Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Le Chatelier's Principle:: Chemistry Study Guide
Le Chatelier's Principle:: Chemistry Study Guide
Uploaded by
Brielle AndersonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Le Chatelier's Principle:: Chemistry Study Guide
Le Chatelier's Principle:: Chemistry Study Guide
Uploaded by
Brielle AndersonCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Study Guide
May 8, 2013
Brielle Anderson Important Factors: Increas
e Temper ature
Chemical Equilibrium
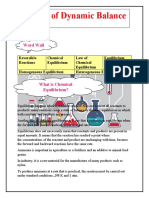
-The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
Le Chateliers Principle:
Temperature Pressure and Concentration affect equilibrium.
favors endothermic reaction. reactants decrease, products increase.
Decreas Favors exothermic e reaction. reactants Temper decrease, products ature
increase.
Press ure
Increase pressureshift toward side with less moles Decrease PressureShift toward side with more moles
Increa se Conce ntrati on
Decrea se Conce ntratio n
other reactant decreases. reaction shift toward opposite side. products increase other reactant increases. reaction shift toward same side. products decrease.
+
Reaction Rate
Measures the increase in product or decrease in the reactant. -Rate= k[A]x[B]y
Ideal Gas Law
Combined Gas Law:
-Boyles and Charles Law The Ideal Gas Law relates combined pressure, temperature, and P1V1=P2V2 volume of an ideal or T1 T2 perfect gas. The Ideal Gas Law can be expressed with the Individual Gas Constant: R= 0.0821 p V = m R atm/mole*k T
Avogadros Law (gasses):
-Quantity- Volume direct relationship
Lorem Ipsum
Issue | Date
Daltons Law of Partial Pressure: -The total pressure of a mixture of gasses is
qual to the sum of the partial pressure of each individual gas. -P
Total
=P
gas 1
+P
gas 2
+P
gas 3
..
Acids
-Electrolyte -Sour Arrhenius Acid: releases H+ ions in an aqueous solution. Bronsted- Lowry acid: Proton (H+) donor Lewis Acid: Electron-pair acceptor -Electrolyte -Bitter
Bases
Arrhenius Base: releases OH- in an aqueous solution.
Bronsted- Lowry base: Proton (H+) acceptor
Lewis Base: Electron-pair donor
Acid- Base Titration:
-Used to determine the concentration of an acid or a base. -When the indicator changes colorthis indicated neutralization has occurred and the end point of titration.
MAVA=MBVB
Dolor Sit Amet 2
Lorem Ipsum
Issue | Date
pH= -log[H3O+] or [H+] pOH= -log[OH-] pH + pOH = 14
pH and pOH
Strong acids and weak bases have high ionization levels
Amphorteric: can behave both as an acid and a base Dolor Sit Amet 3
You might also like
- Che 91166 4pagesDocument0 pagesChe 91166 4pagesapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Equilibrium in Physical ProcessesDocument6 pagesEquilibrium Equilibrium in Physical ProcessesSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical EquilibriumDocument35 pagesChapter 7 Chemical EquilibriumgajenraoNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument7 pagesEquilibrium NotesYASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- 30 Chemical EquilibriumDocument9 pages30 Chemical EquilibriumAlejandro RMNo ratings yet
- Le ChatelierDocument11 pagesLe ChatelierWendy TangNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch07 Equilibrium KvsDocument5 pages11 Chemistry Notes Ch07 Equilibrium Kvsthakursingh143No ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument9 pagesDocument PDFFF ROCKEYNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Chm012Document17 pagesChemical Equilibrium Chm012Elaiza Angelene NacarioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Cheat Sheetprincessrgl_112003705467% (3)
- Equillibrium RevisionDocument6 pagesEquillibrium RevisionMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Final Exam ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Final Exam ReviewerZyriel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- I. TITLE OF EXPERIMENT: The Equilibrium Constant II. Experiment Date: March, 28 Iii. The PurposeDocument24 pagesI. TITLE OF EXPERIMENT: The Equilibrium Constant II. Experiment Date: March, 28 Iii. The PurposeLia Yuli KusumaNo ratings yet
- XI Chem Ch7 Equilibrium Chapter Notes NovDocument10 pagesXI Chem Ch7 Equilibrium Chapter Notes NovmailmelakshayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Section 1: Describing Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChapter 8 - Section 1: Describing Chemical ReactionsIsmail MedhatNo ratings yet
- PH, EquilibriumDocument6 pagesPH, Equilibriumaiswaryaraveendran202No ratings yet
