Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ge/Mckinsey Matrix
Ge/Mckinsey Matrix
Uploaded by
Nashiba MasturaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ge/Mckinsey Matrix
Ge/Mckinsey Matrix
Uploaded by
Nashiba MasturaCopyright:
Available Formats
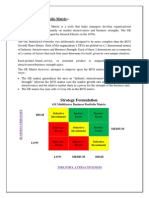
GE/MCKINSEY MATRIX
Background
In consulting engagements with General Electric in the 1970's, McKinsey and Company developed a nine-cell portfolio matrix as a tool for screening GE's large portfolio of strategic business units (SBU). This business screen became known as the GE/McKinsey Matrix and is shown below.
The GE / McKinsey matrix is similar to the BCG growth-share matrix in that it maps strategic business units on a grid of the industry and the SBU's position in the industry. The GE matrix however, attempts to improve upon the BCG matrix in the following two ways:
The GE matrix generalizes the axes as "Industry Attractiveness" and "Business Unit Strength" whereas the BCG matrix uses the market growth rate as a proxy for industry attractiveness and relative market share as a proxy for the strength of the business unit. The GE matrix has nine cells vs. four cells in the BCG matrix.
Industry attractiveness and business unit strength are calculated by first identifying criteria for each, determining the value of each parameter in the criteria, and multiplying that value by a weighting factor. The result is a quantitative measure of industry attractiveness and the business unit's relative performance in that industry.
You might also like
- Creating Shareholder Value: A Guide For Managers And InvestorsFrom EverandCreating Shareholder Value: A Guide For Managers And InvestorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- E GovernanceDocument31 pagesE GovernanceNashiba Mastura50% (2)
- Ge MatrixDocument12 pagesGe Matrixtony_njNo ratings yet
- Ge MatrixDocument4 pagesGe MatrixhaiderhusainNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument6 pagesGE MatrixkhumiNo ratings yet
- Critical Strategic Analysis of One Business Unit Within General ElectricDocument15 pagesCritical Strategic Analysis of One Business Unit Within General ElectricObianuju Onwuasor77% (22)
- The BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementFrom EverandThe BCG Growth-Share Matrix: Theory and Applications: The key to portfolio managementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- GE - McKinsey MatrixDocument4 pagesGE - McKinsey MatrixmohitNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument1 pageOverviewniharikasingh000No ratings yet
- GE - McKinsey Matrix - ADKDocument1 pageGE - McKinsey Matrix - ADKSAERO9No ratings yet
- GE - McKinsey MatrixDocument3 pagesGE - McKinsey MatrixPankaj Kumar100% (1)
- Business Unit Strength: Quickmba StrategyDocument4 pagesBusiness Unit Strength: Quickmba StrategymysterioussurferNo ratings yet
- Ge MatrixDocument3 pagesGe MatrixSantosh JhawarNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument6 pagesGE MatrixManish JhaNo ratings yet
- GE Matrix-MujtabaDocument3 pagesGE Matrix-Mujtabaahmadmujtaba005No ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument15 pagesGE Matrixsatyadarshi ravi singh100% (1)
- Ge / Mckinsey MatrixDocument4 pagesGe / Mckinsey MatrixVishh ChennNo ratings yet
- BCG GrowthDocument5 pagesBCG GrowthAmol NirgudkarNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument15 pagesGE MatrixFijo JoseNo ratings yet
- General Electric (Ge) Mckinsey & Company Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Portfolio AnalysisDocument4 pagesGeneral Electric (Ge) Mckinsey & Company Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Portfolio AnalysisMaaryaAslamNo ratings yet
- STG MNGMNTDocument10 pagesSTG MNGMNTChandan DevNo ratings yet
- General Ele 9 CellDocument15 pagesGeneral Ele 9 CellAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- GE - McKinsey Matrix - ADKDocument3 pagesGE - McKinsey Matrix - ADKViz PrezNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument12 pagesGE MatrixArun ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- GE - Matrix, Aziz Ali AfzalyDocument6 pagesGE - Matrix, Aziz Ali Afzalyali afzalyNo ratings yet
- GE - Matrix, Aziz Ali AfzalyDocument6 pagesGE - Matrix, Aziz Ali Afzalyali afzalyNo ratings yet
- Product and Brand Managemet AssignmentDocument6 pagesProduct and Brand Managemet Assignmentali afzalyNo ratings yet
- Difference Between GE McKinsey and BCG MatricesDocument3 pagesDifference Between GE McKinsey and BCG Matriceskaartik123100% (2)
