllerGhanshyam KashyapNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: Types of Buses in Computer ArchitectureDocument19 pagesUnit-5: Types of Buses in Computer ArchitectureEphrage GurureNo ratings yet
- PC InterfaceDocument50 pagesPC InterfacechiropriyacNo ratings yet
- CW Final Worksheet (Chandigarh University)Document2 pagesCW Final Worksheet (Chandigarh University)Satyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The I/O Buses: Functions of Buses in ComputersDocument12 pagesIntroduction To The I/O Buses: Functions of Buses in ComputersrubinderNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 1Document18 pagesChapter No 1Shreyash JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven Bus and Cards Bus: Processor-Memory Bus (May Be Proprietary)Document10 pagesChapter Seven Bus and Cards Bus: Processor-Memory Bus (May Be Proprietary)minichelNo ratings yet
- Pci eDocument19 pagesPci eapi-3760834No ratings yet
- Chs Assignment 1Document7 pagesChs Assignment 1Kiruba KaranNo ratings yet
- Types of Local Buses: Vesa Bus Pci Bus PCI Express AGPDocument21 pagesTypes of Local Buses: Vesa Bus Pci Bus PCI Express AGPmanibrarNo ratings yet
- 2.sys Bus ArchDocument14 pages2.sys Bus ArchChar MondeNo ratings yet
- Pci Bus Overview: A New StandardDocument4 pagesPci Bus Overview: A New StandardShanayaNo ratings yet
- Pci ExpressDocument43 pagesPci Expresseugen lupuNo ratings yet
- Expansion SlotsDocument9 pagesExpansion SlotsVilmaMiguelHernandezNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit-3Document11 pagesCoa Unit-3singhshiva8082No ratings yet
- Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)Document28 pagesPeripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)rohitsingh2909No ratings yet
- Parallel Bus Device Protocols: Parallel Communication Network Using ISA/EISA PCI/PCI-X Advanced BusesDocument14 pagesParallel Bus Device Protocols: Parallel Communication Network Using ISA/EISA PCI/PCI-X Advanced BusesDarren Neh100% (1)
- Name: Mohamed Hardi Lafou: A Brief DescriptionDocument4 pagesName: Mohamed Hardi Lafou: A Brief DescriptionmohaNo ratings yet
- Pciexpress OverviewDocument46 pagesPciexpress Overvieweugen lupuNo ratings yet
- The PCI Local BusDocument56 pagesThe PCI Local Busatorresh090675No ratings yet
- Serial and Parallel CommunicationDocument21 pagesSerial and Parallel CommunicationHari KrishNo ratings yet
- Computer Buses and InterfacesDocument29 pagesComputer Buses and InterfacesNolduatiga TiNo ratings yet
- Barramento PCI: PDF Generated At: Mon, 29 Apr 2013 11:40:35 UTCDocument50 pagesBarramento PCI: PDF Generated At: Mon, 29 Apr 2013 11:40:35 UTCKay SmithNo ratings yet
- Types of BusesDocument16 pagesTypes of BusesIan Conan JuanicoNo ratings yet
- PCIeDocument5 pagesPCIevijithacvijayanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Input/output Organization Introduction To Bus ArchitectureDocument14 pagesUnit - 6 Input/output Organization Introduction To Bus ArchitectureAyushi SinghNo ratings yet
- SLOTDocument1 pageSLOTmohaNo ratings yet
- Expansion SlotsDocument6 pagesExpansion SlotsMahesh Abnave0% (1)
- Introduction To The I/O Buses Technical and Historical Background For The I/O BusesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To The I/O Buses Technical and Historical Background For The I/O BusesshankyguptaNo ratings yet
- Group 29Document5 pagesGroup 29emanueldakho3No ratings yet
- Lectures 5-8 Types of BusesDocument17 pagesLectures 5-8 Types of BusesaaaaNo ratings yet
- 4 PCI Bus and Memory SystemDocument12 pages4 PCI Bus and Memory Systemrkeditors47No ratings yet
- Form Factor: AT ATX Micro Atx LPX NLX BTXDocument54 pagesForm Factor: AT ATX Micro Atx LPX NLX BTXrh_rathodNo ratings yet
- Standard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"Document10 pagesStandard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"JochumNo ratings yet
- Chapter ModifedDocument107 pagesChapter ModifedgnanaNo ratings yet
- E7520 E7320 Chipsets BriefDocument4 pagesE7520 E7320 Chipsets BriefJhon ErickNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument4 pagesMotherboardMary Ann BalauitanNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Wilmar Jennie V. Motea, MitDocument83 pagesMotherboard: Wilmar Jennie V. Motea, MitGretchen Sarmiento Cabarles AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Its Component: Visit For More Learning ResourcesDocument35 pagesMotherboard and Its Component: Visit For More Learning ResourcesRushikesh TanpureNo ratings yet
- Computer Buses and InterfacesDocument34 pagesComputer Buses and InterfacesSholeh FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- PCI Bus-by-Lauren-Greenfield-Matt-Pozun-Lindsay-Stenger-Olivia-Ting-2004-SpringDocument17 pagesPCI Bus-by-Lauren-Greenfield-Matt-Pozun-Lindsay-Stenger-Olivia-Ting-2004-SpringMahendra MunirathnamNo ratings yet
- Intel Iop333 I/O Processor With Intel Xscale MicroarchitectureDocument4 pagesIntel Iop333 I/O Processor With Intel Xscale Microarchitecturettanand87No ratings yet
