Professional Documents
Culture Documents
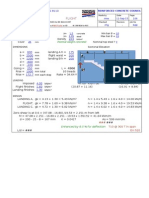
RC03 Bending1
RC03 Bending1
Uploaded by
Rodel Millondaga VenegasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RC03 Bending1
RC03 Bending1
Uploaded by
Rodel Millondaga VenegasCopyright:
Available Formats
Strength of Rectangular Section in Bending
3
3
Floor Framing System
Load Transferred to Beam from Slab
Continuous Beams and One-way Slabs
Bending Moment Envelopes
ACI Moment and Shear Coefficients
Reinforced Concrete Design
Reinforced Concrete Design
Mongkol JIRAVACHARADET
S U R A N A R E E INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
Columns
Stair
Stringer
Floor beam or Girder
Joist
Spandrel
Floor Framing System Floor Framing System
Layout of Beams and Columns
- Occupancy requirements
- Commonly used beam size
- Ceiling and services requirements
To transfer vertical loads on the floor to the beams and columns in a
most efficient and economical way
Loading on Beams Loading on Beams
Tributary area = Area for which the beam is supporting
One-way Floor System (m =S/L < 0.5)
wS kg/m
B1 Loading
Load from B1
B3 Loading
B1 = Secondary Beam
B3 = Primary Beam
If span of B3 is too large, more secondary beam may be used.
C1
B1
B2
B3
S
L
Floor load w kg/m
2
Tributary area
Tributary area = 0.5SL sq.m
Load on beam = 0.5wSL kg/m
Floor load = w kg/sq.m
Precast Concrete Slab
C1
B2
B3
S
L
Long span (AB):
Floor load = w kg/sq.m
Tributary area = SL/2 - S
2
/4 = sq.m
Load on beam kg/m
m
m S 2
4
2
2
3
3
2
m wS
Short span (BC):
Floor load = w kg/sq.m
Tributary area = S
2
/4 sq.m
Load on beam = wS/4 wS/3 kg/m
Two-way Slab
45
o
45
o
45
o
45
o
A
D C
B
S
L
Span ratio m = S/L
B
C
B
C
v.
v.
.aa
.aa
aa
aa
u.a4 +n+Jv
u.a4 +n+Jv
s+
s+
av+vuvaa
av+vuvaa
.v+. - a.......a aa+lr+v
..a.- a+.- .va!-. .- : va a..a
...v:...a..a+...a+ ..+.a...a+.+..
.-::a...v...a a ....
....a.... +aa:.+ua+.+.. ..a ....+
aa . . : . a ::
+.a .+v ........ :. ..a- s vv vu
vuvu. u.+a...va. a.-!.a
CONTINUOUS BEAMS AND SLABS CONTINUOUS BEAMS AND SLABS
Methods of Analysis: Methods of Analysis:
w
L
w
L
w
L
w
L
SHEAR: SHEAR:
MOMENT: MOMENT:
- - Exact analysis: Exact analysis: slope slope- -deflection, moment distribution deflection, moment distribution
- - Approximate analysis: Approximate analysis: ACI shears and moments coefficients ACI shears and moments coefficients
- - Computer: Computer: MicroFEAP, Grasp, SUTStructor, STAAD.Pro, SAP2000 MicroFEAP, Grasp, SUTStructor, STAAD.Pro, SAP2000
LOAD PATTERNS (Live Load) LOAD PATTERNS (Live Load)
Use influence lines for determining load patterns that will give Use influence lines for determining load patterns that will give
the maximum shear force and bending moment the maximum shear force and bending moment
Load pattern for max. positive moment at A Load pattern for max. positive moment at A
A
Influence line for moment at A Influence line for moment at A
Influence line for moment at B Influence line for moment at B
B
Load pattern for max. negative moment at B Load pattern for max. negative moment at B
LOAD PATTERN IN FRAME LOAD PATTERN IN FRAME
Frame Example: Frame Example:
Maximum +M at point B Maximum +M at point B
Draw qualitative Draw qualitative
influence lines influence lines
Resulting pattern load: Resulting pattern load:
checkerboard pattern checkerboard pattern
Arrangement of Live Loads
Arrangement of Live Loads
ACI 318 ACI 318- -05 Sec. 8.9.2: 05 Sec. 8.9.2:
It shall be permitted to assume that the arrangement of live loa It shall be permitted to assume that the arrangement of live load is limited d is limited
to combinations of: to combinations of:
Factored dead load on all spans with full factored live load o Factored dead load on all spans with full factored live load on n
two adjacent spans. two adjacent spans.
