Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worked Example: Example Concept Design Rev
Worked Example: Example Concept Design Rev
Uploaded by
lyhalimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worked Example: Example Concept Design Rev
Worked Example: Example Concept Design Rev
Uploaded by
lyhalimCopyright:
Available Formats
62
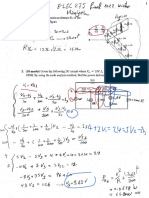
Worked example
Sheet 2 o f 4
Example Concept Design
Rev
A.p.proach I This approach is the simplest, but the most conservative,
v , , , , , , ~= ~ 22.5m/s
c,lt c,lt
Vh,O
Figure NA.1
= I +0.001A (lO/z)"z = I +0.001 ~ 4 ~5 ( 1 0 / 2 7 ) =1.037 "~
= Vh,.lap x
= 1.0
C,lt
NA.2b NA.1
Table NA.1 Table NA.2 4. I
v ~ , , ~= 22.5 x 1.0.?7 = 2.?..?m/s
cd,
Vh
(the maximum from any direction)
L'h,O
= cscasm~c,br
v~,
= 1.0 x 1.0 x2.7.3 =2.?..?m/s = 0.61.7~~~
qh
4.10 and NA.2.18 NA.2. I I
x 10-j = 0..7.3kN/m2 qk, = 0.613 ~2.3.3~ Terrain: country, when wind blowing ,from the east Distance from the sea: 24 k m minimum height z = 27m
c,(z) =3.1
qp(z) = c d z ) qh qp(z)=.?.I xO..?.~ =I.02kN/mZ This peak velocity pressure may he used to determine ,forces on the rtructure in each orthogonal direction.
Figure NA.7
A.p.proach 2 This approach demands knowledge of the upwind terrain all around the site. Examples of two directions, 330" and 60" are shown below, and then the full details of each direction in tabular format. 3.70" 60"
v[,,o
~d,,
= 23.3m/s
(as above)
v h , ~ =23.3m/s (as above)
cdlr
= 0.82
= 0. 7.7
Table NA.1 Table NA.2
~scaro,, = 1.0
Vh
vL,
= cscasm~c,br = 19.1 m/s
L'h,O
Vh
vL,
= cs,,,,,, c,br = 17.0m/s
Vh,O
4.1
= 0.82 x 1.0 x 23.3
= 0. 7.7 x 1.0 ~ 2 3 . 3
T,,
?k,
= 0.613~~:
= 0.613 x 19.12 x lo-.' = 0.22 kN/mZ
q,, q,,
= O.613vk,'
4.10 and NA.2.18
= 0.613 x 17.p x 10"
=0.18kN/m2
Terrain: country Annex AS
Terrain: town b , =8m
x = 30m (the spacing to the ~ i wind p obstructions) 2 x h,,,, < x < 6 x ha,, ? x 8 c30 <6 x 8 16 <30 <48
You might also like
- Antennas - Example Problems From Chapter 2 of BalanisDocument6 pagesAntennas - Example Problems From Chapter 2 of BalanisMauricio Gracia0% (1)
- Calculation Sheet: Calculation Peak Velocity PressureDocument51 pagesCalculation Sheet: Calculation Peak Velocity PressureSeth LyhalimNo ratings yet
- Worked Example: of Example Concept Design RevDocument1 pageWorked Example: of Example Concept Design RevlyhalimNo ratings yet
- Example Concept Design RevDocument1 pageExample Concept Design RevlyhalimNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument9 pages1 PDFalihasan12No ratings yet
- Electrostatics ProblemsDocument10 pagesElectrostatics ProblemsArifNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Efficient Acoustic Antenna ArraysDocument25 pagesOptimal Design of Efficient Acoustic Antenna ArraysBhargav BikkaniNo ratings yet
- Exercises Set 1Document2 pagesExercises Set 1hatceNo ratings yet
- (Solution Manual) Analysis and Design Principles of MEMS DevicesDocument4 pages(Solution Manual) Analysis and Design Principles of MEMS DevicesVincent ChungNo ratings yet
- Electric Flux Density Gauss'S Law DivergenceDocument26 pagesElectric Flux Density Gauss'S Law Divergenceanon_360505511No ratings yet
- Slipstream TheoryDocument28 pagesSlipstream TheoryPallab BanikNo ratings yet
- Finalexam SolutionsDocument8 pagesFinalexam SolutionsJonah BallNo ratings yet
- Sol 1Document25 pagesSol 1Kyoung Su Lee0% (1)
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1rkam243No ratings yet
- SOM Ramamruthum (149-224)Document76 pagesSOM Ramamruthum (149-224)Mohmmad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Fields Assignment 1Document2 pagesFields Assignment 1checkitoutwitharjunNo ratings yet
- Pub 01Document4 pagesPub 01παπαδοπουλοςNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Solutions: 1 Jackson 1.3Document5 pagesHomework 1 Solutions: 1 Jackson 1.3ahsanqauNo ratings yet
- 5 Example - Thin Airfoil TheoryDocument2 pages5 Example - Thin Airfoil TheorybatmanbittuNo ratings yet
- PHYS1314 Spring 2015 Solution of Homework 2Document5 pagesPHYS1314 Spring 2015 Solution of Homework 2AuHoPangNo ratings yet