- Computer Bus Architecture: Von Neumann Computer ModelDocument19 pagesComputer Bus Architecture: Von Neumann Computer ModelJoshua AyoolaNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument15 pagesComputer ArchitectureAbdul KapiteniNo ratings yet
- How PCI Express WorksDocument11 pagesHow PCI Express WorksNick.mkNo ratings yet
- A+ Certification Core Exam Memory TutorialDocument4 pagesA+ Certification Core Exam Memory Tutorialthesingh_0No ratings yet
- Bus StandardsDocument2 pagesBus Standardsweilong100% (1)
- Pci Local Bus: Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)Document41 pagesPci Local Bus: Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)Nizamuddin Chapatle100% (1)
- Expansion Slots and CardsDocument29 pagesExpansion Slots and CardsJAYME JOSWANo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Bus and CardsDocument7 pagesChapter Seven: Bus and CardsYd ManNo ratings yet
- Bus and Memory TransfersDocument11 pagesBus and Memory TransfersSam-eer Neo-paneyNo ratings yet
- Scale Up Network Availability and Performance With Multi-Port Gigabit AdaptersDocument12 pagesScale Up Network Availability and Performance With Multi-Port Gigabit Adaptersnapoleon_snklNo ratings yet
- Nintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8From EverandNintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8No ratings yet
- Professional Experience:: and Publish Them in Dash Board Using AnswersDocument4 pagesProfessional Experience:: and Publish Them in Dash Board Using AnswersVenu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- AuditDocument3 pagesAuditVenu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- FibreChnnel Apple COmputersDocument10 pagesFibreChnnel Apple COmputersVenu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- AIX 6 System Administration I Implementation Student GuideDocument904 pagesAIX 6 System Administration I Implementation Student Guidetdt8450% (2)
- AN30Document3 pagesAN30Venu KoonamneniNo ratings yet
- MB0039 Fall Drive Solved Assignment 2011Document2 pagesMB0039 Fall Drive Solved Assignment 2011Sirish KhNo ratings yet
- Portwell TechnologiesDocument172 pagesPortwell TechnologiesCampiersonNo ratings yet
- Idt Ca91l750 Man 20130619Document337 pagesIdt Ca91l750 Man 20130619karnamsidharNo ratings yet
- 7642v1.0 (G52 76421X1) (890GXM G65)Document110 pages7642v1.0 (G52 76421X1) (890GXM G65)Nicolas BertoaNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Manual: 25 January 2010 Revision N. 3Document32 pagesTechnical Information Manual: 25 January 2010 Revision N. 3elrhysoNo ratings yet
- d1691 PDFDocument34 pagesd1691 PDFAlex CruceruNo ratings yet
- Biostar Mainboard Manual I86GVM4Document67 pagesBiostar Mainboard Manual I86GVM4Victoria KiddNo ratings yet
- Mainboard Foxconn Model-865a01Document44 pagesMainboard Foxconn Model-865a01Nicu LiviuNo ratings yet
- Compal La-5892p r1.0 SchematicsDocument50 pagesCompal La-5892p r1.0 Schematicsadysan73No ratings yet
- ASUS A7v266-C - 100Document100 pagesASUS A7v266-C - 100Radomir ProticNo ratings yet
- 8088Document34 pages8088chandrasekarNo ratings yet
- 1.1-4 Assemble Computer Hardware PDFDocument51 pages1.1-4 Assemble Computer Hardware PDFAyra Zerimar SomarNo ratings yet
- Mainboard 845eiclientDocument35 pagesMainboard 845eiclientHo Thanh Binh100% (1)
- DeckLink ManualDocument75 pagesDeckLink ManualNinoNo ratings yet
- P47G (1.0) - User's GuideDocument41 pagesP47G (1.0) - User's GuideDavid DouglasNo ratings yet
- Chipset Intel 855GMDocument20 pagesChipset Intel 855GMflaviotrabNo ratings yet
- Intel D915gav D915gag D915gev D915gux Productguide EnglishDocument80 pagesIntel D915gav D915gag D915gev D915gux Productguide EnglishgbmelbobNo ratings yet
- C Language Staff ManualDocument153 pagesC Language Staff ManualSRINU PADIGALANo ratings yet
- Megaraid Sas 9260-8I / Megaraid Sas 9260De-8I: Eight-Port 6Gb/S Pci Express Sata and Sas Raid ControllerDocument2 pagesMegaraid Sas 9260-8I / Megaraid Sas 9260De-8I: Eight-Port 6Gb/S Pci Express Sata and Sas Raid ControllerjohnnytvNo ratings yet
- MSI - Megabook PR300 - MSI MS-1313 - Ver1.1 PDFDocument42 pagesMSI - Megabook PR300 - MSI MS-1313 - Ver1.1 PDFDennyTadashiLisboaDaSilvaKatanoNo ratings yet
- Bug ReportDocument37 pagesBug ReportleandroNo ratings yet
- Meu ComputadorDocument268 pagesMeu ComputadortiagogpiresNo ratings yet
- Sahara 3810 Manual EngDocument92 pagesSahara 3810 Manual Engpat98usbNo ratings yet
- Ig31a-M7 Ip31a-A7 Bios 1116Document39 pagesIg31a-M7 Ip31a-A7 Bios 1116silviu_sealNo ratings yet
- Trademarks: Motherboard User's GuideDocument51 pagesTrademarks: Motherboard User's GuidejuanjoticoNo ratings yet
- HP DGS&DDocument35 pagesHP DGS&DsanbarunNo ratings yet
- System Bus Functions and FeaturesDocument21 pagesSystem Bus Functions and FeaturesJerome Salazar CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Dialogic D/120JCT-LS Media Boards by Sangoma: DatasheetDocument7 pagesDialogic D/120JCT-LS Media Boards by Sangoma: DatasheetLarry FailureNo ratings yet