Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-2) : Basic Power Order Why ?
Basic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-2) : Basic Power Order Why ?
Uploaded by
DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aakash Module or DPPDocument17 pagesAakash Module or DPPAmit Ravish50% (2)
- D 5092 - 04 - RduwotiDocument16 pagesD 5092 - 04 - RduwotiDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesPeriodic Classification Questions and AnswersRidhanishaa LoganathanNo ratings yet
- General Series OrdersDocument5 pagesGeneral Series OrdersDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Study Tip: Ight Electrons TWDocument2 pagesStudy Tip: Ight Electrons TWvcpfdgvctwqxtbkfjnNo ratings yet
- Acidic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-1) : Acidic Power Order Why ?Document2 pagesAcidic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-1) : Acidic Power Order Why ?DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Classificationof Elements Q-AnsDocument11 pagesClassificationof Elements Q-AnsSHAJIYA ANo ratings yet
- The P-Block Elements - XI (Lecture Note)Document39 pagesThe P-Block Elements - XI (Lecture Note)Anand KNo ratings yet
- HL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableDocument12 pagesHL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableMarilee HuntNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument9 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsKota Venkata SukumarNo ratings yet
- LuckyDocument61 pagesLuckylucky tiwariNo ratings yet
- Ist Assignment On Amine 1.12.22Document7 pagesIst Assignment On Amine 1.12.22Sprabhu ParamNo ratings yet
- Ionisation EnergyDocument6 pagesIonisation EnergyAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- Lab Report CHM131 - Flame TestDocument6 pagesLab Report CHM131 - Flame Testmior atiqNo ratings yet
- 4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument68 pages4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- Trends PDFDocument4 pagesTrends PDFjayScoreNo ratings yet
- Ionization Energy and Electron AffinityDocument9 pagesIonization Energy and Electron AffinityKhan AaghaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)Document11 pagesUnit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)ellhamnasserNo ratings yet
- 15.0 Nuclear & Atomic Physics My NC Notes PDFDocument29 pages15.0 Nuclear & Atomic Physics My NC Notes PDFHomok NokiNo ratings yet
- Patterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesPatterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableRugen RajNo ratings yet
- Ionisation Energy ClassDocument13 pagesIonisation Energy ClassKordell McShineNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Its Descriptions: Group 5Document12 pagesPeriodic Table and Its Descriptions: Group 5Christian CincoNo ratings yet
- 0 - Mesomeric effec-WPS OfficeDocument11 pages0 - Mesomeric effec-WPS OfficeNida AdreesNo ratings yet
- Complex Ion of Nickel (II) ChlorideDocument5 pagesComplex Ion of Nickel (II) Chloridebasikal petakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AQA Chemistry Physical 1 AnswersDocument31 pagesChemistry AQA Chemistry Physical 1 AnswersEmma FordNo ratings yet
- S and P Block Elements PDF Class 12 Chemistry NotesDocument25 pagesS and P Block Elements PDF Class 12 Chemistry NotesMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 WebDocument26 pagesLecture10 WebAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- 22 Feb Goc 1 - OneDocument19 pages22 Feb Goc 1 - OneShreyaNo ratings yet
- Inductive EffectDocument4 pagesInductive Effectimranahmadshs2014No ratings yet
- Uranium ExtractionDocument9 pagesUranium Extractiont86qpd68z6No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Atomic StructureDocument39 pagesUnit 2 - Atomic StructureAchini SheharaNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms.Document62 pagesElectrons in Atoms.Md.Tanjim reza TurjoNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: First Ionisation EnergiesDocument1 pageChemguide - Answers: First Ionisation EnergiesDaneilla BanksNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2014Document103 pagesChemistry 2014Godfred EkyeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11 - Periodic TrendsDocument7 pagesWorksheet 11 - Periodic TrendsAvocodo FotovatNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFpreeti.2405100% (2)
- ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesElectrolysisitsmetaehyun11No ratings yet
- Che Chapter 3Document7 pagesChe Chapter 3lisaNo ratings yet
- CHP 7Document5 pagesCHP 7aysekrzm07No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalTudio GamingNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table - Dr. MahbubDocument42 pagesPeriodic Table - Dr. MahbubWREAK OFFICIALSNo ratings yet
- Science MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Document10 pagesScience MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Apex InstituteNo ratings yet
- A'Level Inorganic ChemistryDocument84 pagesA'Level Inorganic Chemistrymukisajob586No ratings yet
- Ionisation Energy: AS ChemistryDocument15 pagesIonisation Energy: AS Chemistry吴蔓华No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriNo ratings yet
- Q.1 The First Ionisation Enthalpy of MG Is Higher Than AI. Why? AnsDocument5 pagesQ.1 The First Ionisation Enthalpy of MG Is Higher Than AI. Why? AnsPaheer SharerNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument58 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistryGauravNo ratings yet
- CH 219 Periodic PropertiesDocument12 pagesCH 219 Periodic PropertiesBenson ShayoNo ratings yet
- Bonding study sheet 1Document60 pagesBonding study sheet 1user03213plumberNo ratings yet
- THIAZOLEDocument2 pagesTHIAZOLEALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- JR Che Ipe Que & AnswersDocument24 pagesJR Che Ipe Que & Answersblackdevil041999No ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesSolutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryM Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Mun - Wahidur Rahaman - A Trinuclear Bright Red Luminophore Containing Cyclometallated Ir (III) MotifsDocument3 pagesMun - Wahidur Rahaman - A Trinuclear Bright Red Luminophore Containing Cyclometallated Ir (III) MotifsMithun SarkarNo ratings yet
- 2 13 Ionisation EnergiesDocument6 pages2 13 Ionisation EnergiesRobertLiu100% (2)
- Factors Affecting ElectrolysisDocument42 pagesFactors Affecting ElectrolysisAbdelrhman Alaa100% (1)
- Unit 2 Lesson 1 - FinalDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 1 - FinalremonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Pblock ElementDocument46 pagesChapter 7 Pblock ElementAmrit BorahNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesRadioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsAbdullah MACNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument6 pagesRedoxparth ladaniNo ratings yet
- Get to Know the Chemistry of Colors | Children's Science & NatureFrom EverandGet to Know the Chemistry of Colors | Children's Science & NatureNo ratings yet
- Fdot bb896 RPT PDFDocument178 pagesFdot bb896 RPT PDFDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Abstract Design Mix m30Document2 pagesAbstract Design Mix m30DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- 4078Document11 pages4078Krishnakumar TodarmalNo ratings yet
- Is 4434 1978 PDFDocument18 pagesIs 4434 1978 PDFDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- 057A - Quotation - SOIL INVESTIGATION - ORANGE - GUJRAT - 04.08.16 PDFDocument3 pages057A - Quotation - SOIL INVESTIGATION - ORANGE - GUJRAT - 04.08.16 PDFDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Is 2825 1969Document286 pagesIs 2825 1969DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ConductivityDocument40 pagesHydraulic ConductivityDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Silver Schmidt SF E 04.2013 LowDocument4 pagesSilver Schmidt SF E 04.2013 LowDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Author: Same As of "Kaane - in - Iit - Wav"Document1 pageAuthor: Same As of "Kaane - in - Iit - Wav"DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
Basic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-2) : Basic Power Order Why ?
Basic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-2) : Basic Power Order Why ?
Uploaded by
DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-2) : Basic Power Order Why ?
Basic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-2) : Basic Power Order Why ?
Uploaded by
DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKCopyright:
Available Formats
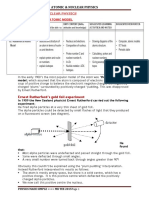
Basic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet- 2)
Basic power Why ? lone pair on N is not used in resonance of -electrons in I. In II lone pair of the ring is I > III > II itself used in delocalisation while that of outside ring in III. OCH3 is strong electron donating group. This is due to I > II > III ortho effect, all the > IV aniline are less basic than p-substituted aniline due to steric hindrance. I (hyper conugation and induction) II I > II > III (induction) IV (ortho > IV effect), ortho effect normally decreases basic nature. Order
1.
2.
3.
4.
In II there is sp3 hybridised C, In I, sp2. II > I > III NO2 is electron withdrawing.