Factored dead load on all spans with full factored live load on
alternate spans.
Moment Envelopes
Moment Envelopes
The moment envelope curve The moment envelope curve
defines the extreme boundary defines the extreme boundary
values of bending moment values of bending moment
along the beam due to critical along the beam due to critical
placements of design live placements of design live
loading. loading.
Moment Envelopes
Moment Envelopes
DL DL
LL LL
Given following beam with a dead load of 1
Given following beam with a dead load of 1
t/m
t/m
and
and
live load 2
live load 2
t/m
t/m
obtain the shear and bending moment
obtain the shear and bending moment
envelopes
envelopes
Moment Envelopes Example
Moment Envelopes Example
6 m 6 m
C C
B B
6 m 6 m
A A
Moment Envelopes Example
Moment Envelopes Example
Shear Diagram Shear Diagram
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
20
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
ft
k
i
p
s
Moment Diagram Moment Diagram
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
ft
k
-
f
t
CASE 1 : DL(full) + LL(full) CASE 1 : DL(full) + LL(full)
6 m 6 m
C C
B B
6 m 6 m
A A
DL DL
LL LL
Moment Envelopes Example
Moment Envelopes Example
CASE 2 : DL(full) + LL(half) CASE 2 : DL(full) + LL(half)
6 m 6 m
C C
B B
6 m 6 m
A A
DL DL
LL LL
Shear Diagram Shear Diagram
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
ft
k
i
p
s
Moment Diagram Moment Diagram
-200
-150
-100
-50
0
50
100
150
200
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
ft
k
-
f
t
The shear envelope
The shear envelope
Shear Envelope
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
0 10 20 30 40
ft
k
i
p
s
Minimum Shear
Maximum Shear
Moment Envelopes Example
Moment Envelopes Example
Moment Envelopes Example
Moment Envelopes Example
The moment envelope
The moment envelope
Moment Envelope
-300
-200
-100
0
100
200
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
ft
k
-
f
t
Minimum Moment Maximum Moment
.:
.:
v...a
v...a
+....a+.a.....a!+.u..aa....
+....a+.a.....a!+.u..aa....
+vv
+vv
.
.
:rrv...
:rrv...
.
.
rrv'u
rrv'u
:
:
:r.rv|eu::e
:r.rv|eu::e
|err.ev:r:.v':.v
|err.ev:r:.v':.v
.c
.c
uv-v..e:.e:a..:rr
uv-v..e:.e:a..:rr
v-v.':.v
v-v.':.v
.
.
.rrav-vurrr
.rrav-vurrr
arar:eve:.uvur:-v.err
arar:eve:.uvur:-v.err
ACI Approximated Coefficients for Moments and Shears ACI Approximated Coefficients for Moments and Shears
o+.++n +c.+ r|:.:v..e:...av|ere:u:ertra c.
(o, r.rvou.o
+) rvrue
ue':.a.va':eu. eau w
u
l
n
2
/11
ue':.a.va-ea.uv.va.evu.eau w
u
l
n
2
/14
.) rvrv w
u
l
n
2
/16
(r, r.rvoau
+) |:.:v.eurrauvara.eau.v..
.:a: . r w
u
l
n
2
/9
.:a:: . r w
u
l
n
2
/10
.) |:.:v.eurraura.eau.vav w
u
l
n
2
/11
(r, r.rvoau (oa,
.) |:.:v.eurraura.eaur.-e-u
n vr:r':.v ..cc :. w
u
l
n
2
/12
rvr:a.eve.n.vera.e.arv a w
u
l
n
2
/12
+) |:.:v.eurrauvra.eau.:r-ea.uv.va.eu.eau
.:a.eau.uvrvrau w
u
l
n
2
/24
.:a.eau.uv.e w
u
l
n
2
/16
(o, a.+.aav
+) ...avrrauvara.eau.v. 1.15 w
u
l
n
/2
.) ...avrraura.eau.av w
u
l
n
/2
(a, o+voa.va+r+oo.+aa+u.+
.eau.uvrvrau.
1/24 1/14
ue':.a.va':e.
0 1/11
.eau.uv.e.
1/16 1/14 1/10 1/11 1/16 1/11 1/11
rvrau(s,a--.)
.eau.uvrvrau
.eau.uv.e
o+vav.uvo va+
.eau
.eau .eau
.e.uv.eau
o+vnao
(b, o+voa.va+aa+u.+
.eau.uvrvrau.
1/24 1/14
ue':.a.va':e.
0 1/11
.eau.uv.e.
1/16 1/14 1/9 1/9 1/14 1/16
(c, uvu.+a+.Ir.ov c .ro.
1/12 1/14 1/12 1/12 1/16 1/12 1/12
(d, o+vz+oa..raou.va.a+r+oo.+ e .n+ra+oa..raou.vao+v
1/12 1/14 1/12 1/12 1/16 1/12 1/12
Ex3.1: A two span beam is supported by spandrel beams at the outer edges and by
a column in the center. Dead load (including beam weight) is 1.5 t/m and live load is
3 t/m on both beams. Calculate all critical service-load shear forces and bending
moments for the beams. The torsional resistance of the spandrel beam is not
sufficient to cause restraint of beam ABC at the masonry walls.
Masonry
Wall
Masonry
Wall
A B C
C
L
D
C
L
E
6 m 6.5 m
Check conditions (a) Loads are uniformly distributed,
(b) LL/DL = 3/1.5 = 2 < 3,
(c) (L
2
L
1
)/L
1
= (6.5 6)/6 = 0.083 < 0.2
B B
Bending Moments M
AB
= -4.5(6)
2
/24 = -6.75 t-m, M
BA
= -4.5(6.25)
2
/9 = -19.5 t-m,
M
CB
= -4.5(6.5)
2
/24 = -7.92 t-m, M
BC
= -4.5(6.25)
2
/9 = -19.5 t-m,
M
D
= 4.5(6)
2
/11 = 14.7 t-m, M
E
= 4.5(6.5)
2
/11 = 17.3 t-m
Masonry
Wall
Masonry
Wall
A B C
C
L
D
C
L
E
6 m 6.5 m
B B
Shear Forces
V
A
= 4.5(6)/2 = 13.5 tons, V
B
= 1.15(4.5)(6)/2 = 15.5 tons,
V
C
= 4.5(6.5)/2 = 14.6 tons, V
B
= 1.15(4.5)(6.5)/2 = 16.8 t-m
Reactions
R
A
= V
A
= 13.5 tons,
R
B
= V
B
+ V
B
= 15.5 + 16.8 = 32.3 tons,
R
C
= V
C
= 14.6 tons
Gravity & Lateral loads on Portal Frame
Gravity & Lateral loads on Portal Frame
W
L R
L R
Portal frame subjected to gravity loads:
L
R
L
R
Portal frame subjected to lateral loads:
Rigid frame deflections
Rigid frame deflections
forces and deformations caused by external shear
Bending Moment in Column & Beam Bending Moment in Column & Beam
You might also like
- Isimba - A Church Management System For STDocument22 pagesIsimba - A Church Management System For STAllan Credo100% (3)
- Chapter 9 TestbankDocument34 pagesChapter 9 Testbankvx8550_373384312100% (5)
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsFrom EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For MV Power Cables & Accessories InstallationDocument9 pagesMethod Statement For MV Power Cables & Accessories InstallationAdil HasanovNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Example 2 2Document76 pagesAppendix A Example 2 2魏学军No ratings yet
- Chapter Three, Yeild Line Analysis 2Document8 pagesChapter Three, Yeild Line Analysis 2Helen NegashNo ratings yet
- Design of Continuous Beams PDFDocument4 pagesDesign of Continuous Beams PDFBlend DlerNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab DesignDocument16 pagesTwo Way Slab DesignAsif Rahman100% (2)
- End Length OffsetsDocument5 pagesEnd Length OffsetsvardogerNo ratings yet
