Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chronic Renal Failure To Esrd: Stage I Diminished Renal Reserve
Chronic Renal Failure To Esrd: Stage I Diminished Renal Reserve
Uploaded by
Sui NarcanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chronic Renal Failure To Esrd: Stage I Diminished Renal Reserve
Chronic Renal Failure To Esrd: Stage I Diminished Renal Reserve
Uploaded by
Sui NarcanCopyright:
Available Formats
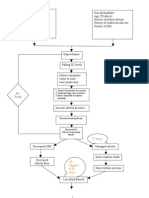
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE TO ESRD
Thickening and/or an in the amount of collagen in the basement membranes of the small vessels
Impaired/sluggish blood flow
Glomerulosclerosis
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) proteinuria
Renal blood
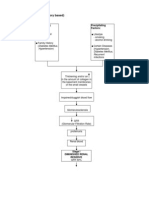
Stage I DIMINISHED RENAL RESERVE GFR 50%
Normal BUN, creatinine More than 75% damage
Stage II RENAL INSUFFICIENCY GFR 20-50% BUN, creatinine levels begin to rise
Remaining nephrons undergo changes to compensate for those damaged nephrons
Filtration of more concentrated blood by the remaining nephrons
Hypertrophy of nephrons Intolerance and exhaustion of the remaining nephrons Further damage of the nephrons 80-90% damage
Stage III RENAL FAILURE GFR 10-20%
Impaired kidney function and Uremia
- Reduction in renal capillaries -Scarring of Glomeruli - Atrophy & Fibrosis of Renal tubules
> 90 % of kidney damage
Malfunction of RAAS
Nitrogenous wastes impairs platelets Bleeding tendencies ANEMIA
Decreased Erythropoietin Production Continuous decline in renal function -fatigue - weakness
Toxins irritate pericardial sac Pericarditis
Toxins impair immune system Decreased Immune system Risk for superinfection
Urea deposits on the skin
Na & H2O retention
Cardiac Tamponade
Uremic frost
Decreased Urine Output Oliguria Hypertension Continuous Multisystem Affectation Multiple Organ Failure Increased blood pressure Edema Pulmonary Edema, Peripheral Edema Stage IV END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE (ESRD) GFR <10% Sepsis
Toxins affect CNS
Uremic Encephalopathy -changes in mentation/ psychiatric symptoms -irritability -fatigue -insomnia
Heart Failure
DEATH
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureBettinaFernando83% (6)
- Vital Signs Monitoring SheetDocument1 pageVital Signs Monitoring SheetSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle - Smoking - Alcohol Drinking - High Na and Fat Diet Pre Renal Causes Intrarenal Causes Postrenal CausesDocument6 pagesLifestyle - Smoking - Alcohol Drinking - High Na and Fat Diet Pre Renal Causes Intrarenal Causes Postrenal CausesSheerie DeangNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureAura Salve Ildefonso AllasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure) Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure) Precipitating FactorsReyna Rose AbonNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureDocument40 pagesPresented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureRavanshi ThakurNo ratings yet
- RTC Acute Renal FailureDocument24 pagesRTC Acute Renal FailureVIDYANo ratings yet
- Dr.P.Sankaranarayanan MD: Emeritus Professor of Medicine Acs Medical College & HospitalDocument81 pagesDr.P.Sankaranarayanan MD: Emeritus Professor of Medicine Acs Medical College & HospitalvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument28 pagesChronic Renal FailuremarshmalouNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failur E: By: Miss Santoshi Naik Assistant Professor Yenepoya Pharmacy College & Research CentreDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failur E: By: Miss Santoshi Naik Assistant Professor Yenepoya Pharmacy College & Research CentreAnusikta PandaNo ratings yet
- Renal Function TestsDocument34 pagesRenal Function TestsMandavi HindNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease. GolwallaDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney Disease. GolwallaAbdul QuyyumNo ratings yet
- Renal Support in Hepatic Patient: by Mohammed Dabbour Lecturer of Anesthesia Ain Shams UniversityDocument36 pagesRenal Support in Hepatic Patient: by Mohammed Dabbour Lecturer of Anesthesia Ain Shams UniversityTrishenth FonsekaNo ratings yet
- Noel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNDocument62 pagesNoel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNagilNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi SharmaDocument36 pagesRenal Diseases: Dr. Nidhi Sharmanidhi261987No ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument21 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryAtif Gazali100% (1)
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocument7 pagesCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- CRFDocument50 pagesCRFKevin MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Renal FailureDocument21 pagesAcute and Chronic Renal FailureStephina ImmaculateNo ratings yet
- Renal FunctionDocument20 pagesRenal FunctionBatrisyia BalqisNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument20 pagesRenal SystemRahul DasNo ratings yet
- End-Stage Renal DiseaseDocument3 pagesEnd-Stage Renal DiseaseAkira Pongchad B100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Children: DR Saiel Al Sarhan MD, PHDDocument48 pagesChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Children: DR Saiel Al Sarhan MD, PHDMAYSAA HamarnehNo ratings yet
- Aki (New)Document40 pagesAki (New)Mithun GowdaNo ratings yet
- The Hepatorenal Syndrome: 11 Pathophysiology and Treatment Ofascites andDocument27 pagesThe Hepatorenal Syndrome: 11 Pathophysiology and Treatment Ofascites andJose JulcaNo ratings yet
- What Is End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) ?Document2 pagesWhat Is End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) ?Vecky TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 CKDDocument53 pagesLecture 3 CKDPharmswipe KenyaNo ratings yet
- Askep Gagal Ginjal - Ns. FitrioDocument32 pagesAskep Gagal Ginjal - Ns. FitriodesyNo ratings yet
- Hellp SyndromeDocument42 pagesHellp SyndromeDexel Putra SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation CKDDocument17 pagesCase Presentation CKDPrabal bhuniaNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Concerns in CKDDocument34 pagesAnaesthesia Concerns in CKDAbhi JeetNo ratings yet
- Copy AKIDocument62 pagesCopy AKIJsai PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument10 pagesAcute Renal FailureSypheruNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument13 pagesChronic Renal FailureAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Nephrologi NotesDocument43 pagesNephrologi NotesSigit Harya HutamaNo ratings yet
- Anemia: CBC Impaired Gas Exchange Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesAnemia: CBC Impaired Gas Exchange Ineffective Tissue PerfusionPaul MahilumNo ratings yet
- Chronic RenalDocument5 pagesChronic Renaljazzy penzNo ratings yet
- crf03 1Document16 pagescrf03 1Aswin DamodaranNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument60 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryAbegail Fermanejo-GeneraoNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure StudyDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure StudyElyne BicaldoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaNo ratings yet
- IRADocument83 pagesIRAMadalina CordonasuNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument38 pagesAcute Renal Failurechesang507No ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Renal FunctionDocument20 pagesClinical Chemistry Renal FunctionNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: DR - SarmisthaDocument19 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: DR - SarmisthaGebby MamuayaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 pagesPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18No ratings yet
- Azotemia: Dept BiochemistryDocument25 pagesAzotemia: Dept BiochemistryPrajna PNo ratings yet
- LP CKD FiksDocument16 pagesLP CKD FiksWahyu7.8No ratings yet
- Nephrology Notes Review - Passmedicine 2012Document33 pagesNephrology Notes Review - Passmedicine 2012adiNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injuri: Professor Ibrahim UmmateDocument46 pagesAcute Kidney Injuri: Professor Ibrahim UmmateElvis obajeNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument9 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsKimberly Bomediano100% (1)
- 4 Kidney Diseases TogleMDDocument1 page4 Kidney Diseases TogleMDMarianneNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure DefinisiDocument4 pagesRenal Failure DefinisiLentinaNo ratings yet
- Renal IndicesDocument6 pagesRenal IndicesSaravanan SridharanNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Pyruvatkinase-Mangel für Patienten und Angehörige: Eine seltene genetische Erkrankung der roten Blutkörperchen Informationen + Mitreden-Können = Bestmöglicher VerlaufFrom EverandFast Facts: Pyruvatkinase-Mangel für Patienten und Angehörige: Eine seltene genetische Erkrankung der roten Blutkörperchen Informationen + Mitreden-Können = Bestmöglicher VerlaufNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoFrom EverandFast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoFrom EverandFast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency for Patients and Supporters: A rare genetic disease that affects red blood cellsFrom EverandFast Facts: Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency for Patients and Supporters: A rare genetic disease that affects red blood cellsNo ratings yet
- Optum Story 8.5x11 V1 PDFDocument2 pagesOptum Story 8.5x11 V1 PDFSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Through: Dr. Alma B. Ungab, BSN, RN, MN, DPA Chief Nurse Vicente Sotto Memorial Medical Center B. Rodriguez ST., Cebu City, Philippines 6000Document1 pageThrough: Dr. Alma B. Ungab, BSN, RN, MN, DPA Chief Nurse Vicente Sotto Memorial Medical Center B. Rodriguez ST., Cebu City, Philippines 6000Sui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Optum: A Health Services and Innovation CompanyDocument2 pagesOptum: A Health Services and Innovation CompanySui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Forest Camp Resort Map A4Document1 pageForest Camp Resort Map A4Sui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Eligible Professional Meaningful Use Core Measures Measure 12 of 13Document3 pagesEligible Professional Meaningful Use Core Measures Measure 12 of 13Sui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Aspe Ceereal Breakfastbrochure FinalDocument16 pagesAspe Ceereal Breakfastbrochure FinalSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Diagnostic Radiology Documentation: Prepared by The Zotec Corporate Coding DepartmentDocument43 pagesComprehensive Diagnostic Radiology Documentation: Prepared by The Zotec Corporate Coding DepartmentSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- You Can Heal Your LifeDocument173 pagesYou Can Heal Your LifeSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Bladder Irrigation & InstallationDocument12 pagesBladder Irrigation & InstallationSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- ANA Code of Ethics For Nurses2Document6 pagesANA Code of Ethics For Nurses2Sui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Resume EntrylevelDocument1 pageResume EntrylevelSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Professional Entry Level ResumeDocument2 pagesProfessional Entry Level ResumeSui NarcanNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument1 pageReaction PaperSui Narcan100% (1)