Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsSolid State Physics: 12.1 Crystal Structure
Solid State Physics: 12.1 Crystal Structure
Uploaded by
pranodanThe document discusses solid state physics, describing crystal structure through translation vectors that define lattices and reciprocal lattices used in X-ray diffraction, and crystal binding including van der Waals, ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding. Four types of crystal binding are defined, and the energy calculation for ionic bonding in NaCl is shown as the difference between cohesive and ionization/electron affinity energies. Covalent bonding depends on spin orientations of constituting electrons, with antiparallel spins having lower potential energy and sometimes allowing binding compared to parallel spins.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Physics Unit 3 AssignmentDocument19 pagesPhysics Unit 3 AssignmentJade50% (2)
- (Solutions) Kittel - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th EditionDocument60 pages(Solutions) Kittel - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th EditionCody Foster0% (1)
- Introduction To Solid State Physics 8ed. - Solution ManualDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Physics 8ed. - Solution ManualWei Chih YangNo ratings yet
- CH 23Document28 pagesCH 23Nelson MeiNo ratings yet
- Ex 02Document2 pagesEx 02Zeynep CihanNo ratings yet
- Diff Razi OneDocument89 pagesDiff Razi OneLuana OlivieriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document3 pagesLecture 5Ramon FerreiraNo ratings yet
- XRD TheoryDocument7 pagesXRD TheoryAdarta MuhNo ratings yet
- Density of States in Graphene: Periodic Boundary ConditionDocument7 pagesDensity of States in Graphene: Periodic Boundary ConditionGemechis D DegagaNo ratings yet
- KP Theory of SemiconductorsDocument13 pagesKP Theory of SemiconductorstransfinitumNo ratings yet
- ch8 ProbsDocument4 pagesch8 ProbsEkrem GüldesteNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellDocument6 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Theory of Impedance Networks: The Two-Point Impedance and LC ResonancesDocument21 pagesTheory of Impedance Networks: The Two-Point Impedance and LC ResonancesKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Natural System of Units in General RelativityDocument5 pagesNatural System of Units in General Relativitymukesh2194No ratings yet
- MIT8 333F13 ExamReview3Document10 pagesMIT8 333F13 ExamReview3Henry De AriesNo ratings yet
- Data and Formula BookletDocument5 pagesData and Formula Booklet王涛No ratings yet
- Bloch FunctionsDocument5 pagesBloch Functionsalvaro562003No ratings yet
- Ko Ordination S ChemieDocument31 pagesKo Ordination S ChemiePaoBenítezNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Concept of Band StructureDocument8 pagesAn Introduction To The Concept of Band StructureMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Standard Model - Supersymmetry by Antoniadia and TziveloglouDocument30 pagesBeyond The Standard Model - Supersymmetry by Antoniadia and Tzivelogloukevinchu021195No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Crystal Binding: Why Do Atoms Form Crystals or Solids? Answer: That Bind AtomsDocument34 pagesChapter Three Crystal Binding: Why Do Atoms Form Crystals or Solids? Answer: That Bind AtomsSartikaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Metal OxidationDocument16 pagesTheory of Metal OxidationDyah Ayu DaratikaNo ratings yet
- Test I Solutions-1Document7 pagesTest I Solutions-1JoshuaNo ratings yet
- CKM Matrix - CERNDocument4 pagesCKM Matrix - CERNNachiket Jhala (RA1911019010065)No ratings yet
- Anti PhaseDocument3 pagesAnti PhaseMansita SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Review of Energy Dispersion Relations in Solids: ReferencesDocument9 pagesReview of Energy Dispersion Relations in Solids: Referencespopeye313No ratings yet
- Weyl Metrics and Wormholes: Gary W. Gibbons, Mikhail S. VolkovDocument38 pagesWeyl Metrics and Wormholes: Gary W. Gibbons, Mikhail S. VolkovCroco AliNo ratings yet
- Fall 2014 HW 11 SolnsDocument22 pagesFall 2014 HW 11 Solnsaleman844No ratings yet
- HW2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesHW2 Solutionsellie<3100% (1)
- Tute 1 ModifiedDocument3 pagesTute 1 ModifiedyoutuberNo ratings yet
- Departament de F Isica Te' Orica, IFIC, Universitat de Val' Encia - CSIC Apt. Correus 2085, E-46071 Val' Encia, Spain E-Mail: Antonio - Pich@uv - EsDocument50 pagesDepartament de F Isica Te' Orica, IFIC, Universitat de Val' Encia - CSIC Apt. Correus 2085, E-46071 Val' Encia, Spain E-Mail: Antonio - Pich@uv - EsCristin LeeNo ratings yet
- The Casimir Effect: Joseph CugnonDocument18 pagesThe Casimir Effect: Joseph CugnonMuhammad Salah100% (1)
- Physics Electric FieldDocument10 pagesPhysics Electric FieldHello HiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1ictoabNo ratings yet
- Charge Density in A Current-Carrying Wire: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Document10 pagesCharge Density in A Current-Carrying Wire: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544André BerninzonNo ratings yet
- Atomic NucleusDocument15 pagesAtomic Nucleussreenivas1990100% (1)
- The Standard Model of Particle Physics: 2.1 Survey of Fundamental Particles and Their InteractionsDocument15 pagesThe Standard Model of Particle Physics: 2.1 Survey of Fundamental Particles and Their InteractionsLuis MNo ratings yet