- Den Hartog - 1931 - Forced Vibrations With Combined Coulomb and Viscous FrictionDocument17 pagesDen Hartog - 1931 - Forced Vibrations With Combined Coulomb and Viscous FrictionKenanNo ratings yet
- PS9Soln 2014Document13 pagesPS9Soln 2014Eddz Del Rosario RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Phased Array Fundamentals 133Document34 pagesPhased Array Fundamentals 133Soso TangoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Axial Flow Turbines 1975 Worked Examples in TurbomachineryDocument15 pagesChapter 4 Axial Flow Turbines 1975 Worked Examples in TurbomachineryKarthik Selvam100% (1)
- Solving Quadratic and Higher-Order Equations Using The Zero Product RuleDocument5 pagesSolving Quadratic and Higher-Order Equations Using The Zero Product RulemomathtchrNo ratings yet
- Antenna For All Application by John D. Kraus, 3rd Edt SolutionDocument40 pagesAntenna For All Application by John D. Kraus, 3rd Edt SolutionOmar Muñoz100% (2)
- Linton 1991 - RADIATION AND DIFFRACTION OF WATER WAVES BY A SUBMERGED SPHERE IN FINITE DEPTHDocument14 pagesLinton 1991 - RADIATION AND DIFFRACTION OF WATER WAVES BY A SUBMERGED SPHERE IN FINITE DEPTHNadji ChiNo ratings yet
- Application Design of Thin Aerofofl Theory of Double Flap Controls Small ChordDocument10 pagesApplication Design of Thin Aerofofl Theory of Double Flap Controls Small ChordkarthipriyaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Uniform Flow - ManningDocument8 pagesExamples of Uniform Flow - Manningshtou2No ratings yet
- Example 2022Document4 pagesExample 2022ellocster21No ratings yet
- Bab 14-Distribusi Tegangan Tanah VertikalDocument41 pagesBab 14-Distribusi Tegangan Tanah VertikalNovia FlorensiaNo ratings yet
- Solution To The Drill Problems of Chapter 05 (Engineering Electromagnetics, Hayt, A.Buck 7th Ed) BEE 4A, 4B & 4C D5.1 (A)Document1 pageSolution To The Drill Problems of Chapter 05 (Engineering Electromagnetics, Hayt, A.Buck 7th Ed) BEE 4A, 4B & 4C D5.1 (A)SHELPTSNo ratings yet
- Best Hydraulic SectionDocument30 pagesBest Hydraulic Sectionfaroukm9175% (4)
- Topic Determination of Source Parameters From Seismic SpectraDocument7 pagesTopic Determination of Source Parameters From Seismic SpectraFrancisco JavierNo ratings yet
- Ballistic EquationDocument53 pagesBallistic EquationJoseph Johnson100% (1)
- CH 08Document44 pagesCH 08claudioNo ratings yet
- Flow of Non Newtonian Fluids Through Eccentric Annuli: Yuejln Luo, "'.M. PedenDocument6 pagesFlow of Non Newtonian Fluids Through Eccentric Annuli: Yuejln Luo, "'.M. PedenqjbsexNo ratings yet
- CentroidDocument19 pagesCentroidragupathiindia100% (1)
- Stresses and Displacements Due To Load Transfer by Fasteners in Structural AssembliesDocument62 pagesStresses and Displacements Due To Load Transfer by Fasteners in Structural AssembliesyijunjieNo ratings yet
- 1979M A KenmotsuDocument12 pages1979M A KenmotsuJose Luis GiriNo ratings yet
- More Maximumminimum Problems. Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesMore Maximumminimum Problems. Reflection and RefractionRaul Humberto Mora VillamizarNo ratings yet
- PS1 08-SolutionDocument7 pagesPS1 08-SolutionNguyễn Vũ Quang Thành100% (1)
- Mste 16 Maxima MinimaDocument5 pagesMste 16 Maxima Minimagino roqueNo ratings yet
- A Simple Control Arithmetic of Step Wave Cascaded Multilevel Inverter With Different Voltage StepDocument5 pagesA Simple Control Arithmetic of Step Wave Cascaded Multilevel Inverter With Different Voltage StepSumit HarwaniNo ratings yet
- Solutions A-03 Applied Mechanics: (June 2003)Document24 pagesSolutions A-03 Applied Mechanics: (June 2003)AdzLinkBalaoangNo ratings yet
- 2 5stokesDocument6 pages2 5stokesSingh AnujNo ratings yet
- Der Bun Ovich 1993Document7 pagesDer Bun Ovich 1993hassanakhlaghiNo ratings yet
- Topic Take-Off Angle Calculations For Fault-Plane Solutions and Reconstruction of Nodal Planes From The Parameters of Fault-Plane SolutionsDocument6 pagesTopic Take-Off Angle Calculations For Fault-Plane Solutions and Reconstruction of Nodal Planes From The Parameters of Fault-Plane SolutionsFrancisco JavierNo ratings yet
- 6046-Article Text PDF-9804-1-10-20130718Document12 pages6046-Article Text PDF-9804-1-10-20130718আসিফহাসানখানNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document16 pagesHW 2Nadine FrisnediNo ratings yet