- Load Distribution From Slab To BeamsDocument18 pagesLoad Distribution From Slab To BeamsMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Important Parts of Culvert DesignDocument6 pagesImportant Parts of Culvert DesignER Rajesh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete FoundationsDocument10 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete FoundationsVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab Design SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesTwo Way Slab Design SpreadsheetLikhon Biswas0% (1)
- Two Way Slab AnalysisDocument58 pagesTwo Way Slab AnalysisBaloch Khan100% (1)
- Design of Concrete & Masonry Structures: Dr. Ye Lu Lecture #7-2 (Week 7)Document20 pagesDesign of Concrete & Masonry Structures: Dr. Ye Lu Lecture #7-2 (Week 7)tien2506onlineNo ratings yet
- Flat Slab DesignDocument2 pagesFlat Slab DesignKim ChanthanNo ratings yet
- Design ExamplesDocument12 pagesDesign ExamplesBrajesh Suman100% (1)
- BridgesDocument40 pagesBridgesAnonymous jLLjBdr100% (1)
- Abutment Design CalculationsDocument12 pagesAbutment Design CalculationsFlexing Thony100% (1)
- Loads and Forces Acting On Retaining Wall and Their CalculationsDocument7 pagesLoads and Forces Acting On Retaining Wall and Their Calculationsswapnil0% (1)
- 2.4 Design ConsiderationsDocument23 pages2.4 Design ConsiderationsglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Slab Design NoteDocument112 pagesSlab Design NoteBeza Getachew100% (1)
- Advanced Foundation AssignmentDocument15 pagesAdvanced Foundation AssignmentafewerkNo ratings yet
- Hollow Pot Design WorksheetDocument7 pagesHollow Pot Design Worksheetpatrick chegeNo ratings yet
- 14792060Document102 pages14792060layaljamal2No ratings yet
- Moment Distribution Method - PDF Structure Chapter 3Document86 pagesMoment Distribution Method - PDF Structure Chapter 3Adlina AifaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 - Analysis of Wind Load Lecture-OneDocument121 pagesChapter-4 - Analysis of Wind Load Lecture-OneTadesse Megersa100% (1)
- Lecture 5 Structural Steel Design MuDocument23 pagesLecture 5 Structural Steel Design MuPenelope MalilweNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Two Way SlabsDocument18 pagesBehavior of Two Way Slabsnirmal sutharNo ratings yet
- Beam Column ConnectionDocument10 pagesBeam Column Connectionmaniram7No ratings yet
- Building Story Drift in ETABS PDFDocument10 pagesBuilding Story Drift in ETABS PDFntirugiribambeNo ratings yet
- 10.4 The Moment Distribution Method For FramesDocument14 pages10.4 The Moment Distribution Method For FramesZairah Ann BorjaNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Retaining Wall - Design CalculationDocument50 pagesCantilever Retaining Wall - Design CalculationMuhammadWazimAkram100% (1)
- Lecture3 - Shallow Foundation IDocument89 pagesLecture3 - Shallow Foundation IChris Adaminovic100% (1)
- Bridge Beam DesignDocument8 pagesBridge Beam DesignAnonymous KQtFm3No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of RCC Box Culvert PDFDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Design of RCC Box Culvert PDFDen Oghangsomban67% (3)
- Prepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum FekheraldinDocument55 pagesPrepared BY Dr. Mohammed Kadhum Fekheraldinhemantkle2uNo ratings yet
- One Way Solid Slab DesignDocument26 pagesOne Way Solid Slab DesignJohn Mejia50% (4)
- RCC71 Stair Flight & Landing - SingleDocument4 pagesRCC71 Stair Flight & Landing - SingleKourosh KhalpariNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Analysis of Flanged Section (Ec2)Document20 pagesTopic 2 - Analysis of Flanged Section (Ec2)RCdesign201267% (3)
- Effect of Eccentricity On Analysis and Design of Isolated FootingsDocument20 pagesEffect of Eccentricity On Analysis and Design of Isolated FootingsAlexandros PapamarinopoulosNo ratings yet
- 5 Numerical On Design of Beam Subjected To TorsionDocument17 pages5 Numerical On Design of Beam Subjected To TorsionAshok Kumar RajanavarNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure of BeamsDocument6 pagesDesign Procedure of Beamsavalaxcia100% (3)
- PROKON Structural Analysis and DesignDocument9 pagesPROKON Structural Analysis and Designmanhal alnoaimy100% (1)
- Structural Design-Strip MethodDocument22 pagesStructural Design-Strip Methodgirma kebedeNo ratings yet
- Lect2 - 1 11 2011 PDFDocument62 pagesLect2 - 1 11 2011 PDFgendadeyu552625100% (1)
- Unconfined Compression Test & Foundation DesignDocument4 pagesUnconfined Compression Test & Foundation DesignmahrbhojiaNo ratings yet
- One Way Slab - NptelDocument25 pagesOne Way Slab - Npteljindal_bharatNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall - BS8110-97-007Document4 pagesShear Wall - BS8110-97-007Kavin TamNo ratings yet
- RectangularTanks PCADocument61 pagesRectangularTanks PCAvictorcivNo ratings yet
- Design of Strip FootingDocument8 pagesDesign of Strip FootingJaime Manalili Landingin0% (1)
- Flat SlabDocument10 pagesFlat SlabPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- RC03 Bending1Document12 pagesRC03 Bending1lavyNo ratings yet
- Beam Design ThumbruleDocument5 pagesBeam Design ThumbrulehipreyashNo ratings yet
- Pile To Slab Bridge Connections: Mohamed I. Ayoub, David H. Sanders and Ahmed IbrahimDocument10 pagesPile To Slab Bridge Connections: Mohamed I. Ayoub, David H. Sanders and Ahmed IbrahimIsom Bahri BahriNo ratings yet
- "Towerplus": A Software Programme Developed To Assist High Voltage Transmission Line DesignDocument4 pages"Towerplus": A Software Programme Developed To Assist High Voltage Transmission Line DesignAdiputra Satria100% (1)
- Eg2002 Design Task OutlineDocument8 pagesEg2002 Design Task OutlineArshad BhoyrooNo ratings yet
- Transmission MonopoleDocument71 pagesTransmission Monopolepavithra2796% (23)
- STRAP Vehicle Loading - Bridge ModuleDocument18 pagesSTRAP Vehicle Loading - Bridge ModuleErnest MufhadiNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of The Tower CraneDocument4 pagesFinite Element Analysis of The Tower CraneGogyNo ratings yet
- Power Electrical Past PaperDocument5 pagesPower Electrical Past PaperNadeesha BandaraNo ratings yet
- Revised Timetable C.E Engr LGDocument2 pagesRevised Timetable C.E Engr LGMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Notification Age Relaxation 2023Document1 pageNotification Age Relaxation 2023Mudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Pre QualificationDocument32 pagesPre QualificationMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Continuous Beams: Numerical DataDocument3 pagesContinuous Beams: Numerical DataMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Civil EngineeringDocument10 pagesCivil EngineeringMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Load Distribution From Slab To BeamsDocument18 pagesLoad Distribution From Slab To BeamsMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Bending Moments in BeamsDocument19 pagesBending Moments in BeamsMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever SlabsDocument2 pagesDesign of Cantilever SlabsMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Design of Rectangular Beams and One-Way SlabsDocument9 pagesChapter - 3: Design of Rectangular Beams and One-Way SlabsMudasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Gayatri MantraDocument2 pagesGayatri MantraAnandh ShankarNo ratings yet
- Joaquin E. David v. Court of Appeals and People of The Philippines, G.R. Nos. 111168-69. June 17, 1998Document1 pageJoaquin E. David v. Court of Appeals and People of The Philippines, G.R. Nos. 111168-69. June 17, 1998Lemrose DuenasNo ratings yet
- Solid Edge Mold ToolingDocument3 pagesSolid Edge Mold ToolingVetrivendhan SathiyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- It 429 - Week 11Document11 pagesIt 429 - Week 11mjdcan_563730775No ratings yet
- Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthDocument2 pagesSworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthKal El DadiNo ratings yet
- Solved Examples: Axes-Zz and - YyDocument8 pagesSolved Examples: Axes-Zz and - YyDeepak SahNo ratings yet
- Kapandji TrunkDocument245 pagesKapandji TrunkVTZIOTZIAS90% (10)
- Shashikala SummaryDocument2 pagesShashikala SummaryKhushbakht FarrukhNo ratings yet
- 1999 Aversion Therapy-BEDocument6 pages1999 Aversion Therapy-BEprabhaNo ratings yet
- ProsidingDocument13 pagesProsidingAlfi Amalia S.E.I, M.E.INo ratings yet
- Vikram-Betal Case StudyDocument5 pagesVikram-Betal Case StudyRavi SawantNo ratings yet
- Chromium-Induced: Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChromium-Induced: Kidney DiseaseBitew KassawNo ratings yet
- Hockey Fans Loved It, But Residents, Businesses Disagree On Costs, Benefits of Winter Classic'Document8 pagesHockey Fans Loved It, But Residents, Businesses Disagree On Costs, Benefits of Winter Classic'fenwaynewsNo ratings yet
- MLR LLRDocument41 pagesMLR LLRKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHNNo ratings yet
- FIELD Study 6 - On Becoming A 21 Century Teacher # 1Document73 pagesFIELD Study 6 - On Becoming A 21 Century Teacher # 1John Patrick ArciteNo ratings yet
- F5 Exam Report June 2012Document3 pagesF5 Exam Report June 2012Muhammad Khaleel RashidNo ratings yet
- Report of Micro Project (2) - 1Document8 pagesReport of Micro Project (2) - 1ythNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans For English Form 5Document2 pagesLesson Plans For English Form 5Hajar Binti Md SaidNo ratings yet
- Wepik Strengthening Digital Defenses An in Depth Exploration of Cyber Security 20231121043209BlIPDocument12 pagesWepik Strengthening Digital Defenses An in Depth Exploration of Cyber Security 20231121043209BlIPsuchdev darshanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Metabolite Concentration ( - )Document2 pagesQuestion Bank: Metabolite Concentration ( - )Kanupriya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Intelligence Test: Three YearsDocument4 pagesIntelligence Test: Three YearsAnshuman TewaryNo ratings yet
- Staircase Lift Design For Elderly at HomeDocument19 pagesStaircase Lift Design For Elderly at Homesabareesh91mechNo ratings yet
- Cordlife BrochureDocument16 pagesCordlife BrochureMelodie YlaganNo ratings yet
- Tide Times and Tide Chart For Dammam PDFDocument8 pagesTide Times and Tide Chart For Dammam PDFAnonymous g5nMjONo ratings yet
- Perlengkapan Bayi Ellena and FamilyDocument9 pagesPerlengkapan Bayi Ellena and FamilyintanchairranyNo ratings yet
- Skullcandy Case Study - Part OneDocument8 pagesSkullcandy Case Study - Part OneUthmanNo ratings yet
- Herbert Morrison BooklistDocument2 pagesHerbert Morrison BooklistGillian HallNo ratings yet