- Trans View v21Document17 pagesTrans View v21ddbyteNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Band Theory of SolidsDocument25 pagesUnit 4 Band Theory of SolidsAshema AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Lecture Notes - IntroductionDocument17 pagesDiffraction Lecture Notes - IntroductionSuvra Sekhar DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State Physics - Kittel, Charles - 8ed Solucionario PDFDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Physics - Kittel, Charles - 8ed Solucionario PDFmanuelomar87No ratings yet
- Physics Formula 63Document1 pagePhysics Formula 63pranodanNo ratings yet
- The Klein-Gordon EquationDocument22 pagesThe Klein-Gordon EquationAnderson CalistroNo ratings yet
- Reiche 2001 0124Document3 pagesReiche 2001 0124Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- The Randall-Sundrum ModelDocument26 pagesThe Randall-Sundrum ModelVictor SantosNo ratings yet
- Solucionario de ProblemarioDocument7 pagesSolucionario de ProblemarioANDREWNo ratings yet
- Mechanics and Electromagnetism: D. Atkinson and O. ScholtenDocument65 pagesMechanics and Electromagnetism: D. Atkinson and O. ScholtenJose PradoNo ratings yet
- Y Y ZXXJ Y Y Yna: ReferencesDocument3 pagesY Y ZXXJ Y Y Yna: ReferencesDaniel Herrera AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Tight BindingDocument5 pagesTight BindingalkeroneNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 - Crystallography IIDocument3 pagesAssignment - 2 - Crystallography IIep21b004No ratings yet
- Set 2 p446 2nd 2022Document4 pagesSet 2 p446 2nd 2022Enas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Physics Solutions For Serway Algebra Physics, Chapter 30Document17 pagesPhysics Solutions For Serway Algebra Physics, Chapter 30edlover9000No ratings yet
- A Symplectic Integrator For Molecular Dynamics OnDocument16 pagesA Symplectic Integrator For Molecular Dynamics OnCaillol Jean MichelNo ratings yet
- Electronic and Band Structure Slater BlochlDocument29 pagesElectronic and Band Structure Slater BlochlKorir Kiptiemoi KipronohNo ratings yet
- ĦC 197 Mev FMDocument31 pagesĦC 197 Mev FMgoxtadNo ratings yet
- C. M. L. de Aragao Et Al - Extra Dimensions, Preferred Frames and Ether-Drift ExperimentsDocument15 pagesC. M. L. de Aragao Et Al - Extra Dimensions, Preferred Frames and Ether-Drift ExperimentsKunma050No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- β ThalassemiaDocument34 pagesβ ThalassemiapranodanNo ratings yet
- Programming C++Document1 pageProgramming C++pranodanNo ratings yet
- 119060672-Organic 125Document1 page119060672-Organic 125pranodanNo ratings yet
- 119060672-Organic 121Document1 page119060672-Organic 121pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 50Document1 pagePhysics Formula 50pranodanNo ratings yet
- 119060672-Organic 122Document1 page119060672-Organic 122pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 43Document1 pagePhysics Formula 43pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 67Document1 pagePhysics Formula 67pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 44Document1 pagePhysics Formula 44pranodanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics: 7.1 Degrees of FreedomDocument1 pageStatistical Physics: 7.1 Degrees of FreedompranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 46Document1 pagePhysics Formula 46pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 45Document1 pagePhysics Formula 45pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 39Document1 pagePhysics Formula 39pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 42Document1 pagePhysics Formula 42pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 47Document1 pagePhysics Formula 47pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 40Document1 pagePhysics Formula 40pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 41Document1 pagePhysics Formula 41pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 108Document1 pagePhysics Formula 108pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 105Document1 pagePhysics Formula 105pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 69Document1 pagePhysics Formula 69pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 65Document1 pagePhysics Formula 65pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 68Document1 pagePhysics Formula 68pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 66Document1 pagePhysics Formula 66pranodanNo ratings yet
- 10.12 Atomic Physics: 10.12.1 SolutionsDocument1 page10.12 Atomic Physics: 10.12.1 SolutionspranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 63Document1 pagePhysics Formula 63pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 61Document1 pagePhysics Formula 61pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 55Document1 pagePhysics Formula 55pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 106Document1 pagePhysics Formula 106pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 64Document1 pagePhysics Formula 64pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 51Document1 pagePhysics Formula 51pranodanNo ratings yet
Solid State Physics: 12.1 Crystal Structure
Solid State Physics: 12.1 Crystal Structure
Uploaded by
pranodan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThe document discusses solid state physics, describing crystal structure through translation vectors that define lattices and reciprocal lattices used in X-ray diffraction, and crystal binding including van der Waals, ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding. Four types of crystal binding are defined, and the energy calculation for ionic bonding in NaCl is shown as the difference between cohesive and ionization/electron affinity energies. Covalent bonding depends on spin orientations of constituting electrons, with antiparallel spins having lower potential energy and sometimes allowing binding compared to parallel spins.
