Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration
Respiration
Uploaded by
Lim Kai YeeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 RespirationDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1 RespirationMohd HanisNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiDocument6 pagesNota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiZuraina ShaharomNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument12 pagesRespirationjimmycrackle710No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1Document22 pagesChapter 1.1ieya_yNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemTeacher JoanNo ratings yet
- Respiration (Part 1)Document15 pagesRespiration (Part 1)Jessie Clarinda JoyceNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Aniket DasDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory System Aniket DasChep KepNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System (Autosaved)Document24 pagesThe Respiratory System (Autosaved)Judah RampersadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Respiratory PhysiologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory PhysiologyKingsley UdeajaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Metric 1rst ChapterDocument13 pages1.3 Metric 1rst ChapterDr. Mariam SahitoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument17 pagesRespiratory SystemMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Human Gas ExchangeDocument25 pages6.6 Human Gas ExchangeyousafNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumanDocument17 pagesGas Exchange in HumanGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory SystemM. Farkhan HabibNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument23 pagesGas Exchange in HumansVNo ratings yet
- bio 统一小考-chapter 8Document8 pagesbio 统一小考-chapter 822 Lee Xin Yong 李芯瑢No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System or Pulmonary SystemDocument53 pagesThe Respiratory System or Pulmonary Systemfharidaismail47No ratings yet
- DescriptionDocument2 pagesDescriptionGliane, Adrie Ann C.No ratings yet
- Breathing and Gaseous Exchnage by Sherrie-Ann Wilson-BrownDocument85 pagesBreathing and Gaseous Exchnage by Sherrie-Ann Wilson-BrownNayoka EnnisNo ratings yet
- Patho PneumoniaDocument26 pagesPatho PneumoniaRenz Ivan FuntilonNo ratings yet
- Respiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentDocument65 pagesRespiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Sistem PernapasanDocument18 pagesSistem PernapasanAgustinus SukurNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesHuman Respiratory Systempraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- C 2 The Respiratory StructureDocument34 pagesC 2 The Respiratory StructurefadlinlinsaiNo ratings yet
- Review of Anaphy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesReview of Anaphy and PhysiologyD A M N E R ANo ratings yet
- Notes On Respiratory System, Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 pagesNotes On Respiratory System, Gaseous Exchangeshelter musasaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesRespiratory SystemVanezaKateYeclaRetinioNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No YesDocument2 pagesGas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yesapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture - 5 PDFDavid JokerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemcharamina13No ratings yet
- Topic 2.3 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 2.3 - Human Respiratory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument37 pagesGaseous ExchangeSolángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesLecture 1 Respiratory SystemArnelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Bio 2 ADocument31 pagesRespiratory System - Bio 2 A20181539No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumanDocument15 pagesGas Exchange in HumanNithika De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument18 pagesGas Exchange in Humans CAIE Biology IGCSEmilesdlaw4455No ratings yet
- Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesIngles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemAgustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse DefinitionDocument4 pagesRespiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse Definitionmiss RN100% (2)
- Respiratory2 0Document26 pagesRespiratory2 0api-258400031No ratings yet
- Biology ResppirationDocument2 pagesBiology ResppirationNeilson KesumaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Document36 pagesTopic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Respiratory Lab - TaggedDocument51 pagesLab 4 - Respiratory Lab - TaggedKimberly LeGalleyNo ratings yet
- Respiration & BreathingDocument18 pagesRespiration & BreathingKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Meri Bing Tugas RespiratoryDocument4 pagesMeri Bing Tugas RespiratoryNona MeyNo ratings yet
- Class 7 RespirationDocument5 pagesClass 7 RespirationGopi SNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismDocument14 pages1.1 The Human Breathing Mechanismziah77No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory Systemkakai0.0No ratings yet
- Fa Ti MaDocument11 pagesFa Ti MaAmani KhalifehNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesThe Human Respiratory Systemkinarlituhayu4No ratings yet
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bio NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- B. Respiration System - Part 2Document15 pagesB. Respiration System - Part 2Helmi ZztNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument34 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEMmamyangie91No ratings yet
- Respiratory System 8Document32 pagesRespiratory System 8Naanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
Respiration
Respiration
Uploaded by
Lim Kai YeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration
Respiration
Uploaded by
Lim Kai YeeCopyright:
Available Formats
RESPIRATION Definition : a process in breaking of glucose ( food ) with the presence of oxygen to produce energy / oxidation of food process.