- BCG Growth-Share MatrixDocument9 pagesBCG Growth-Share MatrixSaurabh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Attractiveness Factor 2 Value by Factor 2 Weighting, Etc. Factor 2 Value by Factor 2 Weighting, EtcDocument2 pagesAttractiveness Factor 2 Value by Factor 2 Weighting, Etc. Factor 2 Value by Factor 2 Weighting, EtcIssa VandanaNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument6 pagesGE Matrixmax_dcosta0% (2)
- Ge 9-CellpptDocument11 pagesGe 9-CellpptjonyshakyaNo ratings yet
- Ge Matrix: Presented By: Sadia Nasir Student Id: 20181-23584Document18 pagesGe Matrix: Presented By: Sadia Nasir Student Id: 20181-23584Hassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- GE Multifactor Portfolio Matrix:-: Strategy FormulationDocument4 pagesGE Multifactor Portfolio Matrix:-: Strategy FormulationHemant TejwaniNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument10 pagesNotesvarun rajNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix: Individual Sale This Year - Individual Sale Last Year Individual Sale Last YearDocument12 pagesBCG Matrix: Individual Sale This Year - Individual Sale Last Year Individual Sale Last YearRitika DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Gec Model Industry AnalysisDocument3 pagesGec Model Industry AnalysisHina Singhvi0% (1)
- Product Strategy Tools - GE - McKinsey Portfolio MatrixDocument5 pagesProduct Strategy Tools - GE - McKinsey Portfolio MatrixSASI KUMAR SUNDARA RAJANNo ratings yet
- Module III - GE Nine Cell MatrixDocument19 pagesModule III - GE Nine Cell MatrixloganathprasannaNo ratings yet
- GE Nine MatrixDocument9 pagesGE Nine MatrixSiddhartha GhoshNo ratings yet
- The BCG Matrix and GE9 MatrixDocument5 pagesThe BCG Matrix and GE9 MatrixAnshul MangalNo ratings yet
- Product Strategy Tools GE MatrixDocument5 pagesProduct Strategy Tools GE MatrixWaseem AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ge Nine Cell MatrixDocument26 pagesGe Nine Cell MatrixAditi ShriyaNo ratings yet
- GE McKinsey MatrixDocument14 pagesGE McKinsey MatrixSASI KUMAR SUNDARA RAJANNo ratings yet
- McKinsey GEC MatrixDocument5 pagesMcKinsey GEC MatrixFaiz Kazi100% (1)
- Difference Between BCG and GE MatrixDocument4 pagesDifference Between BCG and GE MatrixSumati SidharthNo ratings yet
- GE MatrixDocument2 pagesGE MatrixMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 Rizal Iza TigonDocument6 pagesWEEK 6 Rizal Iza TigonVanesa AgootNo ratings yet
- Nhóm 1-Cô Hoàng Anh-Phương Uyên-Dot 7Document5 pagesNhóm 1-Cô Hoàng Anh-Phương Uyên-Dot 7Nguyễn Ngọc YếnNo ratings yet
- SPM Ge MateDocument10 pagesSPM Ge Mateashutosh kankaneNo ratings yet
- The BCG MatrixDocument7 pagesThe BCG MatrixdeepthykNo ratings yet
- GE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsDocument15 pagesGE Nine Cell & Strategic EthicsPratyay DasNo ratings yet
- Ge 9cellDocument2 pagesGe 9cellSimran JoharNo ratings yet
- GE Nine CellDocument3 pagesGE Nine CellVandana Sharma100% (1)
- BCG Matrix & GE - McKinsey Matrix - CI-wikiDocument10 pagesBCG Matrix & GE - McKinsey Matrix - CI-wikiNamrita Gupta0% (1)
- Marketing Matters: A Market Analysis Methodology Leading to a Marketing Simulation CapabilityFrom EverandMarketing Matters: A Market Analysis Methodology Leading to a Marketing Simulation CapabilityNo ratings yet
- Business Chemistry: How to Build and Sustain Thriving Businesses in the Chemical IndustryFrom EverandBusiness Chemistry: How to Build and Sustain Thriving Businesses in the Chemical IndustryJens LekerNo ratings yet
- Financial Steering: Valuation, KPI Management and the Interaction with IFRSFrom EverandFinancial Steering: Valuation, KPI Management and the Interaction with IFRSNo ratings yet
- Starter Motors & Parts (Car OE & Aftermarket) World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandStarter Motors & Parts (Car OE & Aftermarket) World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Fuel Pumps & Fuel Tanks (Car OE & Aftermarket) World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandFuel Pumps & Fuel Tanks (Car OE & Aftermarket) World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- II. Normative, Ethical Thoeries... EditedDocument48 pagesII. Normative, Ethical Thoeries... EditedNashiba MasturaNo ratings yet
- E GovernanceDocument2 pagesE GovernanceNashiba MasturaNo ratings yet
- Production Activity ControlDocument6 pagesProduction Activity ControlNashiba MasturaNo ratings yet