Original Description:
Original Title
Physics Formula 70
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses solid state physics, describing crystal structure through translation vectors that define lattices and reciprocal lattices used in X-ray diffraction, and crystal binding including van der Waals, ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding. Four types of crystal binding are defined, and the energy calculation for ionic bonding in NaCl is shown as the difference between cohesive and ionization/electron affinity energies. Covalent bonding depends on spin orientations of constituting electrons, with antiparallel spins having lower potential energy and sometimes allowing binding compared to parallel spins.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageSolid State Physics: 12.1 Crystal Structure
Solid State Physics: 12.1 Crystal Structure
Uploaded by
pranodanThe document discusses solid state physics, describing crystal structure through translation vectors that define lattices and reciprocal lattices used in X-ray diffraction, and crystal binding including van der Waals, ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding. Four types of crystal binding are defined, and the energy calculation for ionic bonding in NaCl is shown as the difference between cohesive and ionization/electron affinity energies. Covalent bonding depends on spin orientations of constituting electrons, with antiparallel spins having lower potential energy and sometimes allowing binding compared to parallel spins.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Chapter 12
Solid state physics
12.1 Crystal structure
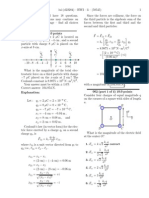
A lattice is dened by the 3 translation vectors ai , so that the atomic composition looks the same from each point r and r = r + T , where T is a translation vector given by: T = u1 a1 + u2 a2 + u3 a3 with ui I N. A lattice can be constructed from primitive cells. As a primitive cell one can take a parallellepiped, with volume Vcell = |a1 (a2 a3 )| Because a lattice has a periodical structure the physical properties which are connected with the lattice have the same periodicity (neglecting boundary effects): ne (r + T ) = ne (r ) This periodicity is suitable to use Fourier analysis: n(r ) is expanded as: n(r ) =
G
nG exp(iG r )
with nG =
1 Vcell
n(r ) exp(iG r )dV
cell
G is the reciprocal lattice vector. If G is written as G = v1 b1 + v2 b2 + v3 b3 with vi I N , it follows for the vectors bi , cyclically: ai+1 ai+2 bi = 2 ai (ai+1 ai+2 ) The set of G-vectors determines the R ontgen diffractions: a maximum in the reected radiation occurs if: k = G with k = k k . So: 2k G = G2 . From this follows for parallel lattice planes (Bragg reection) that for the maxima holds: 2d sin() = n. The Brillouin zone is dened as a Wigner-Seitz cell in the reciprocal lattice.
12.2 Crystal binding
A distinction can be made between 4 binding types: 1. Van der Waals bond 2. Ion bond 3. Covalent or homopolar bond 4. Metalic bond. For the ion binding of NaCl the energy per molecule is calculated by: E = cohesive energy(NaCl) ionization energy(Na) + electron afnity(Cl) The interaction in a covalent bond depends on the relative spin orientations of the electrons constituing the bond. The potential energy for two parallel spins is higher than the potential energy for two antiparallel spins. Furthermore the potential energy for two parallel spins has sometimes no minimum. In that case binding is not possible.
You might also like
- Physics Unit 3 AssignmentDocument19 pagesPhysics Unit 3 AssignmentJade50% (2)
- (Solutions) Kittel - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th EditionDocument60 pages(Solutions) Kittel - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th EditionCody Foster0% (1)
- Introduction To Solid State Physics 8ed. - Solution ManualDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Physics 8ed. - Solution ManualWei Chih YangNo ratings yet
- CH 23Document28 pagesCH 23Nelson MeiNo ratings yet
- Ex 02Document2 pagesEx 02Zeynep CihanNo ratings yet
- Diff Razi OneDocument89 pagesDiff Razi OneLuana OlivieriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document3 pagesLecture 5Ramon FerreiraNo ratings yet
- XRD TheoryDocument7 pagesXRD TheoryAdarta MuhNo ratings yet
- Density of States in Graphene: Periodic Boundary ConditionDocument7 pagesDensity of States in Graphene: Periodic Boundary ConditionGemechis D DegagaNo ratings yet
- KP Theory of SemiconductorsDocument13 pagesKP Theory of SemiconductorstransfinitumNo ratings yet
- ch8 ProbsDocument4 pagesch8 ProbsEkrem GüldesteNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellDocument6 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Theory of Impedance Networks: The Two-Point Impedance and LC ResonancesDocument21 pagesTheory of Impedance Networks: The Two-Point Impedance and LC ResonancesKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Natural System of Units in General RelativityDocument5 pagesNatural System of Units in General Relativitymukesh2194No ratings yet
- MIT8 333F13 ExamReview3Document10 pagesMIT8 333F13 ExamReview3Henry De AriesNo ratings yet
- Data and Formula BookletDocument5 pagesData and Formula Booklet王涛No ratings yet
- Bloch FunctionsDocument5 pagesBloch Functionsalvaro562003No ratings yet
- Ko Ordination S ChemieDocument31 pagesKo Ordination S ChemiePaoBenítezNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Concept of Band StructureDocument8 pagesAn Introduction To The Concept of Band StructureMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Standard Model - Supersymmetry by Antoniadia and TziveloglouDocument30 pagesBeyond The Standard Model - Supersymmetry by Antoniadia and Tzivelogloukevinchu021195No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Crystal Binding: Why Do Atoms Form Crystals or Solids? Answer: That Bind AtomsDocument34 pagesChapter Three Crystal Binding: Why Do Atoms Form Crystals or Solids? Answer: That Bind AtomsSartikaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Metal OxidationDocument16 pagesTheory of Metal OxidationDyah Ayu DaratikaNo ratings yet
- Test I Solutions-1Document7 pagesTest I Solutions-1JoshuaNo ratings yet
- CKM Matrix - CERNDocument4 pagesCKM Matrix - CERNNachiket Jhala (RA1911019010065)No ratings yet
- Anti PhaseDocument3 pagesAnti PhaseMansita SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Review of Energy Dispersion Relations in Solids: ReferencesDocument9 pagesReview of Energy Dispersion Relations in Solids: Referencespopeye313No ratings yet
- Weyl Metrics and Wormholes: Gary W. Gibbons, Mikhail S. VolkovDocument38 pagesWeyl Metrics and Wormholes: Gary W. Gibbons, Mikhail S. VolkovCroco AliNo ratings yet
- Fall 2014 HW 11 SolnsDocument22 pagesFall 2014 HW 11 Solnsaleman844No ratings yet
- HW2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesHW2 Solutionsellie<3100% (1)
- Tute 1 ModifiedDocument3 pagesTute 1 ModifiedyoutuberNo ratings yet
- Departament de F Isica Te' Orica, IFIC, Universitat de Val' Encia - CSIC Apt. Correus 2085, E-46071 Val' Encia, Spain E-Mail: Antonio - Pich@uv - EsDocument50 pagesDepartament de F Isica Te' Orica, IFIC, Universitat de Val' Encia - CSIC Apt. Correus 2085, E-46071 Val' Encia, Spain E-Mail: Antonio - Pich@uv - EsCristin LeeNo ratings yet
- The Casimir Effect: Joseph CugnonDocument18 pagesThe Casimir Effect: Joseph CugnonMuhammad Salah100% (1)
- Physics Electric FieldDocument10 pagesPhysics Electric FieldHello HiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1ictoabNo ratings yet
- Charge Density in A Current-Carrying Wire: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Document10 pagesCharge Density in A Current-Carrying Wire: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544André BerninzonNo ratings yet
- Atomic NucleusDocument15 pagesAtomic Nucleussreenivas1990100% (1)
- The Standard Model of Particle Physics: 2.1 Survey of Fundamental Particles and Their InteractionsDocument15 pagesThe Standard Model of Particle Physics: 2.1 Survey of Fundamental Particles and Their InteractionsLuis MNo ratings yet
- Trans View v21Document17 pagesTrans View v21ddbyteNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Band Theory of SolidsDocument25 pagesUnit 4 Band Theory of SolidsAshema AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Lecture Notes - IntroductionDocument17 pagesDiffraction Lecture Notes - IntroductionSuvra Sekhar DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State Physics - Kittel, Charles - 8ed Solucionario PDFDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Solid State Physics - Kittel, Charles - 8ed Solucionario PDFmanuelomar87No ratings yet
- Physics Formula 63Document1 pagePhysics Formula 63pranodanNo ratings yet
- The Klein-Gordon EquationDocument22 pagesThe Klein-Gordon EquationAnderson CalistroNo ratings yet
- Reiche 2001 0124Document3 pagesReiche 2001 0124Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- The Randall-Sundrum ModelDocument26 pagesThe Randall-Sundrum ModelVictor SantosNo ratings yet
- Solucionario de ProblemarioDocument7 pagesSolucionario de ProblemarioANDREWNo ratings yet
- Mechanics and Electromagnetism: D. Atkinson and O. ScholtenDocument65 pagesMechanics and Electromagnetism: D. Atkinson and O. ScholtenJose PradoNo ratings yet
- Y Y ZXXJ Y Y Yna: ReferencesDocument3 pagesY Y ZXXJ Y Y Yna: ReferencesDaniel Herrera AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Tight BindingDocument5 pagesTight BindingalkeroneNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 - Crystallography IIDocument3 pagesAssignment - 2 - Crystallography IIep21b004No ratings yet
- Set 2 p446 2nd 2022Document4 pagesSet 2 p446 2nd 2022Enas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Physics Solutions For Serway Algebra Physics, Chapter 30Document17 pagesPhysics Solutions For Serway Algebra Physics, Chapter 30edlover9000No ratings yet
- A Symplectic Integrator For Molecular Dynamics OnDocument16 pagesA Symplectic Integrator For Molecular Dynamics OnCaillol Jean MichelNo ratings yet
- Electronic and Band Structure Slater BlochlDocument29 pagesElectronic and Band Structure Slater BlochlKorir Kiptiemoi KipronohNo ratings yet
- ĦC 197 Mev FMDocument31 pagesĦC 197 Mev FMgoxtadNo ratings yet
- C. M. L. de Aragao Et Al - Extra Dimensions, Preferred Frames and Ether-Drift ExperimentsDocument15 pagesC. M. L. de Aragao Et Al - Extra Dimensions, Preferred Frames and Ether-Drift ExperimentsKunma050No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- β ThalassemiaDocument34 pagesβ ThalassemiapranodanNo ratings yet
- Programming C++Document1 pageProgramming C++pranodanNo ratings yet
- 119060672-Organic 125Document1 page119060672-Organic 125pranodanNo ratings yet
- 119060672-Organic 121Document1 page119060672-Organic 121pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 50Document1 pagePhysics Formula 50pranodanNo ratings yet
- 119060672-Organic 122Document1 page119060672-Organic 122pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 43Document1 pagePhysics Formula 43pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 67Document1 pagePhysics Formula 67pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 44Document1 pagePhysics Formula 44pranodanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics: 7.1 Degrees of FreedomDocument1 pageStatistical Physics: 7.1 Degrees of FreedompranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 46Document1 pagePhysics Formula 46pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 45Document1 pagePhysics Formula 45pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 39Document1 pagePhysics Formula 39pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 42Document1 pagePhysics Formula 42pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 47Document1 pagePhysics Formula 47pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 40Document1 pagePhysics Formula 40pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 41Document1 pagePhysics Formula 41pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 108Document1 pagePhysics Formula 108pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 105Document1 pagePhysics Formula 105pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 69Document1 pagePhysics Formula 69pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 65Document1 pagePhysics Formula 65pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 68Document1 pagePhysics Formula 68pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 66Document1 pagePhysics Formula 66pranodanNo ratings yet
- 10.12 Atomic Physics: 10.12.1 SolutionsDocument1 page10.12 Atomic Physics: 10.12.1 SolutionspranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 63Document1 pagePhysics Formula 63pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 61Document1 pagePhysics Formula 61pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 55Document1 pagePhysics Formula 55pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 106Document1 pagePhysics Formula 106pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 64Document1 pagePhysics Formula 64pranodanNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula 51Document1 pagePhysics Formula 51pranodanNo ratings yet