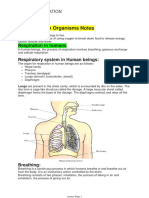
During respiration, humans obtain oxygen which at the same time remove carbon dioxide and water vapour through the respiratory system. Oxygen is obtains through breathing. HUMAN BREATHING MECHANISM
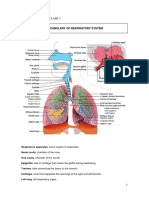
STRUCTURE NASAL CAVITY TRACHEA BRONCHUS BRONCHIOLE ALVEOLUS RIB CAGE LUNG
FUNCTION Air entering from the nostrils is led to the nasal cavity An airway through which respiratory air travels. The rings of cartilage within its walls keep the trachea open. Passage divided from trachea [ singular = bronchus, plural = bronchi ] A narrow tube inside the lungs that branches off the main air passages bronchi Place where exchange of gases take place To protect the lungs and help in breathing mechanism A respiratory organ
INTERCOSTAL MUSCLES Antagonistic muscles that help the movement of rib cage for breathing mechanism DIAPHRAGM A muscular membrane that separates the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity BREATHING MECHANISM INHALATION = a process when air is force into the lungs External intercostal muscle contract, while internal intercostal muscle relax Moves upwards and outwards Contract and become flat Volume increase Decrease Air from outside enters the lungs EXHALATION = a process when air is force out of the lungs External intercostal muscle relax, while internal intercostal muscle contract Move downwards and inwards Relax and become dome shape Volume decrease Increase Air is force out of the lungs
Intercostal muscle Rib cage Diaphragm Thoracic cavity Air pressure in the lung Air movement
You might also like
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 RespirationDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1 RespirationMohd HanisNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiDocument6 pagesNota Ringkas Sains Bab 1 RespirasiZuraina ShaharomNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument12 pagesRespirationjimmycrackle710No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1Document22 pagesChapter 1.1ieya_yNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemTeacher JoanNo ratings yet
- Respiration (Part 1)Document15 pagesRespiration (Part 1)Jessie Clarinda JoyceNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Aniket DasDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory System Aniket DasChep KepNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System (Autosaved)Document24 pagesThe Respiratory System (Autosaved)Judah RampersadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Respiratory PhysiologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory PhysiologyKingsley UdeajaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Metric 1rst ChapterDocument13 pages1.3 Metric 1rst ChapterDr. Mariam SahitoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument17 pagesRespiratory SystemMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Human Gas ExchangeDocument25 pages6.6 Human Gas ExchangeyousafNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumanDocument17 pagesGas Exchange in HumanGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory SystemM. Farkhan HabibNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument23 pagesGas Exchange in HumansVNo ratings yet
- bio 统一小考-chapter 8Document8 pagesbio 统一小考-chapter 822 Lee Xin Yong 李芯瑢No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System or Pulmonary SystemDocument53 pagesThe Respiratory System or Pulmonary Systemfharidaismail47No ratings yet
- DescriptionDocument2 pagesDescriptionGliane, Adrie Ann C.No ratings yet
- Breathing and Gaseous Exchnage by Sherrie-Ann Wilson-BrownDocument85 pagesBreathing and Gaseous Exchnage by Sherrie-Ann Wilson-BrownNayoka EnnisNo ratings yet
- Patho PneumoniaDocument26 pagesPatho PneumoniaRenz Ivan FuntilonNo ratings yet
- Respiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentDocument65 pagesRespiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Sistem PernapasanDocument18 pagesSistem PernapasanAgustinus SukurNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesHuman Respiratory Systempraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- C 2 The Respiratory StructureDocument34 pagesC 2 The Respiratory StructurefadlinlinsaiNo ratings yet
- Review of Anaphy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesReview of Anaphy and PhysiologyD A M N E R ANo ratings yet
- Notes On Respiratory System, Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 pagesNotes On Respiratory System, Gaseous Exchangeshelter musasaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesRespiratory SystemVanezaKateYeclaRetinioNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No YesDocument2 pagesGas Exchange: One (1.8 CM) Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yesapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture - 5 PDFDavid JokerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemcharamina13No ratings yet
- Topic 2.3 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 2.3 - Human Respiratory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument37 pagesGaseous ExchangeSolángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesLecture 1 Respiratory SystemArnelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Bio 2 ADocument31 pagesRespiratory System - Bio 2 A20181539No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumanDocument15 pagesGas Exchange in HumanNithika De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument18 pagesGas Exchange in Humans CAIE Biology IGCSEmilesdlaw4455No ratings yet
- Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesIngles Medico Ii - Clase 3: Vocabulary of Respiratory SystemAgustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse DefinitionDocument4 pagesRespiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse Definitionmiss RN100% (2)
- Respiratory2 0Document26 pagesRespiratory2 0api-258400031No ratings yet
- Biology ResppirationDocument2 pagesBiology ResppirationNeilson KesumaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Document36 pagesTopic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Respiratory Lab - TaggedDocument51 pagesLab 4 - Respiratory Lab - TaggedKimberly LeGalleyNo ratings yet
- Respiration & BreathingDocument18 pagesRespiration & BreathingKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Meri Bing Tugas RespiratoryDocument4 pagesMeri Bing Tugas RespiratoryNona MeyNo ratings yet
- Class 7 RespirationDocument5 pagesClass 7 RespirationGopi SNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismDocument14 pages1.1 The Human Breathing Mechanismziah77No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory Systemkakai0.0No ratings yet
- Fa Ti MaDocument11 pagesFa Ti MaAmani KhalifehNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesThe Human Respiratory Systemkinarlituhayu4No ratings yet
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bio NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- B. Respiration System - Part 2Document15 pagesB. Respiration System - Part 2Helmi ZztNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument34 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEMmamyangie91No ratings yet
- Respiratory System 8Document32 pagesRespiratory System 8Naanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet