Professional Documents
Culture Documents
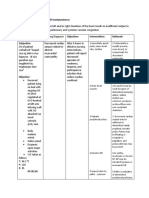
Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Kimberly SolisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
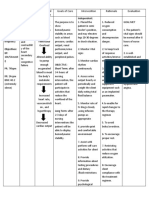
Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Kimberly SolisCopyright:
Available Formats
Cues: Subjective/ Objective Snanghihina nga ako at medyo nahihirapang huminga, as verbalized by the patient.
Background of the disease Decreased ventricular contraction
Nursing diagnosis
Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Decreased cardiac output related to
Goal To demonstrate hemodynamic stability including blood pressure, cardiac output, renal perfusion/urine output, and peripheral pulses.
Independent: 1. Place patient in semifowlers position, and may elevate legs 20-30 degrees in shock situation 2. Monitor vital signs -to note response to activities/ interventions 3. Monitor cardiac rhythm continuously -to note effectiveness of medications and/or -decreases oxygen consumption and risk of decompression.
Goal partially met
After 8 hours of nursing interventions the patient was able report decrease episodes of dyspnea, and angina. Dysarythmias were still evident when
Ventricular overload
altered afterload and
Altered ability to pump
contractility of the heart secondary to congestive heart failure
O- difficulty of breathing -orthopnea -edema on both feet -decreased peripheral pulse -crackles Vital signs: RR -24 cpm
enough oxygenated blood to meet the bodys metabolic requirements
Objectives After 8 hours of nursing interventions,
assistive devices like implanted pacemaker
increased heart rate, vasoconstricti on, and
the patient will be able: a. Report/ demonstrate
4. Assess urine output hourly or periodically and weigh the client daily noting total fluid
-to allow for timely alterations on therapeutic regimen
auscultated. The patient had an increase on
HR -121 bpm
hypertrophy
decrease episodes of
balance 5. Monitor rate of IV drugs closely, using infusion pumps as appropriate 6. Provide quiet and comfortable environment 7. Assist with or perform self-care activities for client -to limit activities that will decrease oxygen consumption 8. Provide information about testing procedures and dietary/fluid restrictions 9. Provide psychological support. Maintain a calm attitude but admit concerns if questioned by client -to promote client participation on the therapeutic regimen -honesty can be reassuring when so much activities and worry are apparent to the client. -to promote adequate rest. -to prevent bolus/overdose
activity tolerance and participates in activities that reduce cardiac workload. RR 22 cpm HR 112 bpm
decreased cardiac output
dyspnea, angina and dysarythmia b. Demonstrate an increase in activity tolerance c. Verbalize knowledge of the disease process, individual risk factors and treatment plan d. Participate in activities that reduce workload of the heart.
Dependent: 1. Administer oxygen via nasal cannula or mask -to increase oxygen available for
as indicated
cardiac function and tissue perfusion
2. Administer fluid replacement, antibiotics and/or diuretics as indicated
-to prevent or alleviate the symptoms of fluid retention
3. Administer analgesics
-to promote comfort/rest
You might also like
- Wiley - Chemical Engineering in The Pharmaceutical Industry - Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, 2nd Edition - 978-1-119-28586-1 PDFDocument2 pagesWiley - Chemical Engineering in The Pharmaceutical Industry - Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, 2nd Edition - 978-1-119-28586-1 PDFsameer sahaan0% (1)
- Silicones&Sulfates - Smart Usage Manual - (2023)Document28 pagesSilicones&Sulfates - Smart Usage Manual - (2023)Alifia AzhaaraNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure NCPDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure NCPShaira Ann Calamba100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureRalph Dumawaa60% (5)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeMei Payumo100% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocument2 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planmanu_gutierrez0891% (11)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To Cardiomyopathywen_pil75% (8)
- Myocarditis NCP 2Document8 pagesMyocarditis NCP 2astro_aaron117375% (4)
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 pagesCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- NCP For CHFDocument11 pagesNCP For CHFqingwen100% (5)
- NCP - Obstructive JaundiceDocument8 pagesNCP - Obstructive JaundiceWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- NCP: DysrhythmiasDocument12 pagesNCP: DysrhythmiasJavie100% (3)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypertension Nursing Care Plangeng gengNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathySoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- NCP AfDocument3 pagesNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotNo ratings yet
- NCP For CHFDocument2 pagesNCP For CHFMayet De Castro Lejano100% (1)
- Cu10-April 9Document2 pagesCu10-April 9kuu faalNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument3 pagesNCP For Acute Coronary Syndromesarahtot75% (4)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEsther RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess NCPAfia TawiahNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarNo ratings yet
- CHF NCPDocument8 pagesCHF NCPZy Hallasgo100% (1)
- NCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument22 pagesNCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeAnnNo ratings yet
- NCP CHFDocument2 pagesNCP CHFaldrin1920No ratings yet
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeJ.G RNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- NCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- NCP Leptospirosis - NewDocument5 pagesNCP Leptospirosis - Newglaiza_requintoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP CHFDocument10 pagesNCP CHFMykel Jake VasquezNo ratings yet
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDocument5 pagesNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- NCP For Dizziness and HeadacheDocument4 pagesNCP For Dizziness and Headachekarthi karthi100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument4 pagesNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam - NP5Document19 pagesDiagnostic Exam - NP5ogiskuadzNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisKian Herrera100% (1)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 pagesFluid Volume ExcessChristine Quirona100% (1)
- Day 1 Patient's Name: Mr. X Age: 61 Address: Larap, Jose Panganiban, Camarines Norte Date / Time Focus Data, Action, Response Chest PainDocument4 pagesDay 1 Patient's Name: Mr. X Age: 61 Address: Larap, Jose Panganiban, Camarines Norte Date / Time Focus Data, Action, Response Chest PainJulliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationsweethoney220% (1)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeTrixia CamporedondoNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity Intolerance (HTN Crisis)Document3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerance (HTN Crisis)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For Infection - DMDocument3 pagesNCP - Risk For Infection - DMcessi18100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanAsylla PajijiNo ratings yet
- NCP BeeaDocument3 pagesNCP BeeaKiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- 1-!nursing Diagnosis:: Myocardial Infarction As Evidenced by Reports of Chest Pain With Radiation in Bilateral ArmDocument3 pages1-!nursing Diagnosis:: Myocardial Infarction As Evidenced by Reports of Chest Pain With Radiation in Bilateral Armون توNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Kiko BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPLevyanne GsanchezNo ratings yet
- CIR Vs ST Lukes (2017)Document13 pagesCIR Vs ST Lukes (2017)Maria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Certification/ Verification of PleadingsDocument3 pagesCertification/ Verification of PleadingsMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Efficient Use of Paper RuleDocument6 pagesEfficient Use of Paper RuleMaria Margaret Macasaet100% (1)
- Que V RevillaDocument3 pagesQue V RevillaMaria Margaret Macasaet100% (2)
- Bondoc v. Judge SimbulanDocument4 pagesBondoc v. Judge SimbulanMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Bondoc V SimbulanDocument14 pagesBondoc V SimbulanMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Cyberbullying FactsDocument6 pagesCyberbullying FactsMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- NTC Vs AlphaomegaDocument11 pagesNTC Vs AlphaomegaMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure - Case DigestsDocument221 pagesCivil Procedure - Case DigestsMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Estrada Vs Desierto: GR NO 146710 (353 SCRA 452)Document3 pagesEstrada Vs Desierto: GR NO 146710 (353 SCRA 452)Maria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- IPL ReviewerDocument45 pagesIPL ReviewerMaria Margaret Macasaet100% (1)
- Calalang V WilliamsDocument1 pageCalalang V WilliamsMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Republic V LabradorDocument7 pagesRepublic V LabradorMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Abra Valley College V AquinoDocument9 pagesAbra Valley College V AquinoMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Week2 Oral CommDocument15 pagesWeek2 Oral CommMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Legal Medicine ReviewerDocument12 pagesLegal Medicine ReviewerMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Aberca v. VerDocument3 pagesAberca v. VerMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- RP Vs LabradorDocument4 pagesRP Vs LabradorMaria Margaret MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Sistoza vs. DesiertoDocument2 pagesSistoza vs. DesiertoMaria Margaret Macasaet100% (1)
- HHu & MWu Brief BioDocument4 pagesHHu & MWu Brief BioQuantumDream, Inc.No ratings yet
- Kitchen GeneralDocument5 pagesKitchen Generaljohn carterNo ratings yet
- Anhedonia Preclinical, Translational, and Clinical Integration (Ch. 1)Document30 pagesAnhedonia Preclinical, Translational, and Clinical Integration (Ch. 1)strillenNo ratings yet
- Delta DTD Instruction SheetDocument7 pagesDelta DTD Instruction SheetBenj8No ratings yet
- ASI4517 R3 V 06Document2 pagesASI4517 R3 V 06Дмитрий СпиридоновNo ratings yet
- Full Version Manual: Silva Marine Compass 100B/H MaintenanceDocument1 pageFull Version Manual: Silva Marine Compass 100B/H Maintenancesanginan100% (1)
- Climate Change and Disaster Risk Management-ProjectDocument5 pagesClimate Change and Disaster Risk Management-ProjectshreyanshNo ratings yet
- Health Condition1Document22 pagesHealth Condition1Barrack koderaNo ratings yet
- KESHAV KASHYAP Lipid ProfileDocument9 pagesKESHAV KASHYAP Lipid Profiletest100% (1)
- Growing in Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) Market To Set New Business Opportunities For Start Up CompanyDocument2 pagesGrowing in Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) Market To Set New Business Opportunities For Start Up CompanyPR.comNo ratings yet
- HIPOT TestersDocument4 pagesHIPOT TesterspassworsNo ratings yet
- Expert Paper Final DraftDocument5 pagesExpert Paper Final Draftapi-540442849No ratings yet
- Navitron Panel AssemblyDocument23 pagesNavitron Panel AssemblyXe CohNo ratings yet
- Package Design GuideDocument11 pagesPackage Design Guideondoy4925No ratings yet
- Series E Environmental Coils: Coils and Electronic ControlsDocument18 pagesSeries E Environmental Coils: Coils and Electronic ControlsMMM-MMMNo ratings yet
- Career Portfolio Juguilon Marjorie T. BSHM 702Document9 pagesCareer Portfolio Juguilon Marjorie T. BSHM 702Ivy Nicole SisonNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms v11 I03 20230622Document15 pagesMicroorganisms v11 I03 20230622Editor IJDMNo ratings yet
- G8 Radial Groundwater Flow in Confined AquiferDocument12 pagesG8 Radial Groundwater Flow in Confined AquiferkurtieberberNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument4 pagesReferensiluluNo ratings yet
- Practical Applications of Water Immersion Recovery.6Document13 pagesPractical Applications of Water Immersion Recovery.6GlendaNo ratings yet
- You Dippy TwatDocument24 pagesYou Dippy Twatjas3113No ratings yet
- What Are The Reasons For The Global Water ShortagesDocument1 pageWhat Are The Reasons For The Global Water ShortagesKhairul ShahmiNo ratings yet
- P31846 Eletrificador Ultra22K Unificado REV0!1!1678975121311Document2 pagesP31846 Eletrificador Ultra22K Unificado REV0!1!1678975121311SEBASTIAN CALLEJAS GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document18 pagesExp 8goblinsbrideNo ratings yet
- Ethical DilemmaDocument5 pagesEthical Dilemmaapi-520874386No ratings yet
- Jurnal Farmakognosi Uji Standarisasi Simplisia Dan Uji Fisikokimia Pada Simplisia Herba MeniranDocument10 pagesJurnal Farmakognosi Uji Standarisasi Simplisia Dan Uji Fisikokimia Pada Simplisia Herba MeniranTiara Putri SakinahNo ratings yet
- Cara Pemeriksaan Kimia DarahDocument3 pagesCara Pemeriksaan Kimia DarahCut MuannasNo ratings yet
- Clariant Brochure TexCare Range 2016 EN PDFDocument7 pagesClariant Brochure TexCare Range 2016 EN PDFDirkNo ratings yet