Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Winsem2012-13 ... Syb Ant Syb
Winsem2012-13 ... Syb Ant Syb
Uploaded by
him92Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Winsem2012-13 ... Syb Ant Syb
Winsem2012-13 ... Syb Ant Syb
Uploaded by
him92Copyright:
Available Formats
Antenna and Wave Propagation
SENSE
B. Tech. Electronics and Communication Engineering
ECE 306 Antenna and Wave Propagation LTPC: 3003
Course Description: This course highlights the characteristics of electromagnetic wave propagation and their behavior and signal losses in medium. In addition the course includes Antenna characteristics, antenna arrays and selection and design of various types of antenna from low frequency range to Terahertz range suitable for wireless application. MATLAB, Microwave office and IE3D will be used for the simulation purposes in different assignments/mini projects Prerequisite: ECE202 Transmission Line and Fields Course Objectives: The objective of this course is that the students will have the skills to: 1. Enable the students acquaint with antenna terminology, antenna and array principles and antenna analysis thereby formulating link budget for different communication Links. 2. 3. 4. Provide in depth knowledge to students in designing antennas for frequencies ranging from KHz ~THz. Introduce students the type of antennas used in Terrestrial communication, Satellite communication and modern wireless communication. Introduce various modes of Electromagnetic wave propagation and provide knowledge of propagation effects in different medium.
Course Learning Outcomes and relationship with Program Outcomes: At the end of the course, students would: 1. Select the type of antenna/arrays for particular communication link and design the antenna to suit the system requirement. (a, e, i, j, k ) 2. 3. Model the propagation path for different medium and interpret its effect on signal magnitude. (a, e, j ) Create link budget for different communication link and analyze for optimum performance. (a, e, j)
Course Syllabus: Unit I : Propagation Mechanism Reflection, refraction and Transmission, Scattering and diffraction. Propagation Model- Path Loss, Free space loss, Plane earth Loss. Noise Modeling. Modes of propagation- Ground wave Propagation, Sky wave Propagation, Space wave, Tropospheric Refraction, Obstruction Loss, Diffraction, Influence of Clutter. - Tropospheric effects, Ionospheric Effects. Link budget. Terrestrial fixed LinkSatellite Fixed Link.
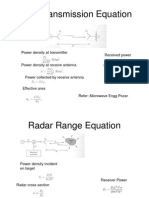
Antenna and Wave Propagation Unit II Radiation mechanism, directivity and gain, bandwidth, polarisation, copolarization and cross polarization level, beam width, input impedance, bandwidth, efficiency, input impedance, antenna effective length and area, Friis transmission equation, radar range radar cross section of antennas and antenna temperature. Measurements - radiation pattern- Gain- Directivity and Impedance measurements.
SENSE
Unit III
Linear Array - Two element array, N-element linear array- broadside array, End fire array- Directivity, radiation pattern. Planar array array factor, beamwidth, directivity. Circular array-array factor. Long wire, V-Antenna, Rhombic antenna, Monopole Antenna. dipole antenna, helical antenna, Spiral antenna, Log periodic antenna, Yagi-Uda antenna. Aperture antenna Horn antenna, parabolic reflector antenna. Micro strip antenna Antennas for Terrestrial mobile communication - mobile handsets and base stations. Antennas for Satellite Communication- MSAT briefcase terminal and vehicle mounted antennas, VSAT and DBS TV antennas. Antenna for Radar systems. Adaptive antenna Ultra wideband antenna. Terahertz antenna
Unit IV
Unit V
Text Book: T1 Balanis, Antenna Theory - Analysis and Design, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2003. T2 K. D. Prasad, Antennas and Wave Propagation, Sathya Prakasan, 3/e, 2005
Reference: R1 J.D.Krauss, Antenna and Wave propagation, TMH, 4/e, 2010 R2 G. S.N.Raju, Antennas and Wave Propagation, 3/e, Pearson Education, 2004
You might also like
- PHY 3216 Lecture Notes Part 1Document111 pagesPHY 3216 Lecture Notes Part 1OGENRWOT ALBERTNo ratings yet
- Awp Course FileDocument14 pagesAwp Course FileLaxmikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument3 pagesAntennas and Wave PropagationShiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Awp Study MaterialDocument151 pagesAwp Study MaterialjeevaNo ratings yet
- Antenna and Wave Propagations PDFDocument150 pagesAntenna and Wave Propagations PDFDamini0% (1)
- Ece3010 Antennas-And-Wave-Propagation TH 1.1 40 Ece3010Document2 pagesEce3010 Antennas-And-Wave-Propagation TH 1.1 40 Ece3010vamshiNo ratings yet
- M.tech. (RF & Microwave Engineering)Document49 pagesM.tech. (RF & Microwave Engineering)Rahul PanwarNo ratings yet
- AWP Lecture Notes-FinalDocument110 pagesAWP Lecture Notes-FinalgopichandNo ratings yet
- AWP Lecture Notes-MIMPDocument110 pagesAWP Lecture Notes-MIMPdesai vijayendra100% (1)
- Antenna & Wave PropagationsDocument150 pagesAntenna & Wave PropagationsAditya SoniNo ratings yet
- AWP Full Printed Ktunotes - inDocument111 pagesAWP Full Printed Ktunotes - inMariam FatimaNo ratings yet
- VIT UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS Ece306 Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument2 pagesVIT UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS Ece306 Antennas and Wave Propagationdivyank50% (2)
- Antennas SyllabusDocument3 pagesAntennas SyllabusPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- 5.AWP R19 SyllabusDocument3 pages5.AWP R19 SyllabusAshoka Womens Engineering College KurnoolNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: M. TulasiramDocument134 pagesLecture Notes: M. Tulasiramzoom09529No ratings yet
- Antenna and WaveDocument2 pagesAntenna and Waverkhanna1965No ratings yet
- M.tech. (RF & Microwave Engineering)Document37 pagesM.tech. (RF & Microwave Engineering)sultan1786No ratings yet
- Antennas & Wave Propagation: B.Tech (Iii Year - I Sem)Document144 pagesAntennas & Wave Propagation: B.Tech (Iii Year - I Sem)Jayant Kumar AryaNo ratings yet
- AWP Syllabus R-09Document3 pagesAWP Syllabus R-09ganesh4u_pNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Anteena FundamentalsDocument4 pagesUnit I: Anteena FundamentalsthrisulNo ratings yet
- Antenna SyllabusDocument2 pagesAntenna SyllabusHimanshu ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Antennas & Wave PropagationDocument328 pagesAntennas & Wave PropagationAstha UnadkatNo ratings yet
- EE423 Syllabus Teaching Plan Spring 2012GDocument2 pagesEE423 Syllabus Teaching Plan Spring 2012Gsurendar147No ratings yet
- Awp Syllabus SoftDocument3 pagesAwp Syllabus Softpriyakanthr5883No ratings yet
- 2.microwave Engineering PDFDocument82 pages2.microwave Engineering PDFsankeerthanreddyNo ratings yet
- 08Document1 page08januaryrekh630No ratings yet
- Ece Vi Antennas and Propagation (10ec64) NotesDocument112 pagesEce Vi Antennas and Propagation (10ec64) NotesMuhammad Ali ShoaibNo ratings yet
- ECE ME SyallabusDocument23 pagesECE ME SyallabusRAMARAJUNo ratings yet
- Bent 4313Document2 pagesBent 4313Shereen LinaNo ratings yet
- EEDXXX - Advanced ElectromagneticsDocument2 pagesEEDXXX - Advanced Electromagneticsnaveenbabu19No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Tri Band Aperture Coupled Feed Microstrip Antenna For Its Application To Filtering AntennaDocument19 pagesDesign and Simulation of Tri Band Aperture Coupled Feed Microstrip Antenna For Its Application To Filtering Antennavbv sharmaNo ratings yet
- AwpDocument137 pagesAwpJeslin AntonioNo ratings yet
- Code: ECT311 Antenna & Wave Propagation Credit: 04 L-T-P: (3-0-2) Course ContentDocument1 pageCode: ECT311 Antenna & Wave Propagation Credit: 04 L-T-P: (3-0-2) Course ContentSubhash Chandra SahuNo ratings yet
- ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION - Q.Bank - I - Mid Term Exams - September-2017 - UPDATED (22 08 17)Document11 pagesANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION - Q.Bank - I - Mid Term Exams - September-2017 - UPDATED (22 08 17)soujanya soujNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document53 pagesLecture 01Mohaira UmarNo ratings yet
- EC-6TH Sem B.Tech. Syllabus MPUDocument12 pagesEC-6TH Sem B.Tech. Syllabus MPUShamsuddin ShamsNo ratings yet
- VIKAS College of Engineering & Technology, Vijayawada VIKAS Group of Institutions, VijayawadaDocument2 pagesVIKAS College of Engineering & Technology, Vijayawada VIKAS Group of Institutions, VijayawadaRajeshNo ratings yet
- JNTU World: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument3 pagesJNTU World: Electronics & Communication EngineeringTaPAsWi AMmUNo ratings yet
- Antenna Theory & Propagation (EC 604A)Document2 pagesAntenna Theory & Propagation (EC 604A)JamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Blanis PDFDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Blanis PDFge120120No ratings yet
- Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument2 pagesAntennas and Wave PropagationkivetiNo ratings yet
