Professional Documents
Culture Documents
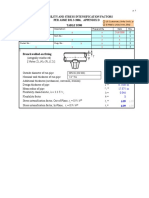
Valve A 36 Steel 0.75 In. Dia.: F A B D
Valve A 36 Steel 0.75 In. Dia.: F A B D
Uploaded by
manmathkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Valve A 36 Steel 0.75 In. Dia.: F A B D
Valve A 36 Steel 0.75 In. Dia.: F A B D
Uploaded by
manmathkCopyright:
Available Formats
294CHAPTER 12.
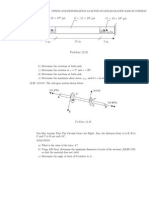
STRESS AND DEFORMATION ANALYSIS OF LINEAR ELASTIC BARS IN TORSION steel bars welded to form a T-section as shown below. Bar AB is normal to CD.
valve A
A 36 steel 0.75 in. dia. L = 2 ft B
F D
A 36 steel 1 in. dia. C F 1 ft
1 ft
Problem 12.22
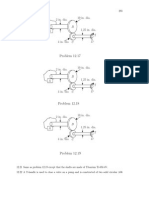
The handle CD is turned by applying equal forces F at points C and D (the forces F act in a plane that is normal to bar AB). Assume that handle CD does not bend signicantly. a) Determine the maximum value of F such that the shear stress in bar AB does not exceed the allowable yield strength in shear of 21 ksi. Use a safety factor of 2. b) What is angle of twist of point B relative to point A (in degrees)? 12.23 A gear system is required to change the torque on an input shaft from 1,000 ft-lb to a torque of 2,000 ft-lb on the output shaft (an example is shown below; other gear boxes may contain several gears with connecting shafts). The input and output shafts are each 12 inches long.
T2
T1
Problem 12.23
The diameter of the input shaft cannot exceed 0.75 in. and that of the output shaft cannot exceed 1.25 in. The bear box, which encloses the gear system, cannot exceed 8 in. on any side. Gears are available in diameters from 2 to 6 in., in increments of 0.5 in. Design the gear system including input and output shaft diameters, gear diameters used, connecting shafts between gears (if used) and materials used for all shafts (document source of material properties used). The design of gear teeth, gear material, etc. should not be considered for this problem. In
You might also like
- ASME B31 4 Calculator V1 1Document11 pagesASME B31 4 Calculator V1 1vazzoleralex6884100% (1)
- Rolling Fig Q A AnalysisDocument11 pagesRolling Fig Q A AnalysisRavinder Antil100% (9)
- Tutorial 4Document6 pagesTutorial 4Ysgn MysgnNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Louvers-1Document7 pagesDesign Calculation of Louvers-1vj8584No ratings yet
- Conveyor Pulley DesignDocument2 pagesConveyor Pulley DesignZoebair100% (2)
- FEM 18ME73 AssignmentsDocument10 pagesFEM 18ME73 AssignmentsFOODIE USNo ratings yet
- Assignment Shaft DesignDocument4 pagesAssignment Shaft DesignHasham Mehmood100% (1)
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 3Document3 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 3NEIVER ALEVIS CASTRO JULIONo ratings yet
- Problemas de Concentracion de EsfuerzosDocument7 pagesProblemas de Concentracion de EsfuerzosJonathan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Fixed End 4,000 LB - In: Problem 12.13Document1 pageFixed End 4,000 LB - In: Problem 12.13manmathkNo ratings yet
- Homework 4Document4 pagesHomework 4Odofin GbengaNo ratings yet
- HW 6Document4 pagesHW 6Dan RiversNo ratings yet
- GATE - IES QuestionsDocument4 pagesGATE - IES QuestionsMahesh Chandrabhan ShindeNo ratings yet
- (Engineering) - : B.Tech. Degree Examtnation, DecemberDocument2 pages(Engineering) - : B.Tech. Degree Examtnation, DecemberBrandon AllenNo ratings yet
- Torque (Examples and Seatwork)Document4 pagesTorque (Examples and Seatwork)Laurence PaulNo ratings yet
- Sif B31 3Document24 pagesSif B31 3vuqar0979100% (1)
- Manufacturing Processes For Mechanical EngineeringDocument21 pagesManufacturing Processes For Mechanical EngineeringRene EsepejoNo ratings yet