- Forced Axial Flow Between Rotating Concentric Cylinders: CitationDocument14 pagesForced Axial Flow Between Rotating Concentric Cylinders: CitationPrabal AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Physics 72 Final Exam Set A Draft 3 (With Feeling Answer Key)Document12 pagesPhysics 72 Final Exam Set A Draft 3 (With Feeling Answer Key)Ronaldyn DabuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Microwaves PDFDocument18 pagesLecture Notes - Microwaves PDFSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Basics - LunchBox SessionsDocument27 pagesHydraulic Basics - LunchBox SessionsAnonymous jlLBRMAr3O50% (2)
- Relay Setting Chart - CompressDocument10 pagesRelay Setting Chart - CompressMohan BabuNo ratings yet
- Fault Finding Aids: Testing Grounding SystemsDocument23 pagesFault Finding Aids: Testing Grounding SystemsShaliniNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument12 pagesRadio Wave Propagationمصطفى نوزادNo ratings yet
- Materials Properties II Thermal Electrical Characteristics - FinalDocument55 pagesMaterials Properties II Thermal Electrical Characteristics - Finalsrivas srinNo ratings yet
- Eddy CurrentDocument9 pagesEddy Currentkrish_cvr2937No ratings yet
- CH 04Document48 pagesCH 04Jabez Daniel GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Interpoles of DC GeneretorsDocument20 pagesInterpoles of DC GeneretorsSankha PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Structures: Applied MechanicsDocument24 pagesStructures: Applied MechanicsArslanNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Contribution From PV Power Plants PDFDocument15 pagesShort Circuit Contribution From PV Power Plants PDFChalitha Kanchana100% (1)
- AVD 07 Funicular MethodDocument13 pagesAVD 07 Funicular Methodabinash SethiNo ratings yet
- Motor Protection Relay: Programmable Input QuantitiesDocument6 pagesMotor Protection Relay: Programmable Input QuantitiesshekooferiahiNo ratings yet
- 3 Quarter Examination IN Integrated ScienceDocument4 pages3 Quarter Examination IN Integrated ScienceShamae Zapico RequinaNo ratings yet
- 1 DC Circuit PDFDocument119 pages1 DC Circuit PDFShivam PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fixtures PDFDocument20 pagesFixtures PDFAbhishek GorkarNo ratings yet
- Models - Acdc.capacitor DCDocument16 pagesModels - Acdc.capacitor DCFrancisco Rafael CerónNo ratings yet
- Round 1: Each Question Carry 4 Point: Quiz Competition - 2019 (Text Book Based Questions, G.K, Applications)Document52 pagesRound 1: Each Question Carry 4 Point: Quiz Competition - 2019 (Text Book Based Questions, G.K, Applications)Sonamm YangkiiNo ratings yet
- PHY2A Prac Guide Updated 2021Document88 pagesPHY2A Prac Guide Updated 2021kikiNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Unit g482 01 Electrons Waves and PhotonsDocument20 pagesQuestion Paper Unit g482 01 Electrons Waves and PhotonsCarolina NainggolanNo ratings yet
- A Buck Converter Based On PID Controller For Voltage Step - Down Application.... Trae Un Circuito Buck Aplicado en MatlabDocument4 pagesA Buck Converter Based On PID Controller For Voltage Step - Down Application.... Trae Un Circuito Buck Aplicado en MatlabDavid RomeroNo ratings yet
- Report On Dynamic Load Test On Cast in Situ PileDocument16 pagesReport On Dynamic Load Test On Cast in Situ PilemdNo ratings yet
- Question Paper CodeDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper CodevinothbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration: Physics Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument14 pagesSpeed, Velocity, and Acceleration: Physics Notes GCE Study Buddycpika520No ratings yet
- Introduction To Wave Optics ModuleDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Wave Optics ModuleR YNo ratings yet
- Inglés 8° - Reading Comprehension Per IiDocument1 pageInglés 8° - Reading Comprehension Per IiNacho MeneesNo ratings yet
- Transmission Loss StrategyDocument42 pagesTransmission Loss StrategyAmmar Lateef GakharNo ratings yet
- MR Switches CatalogueengDocument22 pagesMR Switches CatalogueengPariona Canchari PedroNo ratings yet