- RA15 WSN Course MaterialDocument106 pagesRA15 WSN Course MaterialDr Harjit Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Mod CN LP U1 T5Document8 pagesMod CN LP U1 T5etasureshNo ratings yet
- Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument3 pagesAntennas and Wave PropagationArockia RajaNo ratings yet
- New Jersey and India Constantine A. Isbn: 047166782X ISBN-13: 9780471667827 - and Gary A Thiele. John Wiley 1998. 0-471-02590-9Document1 pageNew Jersey and India Constantine A. Isbn: 047166782X ISBN-13: 9780471667827 - and Gary A Thiele. John Wiley 1998. 0-471-02590-9MfaheemNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument48 pagesUnit IManochandar ThenralmanoharanNo ratings yet
- Electronics, John Wiley and Sons, 1994Document3 pagesElectronics, John Wiley and Sons, 1994Fere GodspowerNo ratings yet
- Awp Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAwp Lesson PlanKasthuri NgarajanNo ratings yet
- Ee6602 Unit IDocument32 pagesEe6602 Unit IMADHINI BALAMURALI ECENo ratings yet
- Antenna Fundamentals and RadiationsDocument28 pagesAntenna Fundamentals and RadiationsElisha NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Notes of Antenna and Wave PropagationDocument136 pagesNotes of Antenna and Wave PropagationSachin Behl100% (2)
- Microwave Engineering PDFDocument93 pagesMicrowave Engineering PDFbhanumanu0% (1)
- Wireless Communications and NetworksDocument3 pagesWireless Communications and NetworksNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani Campus Instruction DivisionDocument2 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani Campus Instruction DivisionAdam BrownNo ratings yet
- ECE3010 Antennas-And-Wave-Propagation TH 1.1 AC40Document2 pagesECE3010 Antennas-And-Wave-Propagation TH 1.1 AC40YashawantBasuNo ratings yet
- Connections Management Strategies in Satellite Cellular NetworksFrom EverandConnections Management Strategies in Satellite Cellular NetworksNo ratings yet
- Radio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericFrom EverandRadio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericNo ratings yet
- Industrial / Development BanksDocument24 pagesIndustrial / Development Bankshim92No ratings yet
- Term End Examination - Model Question Paper Bachelor of Commerce - Computer Application Hum 116 Practical Banking Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Document1 pageTerm End Examination - Model Question Paper Bachelor of Commerce - Computer Application Hum 116 Practical Banking Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100him92No ratings yet
- Lecture27 - Flip Flops: Jagannadha Naidu KDocument0 pagesLecture27 - Flip Flops: Jagannadha Naidu Khim92No ratings yet
- mlmlml7 Sep 2012 - RM01 PDFDocument0 pagesmlmlml7 Sep 2012 - RM01 PDFhim92No ratings yet
- Wilkinson Power DividerDocument21 pagesWilkinson Power Dividerhim92No ratings yet
- LM KLLMDocument83 pagesLM KLLMhim92No ratings yet
- Friss Transmission Equation: Received Power Power Density at TransmitterDocument2 pagesFriss Transmission Equation: Received Power Power Density at Transmitterhim92No ratings yet
- Win1213 PS Re-EvalCircularDocument1 pageWin1213 PS Re-EvalCircularhim92No ratings yet
- Fallsem2013 14 Cp2369 Syb Ece402 Mwe SyllabusDocument2 pagesFallsem2013 14 Cp2369 Syb Ece402 Mwe Syllabushim92No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Switching & Overview of AXE-10 SystemDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Switching & Overview of AXE-10 Systemhim92No ratings yet
- Ocb 283 ProjectDocument32 pagesOcb 283 Projecthim92No ratings yet
- Introduction To Internet Measurement: What, Where, Why and HowDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Internet Measurement: What, Where, Why and Howhim92No ratings yet
- OhphnnknknknknkDocument47 pagesOhphnnknknknknkhim92No ratings yet
- GPS Triangulation ProcedureDocument43 pagesGPS Triangulation Procedurehim92No ratings yet
- ADBAADBDocument5 pagesADBAADBhim92No ratings yet
- Reading An RFC: CS144, Stanford University 1Document5 pagesReading An RFC: CS144, Stanford University 1him92No ratings yet
- DSP Matlab Assignment: Submitted ToDocument7 pagesDSP Matlab Assignment: Submitted Tohim92No ratings yet
- Recharge Talk Time Charges Special Offer On Talk TimeDocument2 pagesRecharge Talk Time Charges Special Offer On Talk Timehim92No ratings yet
- WINSEM2012 13 CP0264 02 Jan 2013 RM01 Btech Marketing and Sales INTRODUCTIONDocument16 pagesWINSEM2012 13 CP0264 02 Jan 2013 RM01 Btech Marketing and Sales INTRODUCTIONhim92No ratings yet