- Live Class Notes 29 02 20Document14 pagesLive Class Notes 29 02 20SantoshNo ratings yet
- 15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIDocument2 pages15A03602 Design of Machine Members - IIJagannath CherkuNo ratings yet
- Assignment #01Document3 pagesAssignment #01Fahad BukhariNo ratings yet
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocument6 pages4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Introduction To Belt Drive: SelectionDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Belt Drive: Selectionsohkimfai6340100% (2)
- Mechanical Desig and Machine Elements ME 322A Jing ZhengDocument6 pagesMechanical Desig and Machine Elements ME 322A Jing ZhengSergio Camacho SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Apgenco (Mechanical) 2017-QpDocument16 pagesApgenco (Mechanical) 2017-QpSamresh GarnaikNo ratings yet
- Ce205 A1m NilloDocument5 pagesCe205 A1m NilloAngelo NilloNo ratings yet
- 1 To 15 MSQDocument100 pages1 To 15 MSQTarun RathoreNo ratings yet
- 0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsDocument3 pages0326 Me 2303 Design of Machine ElementsSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- Ee300mcqwww.allexamreview.comDocument68 pagesEe300mcqwww.allexamreview.comajayvarma02626No ratings yet
- Appendix A 2010Document18 pagesAppendix A 2010Emad KhanNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel StructuresDocument3 pagesDesign of Steel StructuresAbhishek Maji100% (1)
- Sif B31 3Document10 pagesSif B31 3Sergio SmithNo ratings yet
- Common Test Paper of Civil Eng1Document14 pagesCommon Test Paper of Civil Eng1ajaydevmalikNo ratings yet
- Slabs: Serviceability and Shear: WWW - Eurocode2.infoDocument56 pagesSlabs: Serviceability and Shear: WWW - Eurocode2.infoKai Lin TayNo ratings yet
- MDDocument5 pagesMDYogesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- Torsion 01Document20 pagesTorsion 01Danielle Ruthie GalitNo ratings yet
- Detailing MembersDocument43 pagesDetailing Memberschithirai10No ratings yet
- Total Strength Assessment: Buckling and Ultimate StrengthDocument30 pagesTotal Strength Assessment: Buckling and Ultimate Strengthding liuNo ratings yet
- ASME Ch38 p001-018 11-8-08Document18 pagesASME Ch38 p001-018 11-8-08Dan MorganNo ratings yet
- Interference Fits and PressureDocument21 pagesInterference Fits and PressurerwmingisNo ratings yet
- Correct Options: D: Welfare Civil&Mech 2017)Document488 pagesCorrect Options: D: Welfare Civil&Mech 2017)Surya PatanNo ratings yet
- Production Test PaperDocument9 pagesProduction Test Paperfaheemhaider21No ratings yet
- 12me52 MQP-1Document3 pages12me52 MQP-1SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- DTS Py2 01-2013 EngDocument3 pagesDTS Py2 01-2013 EngPaulo SantosNo ratings yet
- Design MabangisDocument156 pagesDesign MabangissedexxNo ratings yet
- Short Columns by CharifDocument21 pagesShort Columns by CharifMiski45No ratings yet
- Machine Design-II EME602 2012-13Document4 pagesMachine Design-II EME602 2012-13nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Composite Beams 2Document38 pagesComposite Beams 2Seifeldin Ali Marzouk100% (1)
- Me 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Document3 pagesMe 2303 - Design of Machine Elements December 2010Ilaya Perumal K0% (1)
- Time Allowed: 1.5 Hours Full Marks: 70: 604 (S) August 2021Document3 pagesTime Allowed: 1.5 Hours Full Marks: 70: 604 (S) August 2021Sourav BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Tute Sheet 5 - Tosion in ShaftsDocument1 pageTute Sheet 5 - Tosion in ShaftsSimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Linotype Manual: Giving Detailed Instructions of the Proper Adjustment and Care of the LinotypeFrom EverandLinotype Manual: Giving Detailed Instructions of the Proper Adjustment and Care of the LinotypeNo ratings yet
