Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview Last Class
Overview Last Class
Uploaded by
raymonezs100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
41 views9 pagesThe document discusses reliability engineering and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA). It explains that reliability engineering aims to design products that can perform their required functions for a stated period of time without failures. An important tool used in reliability engineering is FMEA, which identifies potential failure modes, analyzes their causes and effects, and determines how to reduce or eliminate risks. FMEA provides benefits like improved safety, quality and reliability as well as reduced costs. It can be applied at various stages including concept, design, process, service, and for evaluating equipment purchases.
Original Description:
Original Title
w5ii fmea
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses reliability engineering and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA). It explains that reliability engineering aims to design products that can perform their required functions for a stated period of time without failures. An important tool used in reliability engineering is FMEA, which identifies potential failure modes, analyzes their causes and effects, and determines how to reduce or eliminate risks. FMEA provides benefits like improved safety, quality and reliability as well as reduced costs. It can be applied at various stages including concept, design, process, service, and for evaluating equipment purchases.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
41 views9 pagesOverview Last Class
Overview Last Class
Uploaded by
raymonezsThe document discusses reliability engineering and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA). It explains that reliability engineering aims to design products that can perform their required functions for a stated period of time without failures. An important tool used in reliability engineering is FMEA, which identifies potential failure modes, analyzes their causes and effects, and determines how to reduce or eliminate risks. FMEA provides benefits like improved safety, quality and reliability as well as reduced costs. It can be applied at various stages including concept, design, process, service, and for evaluating equipment purchases.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
• Overview last class
1. DESIGNING FOR TIME-ORIENTED PERFORMANCE (RELIABILITY)
• the ability of a product to perform a required function under stated conditions
for a stated period of time
• the chance that a product will work for the required time
• quality over time
• product should have a long service life with few failures.
as product become more complex, failures increase with operating time
To achieve high reliability - RELIABILITY PROGRAM
Activities involved :
setting overall reliability goals Stress analysis
Apportionment of the reliability goals Design review
Identification of critical parts Reliability prediction
Failure mode & effect analysis ( FMEA ) Selection of suppliers
Control of reliability during manufacturing
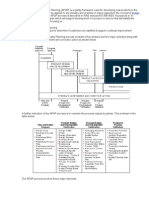
FAILURE MODES EFFECTS ANALYSIS ( FMEA)
• Identifying, analyzing and documenting the possible failure
modes within a system and the effects of each failure on the
system.
• Description of how failures influence system performance and
personnel safety.
• Created by the aerospace industry in the 60’s
• Early application by Ford : used to analyze engineering design
BENEFITS
1. Improvement of safety, quality, and reliability of product
2. Improvement of company’s image and competitiveness
3. Increased satisfaction from a user standpoint
4. Reduction in product development cost
5. Record of actions taken to reduce a product risk
APPLICATION OF FMEA
1. CONCEPT - used to analyze a system or subsystem in the
conception of the design
4. PROCESS - applied to analyze the assembly and manufacturing
processes
7. DESIGN - used for analysis of products before mass production
of the product starts or early in development cycle
10. SERVICE - used to test industry processes for failure prior to
release to customer
13. EQUIPMENT – analyze equipment before the final purchase
You might also like
- AIAG-VDA Design FMEA For PractitionersDocument256 pagesAIAG-VDA Design FMEA For PractitionersMoham'medAlthafAs'lam100% (7)
- Proceeding From The Seminar On Development of Modular ProductsDocument179 pagesProceeding From The Seminar On Development of Modular Productselnegroleo2No ratings yet
- Abstract and AcknowledgementDocument4 pagesAbstract and AcknowledgementperaNo ratings yet
- PR Checklist Stage4 FinalDocument7 pagesPR Checklist Stage4 FinalAhmed SamirNo ratings yet
- Development of Quality System For Engine AssemblyDocument55 pagesDevelopment of Quality System For Engine AssemblysvrbchaudhariNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument4 pagesFMEAMDR PRAPHUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document2 pagesChapter 12Cathy MamigoNo ratings yet
