Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transferred: Electrons Are
Transferred: Electrons Are
Uploaded by
monster40lbsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transferred: Electrons Are
Transferred: Electrons Are
Uploaded by
monster40lbsCopyright:
Available Formats
Ionic Bonding
Electrons are transferred
Electronegativity differences are
generally greater than 1.7
The formation of ionic bonds is
always exothermic!
Determination of
Ionic Character
Compounds are ionic
if they conduct
electricity in their
molten state
Electronegativity
difference is not the
final determination
of ionic character
Coulombs Law
19
1 2
(2.31 10 )
E x J nm
r
| |
=
|
\ .
The energy of interaction between a pair of
ions is proportional to the product of their
charges, divided by the distance between
their centers
1 2
QQ
E
r
| |
|
\ .
Table of
Ion Sizes
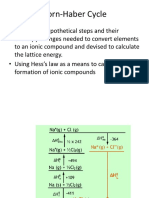
Estimate AH
f
for Sodium Chloride
Na(s) + Cl
2
(g) NaCl(s)
Lattice Energy -786 kJ/mol
Ionization Energy for Na 495 kJ/mol
Electron Affinity for Cl -349 kJ/mol
Bond energy of Cl
2
239 kJ/mol
Enthalpy of sublimation for Na 109 kJ/mol
Na(s) Na(g) + 109 kJ
Na(g) Na
+
(g) + e
-
+ 495 kJ
Cl
2
(g) Cl(g) + (239 kJ)
Cl(g) + e
-
Cl
-
(g) - 349 kJ
Na
+
(g) + Cl
-
(g) NaCl(s) -786 kJ
Na(s) + Cl
2
(g) NaCl(s) -412 kJ/mol
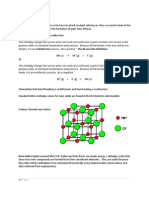
Sodium Chloride Crystal Lattice
Ionic compounds form
solid crystals at ordinary
temperatures.
Ionic compounds organize
in a characteristic crystal
lattice of alternating
positive and negative ions.
All salts are ionic compounds and form crystals.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Structure: Crystalline solids
Melting point: Generally high
Boiling Point: Generally high
Electrical
Conductivity:
Excellent conductors,
molten and aqueous
Solubility in
water:
Generally soluble
You might also like
- Neurotransmitter ChartDocument1 pageNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- Schizophrenia PowerpointDocument53 pagesSchizophrenia Powerpointmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Electrolytic CellsDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY - Electrolytic CellsCherry EmbateNo ratings yet
- Chem 586 C 3Document15 pagesChem 586 C 3Mohammed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- CHEM1100F23 Ch5 Notes Pt2Document26 pagesCHEM1100F23 Ch5 Notes Pt2Adeyinka OluyoleNo ratings yet
- EAMCET QR Chemistry JR Chem 3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42 71Document25 pagesEAMCET QR Chemistry JR Chem 3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42 71pvnchem67% (3)
- Chemical Bonding New PDFDocument52 pagesChemical Bonding New PDFAniruddha KawadeNo ratings yet
- H - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice EnergyDocument31 pagesH - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice Energysepti handayaniNo ratings yet
- Born Haber CycleDocument15 pagesBorn Haber CyclefayNo ratings yet
- 15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyDocument14 pages15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyZara BrookesNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding: A Guide For A Level StudentsDocument86 pagesStructure and Bonding: A Guide For A Level StudentshaidarNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesDocument10 pagesTopic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesHenry SupriNo ratings yet
- Iconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistDocument12 pagesIconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistKingson_786No ratings yet
- Ch07 2 LatticeEnergyDocument9 pagesCh07 2 LatticeEnergyBRUNO RAMOS DE LIMANo ratings yet
- chemmmDocument9 pageschemmmAnîl RåjpütNo ratings yet
- 15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsDocument16 pages15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsGiselle PeachNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsDocument9 pagesIonic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsAnastasia ErshNo ratings yet
- Tema 3. Chemical BondingDocument68 pagesTema 3. Chemical Bondingkarthik tvkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (L-1) JLD 3.0Document69 pagesChemical Bonding (L-1) JLD 3.0Ayush BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42-71Document25 pages3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42-71eamcetmaterials63% (8)
- GE SEM II Ionic BondingDocument21 pagesGE SEM II Ionic BondingSubhradeep MistryNo ratings yet
- Lattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration EnthalpyDocument8 pagesLattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration Enthalpyzubair0% (1)
- Chemical Bonding PDFDocument68 pagesChemical Bonding PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 04 20 2023 LQWDocument30 pagesLecture 20 04 20 2023 LQWAle Hernández MoyersNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding I: Basic ConceptsDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding I: Basic ConceptsstephensreenivasulutNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Chapter - 2Document41 pagesClass 10 - Chapter - 2Nitin SNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument176 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYgsvssumaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Model Lecture 1Document28 pagesIonic Model Lecture 1espanholdNo ratings yet
- Ch09 (Ikatan Kimia) (Compatibility Mode)Document12 pagesCh09 (Ikatan Kimia) (Compatibility Mode)IvanNo ratings yet
- 15 BHaberppDocument22 pages15 BHaberppJigna BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - NotesDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry - Notesn611704No ratings yet
- Chem - MIST Sec A - Chem BondingDocument102 pagesChem - MIST Sec A - Chem BondingRakib HaqueNo ratings yet
- sch3u7-bornhaberDocument15 pagessch3u7-bornhaberpriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument68 pagesChemical BondingHarsh Tyagi100% (2)
- Energi Kisi Dan Born HaberDocument31 pagesEnergi Kisi Dan Born HaberNovi CherlyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09. 28122020 E&MEDocument41 pagesLecture 09. 28122020 E&MEMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry (Final) - 01-TheoryDocument35 pagesElectro Chemistry (Final) - 01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument40 pagesElectrochemistryakshaysinghofficial007No ratings yet
- CM1502 Chapter 3 2013-14Document51 pagesCM1502 Chapter 3 2013-14Minh TieuNo ratings yet
- Chem1 Module8Document23 pagesChem1 Module8carlgavinsletartigasNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Chemical Bonding Molecular Structure STUDDocument35 pagesChapter7 Chemical Bonding Molecular Structure STUDCristian Menéndez FernándezNo ratings yet
- 3 Electro Chemistry 1Document40 pages3 Electro Chemistry 1Kalpana BidhanNo ratings yet
- Chemist Chapter 3Document11 pagesChemist Chapter 3Emelia DeeNo ratings yet
- Inorg 2 - Tut 1 - 2018 - MemoDocument4 pagesInorg 2 - Tut 1 - 2018 - MemoStolo SbaeNo ratings yet
- 03d - Lattice Energi (Uo)Document21 pages03d - Lattice Energi (Uo)Oktanio PraviakoNo ratings yet
- 03d - LATTICE ENERGI (Uo)Document21 pages03d - LATTICE ENERGI (Uo)Oktanio PraviakoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Jan13Document89 pagesChapter 8 Jan13kumutha100% (1)
- 2 Electrochemistry (Electrolytic Cells)Document45 pages2 Electrochemistry (Electrolytic Cells)Gerald Paul SumagpaoNo ratings yet
- 3-ElectrochemistryDocument54 pages3-Electrochemistryshivcr73No ratings yet
- B CyclesDocument21 pagesB CyclesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- Born Haber CycleDocument16 pagesBorn Haber CyclePartha SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Structure: Unit - 3Document24 pagesChemical Bonding and Structure: Unit - 3nahomNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapt7 PDFDocument21 pages4 Chapt7 PDFArunKumarNo ratings yet
- From Last Class: Interatomic BindingDocument27 pagesFrom Last Class: Interatomic BindingPo KaiNo ratings yet
- Bonding in SolidsDocument24 pagesBonding in SolidsMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument2 pages4 PDFChutneyc4064No ratings yet
- 01 Chemical Bonding 1Document15 pages01 Chemical Bonding 1gymnast1No ratings yet
- Atomic Stucture and BondingDocument20 pagesAtomic Stucture and BondingLee Warren Teguh NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument7 pagesChemical EnergeticsRaiyan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Psych 327 #15807 Sec 01 SchlussmanDocument6 pagesPsych 327 #15807 Sec 01 Schlussmanmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Psych 327 #11955 Sec 02 Schnieder - 0001Document8 pagesPsych 327 #11955 Sec 02 Schnieder - 0001monster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Dishwasher: 24 Hours A Day, 7 Days A Week For LG Customer ServiceDocument48 pagesDishwasher: 24 Hours A Day, 7 Days A Week For LG Customer Servicemonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07-IntelligenceDocument91 pagesChapter 07-Intelligencemonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Motivation and EmotionDocument56 pagesMotivation and Emotionmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- 10 Memory: Reconstructing The Past The Biology of MemoryDocument60 pages10 Memory: Reconstructing The Past The Biology of Memorymonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Cook Handout AppendixDocument22 pagesCook Handout Appendixmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Depression: WWW - Bradfordvts.co - UkDocument28 pagesDepression: WWW - Bradfordvts.co - Ukmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Development, Maturation, Aging, and Death: Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Long, Monroe Community CollegeDocument62 pagesDevelopment, Maturation, Aging, and Death: Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Long, Monroe Community Collegemonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- By: Margaret Wise Brown Adapted By: Jessie Moreau, M.Ed., NBCTDocument18 pagesBy: Margaret Wise Brown Adapted By: Jessie Moreau, M.Ed., NBCTmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Cognition and Emotion: November 13-20, 2008Document90 pagesCognition and Emotion: November 13-20, 2008monster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Understanding Psychology: The Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument79 pagesUnderstanding Psychology: The Biological Basis of Behaviormonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Physiological Mechanism of RegulationDocument11 pagesPhysiological Mechanism of Regulationmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- 9.00 Exam 3 Notes: Please Pardon Any Spelling Errors or Typos!Document9 pages9.00 Exam 3 Notes: Please Pardon Any Spelling Errors or Typos!monster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Powerpoint With Extra SlidesDocument111 pagesChapter 5 Powerpoint With Extra Slidesmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDocument50 pagesLecture 9 - Inductive and Deductive Reasoningmonster40lbs0% (1)
- Visual Attention PartDocument3 pagesVisual Attention Partmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Module3 - Psychology PowerpointDocument12 pagesModule3 - Psychology Powerpointmonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- L Basic Neuroscience Lecture 13Document17 pagesL Basic Neuroscience Lecture 13monster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet For 9 - 27Document2 pagesLearning Worksheet For 9 - 27monster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Emotion RegulationDocument53 pagesEmotion Regulationmonster40lbs100% (1)
- A Bitter EndingDocument15 pagesA Bitter Endingmonster40lbsNo ratings yet