Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic Diagram
Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic Diagram
Uploaded by
Omar EusebioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic Diagram
Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic Diagram
Uploaded by
Omar EusebioCopyright:
Available Formats
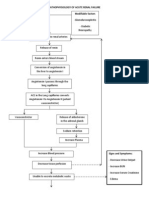
Chronic Kidney Disease
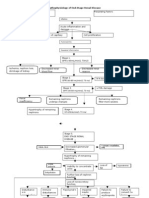
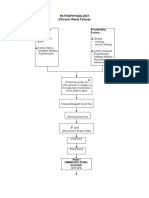
A. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY a. Schematic Diagram
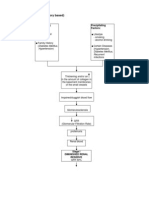
Non-Modifiable Factors -Hereditary -Age greater than 60 years old -Gender -Race Modifiable Factors -Diabetic Mellitus -Hypertension -Increase Protein and Cholesterol Intake -Smoking -Use of analgesics
Decreased renal blood flow Primary kidney disease Damage from other diseases Urine outflow obstruction
Decreased glomerular filtration Hypertrophy of remaining nephrons Inability to concentrate urine Further loss of nephron function Serum Creatinin e
BUN
Dilute Polyuri a
Dehydration
Loss of Sodium in Urine
Hyponatremi a
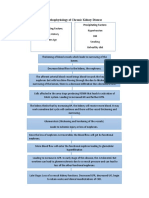
Loss of nonexcretory renal function
Failure to convert inactive forms of calcium Calcium absorption
Failure to produce eryhtropoietin
Impaired insulin action
Production of lipids Advanced atherosclerosis
Immune disturbances
Disturbances in reproduction
Anemi a Pallor
Erratic blood glucose levels
Delayed wound healing
Infectio n
Libid o
Infertility
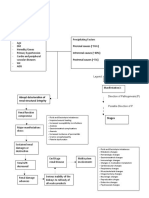
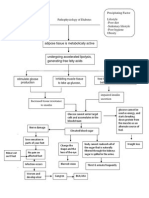
1 Hypocalcemi a Excretion of nitrogenous waste Uremia Osteodystroph y Decreased sodium reabsorption in tubule Water Retention
Loss of excretory renal function Decreased potassium excretion Decreased phosphate excretion Decreased hydrogen excretion
Hyperkalemia
Hyperphosphatemi a Decreased calcium absorption
Metabolic acidosis
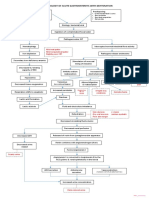
BUN, Creatinine Uric Acid
Hypertension Heart Failure Edema
Proteniuria
Hypocalcemi a Hyperparathyroidism Decreased potassium excretion
Peripheral nerve changes
Pericarditi s
Increased potassium
CNS changes
Pruritu s Altered Taste Bleeding Tendencie s
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureBettinaFernando83% (6)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Pathophysiology Renal FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Renal FailureHampson Malekano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CKDReymon Mary Janine100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failuresugarmontejo67% (3)
- CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Secondary To Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument31 pagesCHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Secondary To Chronic GlomerulonephritisJerwin Jade Bolor33% (3)
- CKDDocument3 pagesCKDMarc Lawrence Balderas CAra100% (2)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of UTIDocument1 pagePathophysiology of UTIKeannepotz83% (6)
- Chronic Kidney Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiologybilliam123100% (1)
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCKD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Concept Map: End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument4 pagesConcept Map: End Stage Renal DiseaseAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failurekristel_nicole18yaho100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology HypokalemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology HypokalemiaRnspeakcom0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of NephrolithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nephrolithiasisanreilegarde80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document5 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2LesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of NephrolithiasisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrolithiasismissmakai100% (2)
- Pathophysiology - HypokalemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology - HypokalemiaYannah Mae Espineli33% (3)
- Acute Renal Failure DiagramDocument3 pagesAcute Renal Failure DiagramMichelle BarojaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoNo ratings yet
- PatofkuDocument3 pagesPatofkunisaaa88No ratings yet
- CKD PathoDocument5 pagesCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureAura Salve Ildefonso AllasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ESRDDocument9 pagesPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of ESRDDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of ESRDjake90210100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNDocument1 pagePathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNNathan Vince CruzNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoNo ratings yet
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina Samson0% (1)
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 pagesPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18No ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJacinthaVanathayahNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Document7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Esrd Diagram PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesEsrd Diagram PathophysiologySTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pagePathophysiology DMMJ AmarilloNo ratings yet
- EsrdDocument3 pagesEsrdRonald Lavada RN100% (1)
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysioDocument4 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis Pathophysioshaider1190% (1)
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of DiabetesDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of DiabetesJeffrey Ramos GironNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGE With DHNDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGE With DHNFarr Krizha Tangkusan50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of UrolithiasisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of UrolithiasisNavjot Brar100% (2)
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Document3 pagesPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Sumit Kumar, MD, MPH Presbyterian Hospital, Dallas, TXAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument18 pagesKidneyRacha MougharbelNo ratings yet
- MNT Penyakit GinjalDocument41 pagesMNT Penyakit GinjalNurfitriana DwiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument36 pagesChronic Kidney Diseasejabir100% (1)
- Kidney FailureDocument27 pagesKidney FailureKash JamasaliNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument54 pagesChronic Renal Failuresanjivdas100% (3)
- HYPOCALCEMIADocument27 pagesHYPOCALCEMIAJeffri SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPDDocument35 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPDRikkiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument13 pagesChronic Renal FailureAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseTamzid Rabby TanmoyNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases: Ivan Surya PradiptaDocument29 pagesKidney Diseases: Ivan Surya PradiptaAthirah BidinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaNo ratings yet