- All Tools in OneDocument38 pagesAll Tools in Oneom_3334No ratings yet
- Qgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionDocument103 pagesQgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionVINOTH100% (2)
- Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisDocument5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects AnalysisBoBo KyawNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis in Reliability CenteredDocument41 pagesFailure Mode and Effects Analysis in Reliability CenteredAkanksha KumariNo ratings yet
- Incorporate Maintainability Into Revamp and Greenfield ProjectsDocument9 pagesIncorporate Maintainability Into Revamp and Greenfield Projectsmg2001No ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- The 5 Core ToolDocument17 pagesThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument29 pagesFMEAKarthik Kr100% (1)
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument8 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryBONFRINGNo ratings yet
- FMEA TrainingDocument49 pagesFMEA Trainingeidlberto casedoNo ratings yet
- Es-Unit 3 Edlc-Iii EeeDocument45 pagesEs-Unit 3 Edlc-Iii EeepriyadarshniNo ratings yet
- EGF305 Topic 5-Intro To Failure Analysis PDFDocument34 pagesEGF305 Topic 5-Intro To Failure Analysis PDFasdfasdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software TestingDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Software TestingValentin IordacheNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocument36 pagesFailure Mode Effect AnalysisCharanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993Document5 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993JeevanNo ratings yet
- Fmea Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: Thought For The DayDocument55 pagesFmea Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: Thought For The Dayjd4u100% (1)
- Eaton ApqpDocument142 pagesEaton ApqpAmolPagdalNo ratings yet
- 1) FMEA - ExcerptsHandbookDocument9 pages1) FMEA - ExcerptsHandbookchanseshpNo ratings yet
- TQM Unit 4 Lecture 5 TPMDocument22 pagesTQM Unit 4 Lecture 5 TPMtamilselvansambathNo ratings yet
- FMEA Failure Modes Effects Analysis PDFDocument32 pagesFMEA Failure Modes Effects Analysis PDFVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064100% (1)
- Cbme ReportDocument38 pagesCbme ReportNessa VillaralboNo ratings yet
- What Is A Failure Mode?Document16 pagesWhat Is A Failure Mode?Cuenta PokemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 ReliabilityDocument2 pagesChapter 11 Reliabilityayawireless7No ratings yet
- Software Life Cycle ModelsDocument15 pagesSoftware Life Cycle Modelsumang patelNo ratings yet
- APQP - Core Tools of QualityDocument108 pagesAPQP - Core Tools of Qualitykiran kumar psNo ratings yet
- Alternative Methods For Building Information SystemsDocument3 pagesAlternative Methods For Building Information SystemssarojNo ratings yet
- MAnagementDocument26 pagesMAnagementEngr.Arslan AbbasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - 2 DevOps and Continuous TestingDocument13 pagesUnit 2 - 2 DevOps and Continuous TestingAbhinav SikharamNo ratings yet
- Safety Process Equipment Design Operation: Risk Minimization ApproachDocument4 pagesSafety Process Equipment Design Operation: Risk Minimization ApproachalijadoonNo ratings yet
- Software Quality ManagementDocument22 pagesSoftware Quality ManagementAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Unit7 Test ManagementDocument29 pagesUnit7 Test ManagementAryan ShendeNo ratings yet
- Design For Quality and Product Excellence Cbme 1Document16 pagesDesign For Quality and Product Excellence Cbme 1Jayvee Joble BigataNo ratings yet
- NDT Overview M1 Part2Document55 pagesNDT Overview M1 Part2Leon Heart FC100% (1)
- Supplier APQP Process Training (In-Depth)Document142 pagesSupplier APQP Process Training (In-Depth)A MNo ratings yet
- DFMEA - Training ManualDocument45 pagesDFMEA - Training ManualAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- PM-Software Quality AssuranceDocument22 pagesPM-Software Quality AssuranceHusnainNo ratings yet
- Course Material Process FMEA 4th EditionDocument84 pagesCourse Material Process FMEA 4th EditionRaju.Pal100% (1)
- FMEA PresentationDocument68 pagesFMEA PresentationParas KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Api RP 17N Workshop: Executive Summary of MeetingDocument97 pages1 Api RP 17N Workshop: Executive Summary of MeetingIrsalina NHNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Product Development ProcessDocument24 pages2.0 Product Development ProcessMohd Nazim Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument64 pagesFMEAbipin.chouguleNo ratings yet
- Product and Service Design: Presented By: Alona B. Abiog Catherine A. Zuñiga Mba 2-BDocument37 pagesProduct and Service Design: Presented By: Alona B. Abiog Catherine A. Zuñiga Mba 2-BAaminah BeathNo ratings yet
- Design Review Procedure For Projects in Fertilizer PlantsDocument9 pagesDesign Review Procedure For Projects in Fertilizer PlantsmanuNo ratings yet