5.
lone pair on N is used in delocalisation of electrons in aromatic amines while III > I > II cyclohexyl is electron repelling (III); in II, lone pair on N is used by two benzene ring. NO2 is electronwithdrawing, thus nitro-anilines are less I > II > III basic than aniline. IV is > IV less basic than III because NO2 is closer and exerts a stronger inductive effect.
6.
7.
phenyl and COCH3 are electronwithdraIII > I > II wing and C6H5 < COCH3
8.
Electron donating I < II < III nature of C2H5 > CH3 So more basic strength.
9.
I < II < III ortho effect in I.
10.
I < II < III ortho effect in (I)
You might also like
- Aakash Module or DPPDocument17 pagesAakash Module or DPPAmit Ravish50% (2)
- D 5092 - 04 - RduwotiDocument16 pagesD 5092 - 04 - RduwotiDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesPeriodic Classification Questions and AnswersRidhanishaa LoganathanNo ratings yet
- General Series OrdersDocument5 pagesGeneral Series OrdersDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Study Tip: Ight Electrons TWDocument2 pagesStudy Tip: Ight Electrons TWvcpfdgvctwqxtbkfjnNo ratings yet
- Acidic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-1) : Acidic Power Order Why ?Document2 pagesAcidic Powers & Their Orders (Chemistry Fact Sheet-1) : Acidic Power Order Why ?DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Classificationof Elements Q-AnsDocument11 pagesClassificationof Elements Q-AnsSHAJIYA ANo ratings yet
- The P-Block Elements - XI (Lecture Note)Document39 pagesThe P-Block Elements - XI (Lecture Note)Anand KNo ratings yet
- HL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableDocument12 pagesHL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableMarilee HuntNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument9 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsKota Venkata SukumarNo ratings yet
- LuckyDocument61 pagesLuckylucky tiwariNo ratings yet
- Ist Assignment On Amine 1.12.22Document7 pagesIst Assignment On Amine 1.12.22Sprabhu ParamNo ratings yet
- Ionisation EnergyDocument6 pagesIonisation EnergyAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- Lab Report CHM131 - Flame TestDocument6 pagesLab Report CHM131 - Flame Testmior atiqNo ratings yet
- 4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument68 pages4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- Trends PDFDocument4 pagesTrends PDFjayScoreNo ratings yet
- Ionization Energy and Electron AffinityDocument9 pagesIonization Energy and Electron AffinityKhan AaghaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)Document11 pagesUnit 2 HL (Atomic Structure HL)ellhamnasserNo ratings yet
- 15.0 Nuclear & Atomic Physics My NC Notes PDFDocument29 pages15.0 Nuclear & Atomic Physics My NC Notes PDFHomok NokiNo ratings yet
- Patterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableDocument7 pagesPatterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableRugen RajNo ratings yet
- Ionisation Energy ClassDocument13 pagesIonisation Energy ClassKordell McShineNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Its Descriptions: Group 5Document12 pagesPeriodic Table and Its Descriptions: Group 5Christian CincoNo ratings yet
- 0 - Mesomeric effec-WPS OfficeDocument11 pages0 - Mesomeric effec-WPS OfficeNida AdreesNo ratings yet
- Complex Ion of Nickel (II) ChlorideDocument5 pagesComplex Ion of Nickel (II) Chloridebasikal petakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AQA Chemistry Physical 1 AnswersDocument31 pagesChemistry AQA Chemistry Physical 1 AnswersEmma FordNo ratings yet
- S and P Block Elements PDF Class 12 Chemistry NotesDocument25 pagesS and P Block Elements PDF Class 12 Chemistry NotesMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 WebDocument26 pagesLecture10 WebAbdul Azeem KhosoNo ratings yet
- 22 Feb Goc 1 - OneDocument19 pages22 Feb Goc 1 - OneShreyaNo ratings yet
- Inductive EffectDocument4 pagesInductive Effectimranahmadshs2014No ratings yet