- Equilibrium 3Document8 pagesEquilibrium 3francis JASNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Final Exam Study GuideDocument9 pagesChemistry Final Exam Study GuideJosh MorganNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium NotesSaumiaDevadasNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2, 5th ADocument12 pagesAssignment # 2, 5th Auw-19-chm-bs-091No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria NotesDocument7 pagesChemical Equilibria NotesImranMalikNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument3 pagesChemical EquilibriumNhie AiyuNo ratings yet
- Articulo Equilibrioquimico 19661Document4 pagesArticulo Equilibrioquimico 19661dexgigiNo ratings yet
- Chem 111-2Document10 pagesChem 111-2lets.torque.laterNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium .PresentationDocument17 pagesChemical Equilibrium .PresentationtalhawasimNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Le Chatelier Dan KatalisisDocument19 pagesPrinsip Le Chatelier Dan KatalisisLestari zaiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Equilibrium ConceptsDocument21 pagesFundamental Equilibrium Conceptsnxumalopat2No ratings yet
- CH 15 - Chemical Equilibrium Compatibility ModeDocument16 pagesCH 15 - Chemical Equilibrium Compatibility ModeIcha Meisyarani IINo ratings yet
- Definitions Module 5Document10 pagesDefinitions Module 5CHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem Kinetics Auto Saved)Document127 pagesChapter 1 Chem Kinetics Auto Saved)Mohd IzzudinNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes EquilibriumDocument10 pages11 Chemistry Notes Equilibriumgansan105No ratings yet
- Chemistry EquilibriumDocument4 pagesChemistry EquilibriumWiktoria KaczmarzykNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument5 pagesEquilibriumnanaNo ratings yet
- A State of Dynamic Balance - FactsDocument15 pagesA State of Dynamic Balance - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Reviewer - Long TestDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Reviewer - Long TestYuan Lei CastilloNo ratings yet
- 10 Gases 2b PDFDocument10 pages10 Gases 2b PDFchewazableNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument10 pagesEquilibriumKainshk GuptaNo ratings yet
- Uzair ChemistryDocument6 pagesUzair ChemistryTalbia SyedNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Cheat Sheet InhouseDocument2 pagesEquilibrium Cheat Sheet InhouseShirleyLinNo ratings yet
- Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesDocument53 pagesStructure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesAdzimahNo ratings yet
- Le Chatelier's Principle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesLe Chatelier's Principle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlfred RogerNo ratings yet
- Notes of EuillibriumDocument4 pagesNotes of EuillibriumMegha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Formulas To RememberDocument7 pagesFormulas To RememberAaron MacauyagNo ratings yet
- Fucking KineticsDocument28 pagesFucking KineticsReginal MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chem 17 Finals ReviewerDocument9 pagesChem 17 Finals ReviewerJamie Joice Noche100% (1)
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument23 pagesChemical Equilibriumabdihakimhasssan344No ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument18 pagesChemical EquilibriumChristian Rogel De TorresNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument8 pagesEquilibriumLionel Munya ChigwidaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument10 pagesEquilibrium NotesAlana SebyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument10 pagesEquilibrium NotesAlana SebyNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and Technology University: Chemical Engineering Department Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument31 pagesAddis Ababa Science and Technology University: Chemical Engineering Department Chemical Reaction EngineeringTalew TadesseNo ratings yet
- Sceince 10 HandoutsDocument6 pagesSceince 10 HandoutsClyde NaridoNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument12 pagesEquilibrium Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry-EquilibriumDocument71 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry-EquilibriumkrkdjcjjddjNo ratings yet
- Homework - 8chemical Equilibrium FINALDocument20 pagesHomework - 8chemical Equilibrium FINALNwachukwu ObiNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry IIDocument23 pagesInorganic Chemistry IIAlvin Garcia PalancaNo ratings yet
- 8th 10th Day GasesDocument78 pages8th 10th Day GasesIsabel Velan ViernesNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7Document11 pagesEquilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7Kanishk RanjitNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet