Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology Hemor CVA
Pathophysiology Hemor CVA
Uploaded by
Matthew Emmanuel M. MartinezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology Hemor CVA
Pathophysiology Hemor CVA
Uploaded by
Matthew Emmanuel M. MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
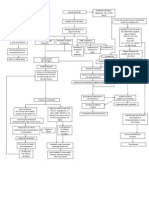
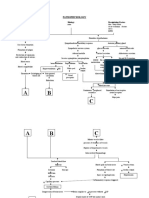
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Hemorrhagic Stroke (CVA)
Risk Factors: Etiology: Unknown
Modifiable: o o o o o o HPN Heart disease Obesity Fatty/salty diet Vices (alcohol/ smoking) Sedentary lifestyle
Non-Modifiable: o o o Age (58 y/o) Sex (male) Heredity (family history of HPN)
Deposition of fatty materials on vessel walls
Formation of atherosclerotic plaque
Hypoperfusion of blood going to vital organs
RAAS activation and SNS Stimulation
Vasoconstriction
Blood Volume
Blood Pressure
Weakening of blood vessels
Aneurism formation
Rupture of Artery supplying the brain
Intracranial Hemorrhage Blood leaks into the brain tissue ICP Destruction of motor and sensory neurons
Inflammatory Response (compression of the brain due to swelling from Hemorrhage)
Loss of function to its pyramidal pathway
Cerebrum LOC Headache N/V Dizziness Seizure Drooling Muscle twitching
Neurologic deficits depending on the area of brain affected
Right Hemisphere
Left Hemisphere
Left Hemiparesis Dysphagia Decreased eye movement Poor judgment Impaired proprioception Contralateral Neglect Impaired visual motor perception blurring of vision
Anterior Carotid Artery
Middle Cerebral Artery
Parietal lobe
Temporal lobe
Primary Somatosensory area Tactile agnosia Paresthesias Disturbed sensory perception Gustatory area No taste perception Pre-motor area Disturbed motor activities of complex/abstract sequential motor abilities (writing name, etc)
Wernickes area Difficulty in interpreting speech/language (receptive aphasia) Primary Auditory area Impaired sound perception/interpretation Auditory Association area Impaired sound, music, speech, noise perception Olfactory area Impaired smell perception
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeLarisse de Leon82% (11)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentPaulo de Jesus86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJames John Galac88% (8)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 pagesPathophysiology CVATerence Valdehueza67% (3)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeJoy Rachelle Fermin100% (2)
- Cancer Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageCancer Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVADocument11 pagesPathophysiology CVAallyana kim figueroa lavarias100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoNo ratings yet
- 3 PathophysiologyDocument4 pages3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- CVA PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Pathophysiology CVDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 pagePathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Meniere FinalDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Meniere Final1S VILLEGAS GabrielNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNo ratings yet
- Client-Based Pathophysiology CVADocument1 pageClient-Based Pathophysiology CVAJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologynitlihpNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoNo ratings yet
- Final CVADocument76 pagesFinal CVAGabriel Apalisok100% (1)
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADocument10 pagesSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument8 pagesCerebrovascular Accidentplethoraldork100% (10)
- CvaDocument170 pagesCvaApril Jumawan ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument60 pagesGroup 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeKitz T AnasarioNo ratings yet
- Final patho-HCVDDocument2 pagesFinal patho-HCVDAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathoDocument15 pagesStroke PathoWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaNo ratings yet
- DuphalacDocument2 pagesDuphalacianecunarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoNo ratings yet
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Cva Concept MapDocument1 pageCva Concept MapAnn Justine OrbetaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular DiseasekathyfacaNo ratings yet
- HCVD KoDocument10 pagesHCVD KoMarianne BaquilalaNo ratings yet
- Patof DMDocument1 pagePatof DMxerwaneNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument41 pagesCase StudychaSeph292784100% (6)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Accident: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: - HPNDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Accident: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: - HPNJohn Mark Alvin TorresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident CVADocument8 pagesCerebrovascular Accident CVAFlora Angeli PastoresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Stroke - Highlights On Pathophysiology, Clinical PresentationDocument39 pagesLecture 3 - Stroke - Highlights On Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentationepic sound everNo ratings yet
- PPT On CVA (Stroke)Document25 pagesPPT On CVA (Stroke)PRASANJIT BISWASNo ratings yet
- Path o Client BasedDocument3 pagesPath o Client BasedJane TuazonNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog60% (5)
- Chapter V Summary, Conclusions, and RecommendationsDocument3 pagesChapter V Summary, Conclusions, and RecommendationsMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez72% (32)
- Preliminary Page 1 ABSTRACT FinaleDocument2 pagesPreliminary Page 1 ABSTRACT FinaleMatthew Emmanuel M. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesHyperthermia NCPMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez0% (1)
- Acute Pain NURSING CARE PLANDocument2 pagesAcute Pain NURSING CARE PLANMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (4)