- Uranium ExtractionDocument9 pagesUranium Extractiont86qpd68z6No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Atomic StructureDocument39 pagesUnit 2 - Atomic StructureAchini SheharaNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms.Document62 pagesElectrons in Atoms.Md.Tanjim reza TurjoNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: First Ionisation EnergiesDocument1 pageChemguide - Answers: First Ionisation EnergiesDaneilla BanksNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2014Document103 pagesChemistry 2014Godfred EkyeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11 - Periodic TrendsDocument7 pagesWorksheet 11 - Periodic TrendsAvocodo FotovatNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 5 Atomic Physics Notes PDFpreeti.2405100% (2)
- ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesElectrolysisitsmetaehyun11No ratings yet
- Che Chapter 3Document7 pagesChe Chapter 3lisaNo ratings yet
- CHP 7Document5 pagesCHP 7aysekrzm07No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalTudio GamingNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table - Dr. MahbubDocument42 pagesPeriodic Table - Dr. MahbubWREAK OFFICIALSNo ratings yet
- Science MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Document10 pagesScience MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Apex InstituteNo ratings yet
- A'Level Inorganic ChemistryDocument84 pagesA'Level Inorganic Chemistrymukisajob586No ratings yet
- Ionisation Energy: AS ChemistryDocument15 pagesIonisation Energy: AS Chemistry吴蔓华No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriNo ratings yet
- Q.1 The First Ionisation Enthalpy of MG Is Higher Than AI. Why? AnsDocument5 pagesQ.1 The First Ionisation Enthalpy of MG Is Higher Than AI. Why? AnsPaheer SharerNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument58 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistryGauravNo ratings yet
- CH 219 Periodic PropertiesDocument12 pagesCH 219 Periodic PropertiesBenson ShayoNo ratings yet
- Bonding study sheet 1Document60 pagesBonding study sheet 1user03213plumberNo ratings yet
- THIAZOLEDocument2 pagesTHIAZOLEALISYA SOPHIA MOHAMMAD ABU SHAHID CHRISNo ratings yet
- JR Che Ipe Que & AnswersDocument24 pagesJR Che Ipe Que & Answersblackdevil041999No ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesSolutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryM Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Mun - Wahidur Rahaman - A Trinuclear Bright Red Luminophore Containing Cyclometallated Ir (III) MotifsDocument3 pagesMun - Wahidur Rahaman - A Trinuclear Bright Red Luminophore Containing Cyclometallated Ir (III) MotifsMithun SarkarNo ratings yet
- 2 13 Ionisation EnergiesDocument6 pages2 13 Ionisation EnergiesRobertLiu100% (2)
- Factors Affecting ElectrolysisDocument42 pagesFactors Affecting ElectrolysisAbdelrhman Alaa100% (1)
- Unit 2 Lesson 1 - FinalDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 1 - FinalremonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Pblock ElementDocument46 pagesChapter 7 Pblock ElementAmrit BorahNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsDocument5 pagesRadioactivity or Radioactive Decay:: Topic 5 - Atomic PhysicsAbdullah MACNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument6 pagesRedoxparth ladaniNo ratings yet
- Get to Know the Chemistry of Colors | Children's Science & NatureFrom EverandGet to Know the Chemistry of Colors | Children's Science & NatureNo ratings yet
- Fdot bb896 RPT PDFDocument178 pagesFdot bb896 RPT PDFDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Abstract Design Mix m30Document2 pagesAbstract Design Mix m30DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- 4078Document11 pages4078Krishnakumar TodarmalNo ratings yet
- Is 4434 1978 PDFDocument18 pagesIs 4434 1978 PDFDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- 057A - Quotation - SOIL INVESTIGATION - ORANGE - GUJRAT - 04.08.16 PDFDocument3 pages057A - Quotation - SOIL INVESTIGATION - ORANGE - GUJRAT - 04.08.16 PDFDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Is 2825 1969Document286 pagesIs 2825 1969DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ConductivityDocument40 pagesHydraulic ConductivityDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Silver Schmidt SF E 04.2013 LowDocument4 pagesSilver Schmidt SF E 04.2013 LowDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Author: Same As of "Kaane - in - Iit - Wav"Document1 pageAuthor: Same As of "Kaane - in - Iit - Wav"DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet