Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carries Impulses From Sensory Cells To CNS
Carries Impulses From Sensory Cells To CNS
Uploaded by
Anjolaoluwa Omolola OyebanjiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carries Impulses From Sensory Cells To CNS
Carries Impulses From Sensory Cells To CNS
Uploaded by
Anjolaoluwa Omolola OyebanjiCopyright:
Available Formats
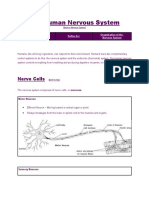
Neurones
13 May 2013 19:00
Sensory Neurone Carries impulses from sensory cells to CNS. Cell body - contains nucleus and cell
organelles within the cytoplasm.
nucleus
Axon terminal
Dendrites body.
conduct
Node of Ranvier
Axon - transmits
impulses away from the cell body.
impulses towards the cell
Myelin Sheath made from Schwann cells
Relay neurone Joins sensory neurone to motor neurone dendrites
Axon terminal
Motor neurone Conducts impulses from CNS to effector
Axon terminal
Biology Topic 8 Page 1
Sensory Neurones Relay Neurones Motor Neurones Cell body and Found within the CNS Dendrites and cell dendrite are outside body located in spinal of the spinal cord. cord. Axon outside Cell body in dorsal spinal cord. root ganglion. Carries impulses Interconnects sensory Conduct impulse from from sensory cells to neurone to motor CNS to effector CNS. neurone (Muscle or gland). Long dendrites and Short dendrites, short Short dendrites and short axon or long axon. long axons
Schwann cells wrap their cell membrane around the axon many times in a spiral to form a thick insulating lipid layer called the myelin sheath.
Myelin sheath acts as an electrical insulator along most of the axon, preventing any flow of ions across the membrane.
The gaps called nodes of Ranvier occur in the myelin sheath at regular intervals and these are the only place where depolarisation can occur.
Impulse effectively jumps from one node to the next. This is much faster than a wave of depolarisation along the whole membrane. This jumping conduction is called saltatory conduction.
Biology Topic 8 Page 2
You might also like
- Unit 11 Nervous SystemDocument117 pagesUnit 11 Nervous SystemChandan Shah100% (1)
- Anatomy Reviewer Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy Reviewer Nervous SystemCristinNo ratings yet
- Physiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)Document35 pagesPhysiology Handouts (Topic 16-26)bc200411046No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document51 pagesUnit 5JAYANT CH (RA2111004010265)No ratings yet
- FINALS 2 5-Nervoustissue-161014172642Document56 pagesFINALS 2 5-Nervoustissue-161014172642Maika Ysabelle RavaloNo ratings yet
- Physiology & Anatomy Nervous System: MuscleDocument2 pagesPhysiology & Anatomy Nervous System: MuscleEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nervous ControlDocument15 pagesNervous ControlzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Double AwardDocument4 pagesNervous System-Double AwardTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Immune SystemDocument51 pagesUnit 5-Immune SystemAnih Kishor (RA1911002010062)No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous TissueDocument54 pagesAnatomy of Nervous TissueNand PrakashNo ratings yet
- The Human Nervous System A2Document33 pagesThe Human Nervous System A2Melody PamireNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous Tissue 2010Document39 pagesHistology of Nervous Tissue 2010Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NerveDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The NervejudssalangsangNo ratings yet
- Coordination Biology 1Document33 pagesCoordination Biology 1stevhobikhoNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxDocument36 pages4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxZaara RashéidNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS NeuronsDocument20 pagesCNS PNS NeuronsTyrese SmithNo ratings yet
- Intro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Document97 pagesIntro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Jojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 (Anaphy)Document2 pagesChapter 8 (Anaphy)SKYdrum H20No ratings yet
- The Nervous System RECORDINGSDocument52 pagesThe Nervous System RECORDINGSKathy Angeli Bel-idaNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Module 14Document65 pagesModule 14sukhleenNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument14 pagesFinalsukhleenNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Excitable TissueDocument117 pagesExcitable Tissueur.yared21No ratings yet
- Psy 413 ProjectDocument38 pagesPsy 413 ProjectDumebi AneneNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue - UpdatedDocument129 pagesNervous Tissue - UpdatedPojangNo ratings yet
- NeuroconductivityDocument16 pagesNeuroconductivitysandrajoshy06No ratings yet
- Histology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureDocument7 pagesHistology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureAli HayderNo ratings yet
- NervusDocument8 pagesNervusAndika Anjani AgustinNo ratings yet
- Neural TissueDocument9 pagesNeural TissueJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Neuro Dan Neuroglia - Id.enDocument26 pagesNeuro Dan Neuroglia - Id.enRizka DeftianiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesNervous SystemJhemDelfinNo ratings yet
- N 4Document85 pagesN 4Riya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- GenBio2 Lesson 1 Muscular and Nervous TissuesDocument5 pagesGenBio2 Lesson 1 Muscular and Nervous TissuesAnne BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument25 pagesNervous TissueSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of Behaviour chp2Document2 pagesBiological Basis of Behaviour chp2jeevisha09No ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous TissueDocument35 pagesHistology of Nervous TissueGlenn Rey D. AninoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Histology College of Education34351Document6 pagesLecture 9 Histology College of Education34351Zelal Doski100% (1)
- Nervous System I Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument30 pagesNervous System I Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Document115 pagesBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nervous SystemDocument58 pagesStructure and Function of Nervous SystemFUN FLARE SHADOWNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CDocument3 pagesSamenvatting Hoofdstuk 3 B&CMarlijn Ter MorsNo ratings yet
- Neuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve CellDocument10 pagesNeuron Is The Scientific Name For A Nerve Cellirene_bayubaycuteNo ratings yet
- Myers 8th Ed. CH 2 NotesDocument85 pagesMyers 8th Ed. CH 2 NotesEric RedderNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- Itzar - Neurohistology PDFDocument186 pagesItzar - Neurohistology PDFahmad aqilNo ratings yet
- Animal Nervous System: Logo HereDocument32 pagesAnimal Nervous System: Logo HereAnne Claudette Capin TeofiloNo ratings yet
- A2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 1 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanDocument10 pagesA2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 1 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanAwais BodlaNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument364 pagesNeurophysiologyTaimoor Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocument24 pages9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Physio CH-2Document24 pagesPhysio CH-2aliraza67570No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomy of Nervous SystemGrace CosmodNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDR. KUMARASWAMI HEALTH CENTRE COLLEGE OF NURSING KANYAKUMARINo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafDocument31 pagesKonsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafdiandraNo ratings yet
- Structure of The NeuronDocument7 pagesStructure of The NeuronSmitaNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- The Nervous System 2Document84 pagesThe Nervous System 2Erika MatiasNo ratings yet