- Null Field Torsion.6Document1 pageNull Field Torsion.6manmathkNo ratings yet
- Case A: (X) 5x (In-Lb/in) 3000 (In-Lb)Document1 pageCase A: (X) 5x (In-Lb/in) 3000 (In-Lb)manmathkNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 30Document1 pageChapter12 30manmathkNo ratings yet
- Fixed End 4,000 LB - In: Problem 12.13Document1 pageFixed End 4,000 LB - In: Problem 12.13manmathkNo ratings yet
- Null Field Torsion.4Document1 pageNull Field Torsion.4manmathkNo ratings yet
- Null Field Torsion.5Document1 pageNull Field Torsion.5manmathkNo ratings yet
- Axial Load Cell Torsion Load Cell Upper Jaw Grip Circular Rod SpecimenDocument1 pageAxial Load Cell Torsion Load Cell Upper Jaw Grip Circular Rod SpecimenmanmathkNo ratings yet
- Problem 12.6: 2,200 LB - FT 2 in 8 in PsiDocument1 pageProblem 12.6: 2,200 LB - FT 2 in 8 in PsimanmathkNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 27Document1 pageChapter12 27manmathkNo ratings yet
- Deep Thought: Torsion: A Threat To Mankind !Document1 pageDeep Thought: Torsion: A Threat To Mankind !manmathkNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 14Document1 pageChapter12 14manmathkNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 23Document1 pageChapter12 23manmathkNo ratings yet
- A B C X: 1 60 In-Lb/in 400 In-LbDocument1 pageA B C X: 1 60 In-Lb/in 400 In-LbmanmathkNo ratings yet
- 12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion of A Bar: (X + X) (X) (X) (X)Document1 page12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion of A Bar: (X + X) (X) (X) (X)manmathkNo ratings yet
- φ M G J x x φ ⇒ c = 0: M M P PDocument1 pageφ M G J x x φ ⇒ c = 0: M M P PmanmathkNo ratings yet
- 12.3. Example ProblemsDocument1 page12.3. Example ProblemsmanmathkNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 16Document1 pageChapter12 16manmathkNo ratings yet
- 12.3 Example Problems: φ (x M JG dxDocument1 page12.3 Example Problems: φ (x M JG dxmanmathkNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 10Document1 pageChapter12 10manmathkNo ratings yet
- 12.3. Example Problems: T T T T T T TDocument1 page12.3. Example Problems: T T T T T T TmanmathkNo ratings yet
- A B C B: 12.3. Example ProblemsDocument1 pageA B C B: 12.3. Example ProblemsmanmathkNo ratings yet
- y dA = rdrdθ: xθ xθ xθ xθ xθDocument1 pagey dA = rdrdθ: xθ xθ xθ xθ xθmanmathkNo ratings yet
- z a u u a φ: u u u - Strains (Kinematics)Document1 pagez a u u a φ: u u u - Strains (Kinematics)manmathkNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 7Document1 pageChapter12 7manmathkNo ratings yet
- 12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion Of A Bar: y a a u u φ θ r u a a y y a φ aDocument1 page12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion Of A Bar: y a a u u φ θ r u a a y y a φ amanmathkNo ratings yet
- Free-Body Cut: X Direction On The Left Face (TorqueDocument1 pageFree-Body Cut: X Direction On The Left Face (TorquemanmathkNo ratings yet
- 12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion of A BarDocument1 page12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion of A BarmanmathkNo ratings yet
- Stress and Deformation Analysis of Linear Elastic Bars in TorsionDocument1 pageStress and Deformation Analysis of Linear Elastic Bars in TorsionmanmathkNo ratings yet
- 12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion of A BarDocument1 page12.2. Theoretical Development For Torsion of A BarmanmathkNo ratings yet
- Tension TestDocument7 pagesTension TestmanmathkNo ratings yet