- Ch2 ReliabilitymanagementDocument57 pagesCh2 ReliabilitymanagementyitongcytNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - 20 July 2018Document32 pagesUnit 2 - 20 July 2018CHIRANJIT DASNo ratings yet
- Advanced Product Quality PlanningDocument35 pagesAdvanced Product Quality Planninggerry3854100% (2)
- Reviewer: TQM Chapter 1 To 4Document3 pagesReviewer: TQM Chapter 1 To 4WellaNo ratings yet
- 06 SPM Quality ManagementDocument80 pages06 SPM Quality ManagementThuận AnhNo ratings yet
- PWC Systems Implementation Lessons LearnedDocument30 pagesPWC Systems Implementation Lessons Learnedsnandal2No ratings yet
- Assurance Technologies Principles and Practices: A Product, Process, and System Safety PerspectiveFrom EverandAssurance Technologies Principles and Practices: A Product, Process, and System Safety PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Manufacturing Operations Management: ISA-95 Best Practices Book 1.0From EverandThe Hitchhiker’s Guide to Manufacturing Operations Management: ISA-95 Best Practices Book 1.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Picture Completion-4Document12 pagesPicture Completion-4RafiaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Marketing ResearchDocument3 pagesImportance of Marketing ResearchHarsh koriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (8601) - Muhammad Farhan - 0000237611 - Spring22Document27 pagesAssignment 2 (8601) - Muhammad Farhan - 0000237611 - Spring22Malik Farhan AwanNo ratings yet
- (Gil-Garcia & Pardo 2006) Multi-Method Approaches To Understanding The Complexity of E-GovernmentDocument16 pages(Gil-Garcia & Pardo 2006) Multi-Method Approaches To Understanding The Complexity of E-GovernmentZackNo ratings yet
- Phi Coefficient Example Power Point 97-03Document14 pagesPhi Coefficient Example Power Point 97-03Rineeta BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Final Paper PDFDocument60 pagesFinal Paper PDFJenina P. AnielNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper On Video GamesDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper On Video Gamesyscgudvnd100% (1)
- EIA ReportDocument178 pagesEIA Reportengr_afsoomro3147100% (1)
- Dissertation Tu Dortmund EldoradoDocument6 pagesDissertation Tu Dortmund EldoradoBuyingPapersOnlineCollegeRochester100% (1)
- Septic Shock Nursing Research Final ProjectDocument8 pagesSeptic Shock Nursing Research Final Projectapi-313061106No ratings yet
- Research Article Basic Competence of Intensive Care Unit Nurses: Cross-Sectional Survey StudyDocument13 pagesResearch Article Basic Competence of Intensive Care Unit Nurses: Cross-Sectional Survey StudyAi Indah NazriahNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Control System Integration Part 3: Activity Models of Manufacturing Operations ManagementDocument104 pagesEnterprise Control System Integration Part 3: Activity Models of Manufacturing Operations ManagementJeff HekmatiNo ratings yet
- A Study of Recent Accounting Trends in India's Corporate Sector With Special Reference To International Financial Reporting StandardsDocument9 pagesA Study of Recent Accounting Trends in India's Corporate Sector With Special Reference To International Financial Reporting StandardsManagement Journal for Advanced ResearchNo ratings yet
- MAESP 202 Detection & Estimation TheoryDocument4 pagesMAESP 202 Detection & Estimation TheoryRashi JainNo ratings yet
- BstatDocument49 pagesBstatLeonard KimuliNo ratings yet
- 3is (Act1-3)Document4 pages3is (Act1-3)Aira ApellidoNo ratings yet
- Underlying Causes of Rework in ConstructionDocument24 pagesUnderlying Causes of Rework in ConstructionStefanBelibouNo ratings yet
- We Googled YouDocument8 pagesWe Googled YoumdgulfamansariNo ratings yet
- SSP Comprehensive Summary - MANLUCOB, Lyra Kaye B.Document10 pagesSSP Comprehensive Summary - MANLUCOB, Lyra Kaye B.LYRA KAYE MANLUCOBNo ratings yet
- Cable Modelling For Electromagnetic Transients in Power SystemsDocument143 pagesCable Modelling For Electromagnetic Transients in Power Systemsalpcruz100% (1)
- Cte STD Career PracticumDocument8 pagesCte STD Career Practicumapi-307849917No ratings yet
- Ss 1Document6 pagesSs 1drishtisorathiya08No ratings yet
- 4.1 Notes2Document12 pages4.1 Notes2Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- APA Handout 2013 PDFDocument6 pagesAPA Handout 2013 PDFsjbloraNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1 - Kelas H - Estimation of OGIP in A Water Drive Gas Reservoir Coupling Dynamic Material Balance and Fetkovich Aquifer ModelDocument11 pagesKelompok 1 - Kelas H - Estimation of OGIP in A Water Drive Gas Reservoir Coupling Dynamic Material Balance and Fetkovich Aquifer ModelJassen EstefanNo ratings yet
- SM 316 - Spring 2019 Homework 7 SolutionsDocument9 pagesSM 316 - Spring 2019 Homework 7 SolutionsShelaNo ratings yet
- Course: Code: Test: Time:: Universiti MaraDocument5 pagesCourse: Code: Test: Time:: Universiti MaraIkhmal AlifNo ratings yet
- Healing ArchitectureDocument16 pagesHealing ArchitectureZoona JerralNo ratings yet
- Challenges Encountered by Pre-Service Education StudentsDocument18 pagesChallenges Encountered by Pre-Service Education StudentsPinpin Cindy D.No ratings yet